BPK 241 Lecture 6
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Thorax
Neck
Diaphragm
Thoracic vertebrae - protect vital organs
Ribs, sternum, muscles
Bones
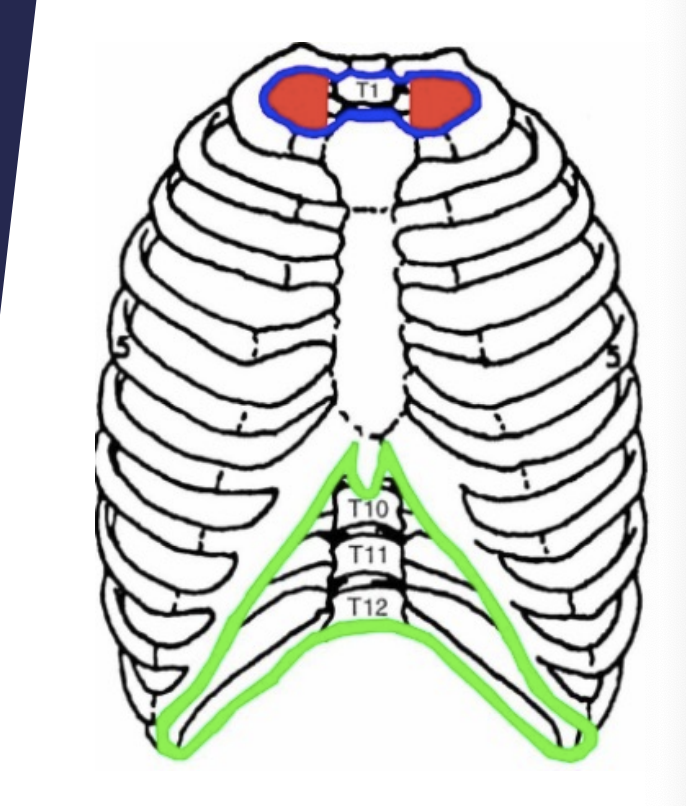
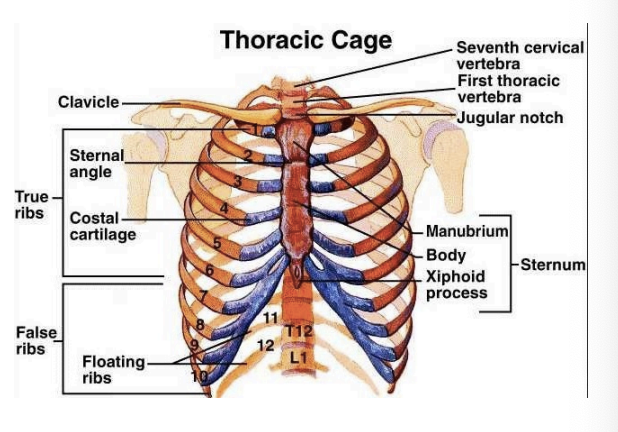
12 thoracic vertebrae
Sternum
Manubrium, body, xiphoid process
12 pairs of ribs
Ribs 1 to 7
Attach to sternum by individual cartilage (costochondral) - have their own attachment at the front of the sternum
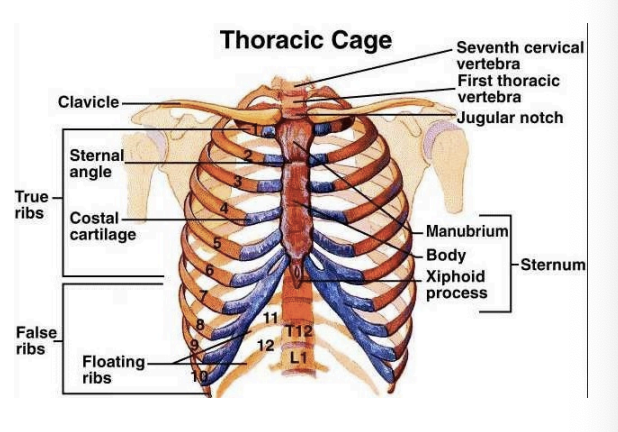
Ribs 8 to 10
Share one attachment
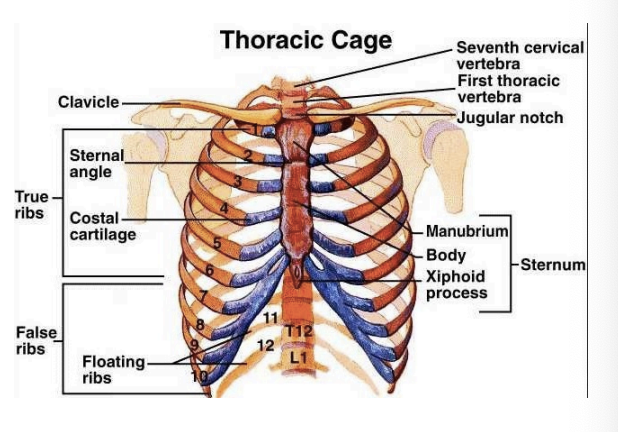
Ribs 11 and 12
Do not attach to the sternum
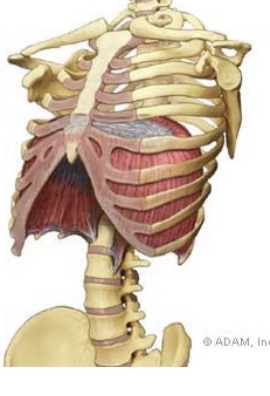
Respiratory muscles
Diaphragm → increase space of thoracic cavity (have negative pressure inside)
Intercostal muscles
Sternocleidomastoid
Accessory muscles of respiration
Inspiration
Ribs + intercostal muscles expand → diaphragm contracts (negative lung pressure)
Expiration
Diaphragm relaxes back to parachute shape → push up on lungs
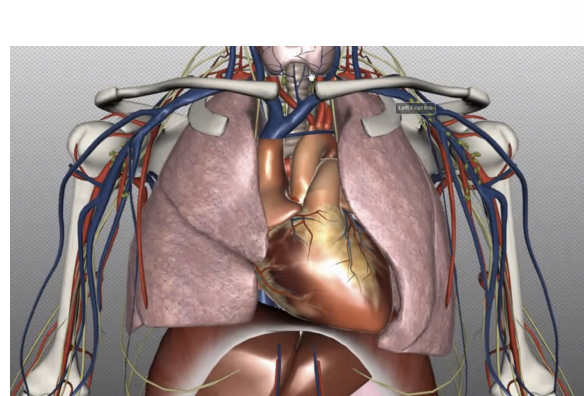
Thorax Contents
Lungs
Heart
Aorta and various branches
Superior vena cava and tributaries
Azygous vein
Trachea
Esophagus (oesophagus)
Vagus nerve & others
Muscle strains
Common in running - forceful breathing
Intercostals, diaphragm, others
SSx:
Pain under the thoracic cage on deep inspiration, dyspnea (difficulty breathing)
Tenderness
Tx:
Rest, analgesics
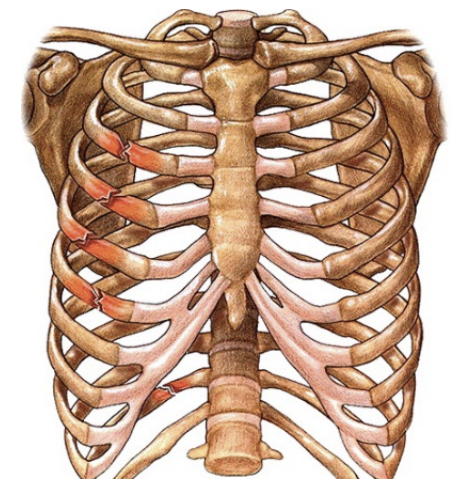
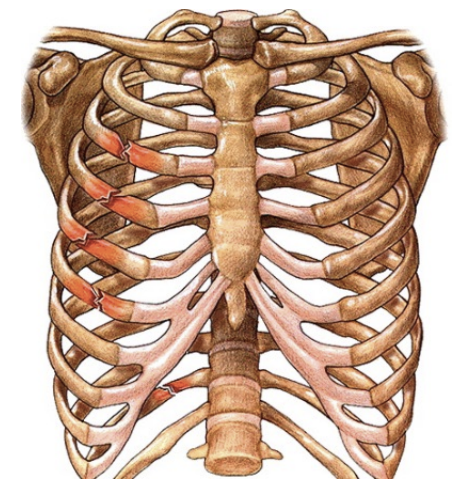
Rib fracture
Direct blow; compression (tackle)
SSx:
