Gravitational fields
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Just some useful questions to practice
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
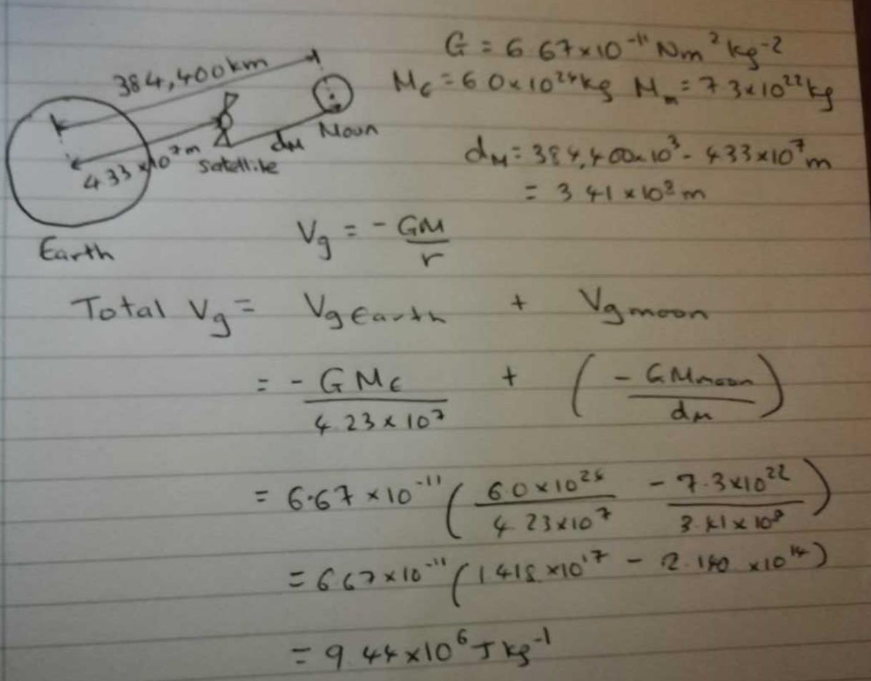
What is the total gravitational potential at a point where the orbit of a geostationary satellite crosses the line directly between the centres of the Earth and Moon?
Data:
Average radius of Moon’s orbit = 384,400 km
Radius of geostationary Earth orbit = 4.23 x 107 m
Mass of Earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg
Mass of Moon = 7.3 x 1022 kg
Use the equation 𝑉𝑔 = −𝐺𝑀/𝑟 to calculate the change in potential in going from the Earth’s surface to the International Space Station.
Data:
RE = 6400 km
ME = 6.0 x 1024 kg
G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2
Average height of ISS above Earth = 383 km

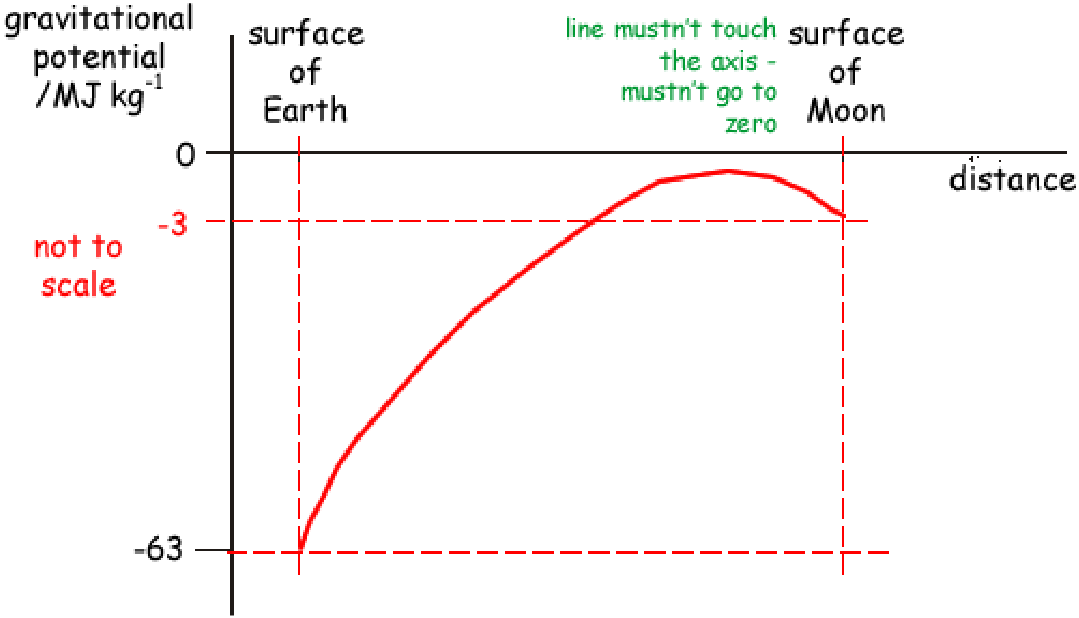
Sketch a graph of gravitational potential (y-axis) vs distance (x-axis) from the surface of the Earth to the surface of the moon.
Data:
Vg on surface of Earth = -63 MJkg-1
Vg on surface of moon = -3 MJkg-1
Potential is a scalar so two non-zero potentials CANNOT combine to give zero.
Just because there is a point where forces are balanced DOESNT mean the potential is zero at that point.
A rocket moves from r1 to r2.
Write down its change in displacement
Write down its gravitational potential Vg1 at r1
Write down its gravitational potential Vg2 at r2
Express its change in gravitational potential Vg2-Vg1
r2 - r1
Vg1 = - GM / r1
Vg2 = - GM / r2
Vg2 - Vg1= - GM/r2 - (-GM/r1) = - GM(1/r2 - 1/ r1)
What is the GPE of the ISS at the Earth’s surface?
What is the GPE of the ISS in its orbit?
What is the minimum energy required to place it in orbit?
Why is this value a minimum?
Data:
Mass of ISS = 420 tonnes (1 tonne = 1000 kg)
Mass of Earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg
Radius of Earth = 6400 km
Average height of ISS above Earth = 383 km
-2.63 x 1013 J
-2.48 x 1013 J
1.5 x 1012 J
This is a minimum because the satellite will also need kinetic energy for this orbit
A satellite of mass 200 kg has a velocity of 5.6 x 103 ms-1 and is orbiting at a distance of 1.28 x 107 m from the centre of the Earth. The Earth has mass 6.0 x 1024 kg. Calculate the KE, GPE and total energy of the satellite.
KE = 3.14 x 109 J
GPE = - 6.25 x 109 J
Total energy = - 3.12 × 109 J
Calculate the escape velocity for Earth
Data:
Mass of Earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg
G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2
Radius of Earth = 6400 km
v = 1.12 x 104 m s-1