CompTIA A+ 220-1101: 3.1 - Basic cable types and their connectors, features, and their purposes.
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Twisted Pair Copper Cabling
A type of cable made by putting two separate insulated copper wires together in a twisted pattern and running them parallel to each other. This type of cable is widely used in different kinds of data and voice infrastructures.
Twisted Pair Copper Cabling details
Balanced pair operation
-Two wires with equal and opposite signals
-Transmit+, Transmit-/Receive+, Receive-
The twist is key
-Keeps a single wire constantly moving away from interference
- Opposite ends are compared to each other
Pairs have different twist rates, so one pair within a cable may have a tighter twist than the other pairs within the cable.
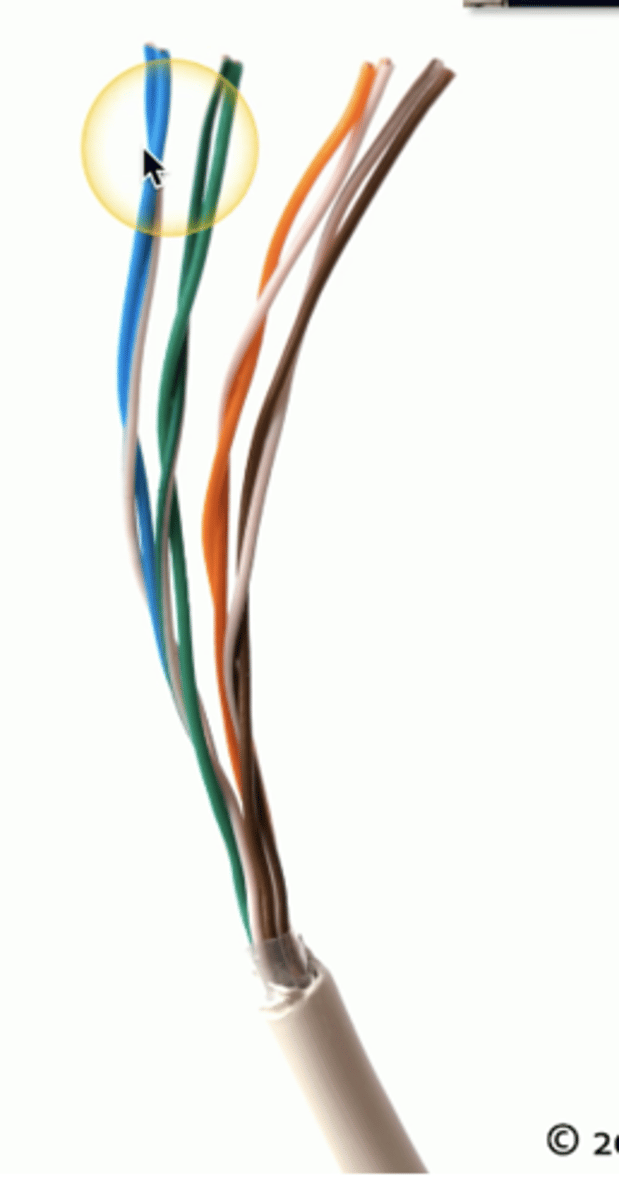
Categories of Cables (Types of Twisted Pair Copper Cabling)
1000BASE-T
- CAT5
- 100 Mbps
- Max distance: 100 meters
1000BASE-T
- CAT5e(enhanced)
- 1 Gbps
- Max distance: 100 meters
10GBASE-T
- CAT6
- 10 Gbps
- Max distance : 55 meters (unshielded), 100 meters (shielded)
10GBASE-T
- CAT6A (augmented)
- Max distance: 100 meters
CAT5 (UTP Type)
A category of twisted cable.
Uses four pairs of internal cables.
Max speed: 100 Mbps
Max length: 100 meters.
CAT5e (UTP Type)
A category of twisted cable.
Max speed: 1000 Mbps, or 1 Gbps
Max length: 100 meters
CAT6 (UTP Type)
A category of twisted cable.
Max speed: 10 Gbps
Max length: 100 meters
CAT6a (UTP Type)
A category of twisted cable.
Augmented
Max speed: 10 Gbps
Max length: Can support 10 Gbps for 100 meters between node and switch.
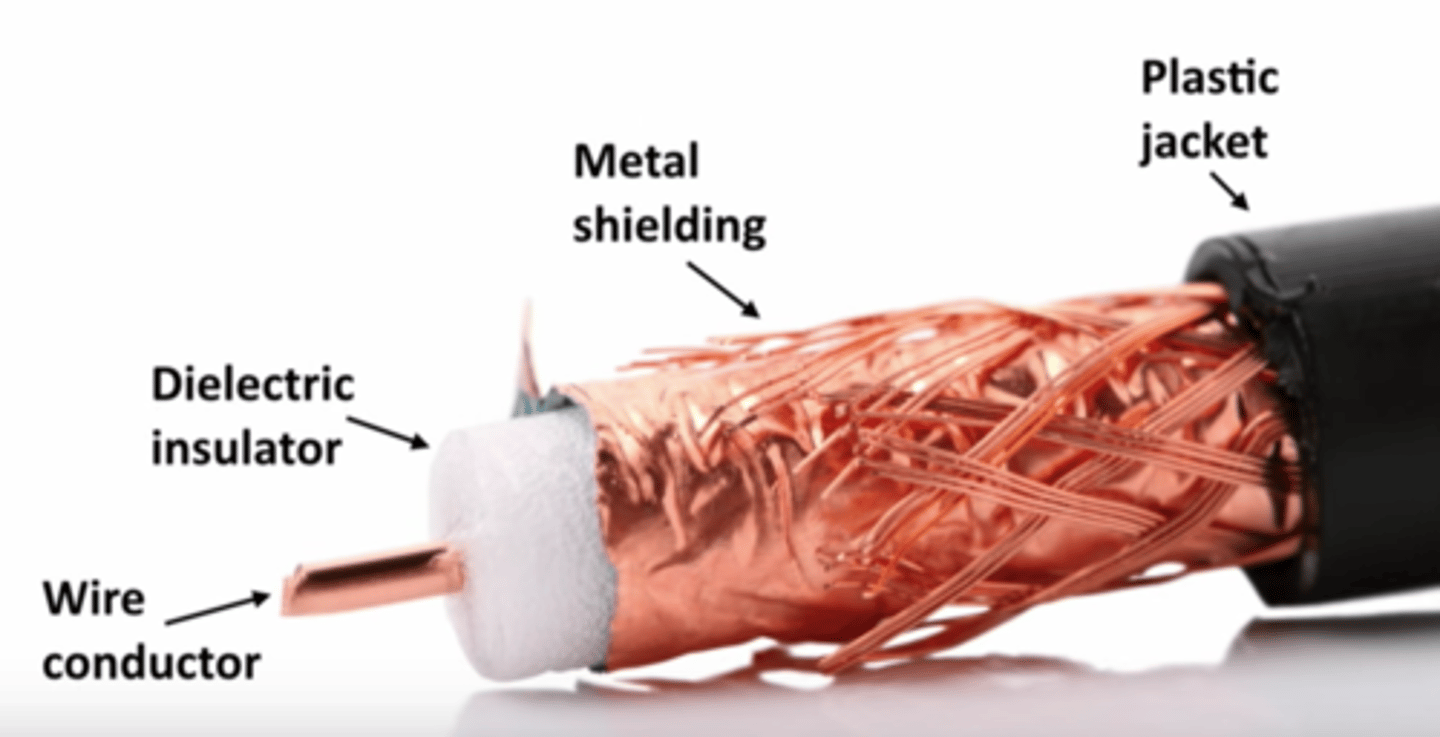
Coaxial Cable
Cabling in which an internal conductor is surrounded by another, outer conductor, thus sharing the same axis.
Coaxial Cable details
Two or more forms share a common axis.
RG-6 used in television/digital cable.
- And high-speed internet over cable.
Plenum
Refers to an air handling space, including ducts and other parts of the HVAC system in a building.
Plenum Rated Cable
Traditional Cable Jacket
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Fire-rated cable jacket
- Flourinated ethylene polymer (FEP) or
low-smoke polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Plenum-rated cable may not be as flexible (may not have same bend radius)
Worst-case planning
- Important concerns for any structure.
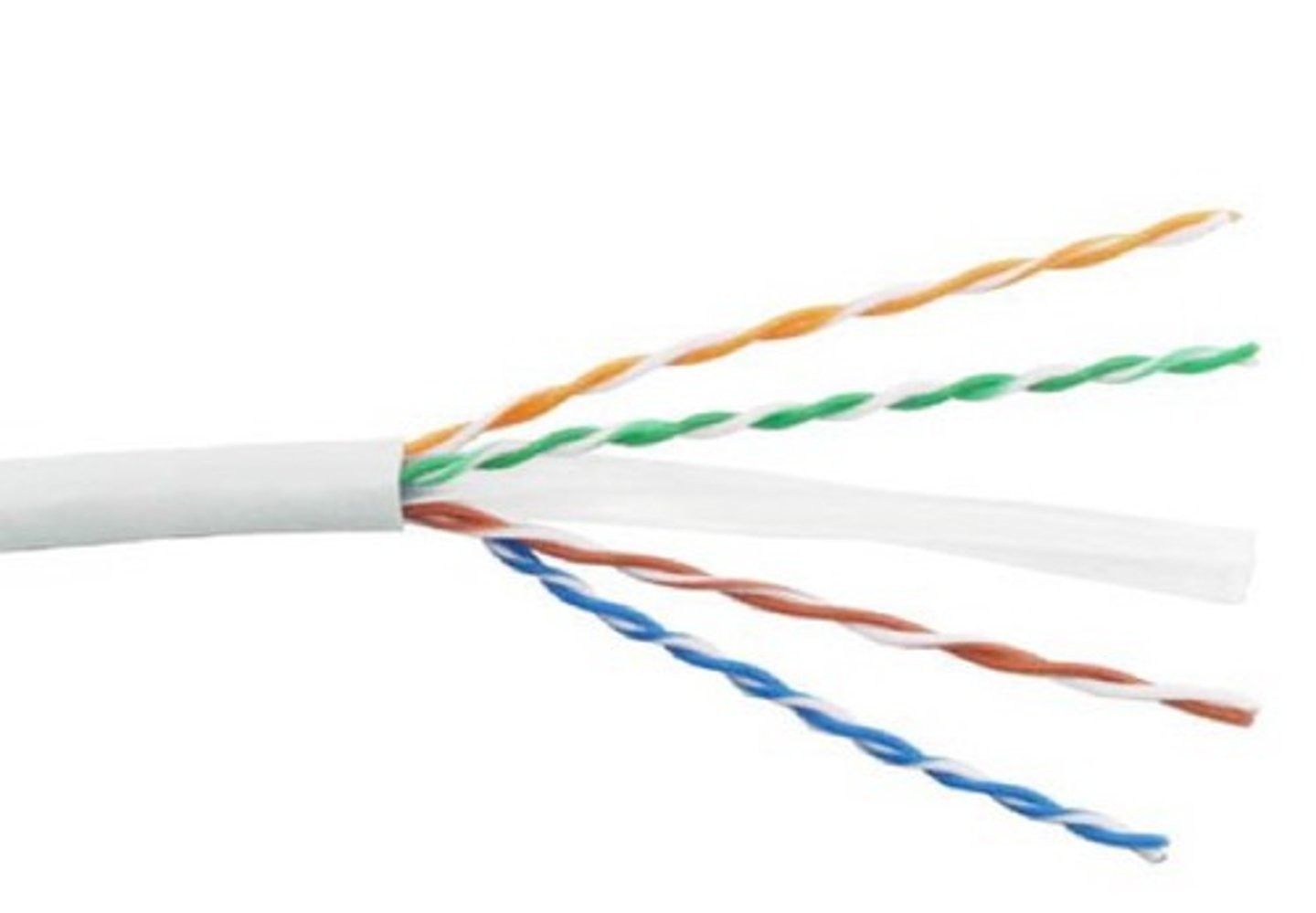
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
Popular type of cabling for telephone and networks, composed of pairs of wires twisted around each other at specific intervals. The twists serve to reduce interference (also called crosstalk). The more twists, the less interference. This cable has no metallic shielding to protect the wires from external interference.
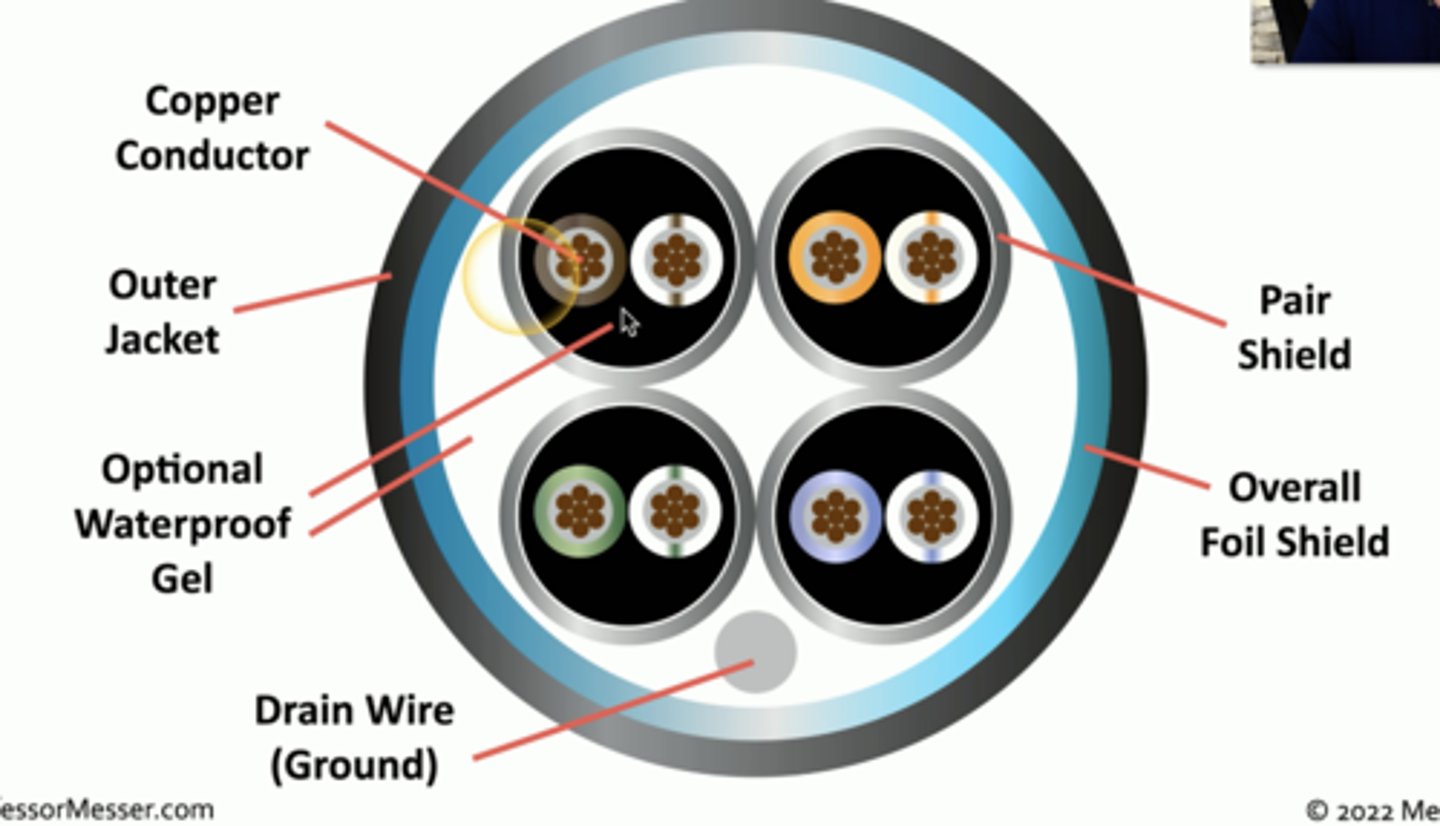
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair)
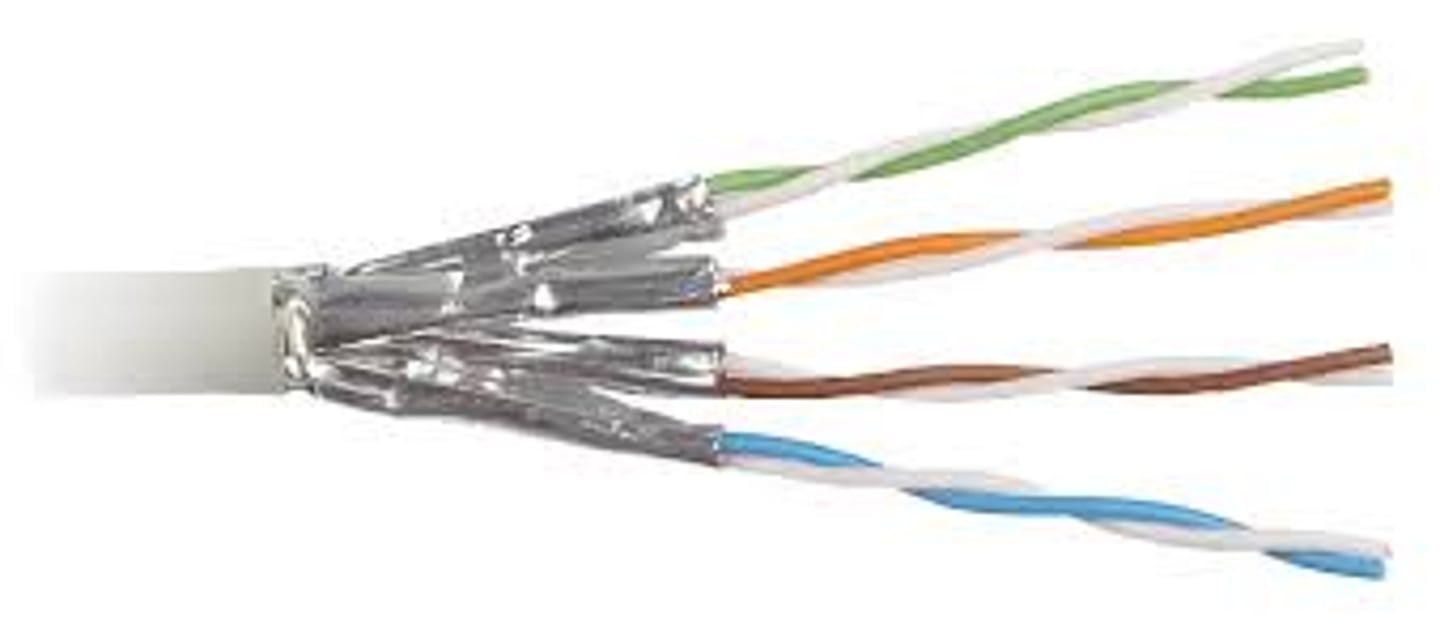
A cabling for networks composed of pairs of wires twisted around each other at specific intervals. The twists serve to reduce interference (also called crosstalk). The more twists, the less interference. The cable has metallic shielding to protect the wires from external interference.