Severe inspiratory pain & dyspnea
Tenderness, maybe crepitus
X-Ray often not helpful
Difficult to spot it cuz of movement
Tx:
Rest, analgesics (pain meds - no codine)
Costochondral sprain or dislocation
Same Hx, SSx, Tx as strain, plus crepitus, deformity?(surgery?)
localized pain, difficulty pain
Prolotherapy
Injection of sucrose solution(sugar water) - stabilize water. “Helps aid the healing of rib”
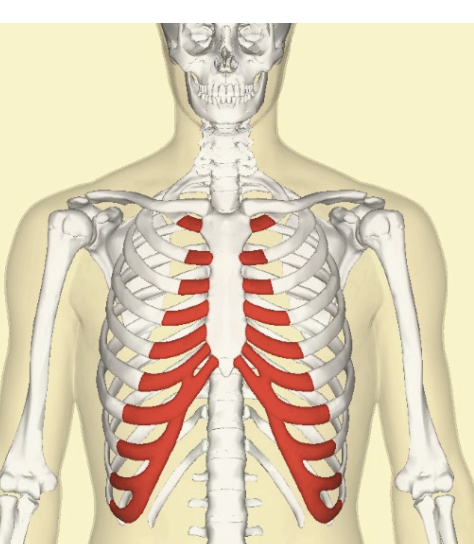
Costovertebra
Back of the the thorax where ribs join the spine (joint). Sprain ribs might puncture the lungs from treatment
Thorax life threatening injuries
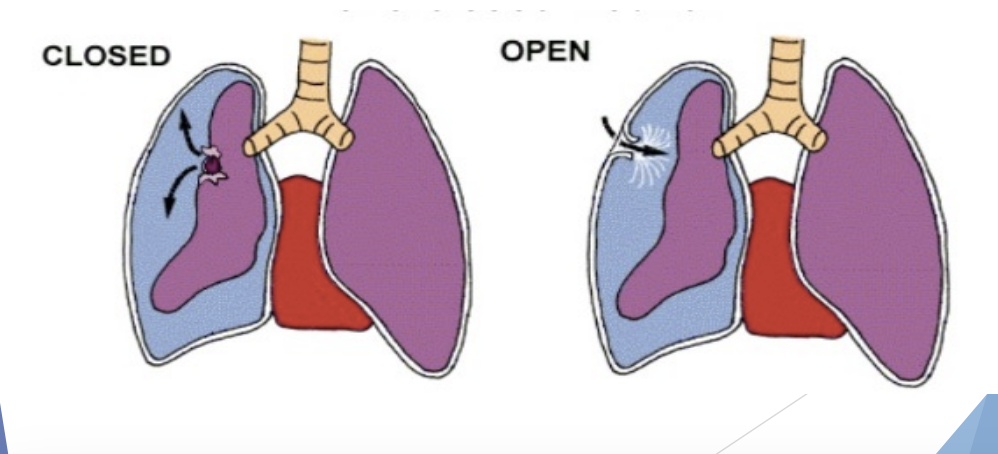
Pneumothorax (air into the thoracic cavity/ collapse lung)
Open vs closed
SSx: Severe dyspnea, shock, cyanosis (decrease in blood oxygen), rapid RR (respiratory rate), Hx of puncture if open, lips blue
Tx: cover opening, NPO, hospital ASAP
Open thorax injury
Air goes in (rushing into opening) - pierce thoracic cage; more common in shooting/stabbings than sports
Closed thorax injury
Tear in lung cause lung to collapse (air escape the cavity) - no oxygenated blood
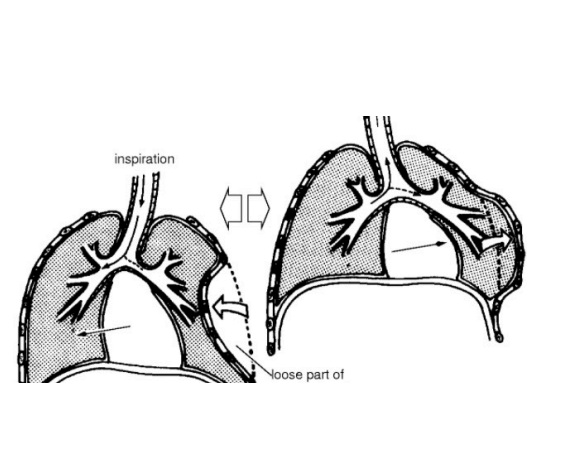
Flail chest
Multiple rib fractures
Paradoxical (opposite motion) motion of part of chest wall
SSx & Tx = as for pneumothorax
Free body segment in middle sucked in. When we breathe, free body segment is pushed out
Commotio cortis
Impacts/blows to the chest causing heart to stop
Affects electrical activity in the heart
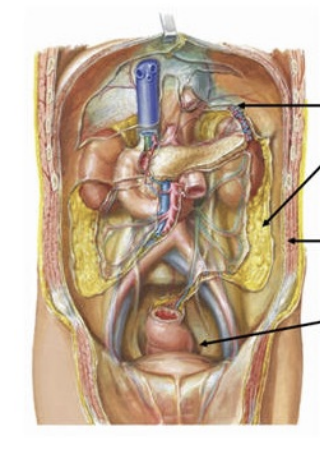
Abdomen boundaries
Diaphragm (superior) , pelvis (Inferior), abdominal muscles (lateral)
Vertebrae, lower ribs, back muscles (posterior)
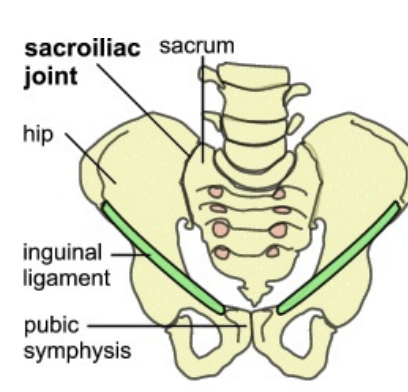
Inguinal area
Inguinal ligament
ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine) to pubic tubercle - bony prominence in front of pelvis
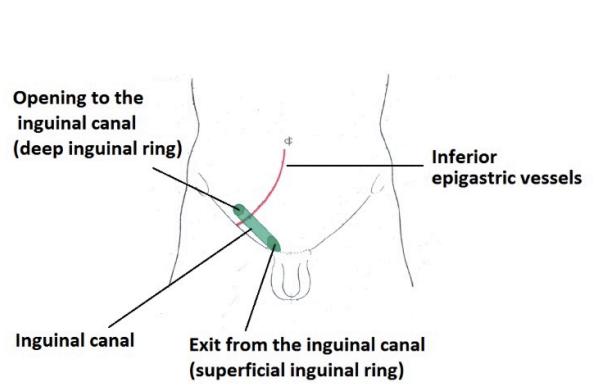
Inguinal ligament
Above Inguinal canal and site of inguinal herniation. Internal and external inguinal rings
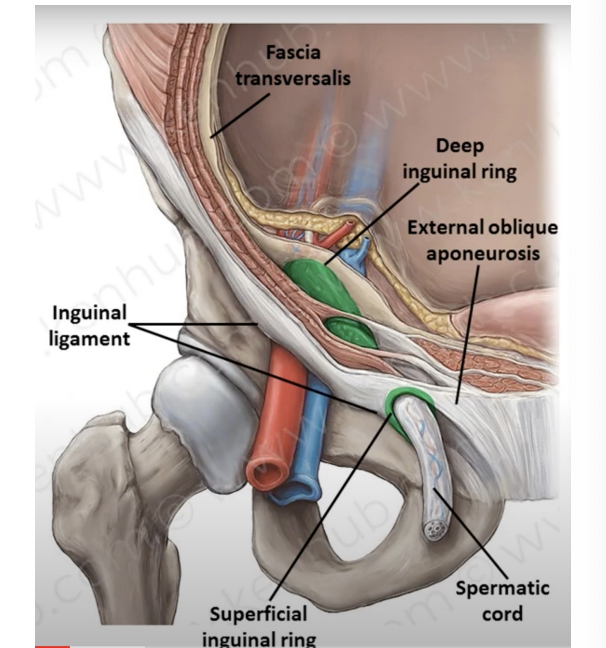
Inguinal canal
Passage in lower part of anterior abdominal wall for spermatic cord in ales or round ligament of uterus for females
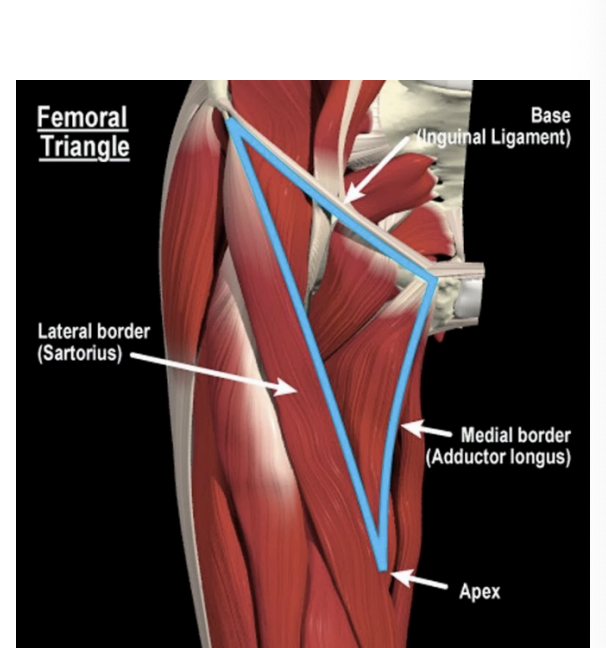
Femoral triangle
Below inguinal ligament
Femoral artery, nerve & vein are subcutaneous
Site of femoral herniation
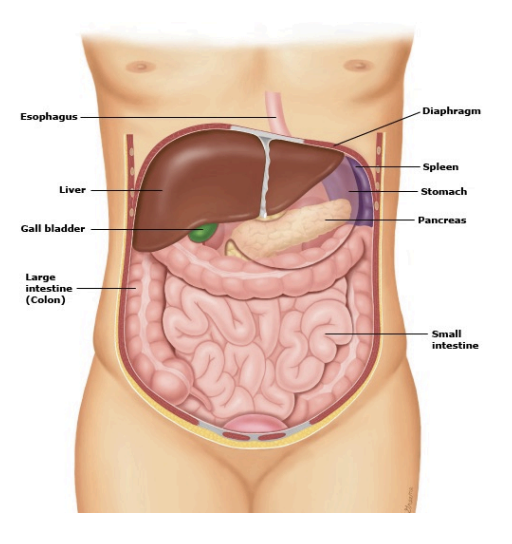
Abdominal contents
Solid organs (bleed profusely)
Liver (RUQ)
Spleen (LUQ)
Kidneys (flanks)
Intestines and glands
Stomach, duodenum, ileum, jejunum, colon (appendix in RUQ)
Pancreas, gall bladder
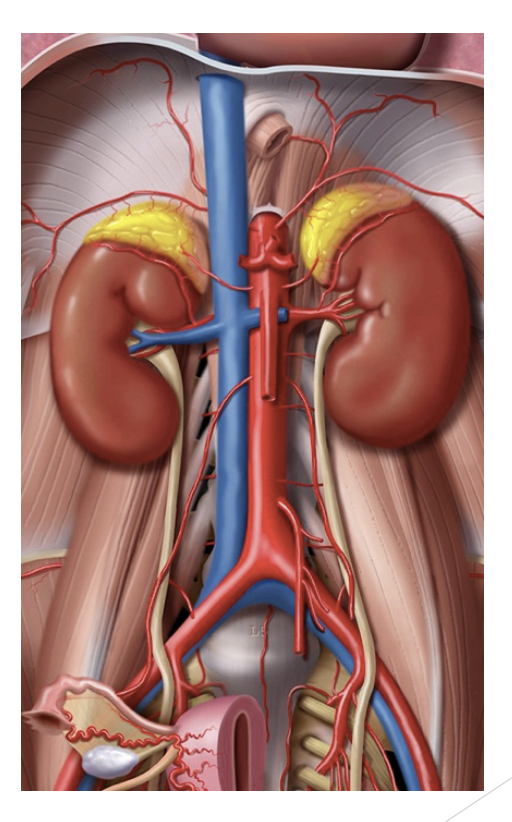
Abdomen Vessels
Abdominal aorta, inferior vena cava
“Visitors”
Uterus in pregnancy
Bladder if distended (quite full)
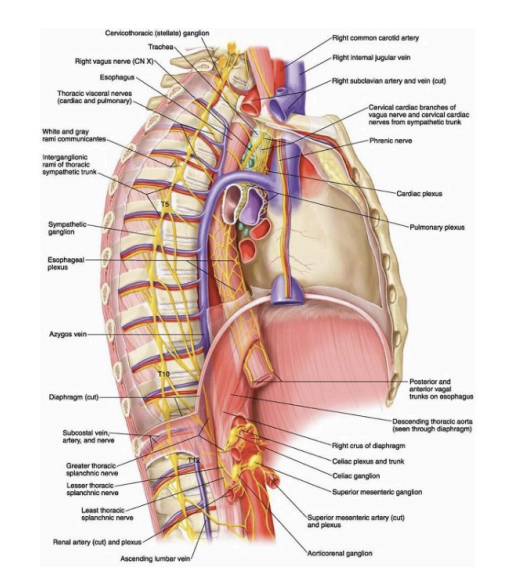
Blow to coeliac (solar) plexus
Mechanism:
Trauma to central abdomen leads to nerve concussion (wind knocked out which contuse solar plexus)
Transient paralysis of diaphragm
SSx:
Ache, shortness of breathing/dyspnea, anxiety
Tx:
Relaxation (short inhalation, long exhalation), reassurance, observe!