UTP/STP details
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
- No additional shielding.
- The most common twisted pair cabling.
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair)
- Additional shielding protects against interference.
- Shield each pair and/or the overall cable.
- Requires the cable to be grounded.
UTP/STP abbreviations
U = Unshielded
S = Braided shielding
F = Foil shielding
(Overall cable)/(individual pairs)TP
- Braided shielding around the entire cable and foil around the pairs is S/FTP.
- Foil around the cable and no shielding around the pairs is F/UTP.
Direct Burial STP
Overhead cable isn't always a good option.
- Put the cable in the ground.
Provides protection from the elements.
- Designed to be waterproof.
- Often filled with gel to repel water.
- Conduit may not be needed.
Shielded Twisted Pair
- Provides grounding.
- Add strength.
- Protects against signal interference.
Fiber Communication
Transmission by light
• The visible spectrum
No RF signal
• Very difficult to monitor or tap
Signal slow to degrade
• Transmission over long distances
Immune to radio interference
• There's no RF
Fiber Optic Cable Diagram
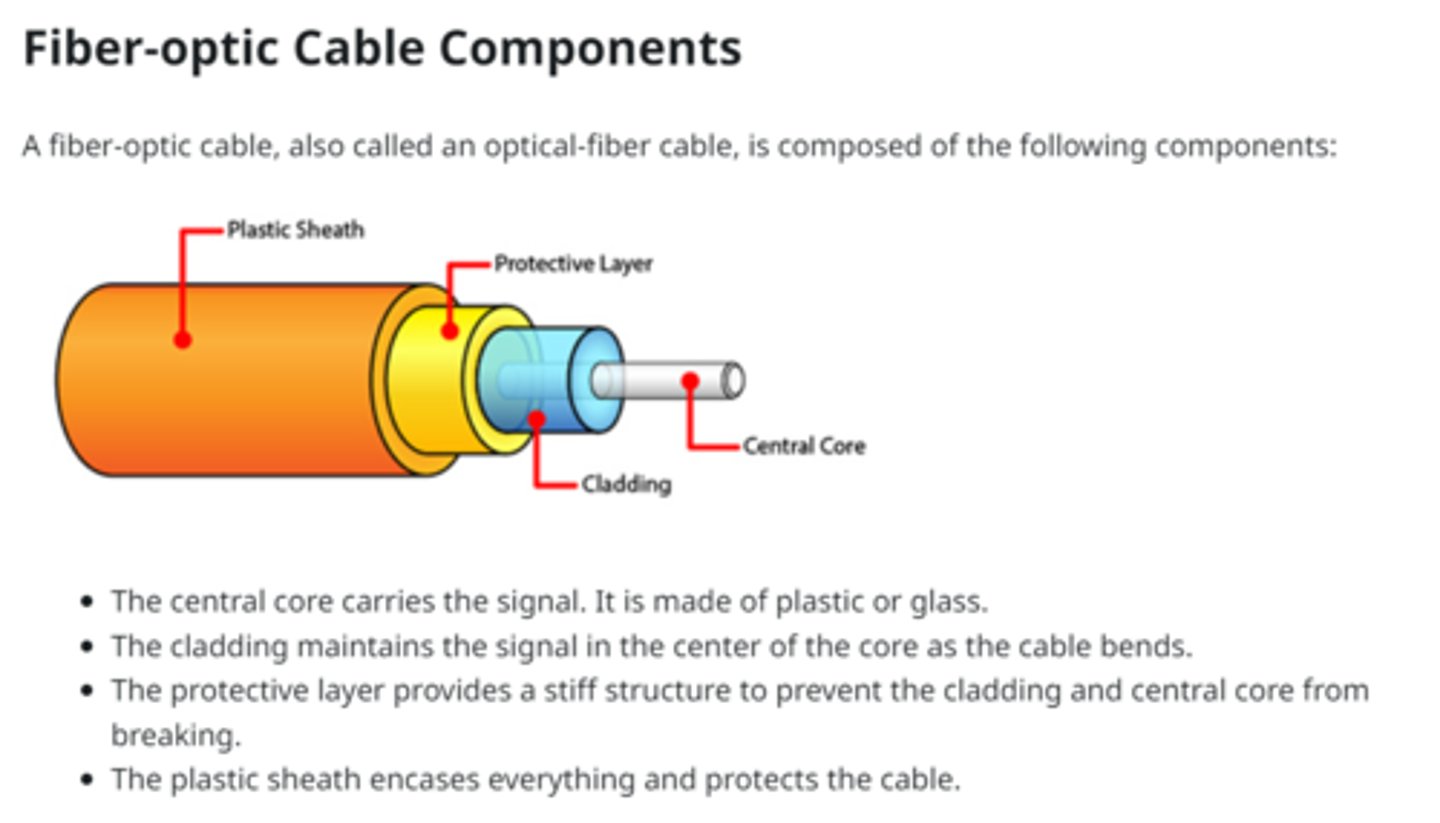
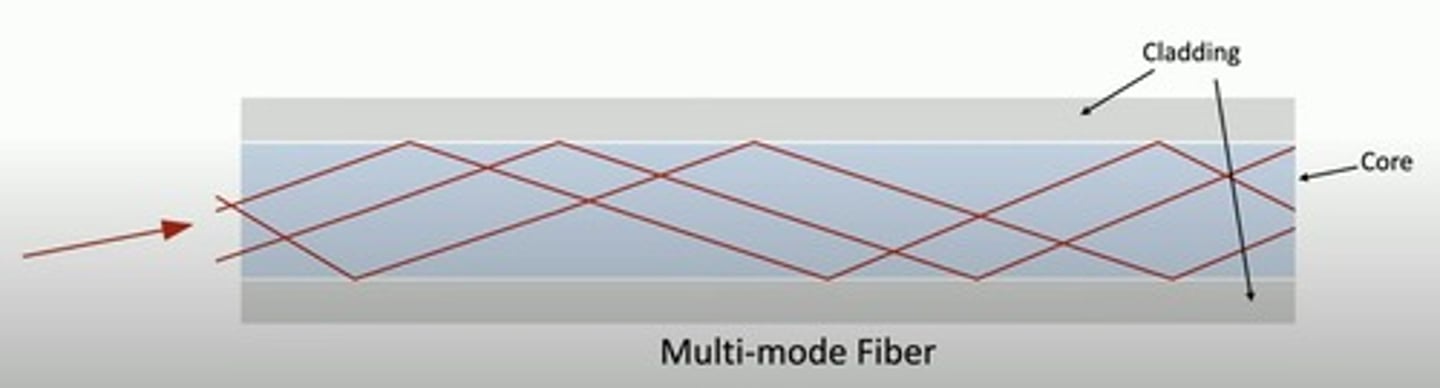
Multimode (Fiber Optic Cable)
A type of fiber optic cable that has a large core-diameter, and uses LEDs to send light signals, all at the same time, each using a different reflection angle within the core of the cable.
The multiple reflection angles tend to disperse over long distances, so these are used for relatively short distances.
Quite common.
Multimode details
Short-range communication
- Up to 2 km
Relatively inexpensive light source.
- i.e., LED
Single Mode (Fiber Optic Cable)
A type of fiber-optic cable that has a small core diameter and uses laser light to send light signals.
Allows for very high transfer rates over long distances.
Except for long distance links, this type is quite rare.
Single Mode details
Long-range communication.
- Up to 100 km without processing.
Expensive light source.
- Commonly uses lasers.

Structured Cabling Standards
International ISO/IEC 11801
cabling standards
- Defines classes of networking standards
Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
- Standards, market analysis, trade shows,
government affairs, etc.
- ANSI/TIA-568: Commercial Building Telecommunications
Cabling Standard
- http://www.tiaonline.org
Commonly referenced for pin and
pair assignments of eight-conductor
100-ohm balanced twisted pair cabling
- T568A and T568B
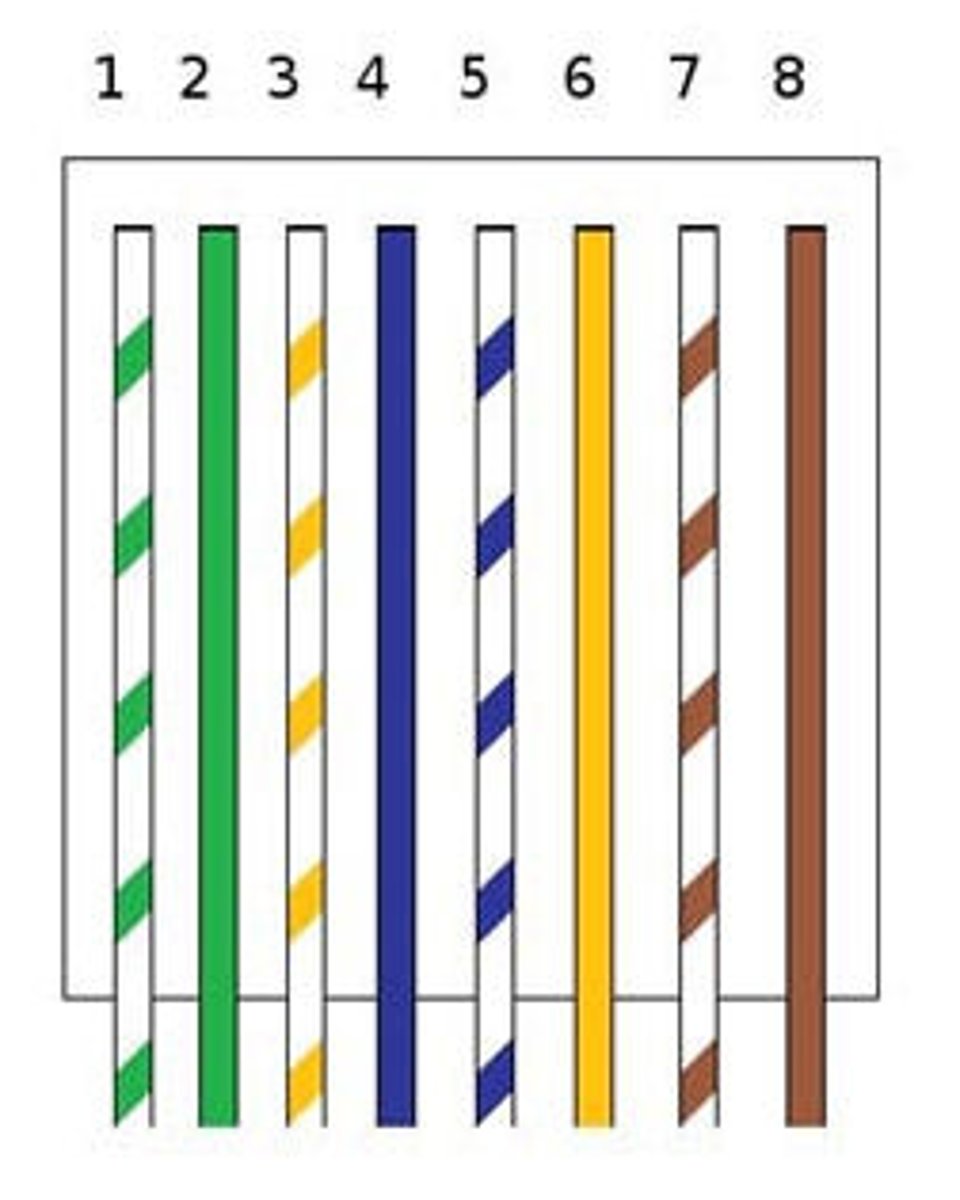
T568A
Standards for wiring twisted-pair network cabling and RJ-45 connectors and have the green pair connected to pins 1 and 2 and the orange pair connected to pins 3 and 6.
Usually associated with horizontal cabling.
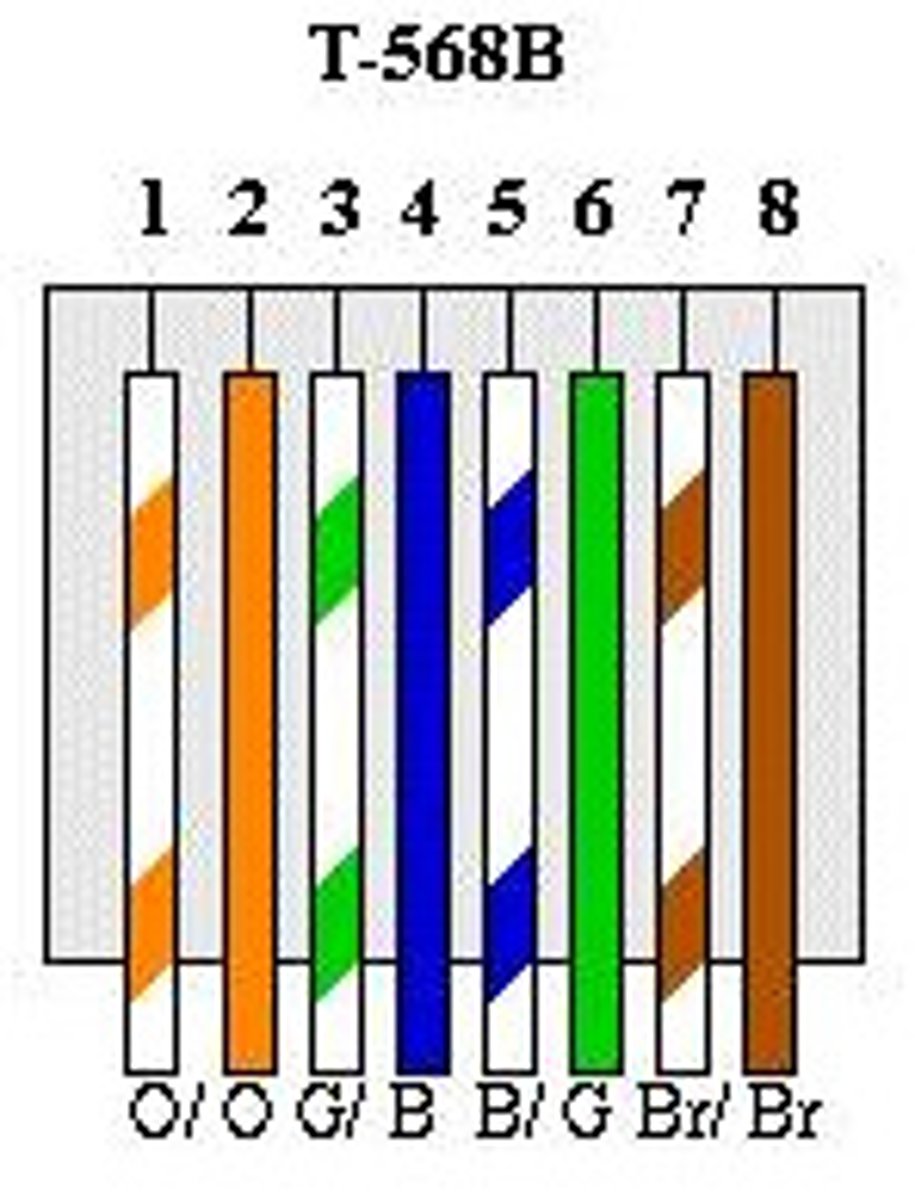
T568B
Standards for wiring twisted-pair network cabling and RJ-45 connectors and have the orange pair using pins 1 and 2 and the green pair connected to pins 3 and 6.
Usually associated with end-user connections.
T568A/T568B Termination
Pin assignment from EIE/TIA-568-B standard
-8 conductor 100 ohm balanced twisted-pair cabling
T568A and T568B are different pin assignments for 8P8C connectors.
Many organizations traditionally use 568B
-Difficult to change mid stream
You can't terminate one side with the other type connector.