Knees to chest
“Side Stitch”
Strain or contusion of abdominal muscle (any muscles wrapped around abdominal area - can get cramping)
SSx:
Crampy pain, worse with inspiration
Tx:
Stretching, analgesics, rest
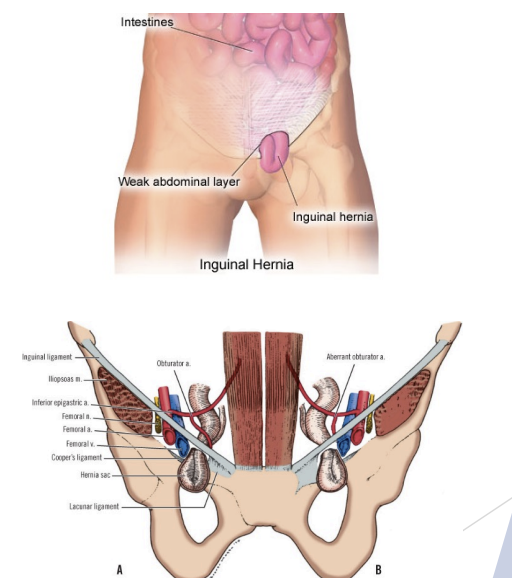
Hernia
Intestine being pushed down onto inguinal canal, stretching up the internal inguinal ring and may come out the external inguinal ring - can feel intestines pushing out
Protrusion of abdominal contents through defect in muscle/fascia
Predisposition (weakness)
Valsalva or direct blow
Degrees:
Reducible (reposition of abdominal muscles)
Incarcerated (head to reposition - hard to push off)
Strangulated (being strangled - blood + oxygen cut off))
Types:
Inguinal (majority, male or female)
Femoral (uncommon; more common in females)
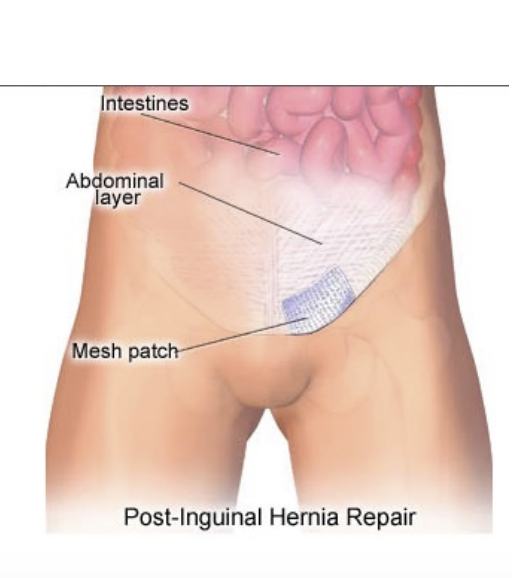
Hernia Symptoms and Treatment
SSx:
“pull” or weakness
Aching pain
Swelling & tenderness above (inguinal) or below (femoral) inguinal ligament
Pain & swelling worsen with cough or repeated valsalva
Shock, nausea
Tx:
Strengthening abdomen
Surgery
Strangulated = emergency
Nausea, vomiting, intense pain
NPO, transport to Hospital ASAP
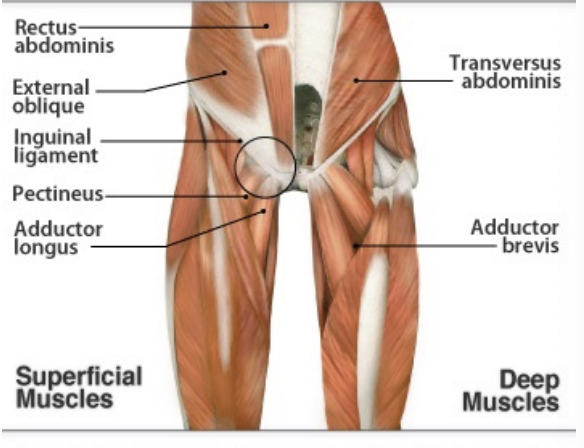
Sports Hernia
Athletic pubulga
SSx: Chronic groin pain, pain with twisting, hip extension, possible pain into testicle
Ax: pt history, physical exam, MRI
Tear of abdominal muscles or tendon (rectus abdominis, external oblique, internal oblique) at attachment to pubic tubercle
Entrapment of inguinal or genitofemoral nerve
Often labral tear and adductor strain associated with it
Tx: rest, surgery
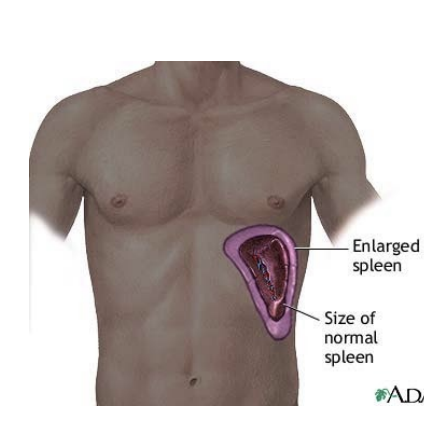
Mononucleosis
Enlarged spleen (no contact sports until MD approved). Delayed abdominal pain after contusion to abdomen? send to MD!
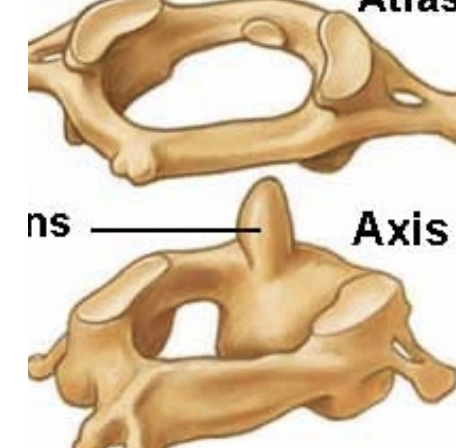
Cervical spine
C1 = atlas (skull flexion/extension) - circular ring
C2 = axis (rotation - C1 pivots on C2 odontoid (dens)) - bony projection
C7 = Vertebrae prominens
Spinal nerves
C1 - C7 exit above same vertebrae
C8 exits between C7 & T1
C5 - T1 form brachial plexus
C3 - C5 innervate diaphragm
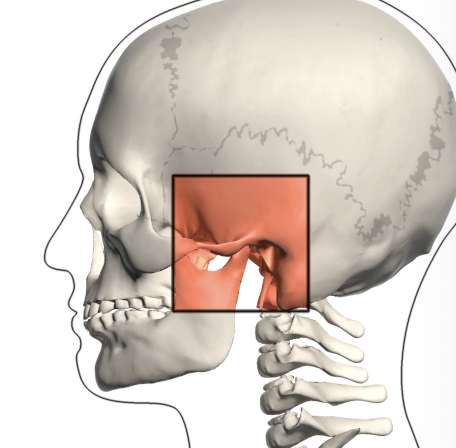
Skull
Inexpansible; brain & sense organs
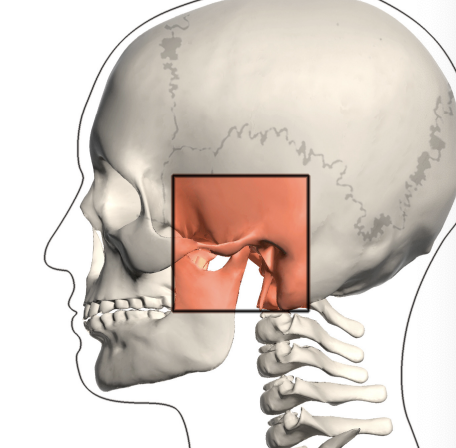
Facial bones
Fragile (except mandible); TMJ
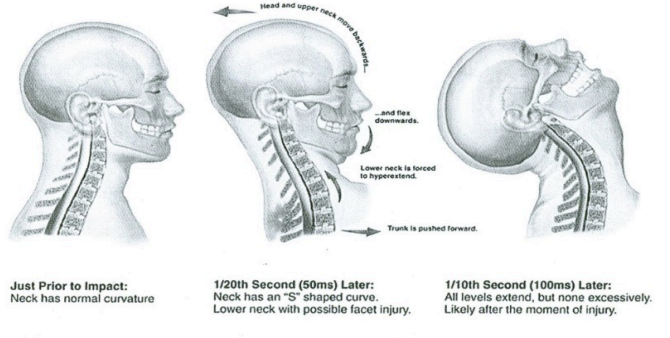
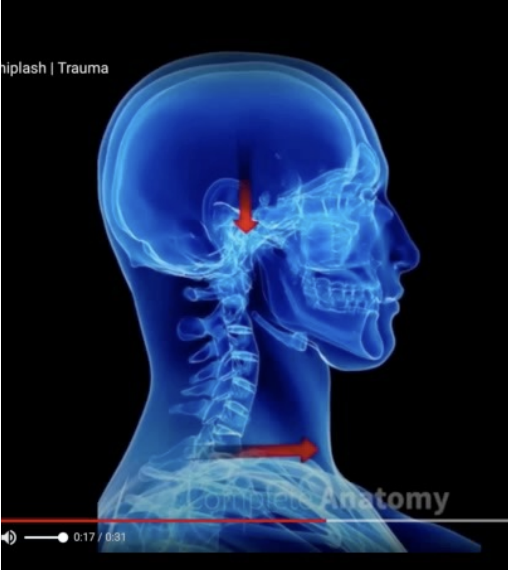
Neck Mechanisms
Flexion & extension (whiplash)
Torsion (twisting)
Compression (load down through the spine)
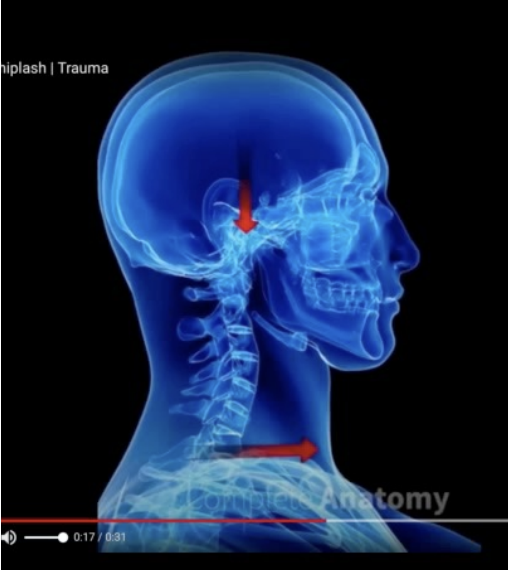
Neck injuries
SSx:
Pain, tenderness
Spasm (delayed?)
Restricted ROM
Headaches
N.B. check for evidence of bony and/or neurologic injury (ABCDs)
Numbness? Weakness or paralysis?
Point tenderness over spinous process?
Stabilize; to hospital ASAP
Neck Management
Stabilize; physician to access
If Hx severe trauma, or neurologic SSx exist, assume fracture/ nerve damage
May not be apparent at first
May lead to permanent brachial plexus or spinal cord injury
Follow up for strain or sprain
Rest (soft collar) - stabilizes neck
NSAID
Physiotherapy or massage therapy
Flexibility & strengthening exercises - ROM
Recurrence is common
Primum non nocere
Neck injury or Concussion?