USB (Universal Serial Bus)
General-purpose serial interconnect for keyboards, printers, joysticks, and many other devices. Enables hot-swapping of devices.
USB details
Simplify connections
• Printers, storage devices, keyboard, mouse.
USB 1.1
• Low speed: 1.5 megabits per second, 3 meters.
• Full speed: 12 megabits per second, 5 meters.
USB 2.0
• 480 megabits per second, 5 meters.
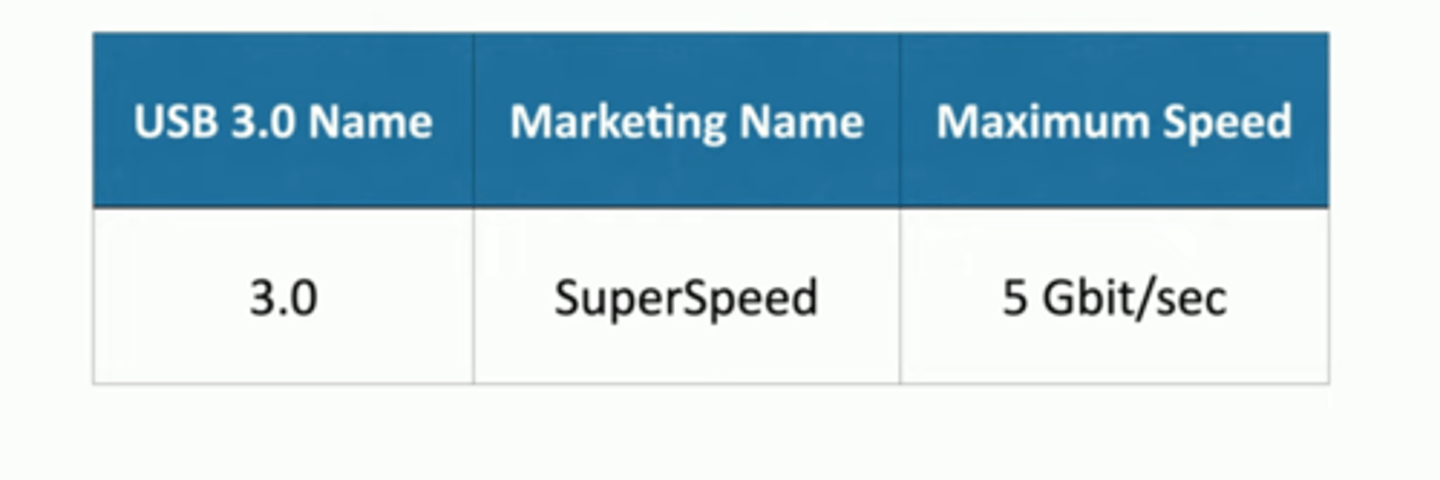
USB 3.0
• SuperSpeed
• 5 gigabits per second, ~3 meters
• Standard does not specify cable length.
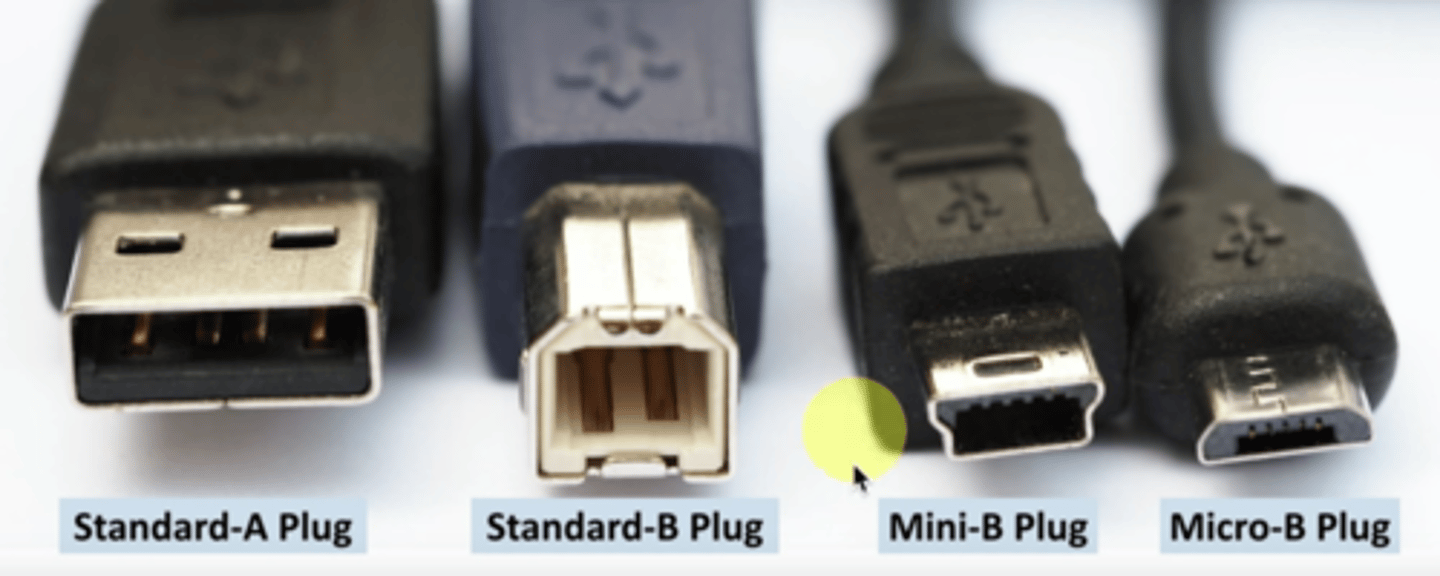
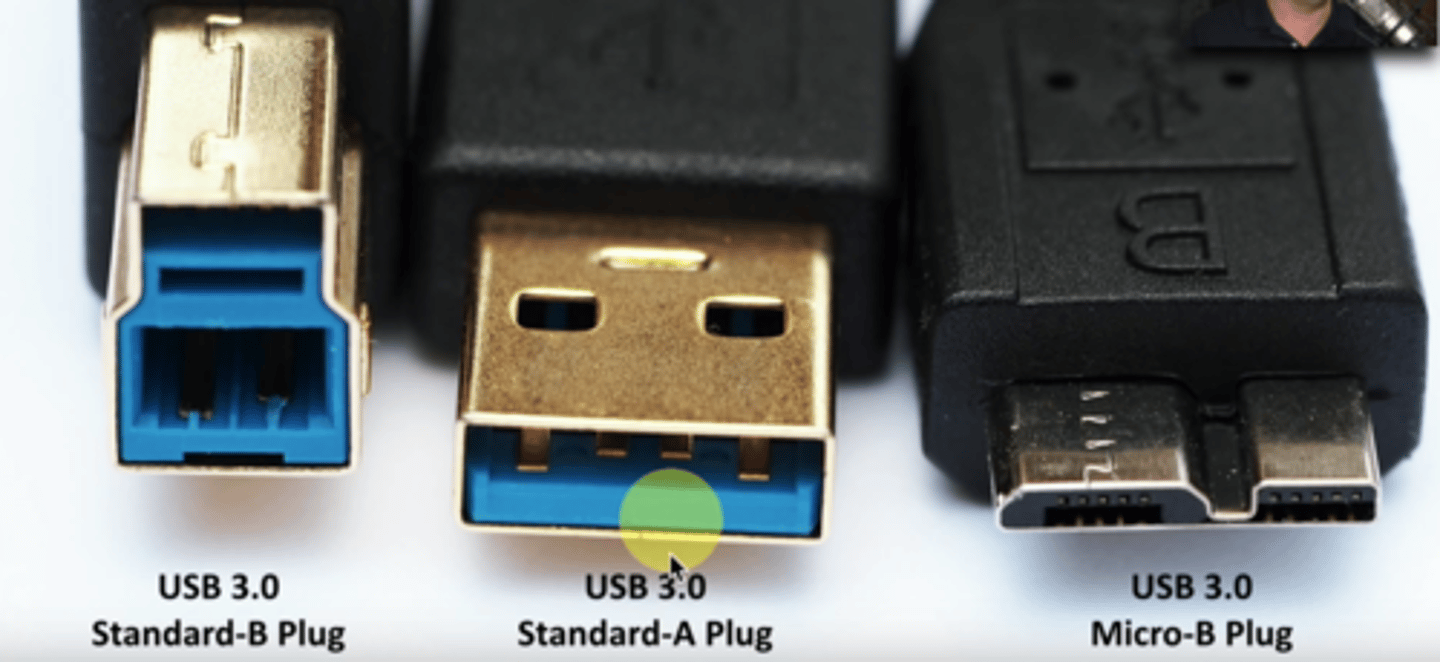
USB 1.1/2.0 Connectors
- Standard A: Connects to computer
- Standard B,
Mini-B,
Micro-B: all connect to peripherals/devices
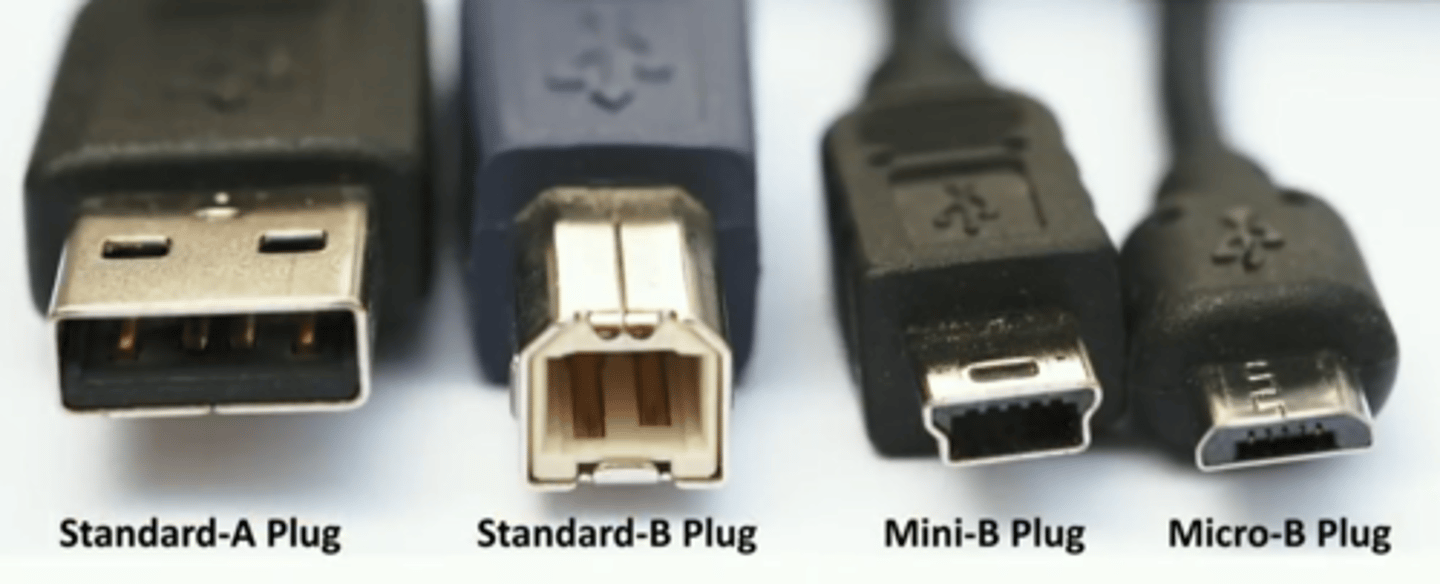
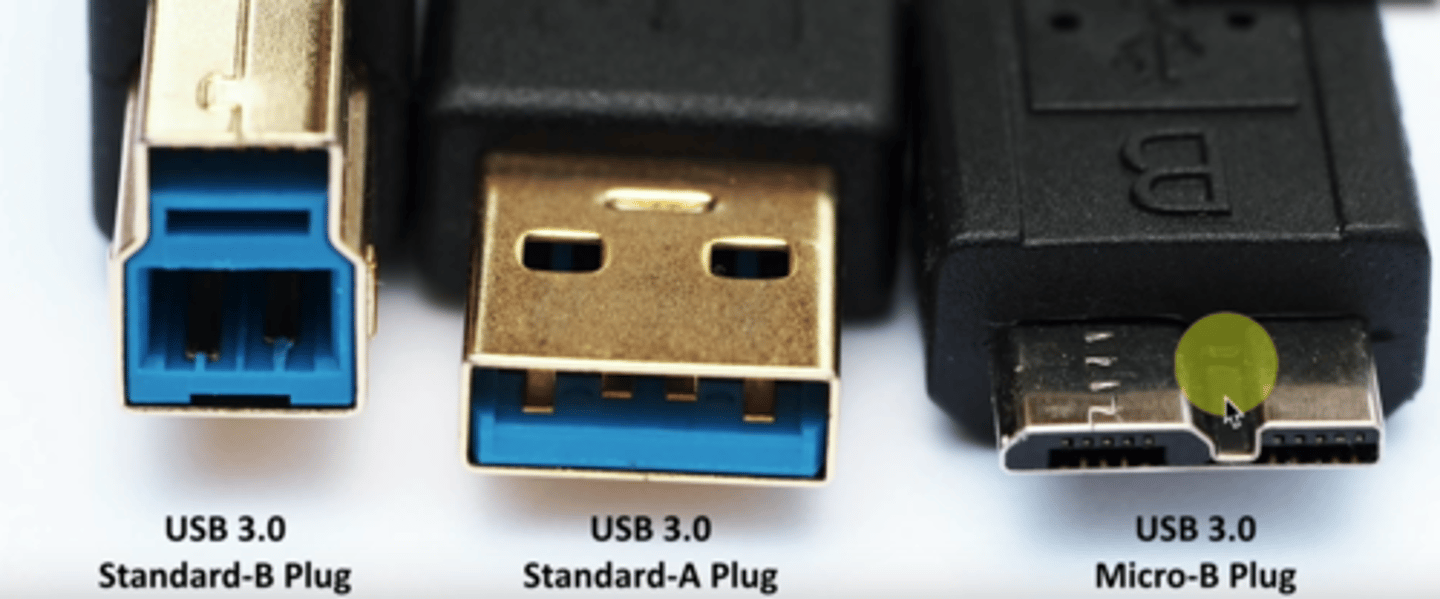
USB 3.0 Connectors
- USB 3.0 Standard-B plug
- USB 3.0 Standard-A plug
- USB 3.0 Micro-B plug

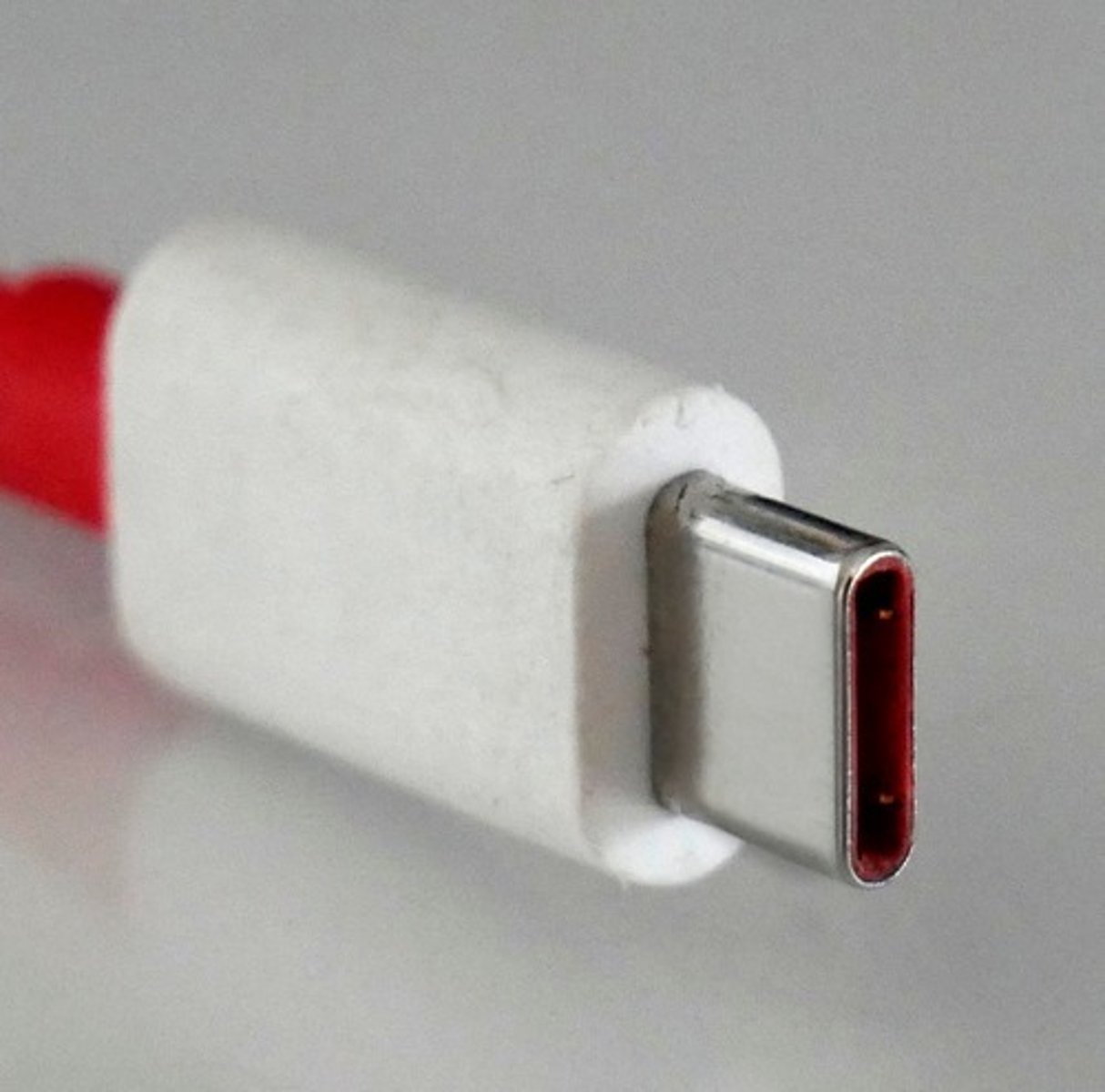
USB Type-C (connector)
Reversible USB type cable that supports up to USB 3.1 with a top speed of 10 Gbps. Quickly becoming the de facto standard port on Android devices. Thunderbolt-enabled versions can reach top speeds of 40 Gbps.
USB Type-C details
USB has a lot of different connectors
- And they have changed over time
Can be annoying to connect USB-A
- Third time's the charm
USB-C replaces all of these
- One connector to rule them all
USB-C describes the physical connector
- It doesn't describe the signal
USB versions and naming
There's a lot to keep track of
- The names keep changing
The standard doesn't change
- Just the names
USB 3.1
Released July 2013
- Doubled the throughput over USB 3.0
USB 3.0 is USB 3.1 Gen 1
- SuperSpeed USB
- 5 Gbit/sec
USB 3.1 is USB 3.1 Gen 2
- SuperSpeed+
- Twice the rate of USB 3.0/USB 3.1 Gen 1
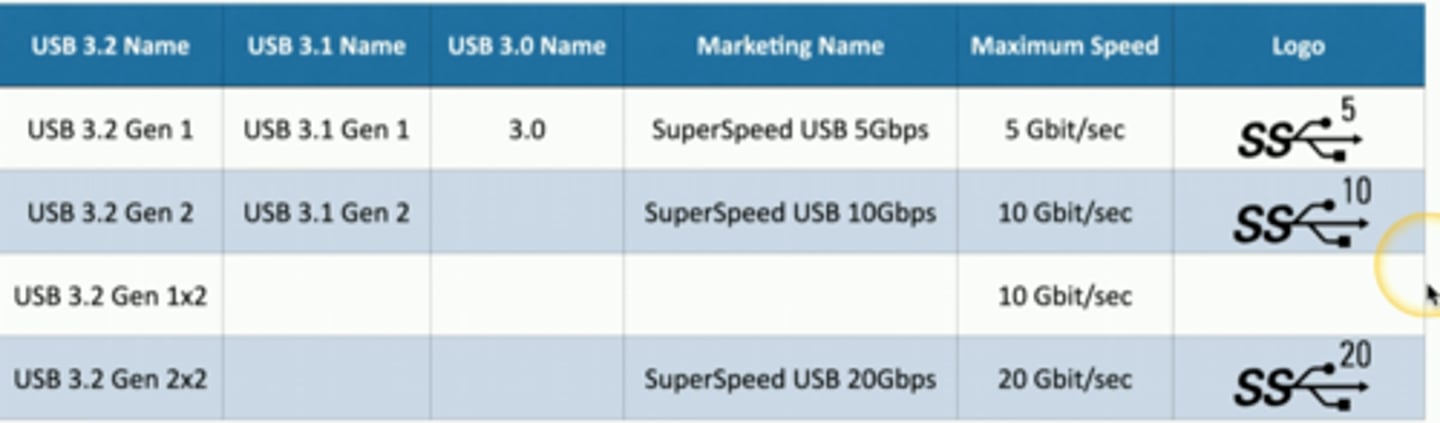
USB 3.2
Recent type of USB released in September 2017.
Bandwidth can double with USB-C cables.
Uses an extra "lane" of communication associated with the flip-flop wires in USB-C.
USB naming standards update
With the release of USB 3.2, the naming standards USB changed.
USB 3.0, which became USB 3.1 Gen 1, is now called USB 3.2 Gen 1.
- Also called SuperSpeed USB 5 Gbps (single lane).
USB 3.1, which became USB 3.1 Gen 2, is now called USB 3.2 Gen 2
- Also called SuperSpeed USB 10 Gbps (single lane).
USB 3.2 details
USB 3.2 Gen 1x2
- 10 Gbps using two "Gen 1" lanes.
USB 3.2 Gen 2x2
- Superspeed USB 20 Gbps using two "Gen 2" lanes.
Thunderbolt
An open standards connector interface that is primarily used to connect peripherals to devices, including mobile devices, if they have a corresponding port.
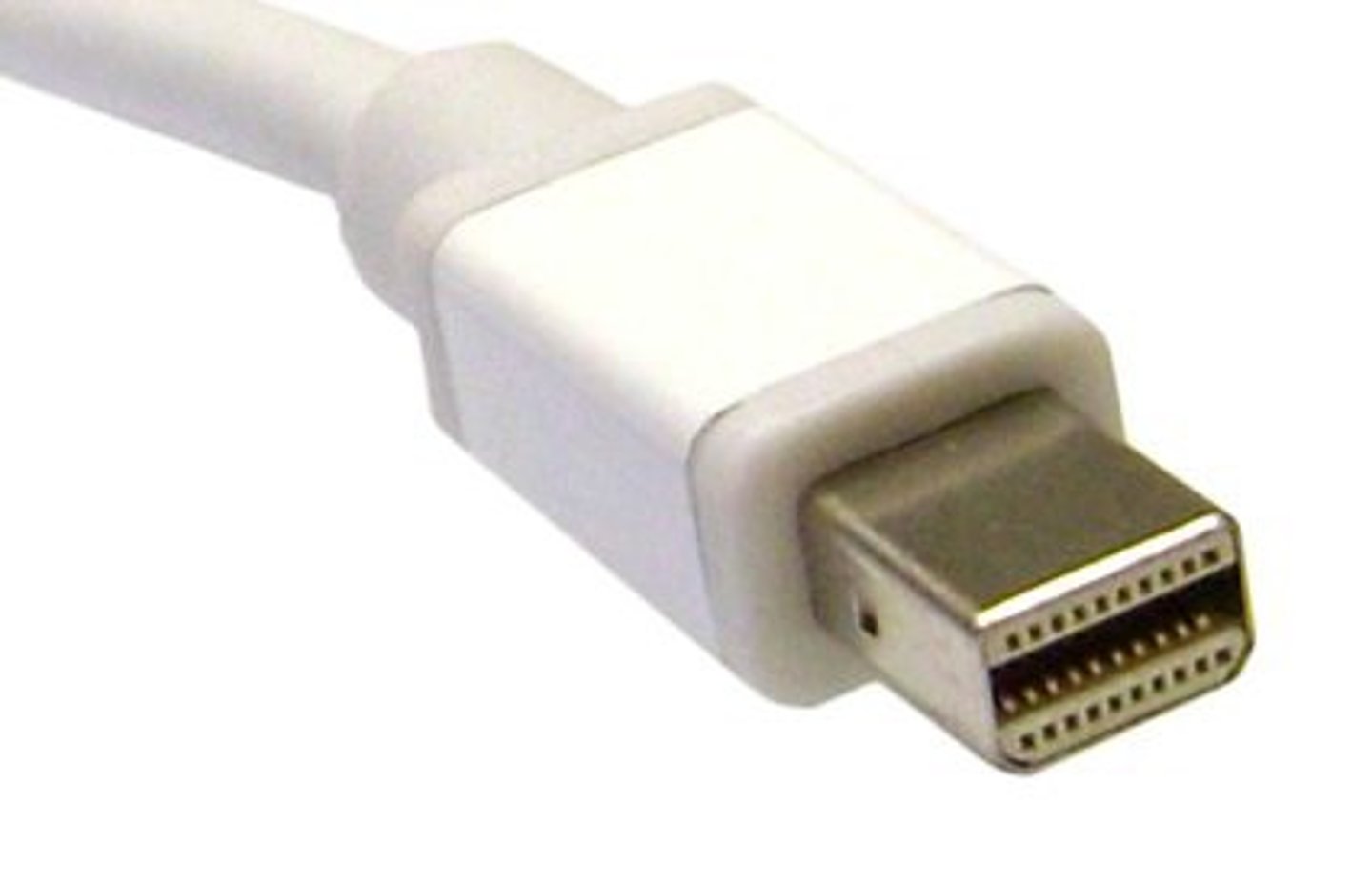

Thunderbolt connector types
Thunderbolt v1
- Two channels
- 10 Gbit/s per channel.
- 20 Gbit/s total throughput.
- Mini DisplayPort Adapter
Thunderbolt v2
- 20 Gbit/s aggregated channels.
- Mini DisplayPort connector.
Thunderbolt v3
- 40 Gbit/s aggregated channels
-USB-C connector
Thunderbolt details
High-speed serial connector.
- Data and power on the same cable.
- Based on Mini DisplayPort (MDP) standard.
Maximum 3 meters (copper)
- 60 meters optical
- Daisy-chain up to 6 devices.
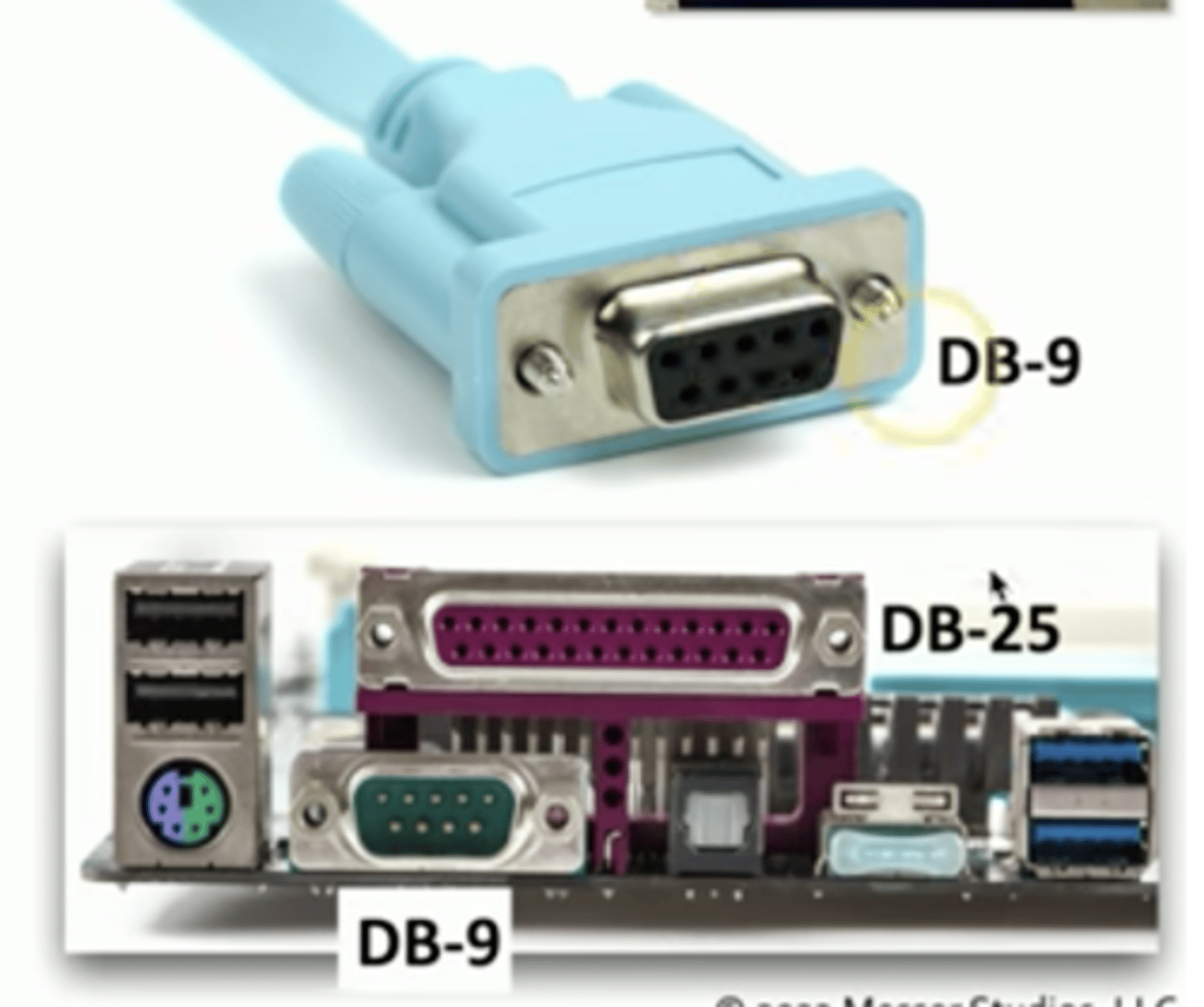
Serial Console Cables
D-subminiature or D-sub
- The letter refers to the connector size
Commonly used for RS-232
- Recommended Standard 232
- An industry standard since 1969
Serial communications standard
- Built for modem communication
- Used for modems, printers, mice, networking
Now used as a configuration port

VGA (Video Graphics Array)
A 15-pin, three-row, D-type VGA monitor connector. Goes by many other names, such as D-shell, D-subminiature connector, DB-15, DE15, and HD15. The oldest and least-capable monitor connection type.
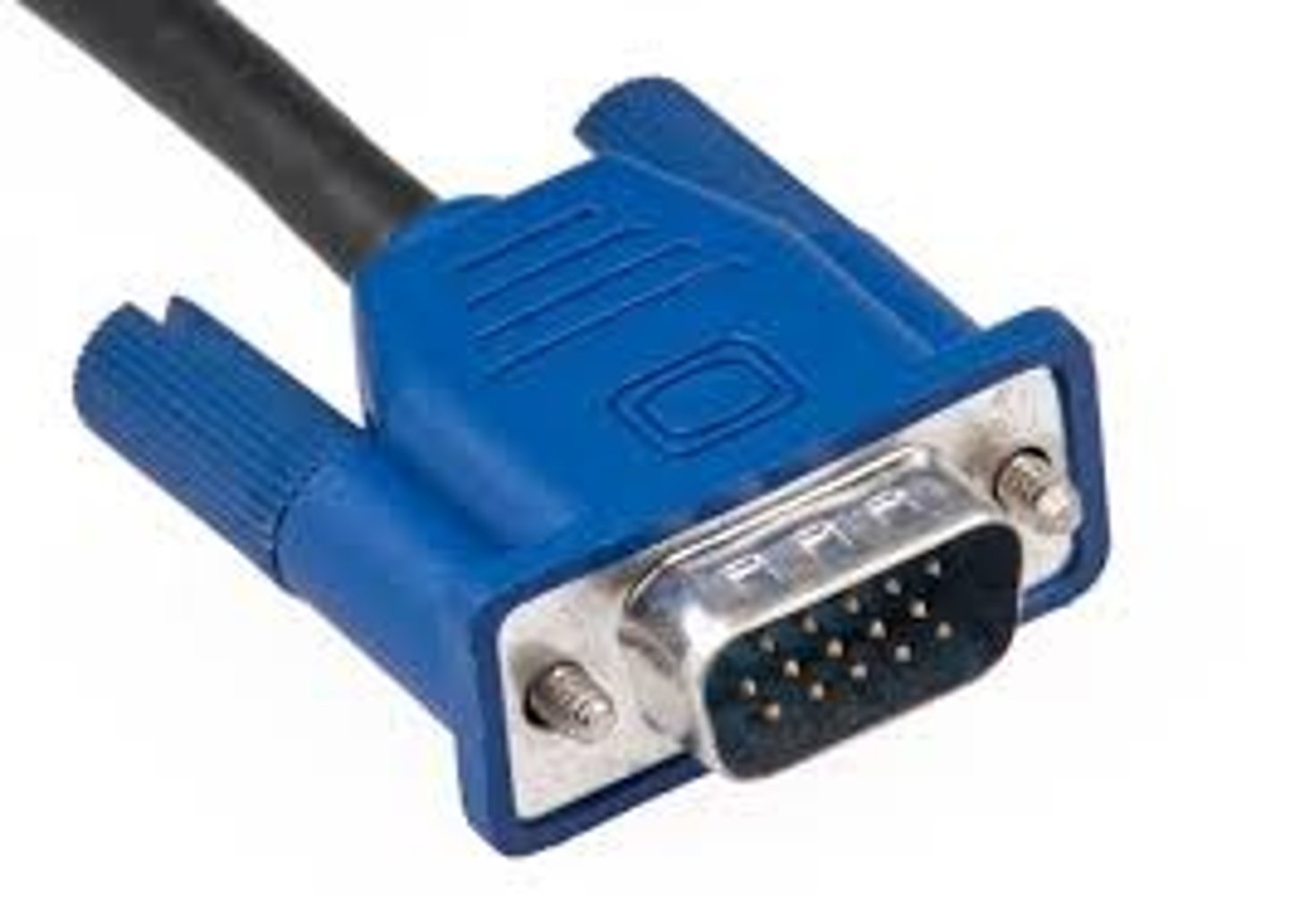

VGA details
DB-15 connector
- More accurately called DE-15
Blue color
- PC System Design Guide Standard
Video only
- Does not transmit audio signal.
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
Single multimedia connection that includes both high-definition video and audio. One of the best connections for outputting to television. Also contains copy protection features.
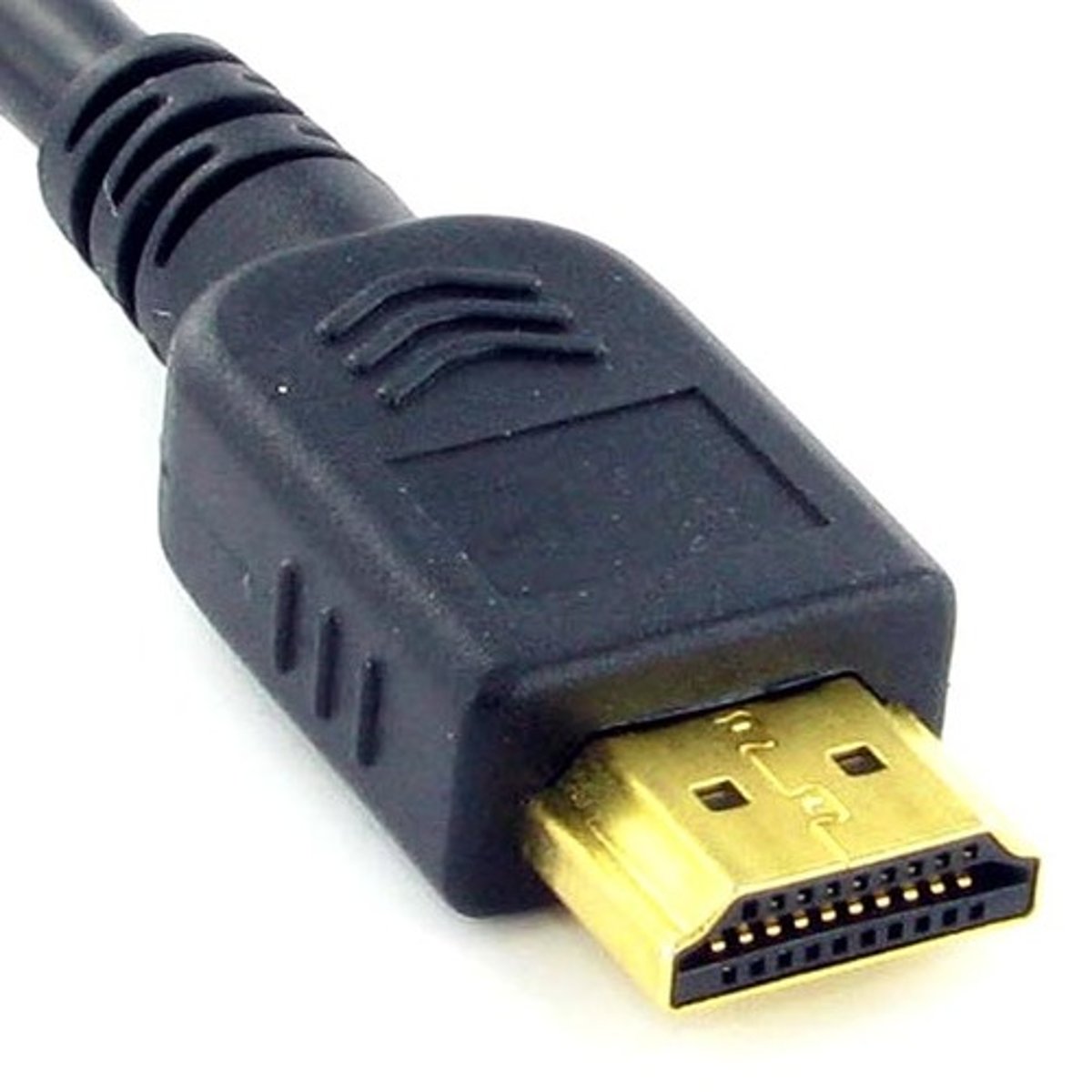