For a cervical spine injury (sprain or strain) to occur, only require 4.5G of force
For a concussion need 70 to 120G of force
There you CANNOT have a concussion without injuring your neck
Many neck injuries produce symptoms similar to a concussion
Concussion
Immediate, transient neurologic dysfunction due to trauma to brain
Aka Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI)
Concussion represent 8.9% of high school athletic injuries and 5.8% of all collegiate athletic injuries
Coup
Initial
Contre Coup
After
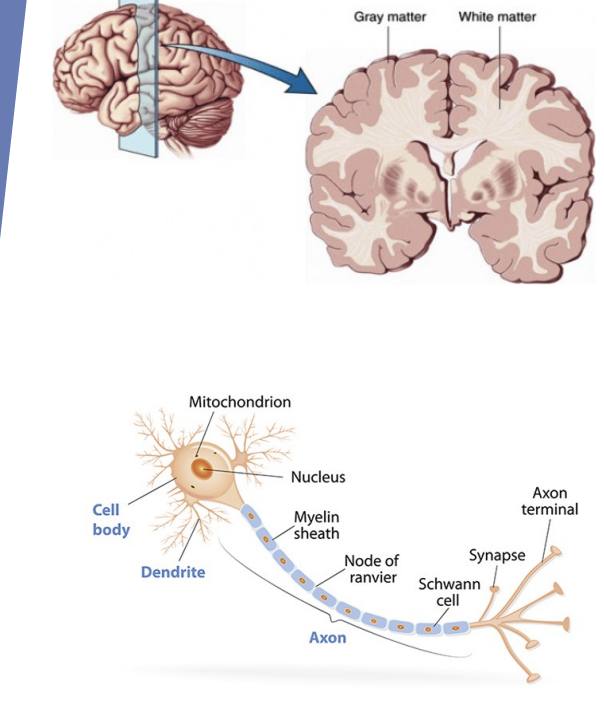
Neurons and Axons
Neurons form grey matter and axons form white matter. Together they carry down signals to dendrites
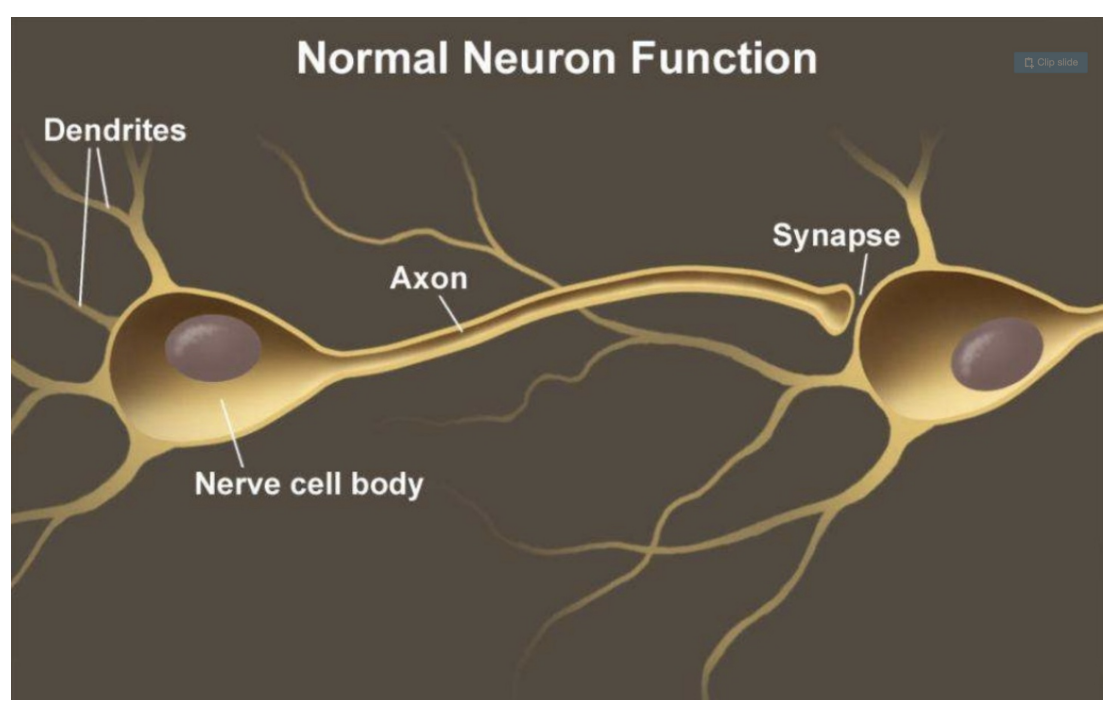
Normal Neuron Function
Signal arrives at neuron
Signal travels down axon to another cell
Neurotransmitters are released in an organized manner, triggering the next cell with a specific coded message
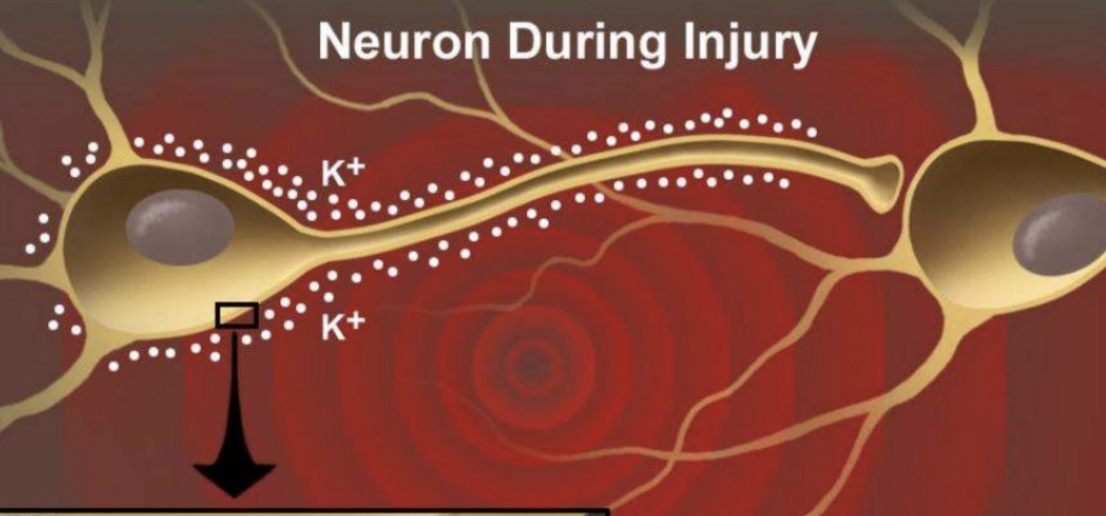
Neuron During Injury
During injury, potassium ions (K+) rush out of the cell and toxic calcium ions (Ca2+) rush into the cell, leading to metabolic dysfunction
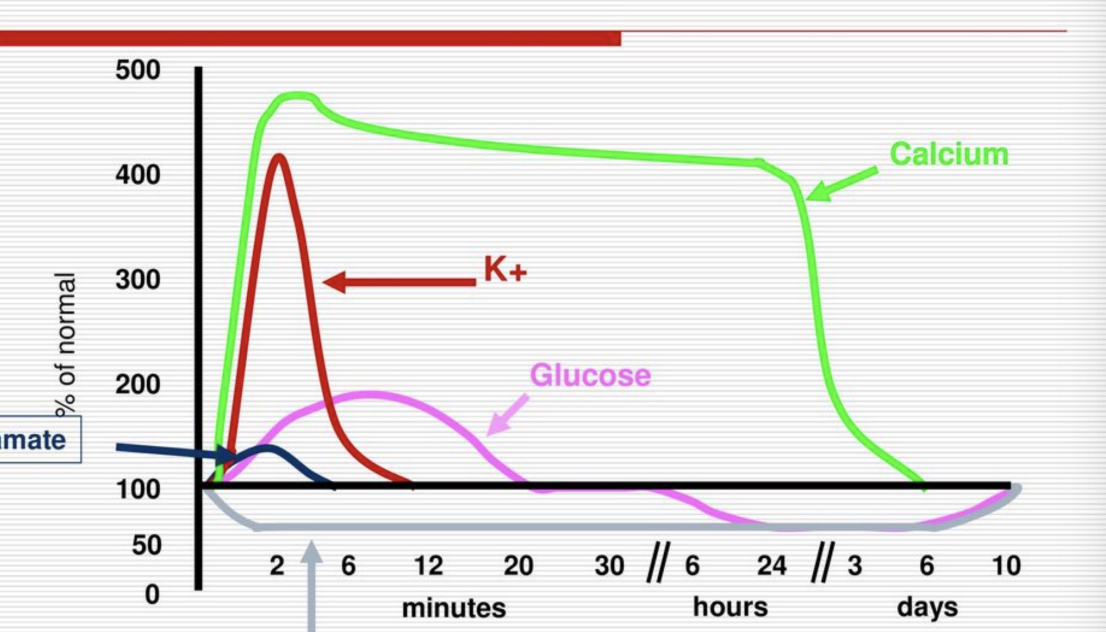
Neurometabolic Cascade Following Cerebral Concussion
Decreased cerebral blood flow for 10 days - protective measure
Increase of calcium within few minutes up to 3-6 days
Increase of glucose as body attempts to heal itself but after 6 days it decreases for 10 days
Increase of Potassium for 12 minutes
Neurometabolic Cascade of Concussion
Excitation Phase and Spreading Depression Phase
Excitation Phase
Calcium elevated 500% for up to 6 days
Potassium elevated 400% within 12 minutes
Glutamate elevated 133% for 6 minutes
Glucose elevated to 200% of normal in first 20 minutes slowly, but then drops below normal for up to 10 days
40% decrease in cerebral blood flow
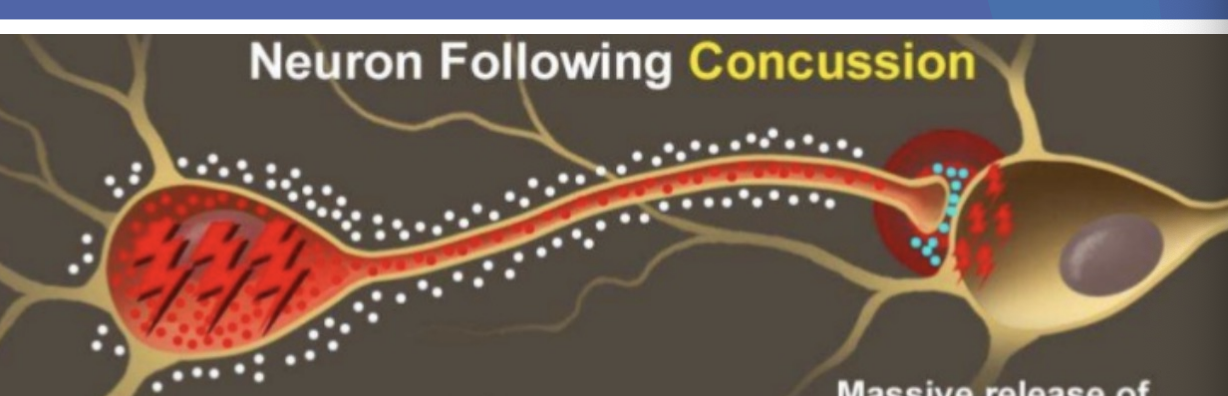
Neuron Following Concussion
Metabolic dysfunction results in ENERGY CRISIS
Massive release of neurotransmitters interferes with cell communications
It may take many days for the nerve cells to return to their normal condition
Nerve cells is extremely vulnerable in this condition, and further injury or stress may cause cell death or serious cell damage
Spreading Depression Phase
Energetic management problem
How do we maintain balance of Na+, Ca+ inside cells and K+ outside cells\
Na/K pump (lots of it)
Requires ATP from mitochondria but high levels of Ca+ is poisonous for mitochondria
Energy crisis
Increased ATP demand from Na/K pump
Decreased ATP production by mitochondria
Decrease blood glucose for up to 10 days
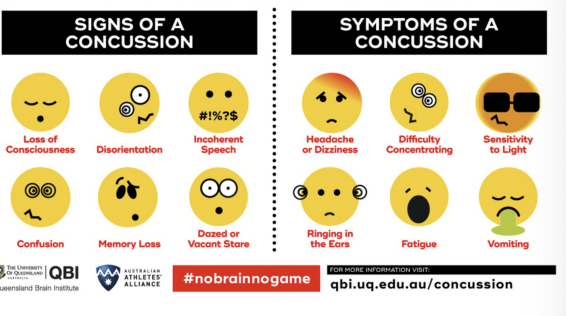
Concussion Signs & Symptoms
SSx:
Physical
Behavioural/Emotional
Thinking/ Cognitive
Physical Symptoms of Concussion
Headache
Dizziness
Ringing in the ears
Pressure in the head
Neck pain/ stiffness
See stars/ flashing lights
Vision problems
Balance problems
Nausea/ vomiting
Behavioural/ Emotional Symptoms of Concussion
Personality change
Concentration problems
Confusion, disorientation
Sleeping more of less than usual
Trouble falling asleep or staying asleep
Drowsiness/ fatigue
Emotional/ irritable/ anxious/ depressed
Thinking/Cognitive Symptoms of Concussion
Memory problems - events loading up to the injury and events after the injury
Concentration problems
Feeling mentally foggy
Slow to respond to questions
Trouble finding words
Confusion/ disorientation
Concussion Assessment Tools
SCAT - sport concussion assessment tool
Concussion Assessment Tools
Online concussion testing problems
imPACT neurocognitive testing
Concussion Vital Signs
HeadCheck
King Devick
Concussion Treatment
Tx:
In unconscious - stabilize (neck too); to hospital ASAP
ABCD’s (serial assessments, 24 hours)
Limit screen time, gradually increase physical activity, moderate rest 24 to 48 hours
No sports until SSx absent for week(s)
Symptoms gone = Recovered right?