HDMI details
Video and audio stream
- All digital, no analog.
- ~20 meter distance before losing to much signal.
19-pin (Type A) connector.
- Proprietary connector.
DisplayPort (DP)
Digital video connector used by some Apple Mac desktop models and some PC's, notably from Dell. Designed by VESA as a royalty-free connector to replace VGA and DVI.
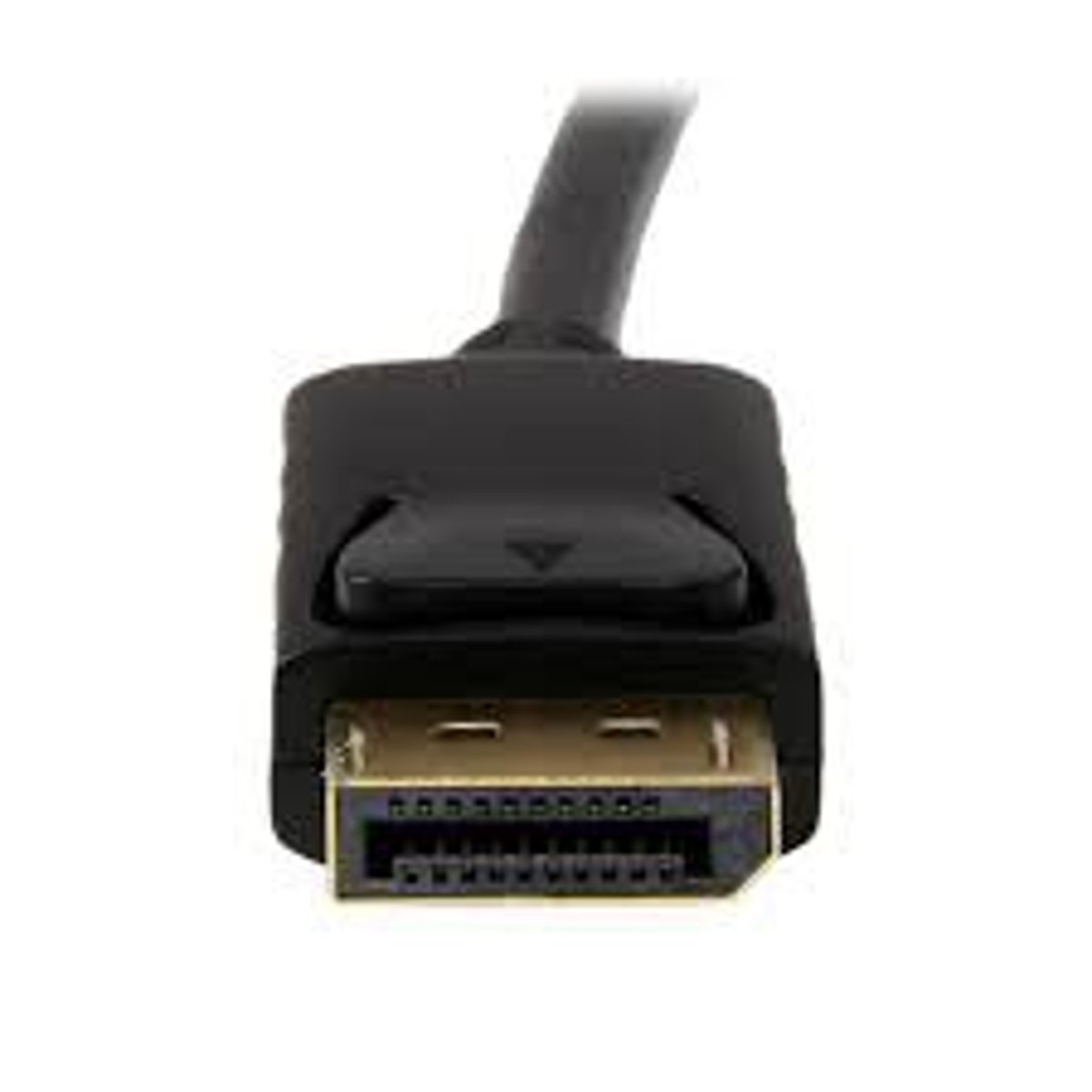

DP details
Digital information sent in packetized form.
- Like Ethernet and PCI Express.
- Carries both audio and video.
Compatible with HDMI and DVI
- Passive adapter.
- DisplayPort -> HDMI
- DisplayPort -> DVI

DVI (Digital Visual Interface)
Special video connector designed for digital-to-digital connections; most commonly seen on PC video cards and LCD monitors. Some versions also support analog signals with a special adapter.
DVI interface types
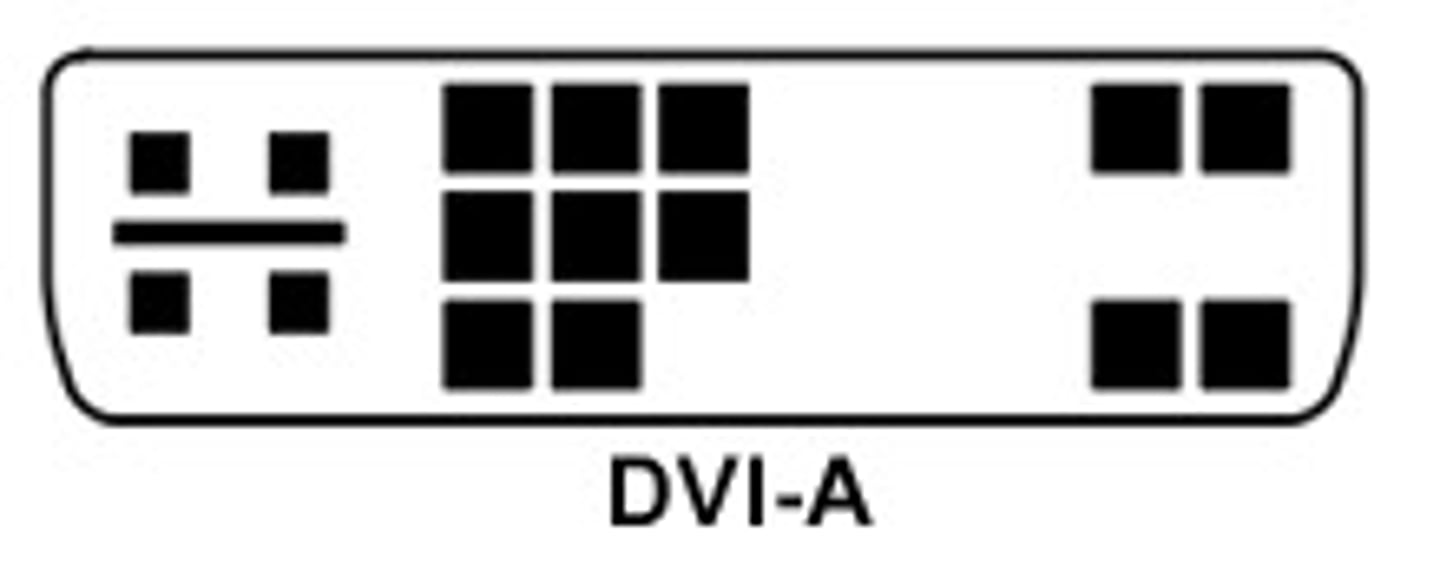
DVI-A
- Analog signals.
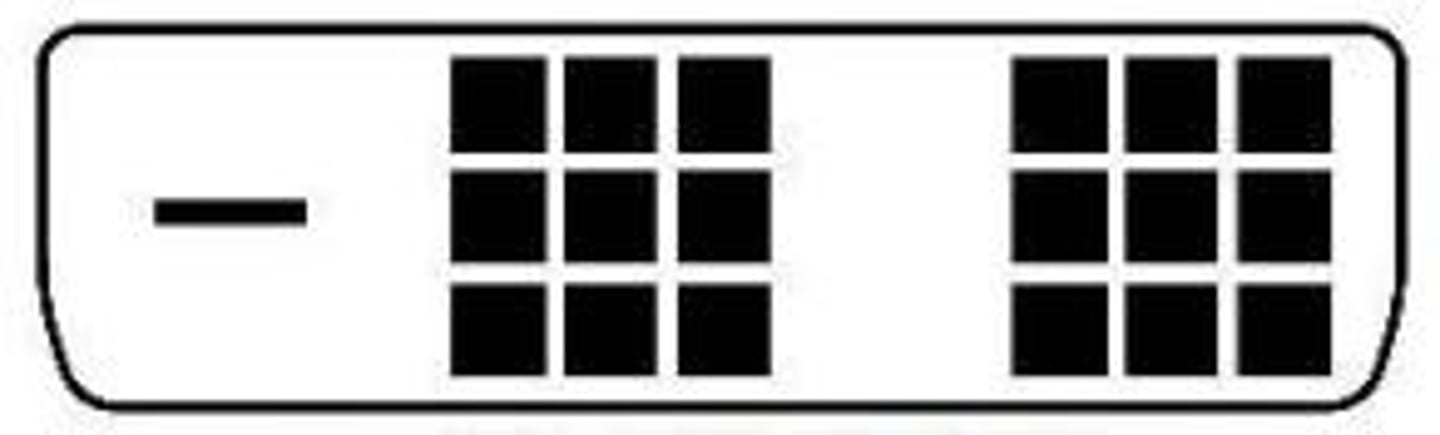
DVI-D
- Digital signals
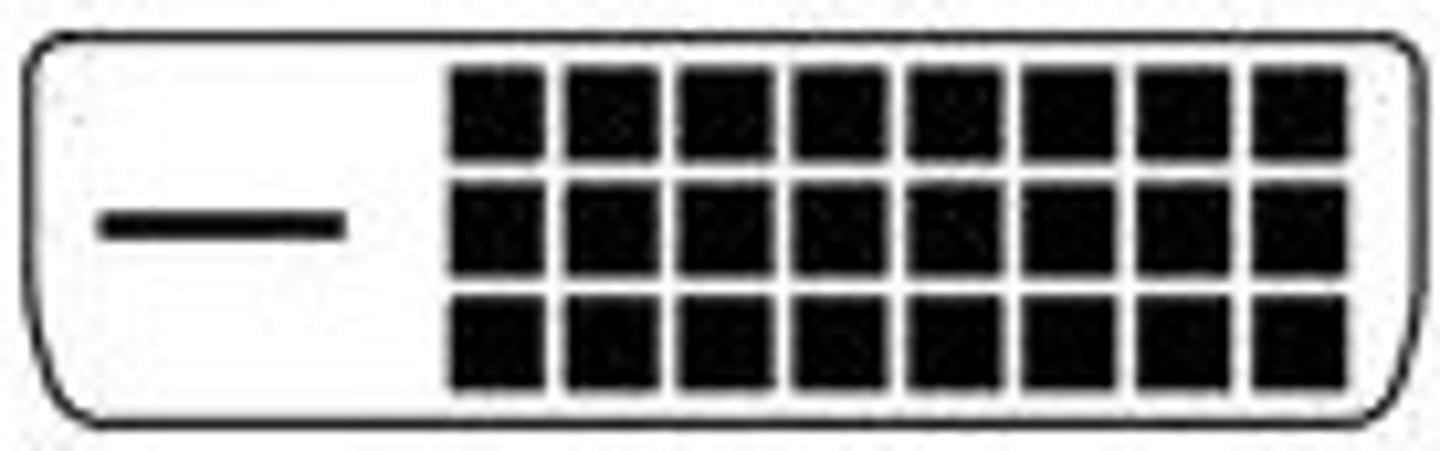
DVI-I
- Integrated
- Digital and analog in the same connector.
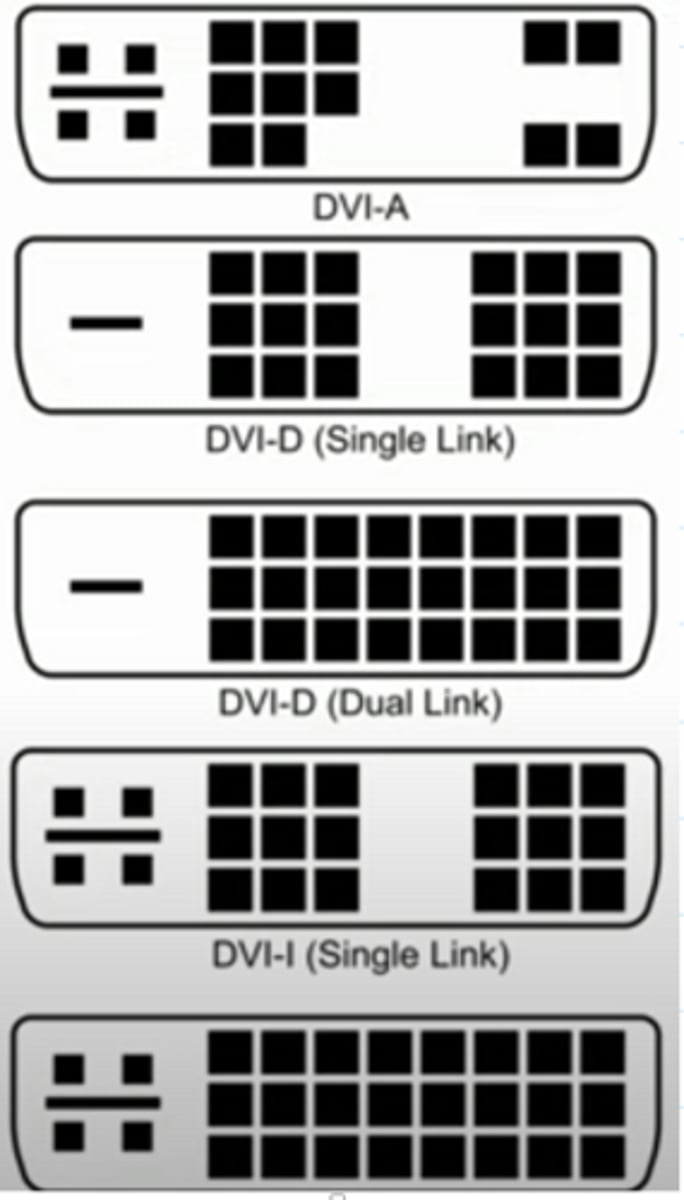
DVI details
Single link and dual link video.
- Single link; low resolution, 3.7 Gbps (HDTV at 60 fps)
- Dual link; high resolution, 7.4 Gbps (HDTV at 85 fps)
- No audio support.
DVI-A
Analog
DVI-D Single Link
Digital - Low resolution
DVI-D Dual Link
Digital - High resolution
DVI-I Single Link
Analog & Digital - Low Resolution