SCAT normalized in 2 to 5 days
Balance (BESS) scores return to normal by 3 to 5 days
Cognitive processing and memory normalizes by 7 days
Ca+ levels normalize, cerebral blood flow 7 to 10 days
Symptoms resolution 7 to 10 days
BUT full metabolic recovery 30 to 45 days!
What happens if we get another impact in that time?
2nd impact during this time may have axonal damage that has not recovered
2nd impact syndrome
What happens if don’t recover energy balance?
Persisted concussion symptoms
Post concussion syndrome
Concussion: Return to Play
Absence of symptoms before Return to Play protocol
Clearance from medical professional
Return to play protocol
Physical testing
Buffalo treadmill test
Blackwork test
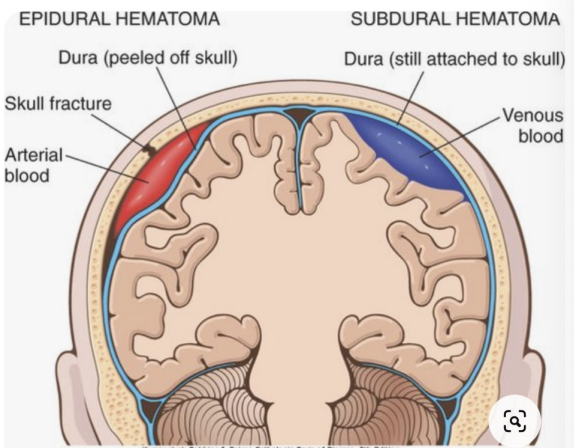
Concussion - Complications
Epidural haematoma (arterial)
Subdural haematoma (venous)
Airway obstruction
Skull fracture (leads to infection)
NFL Return to Play Protocol
Phase 1: Symptom Limited Activity
Phase 2: Aerobic Exercise
Phase 3: Football Specific Exercise
Phase 4: Club-Based Non-Contact Training Drills
Phase 5: Full Football Activity/ Clerance
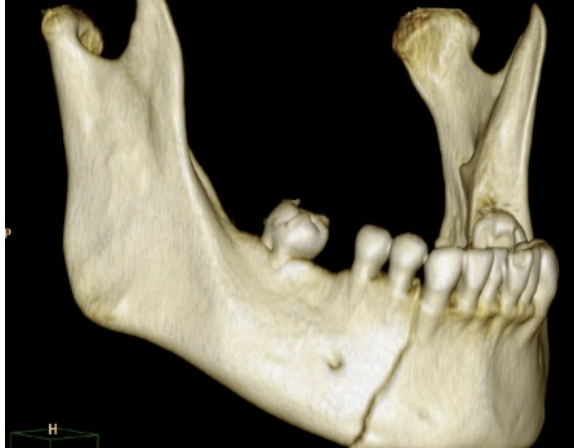
Head Injuries
Mandibular fracture or/and temporomandibular dislocation
Hx: direct blow
SSx: deformity, spasm+++
Airway is threatened
Tx: ABCD’s, stabilize, hospital ASAP
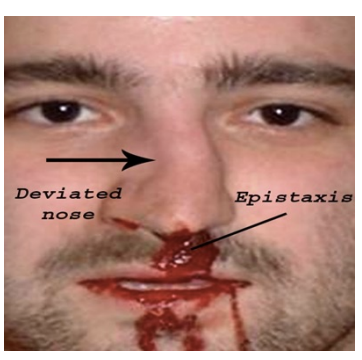
Nasal Injuries
Fracture
Hx: direct blow
SSx: pain, swelling, crepitus, deformity, epistasis, uneven air entry
Tx: cold compress; to MD soon
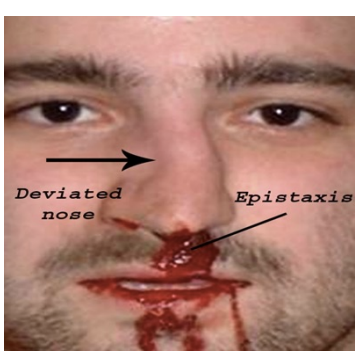
Epistaxis
Hx: direct blow, sinusitis, “digital”
Tx: elevation, cold, pressure
MD to assess & Tx if persists or recurs

External air contusion
Hx: direct blow
SSx: swelling, bruising, tenderness
Complication = deformity
Tx: cold pack, compress, MD may aspirate
Prevention (ear protection)
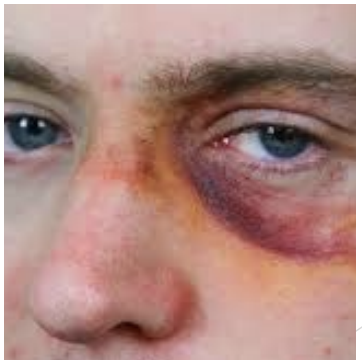
Eye Injuries
All are important - MD to see!
Contusion
Foreign body, laceration, abrasion
Infection
Teeth fractures
Save fragment (cold milk)
To dentist within 2 hours
What can we do to decrease the incidence of concussions in sports?
Helmets, guardian cps, head protection equipment
Less tackles during practice
New policy on hitting and impact to head
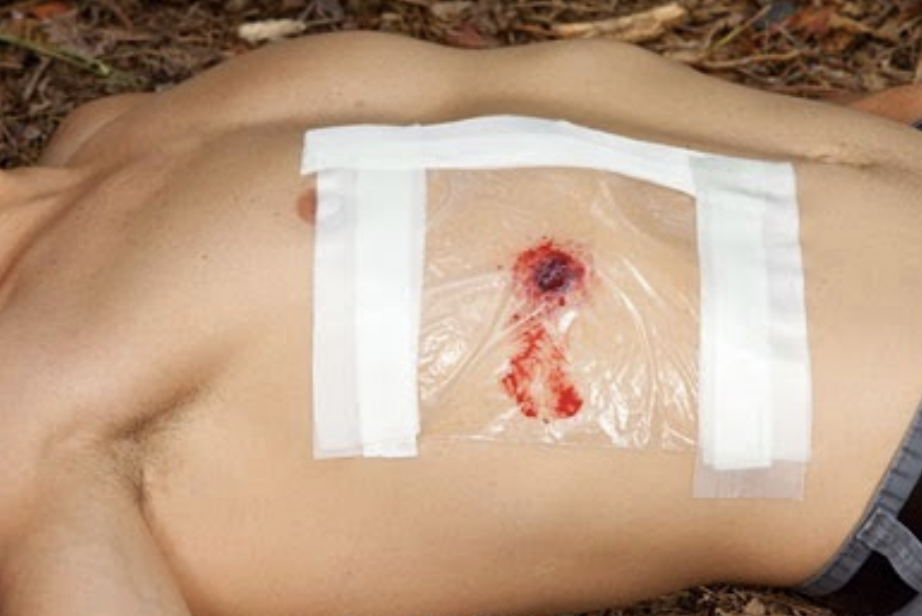
Impermeable barrier
Creating negative pressure
Air can escape from untaped area