DVI-I Dual Link
Analog and Digital - High resolution

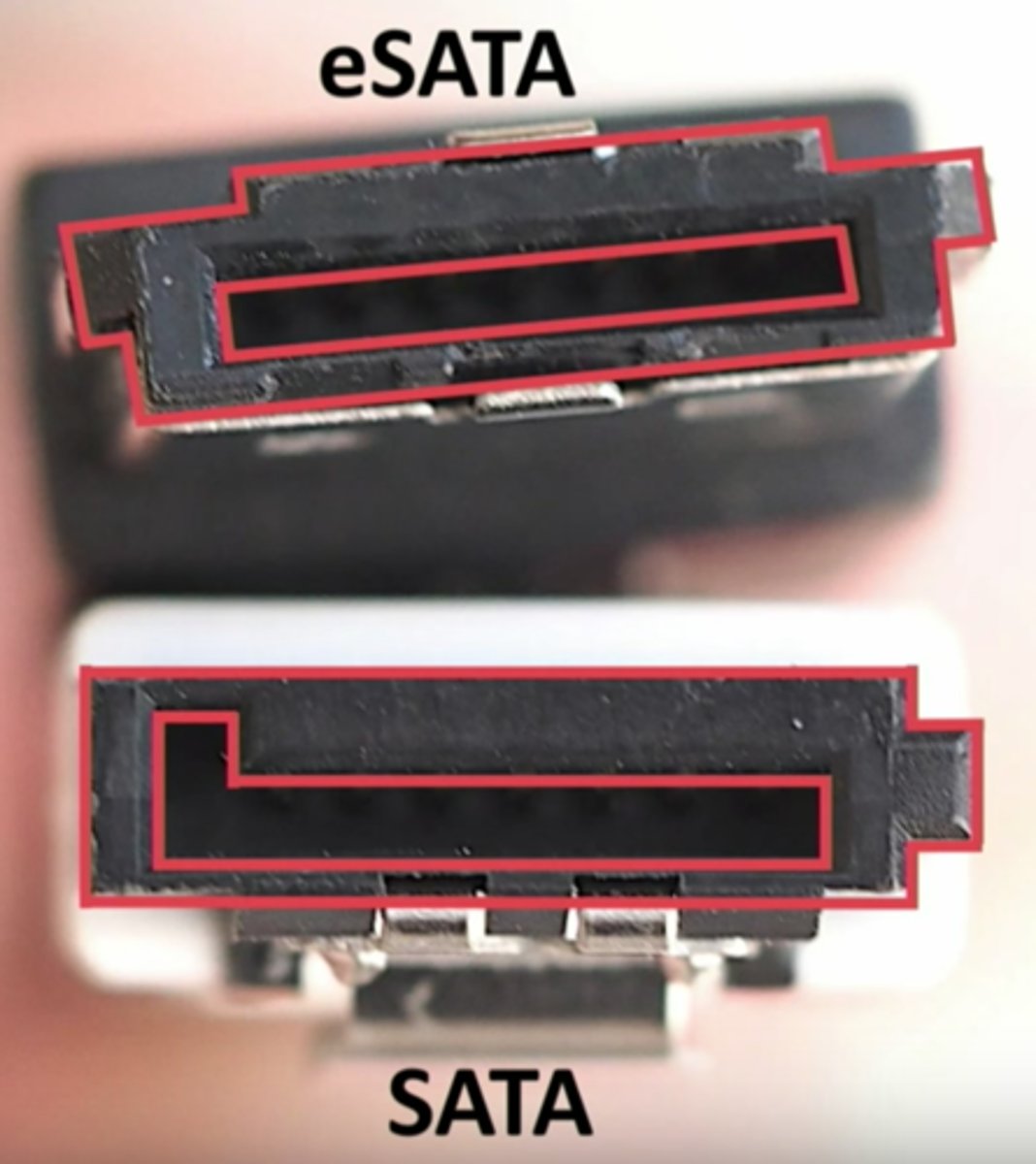
SATA (Serial AT Attachment)
A standard for transferring data between a computer's central circuit board and storage devices.
A computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. It succeeded the earlier PATA standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices.
Refers to two separate connections from the motherboard to the storage device. Power and Data.
SATA versions
SATA Revision 1.0
- SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, 1 meter
SATA Revision 2.0
- SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 1 meter
SATA Revision 3.0
- SATA 6.0 Gbit/s, 1 meter
SATA Revision 3.2
- SATA 16 Gbit/s, 1 meter
eSATA (external SATA)
- Matches the SATA version 2 meters
SATA Power and Data
Two separate cables.
You have SATA power cables and SATA data cables. Both are required to use SATA devices such as HDDs, SSDs, and Optical Drives.
- Power cable goes from PSU -> to your SATA device.
- Data cable goes from Motherboard SATA header -> to your SATA device.
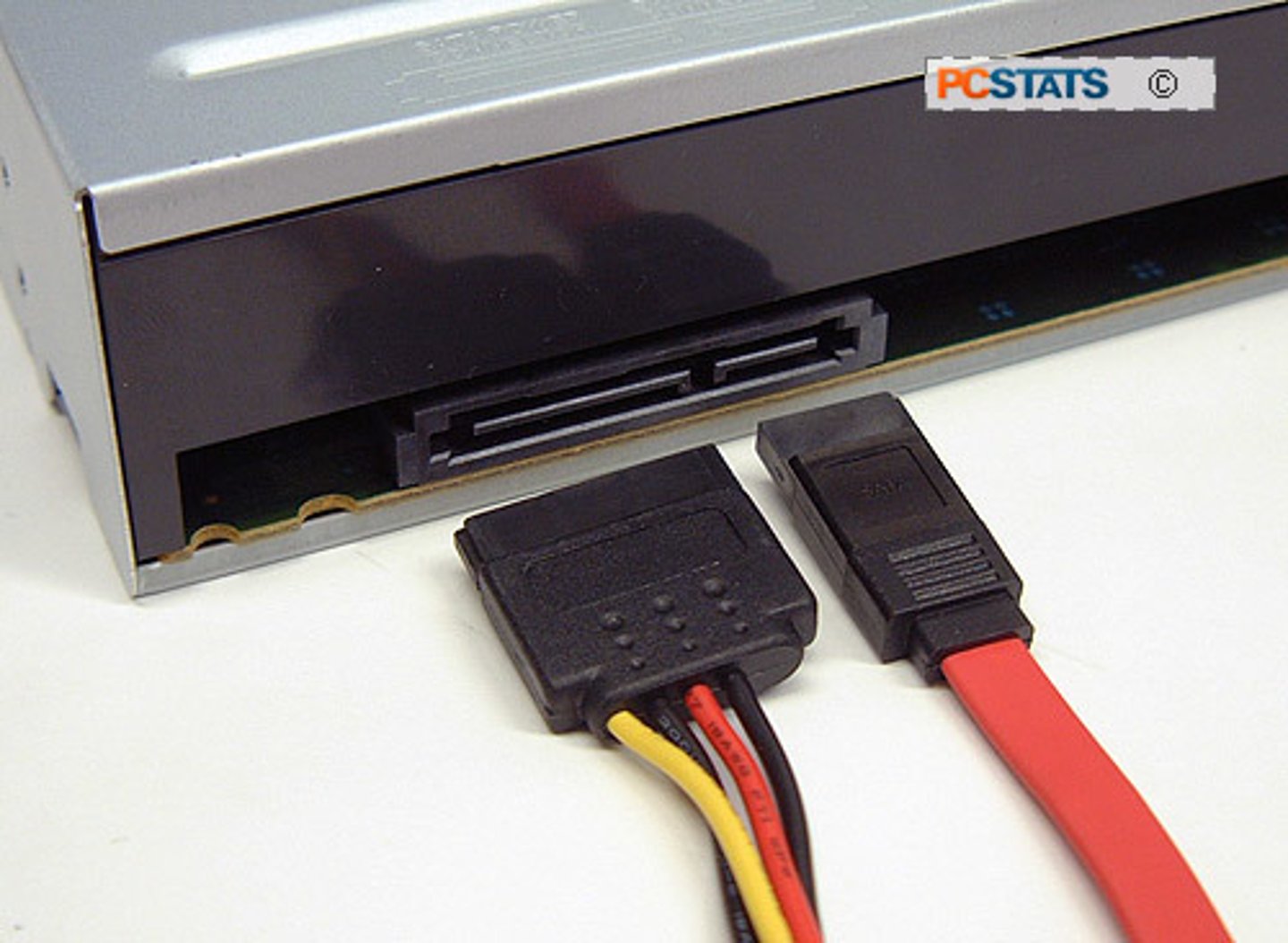

eSATA (External SATA)
SATA based connector for external storage devices, such as hard drives and optical drives.

SATA vs eSATA
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface)
Long-lived storage drive technology once common in the server market. Has been through many iterations. Today, the command set lives on in the Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) hard drives.
Predates the SATA and USB standards, this standard of connector was used for peripherals.
SCSI details
Small Computer Systems interface.
- Not really "small" anymore.
Originally designed to string many peripherals together onto a single cable/controller.
- Up to 16 devices in a SCSI "chain".
Many different formats.
- Fast SCSI, Ultra SCSI, Ultra Wide SCSI, Ultra2 SCSI, Ultra3 SCSI, Ultra-320 SCSI, Ultra-640 SCSI, iSCSI (SCSI over IP).
Parallel and serial options.
SCSI advantages
Not just for hard drives.
- Scanners, tape drives, CD-ROM drives.
Many devices on a single bus.
- 8 on narrow bus, 16 on a wide bus.
Very intelligent interface functionality.
- Much of the difficult configuration work is done between the SCSI devices.
Industry longevity.
- Well supported in the enterprise.
- A standard drive for virtual systems.
SCSI ID and logical unit (LUN)
Every SCSI device on a single bus is assigned
a separate ID number
• SCSI ID 0 (SCSI controller), ID 2 (hard drive),
ID 3 (CD-ROM)
Logical units (LUNs) are defined within each SCSI ID
• Separate drives in a storage array or virtual machine
The signal at the "end" of a physical SCSI bus is terminated
• Can be internal to the device or a separate termination device
Serial attached SCSI (SAS) devices have no jumpers, terminators, or settings.
Serial attached SCSI
Move from parallel to serial.
- Increased throughput.
- Similar to the move from PATA to SATA.
Point-to-point connectioin
- No more daisy chains.
No termination required.
- The bus has two devices on it.
The control and management of SCSI
- The speed of a serial connection.
PATA (Parallel ATA)
A legacy standard for transferring data between a computer's central circuit board and storage devices. Precursor to SATA.
Works in Parallel instead of Serial.
No longer in widespread use.
Comes in 40 pin and 80 pin variations.
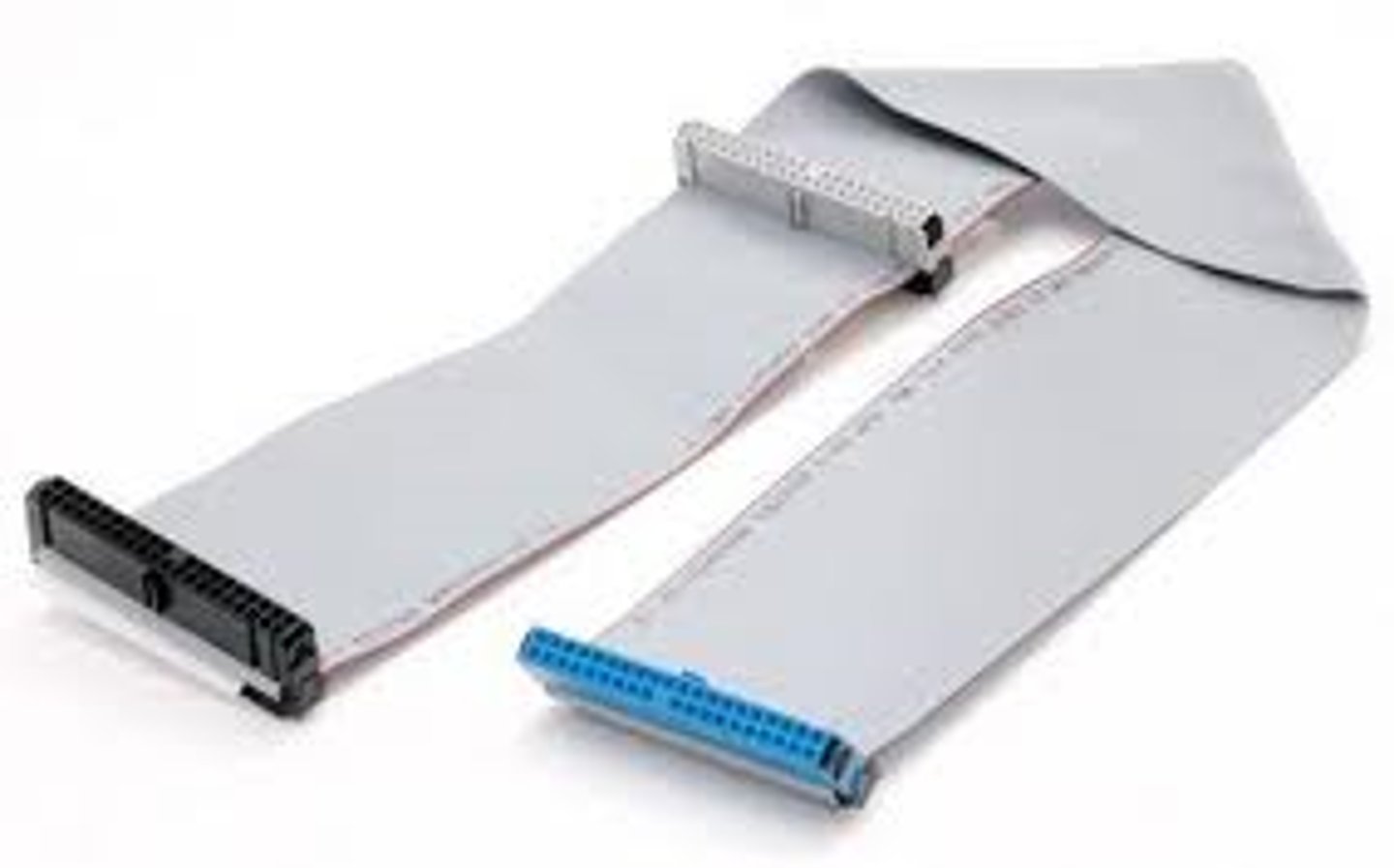

PATA details
Parallel AT attachment, Parallel ATA, ATA.
- Remember the PC/AT?
An evolutionary process.
- Circa 1999
Originally called IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics)
- A Western Digital invention.
- 2nd generation called EIDE (Enhanced IDE).
The evolution.
- Promised faster speeds (from 16 MB/s through 133 Mb/s).
- Additional devices (CD-ROM drives, etc).
Now called PATA (Parallel ATA).
PATA vs SATA
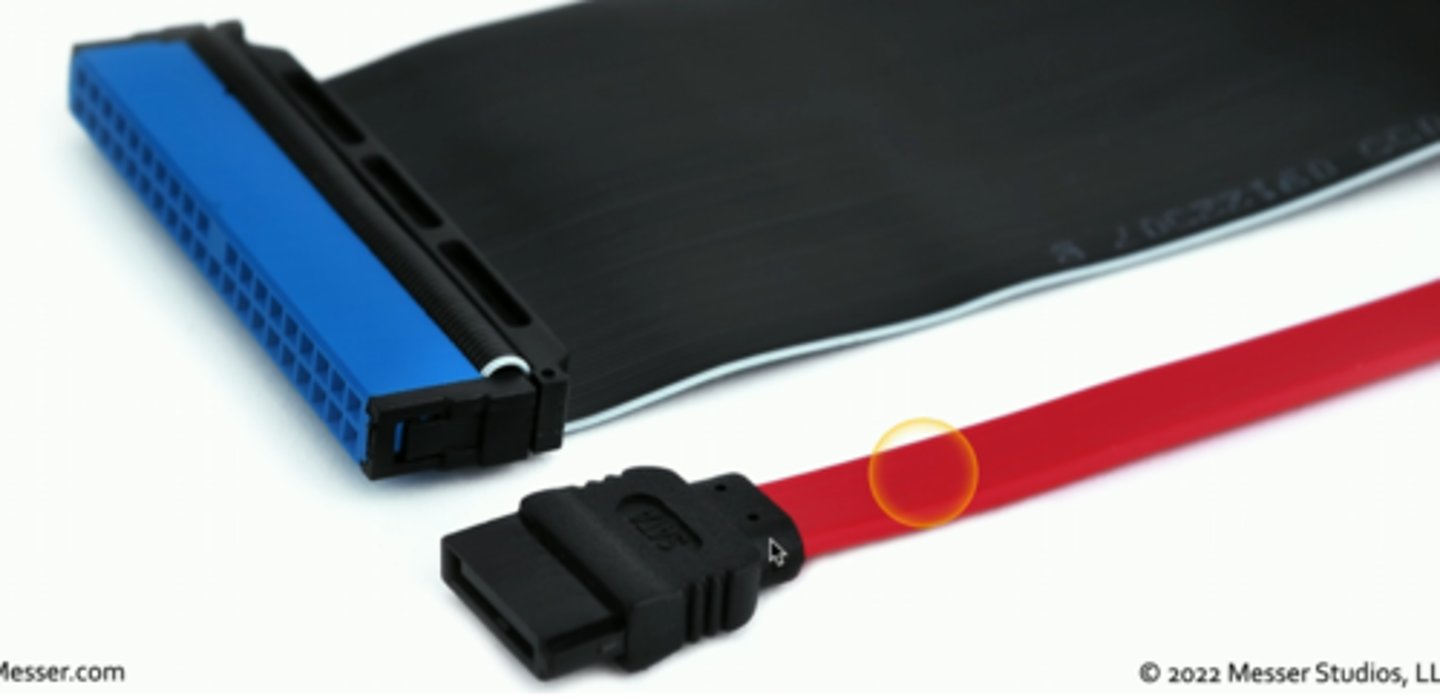

Adapters and Converters
The best laid plans...
• Need an adapter
Convert between different connectors
• Electrically compatible.
Convert from one format to another.
• You need Ethernet but you only have USB.
A good temporary fix
• Or a good permanent one.
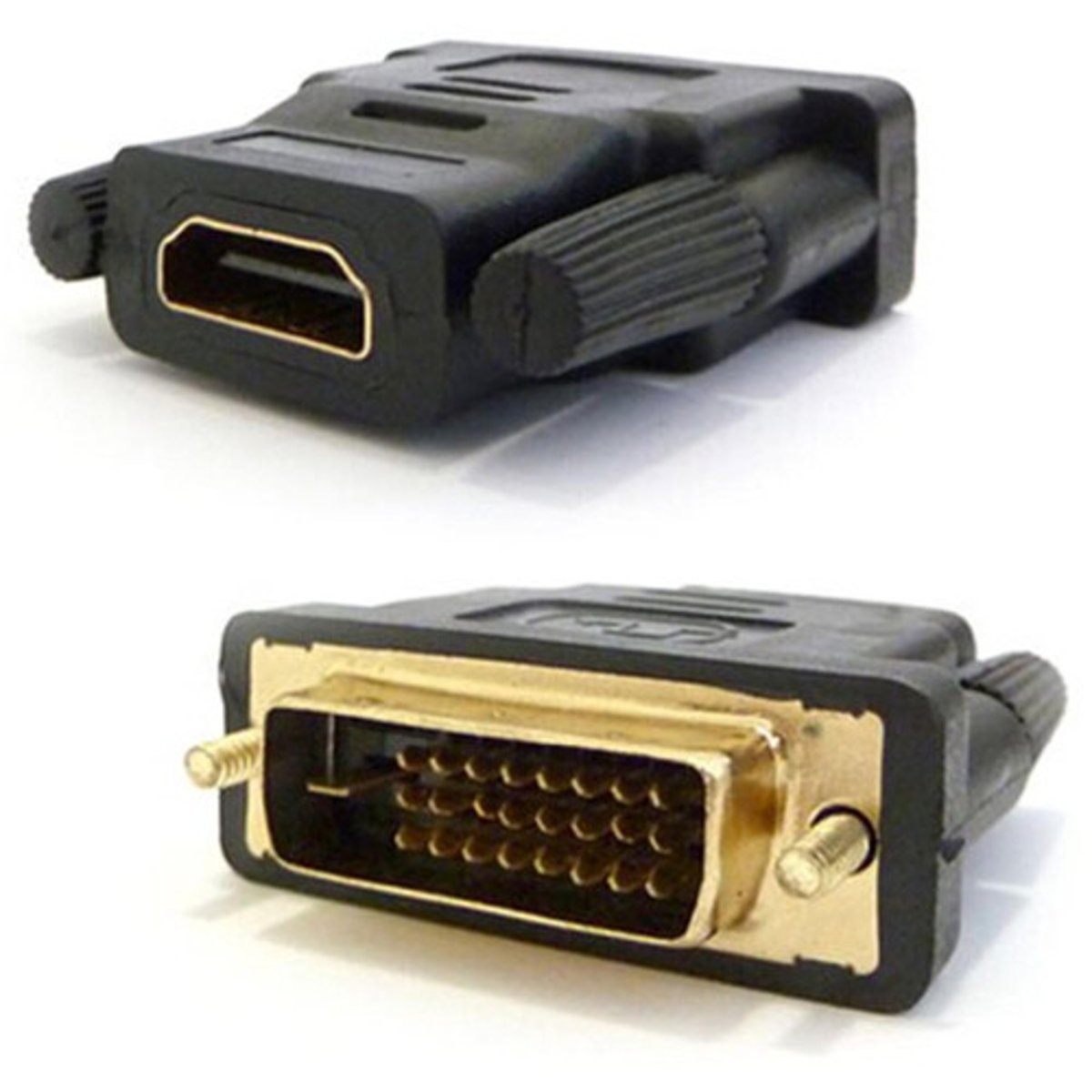
DVI to HDMI Adapter
DVI-D and HDMI are electrically compatible
- HDMI is backward-compatible with DVI-D
- No signal conversion required
- No loss of video quality

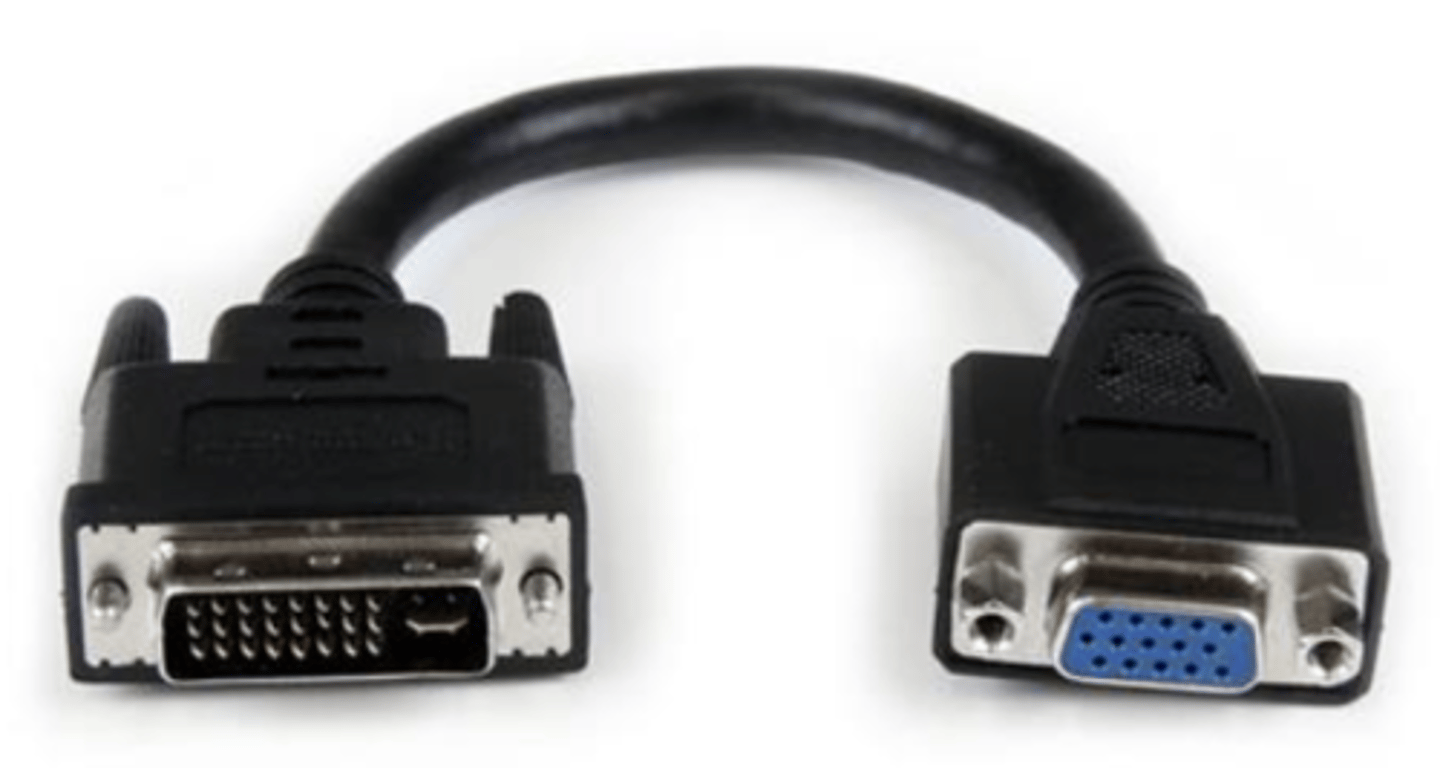
DVI to VGA Adapter
DVI-A includes analog signals
- Backwards compatible with VGA
- Only 640 x 480 resolution supported
- May only need an adapter
- VGA to DVI Digital will need a converter

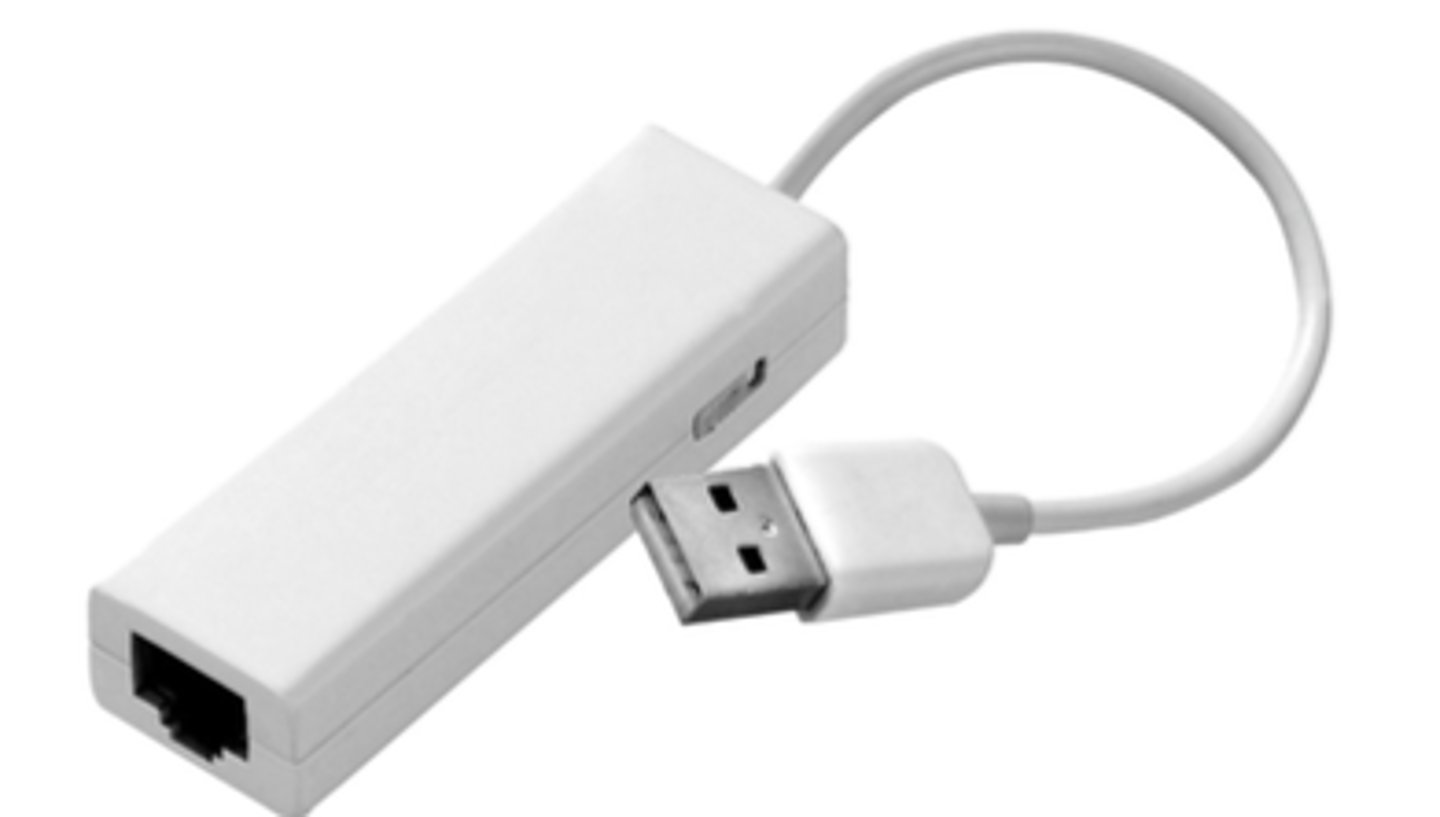
USB to Ethernet Adapter
Some laptops don't have an Ethernet connection
- Convert USB to Ethernet

USB-C to USB-A Adapter
Merge the new with the old.
- Use your older peripherals.
- May need to then be daisy chained with a USB to Ethernet adapter as well.
USB Hub
Device that extends a single USB connection to two or more USB ports, almost always directly from one of the USB ports connected to the root hub.
USB Hub details
Connect many devices.
- High speed USB connectivity.

RJ11 Connector
6 position, 2 conductor (6P2C)
- Some cables will wire additional conductors.
Telephone or DSL connection.
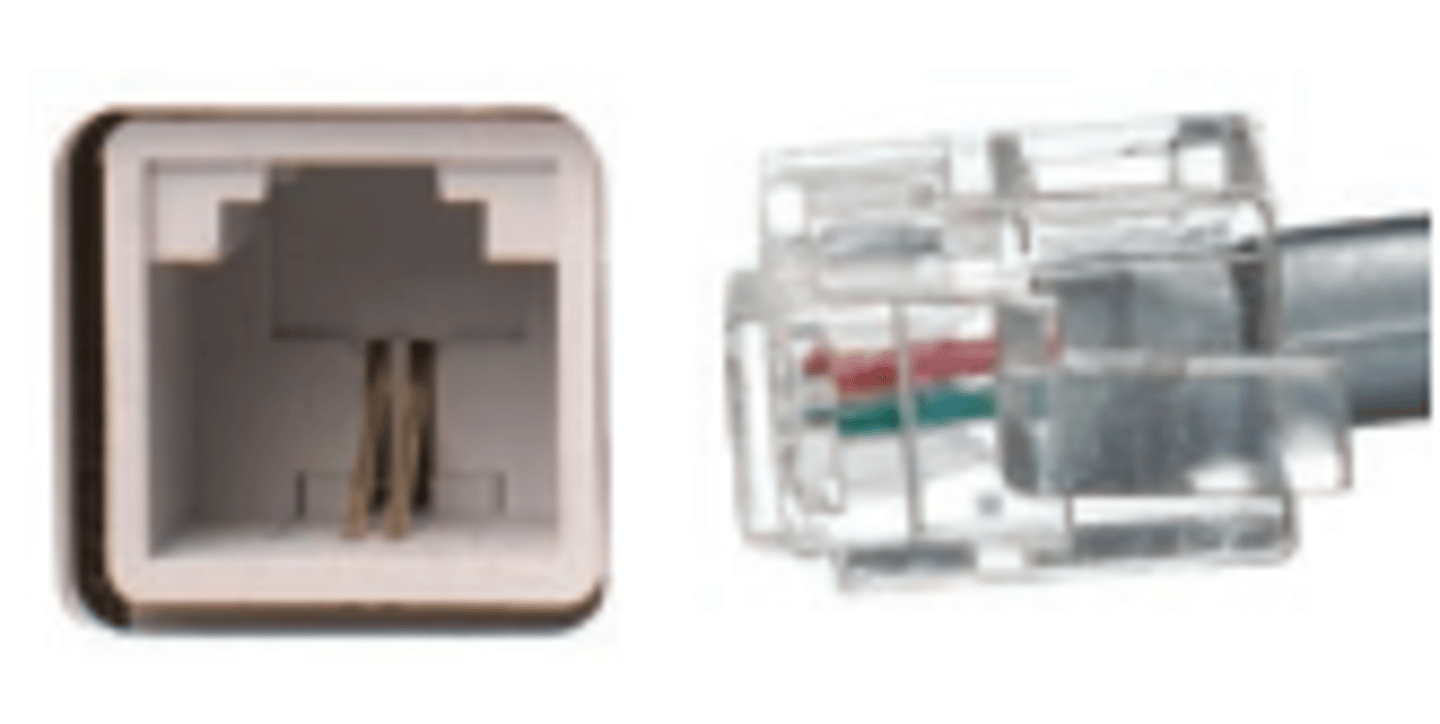
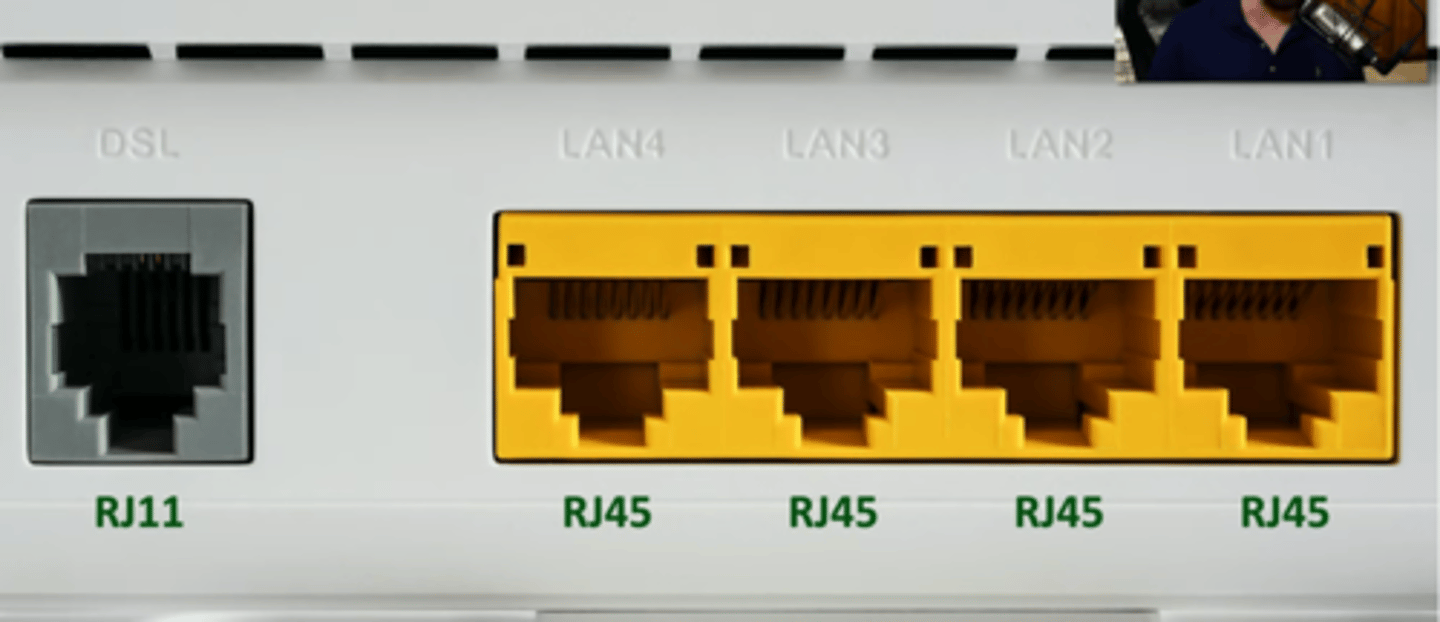
RJ45 Connector
Registered Jack type 45
8 position, 8 conductor (8P8C)
- Modular connector.
- Mainly used for Ethernet, but be used other connections as well.
RJ11 vs RJ45

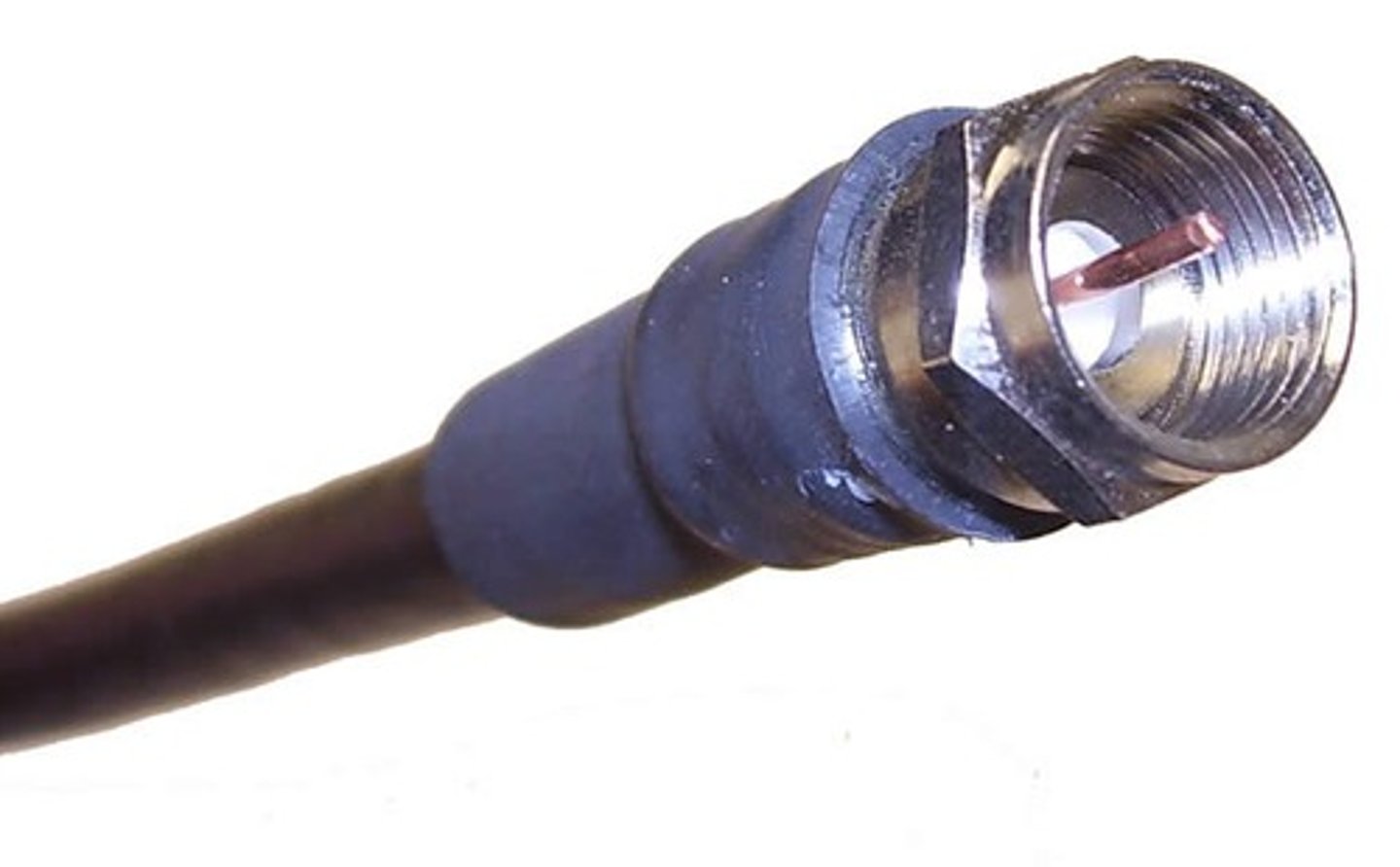
F-Connector
Cable television
- Cable modem.
- Uses Coaxial cable.
- DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification)

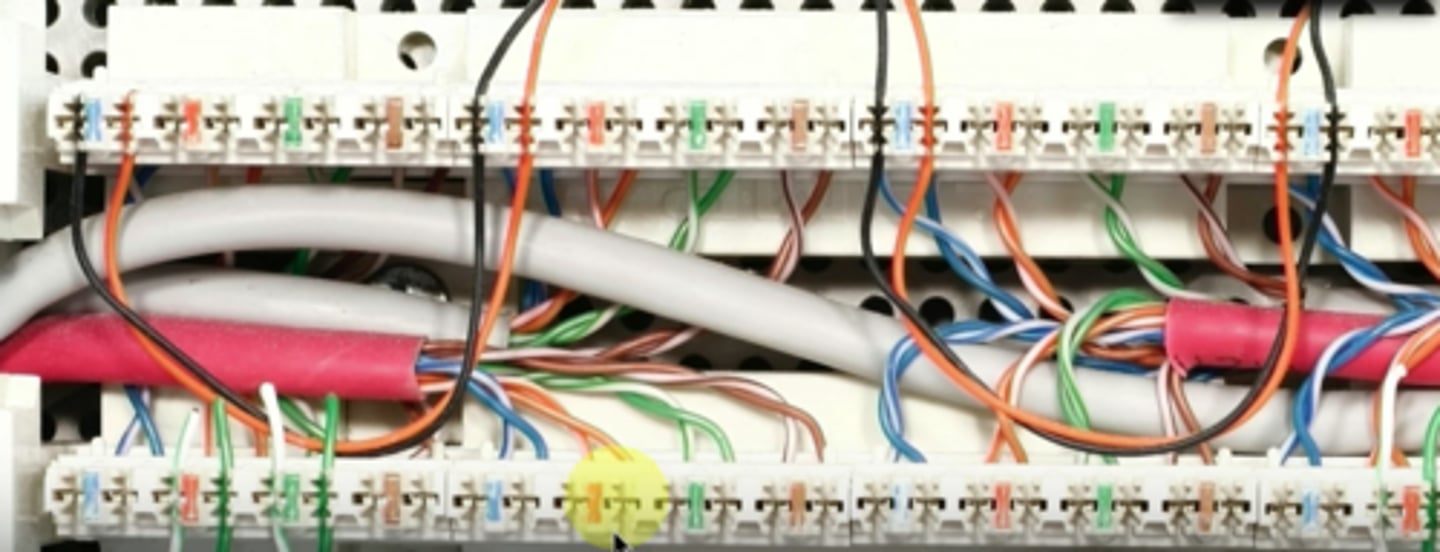
Punchdown block
Wire-to-wire patch panel
- No intermediate interface required
Wires are "punched" into the block
- Connecting block is on top
Additional wires punched into connecting block
- Patch the top to the bottom
USB 1.1/2.0 connectors
USB 3.0 connectors

USB-C connector
24-pin double sided USB connector.
- Used for both hosts and devices.
Used for USB, Thunderbolt.
- Interface is the same, signal can vary.

Molex connector
Computer power connector used by devices INSIDE your computer, such as optical drives, hard drives, and case fans. Keyed to prevent it from being inserted into a power port improperly.
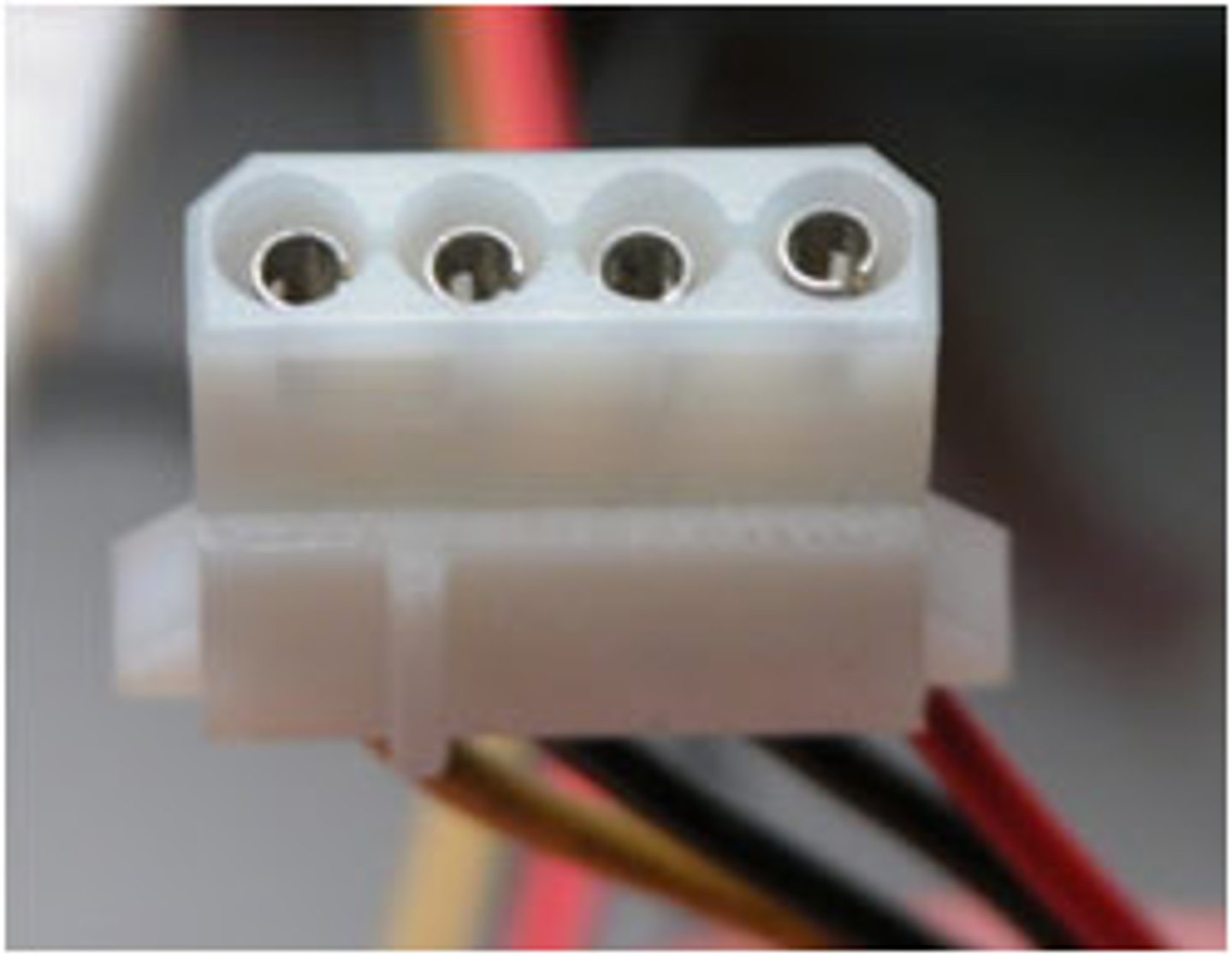
Molex details
4-pin peripheral power connector.
- Molex Connector Company.
- AMP MATE-N-LOK
- Proves +12 V and +5 V
Power for many devices in the computer case.
- Storage devices.
- Optical drives.
- Fans
- Other peripherals
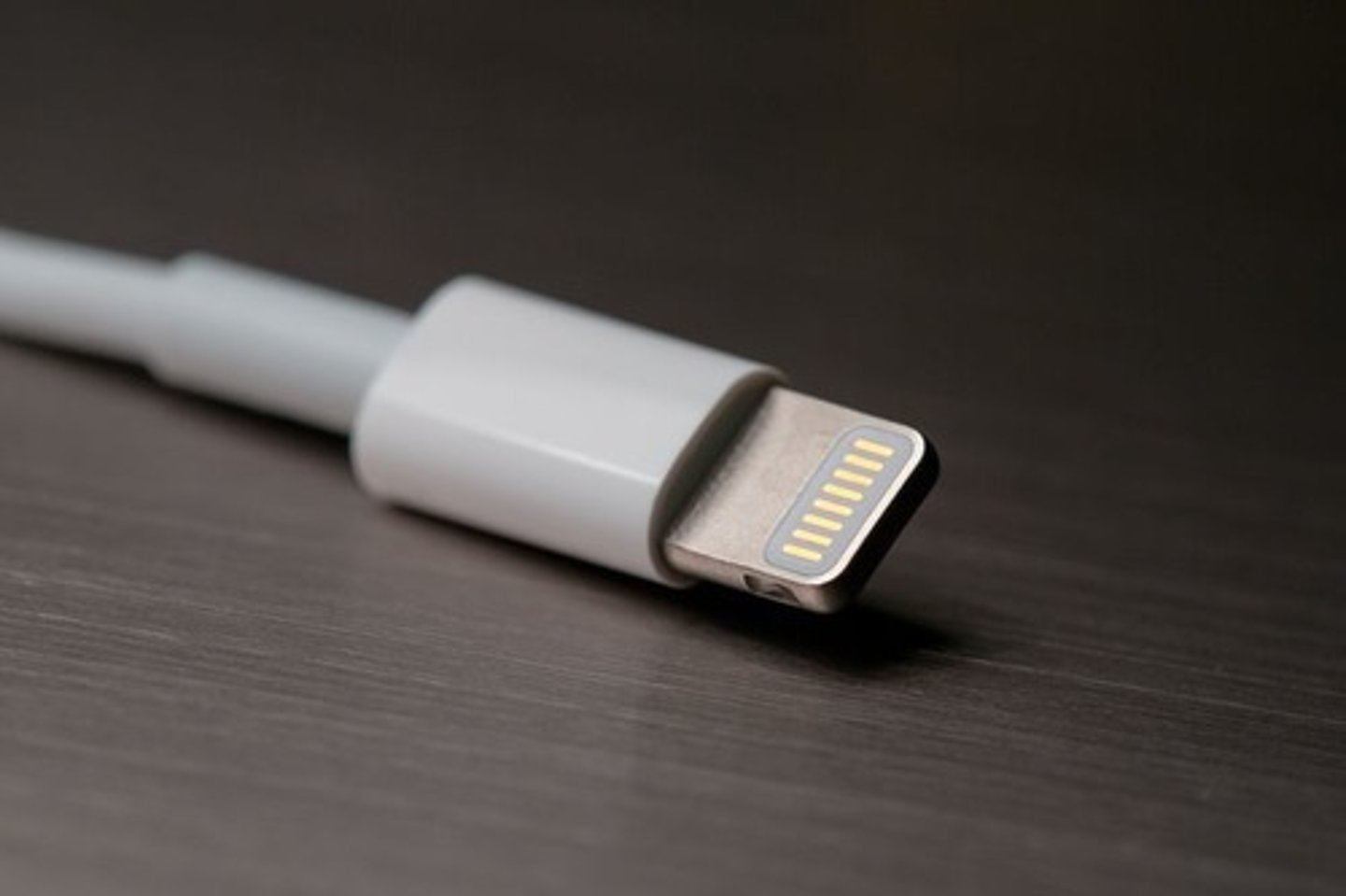
Lightning Connector
Apple proprietary connector.
- 8 pin, digital signals.
- iPhone, iPad, iPod devices.
Some advantages over Micro-USB
- Higher power output for phones and tablets.
- Can be inserted either way.

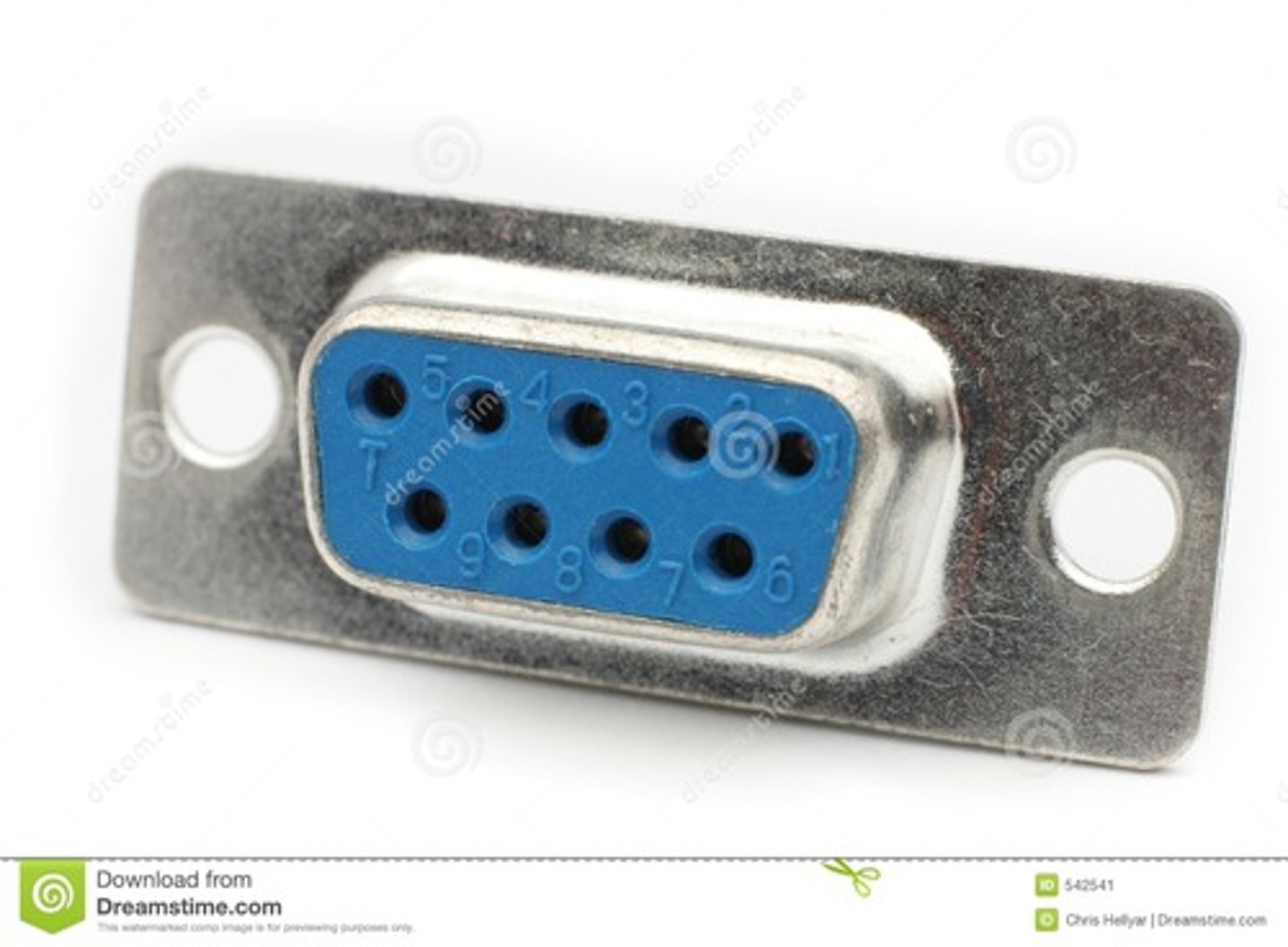
DB-9 Connector
D-Subminiature or D-sub
- The letter refers to the connector size.
Commonly used for RS 232
- Recommended Standard 232
- An industry standard since 1969.
Serial communications standard.
- Built for modem communication.
- Used for modems, printers, mice, switches, routers, networking.

Fiber Connectors
Connectors for Fiber Optic cables.
- LC (Local Connector)
- ST (Straight Tip)
- SC (Subscriber/Square Connector)
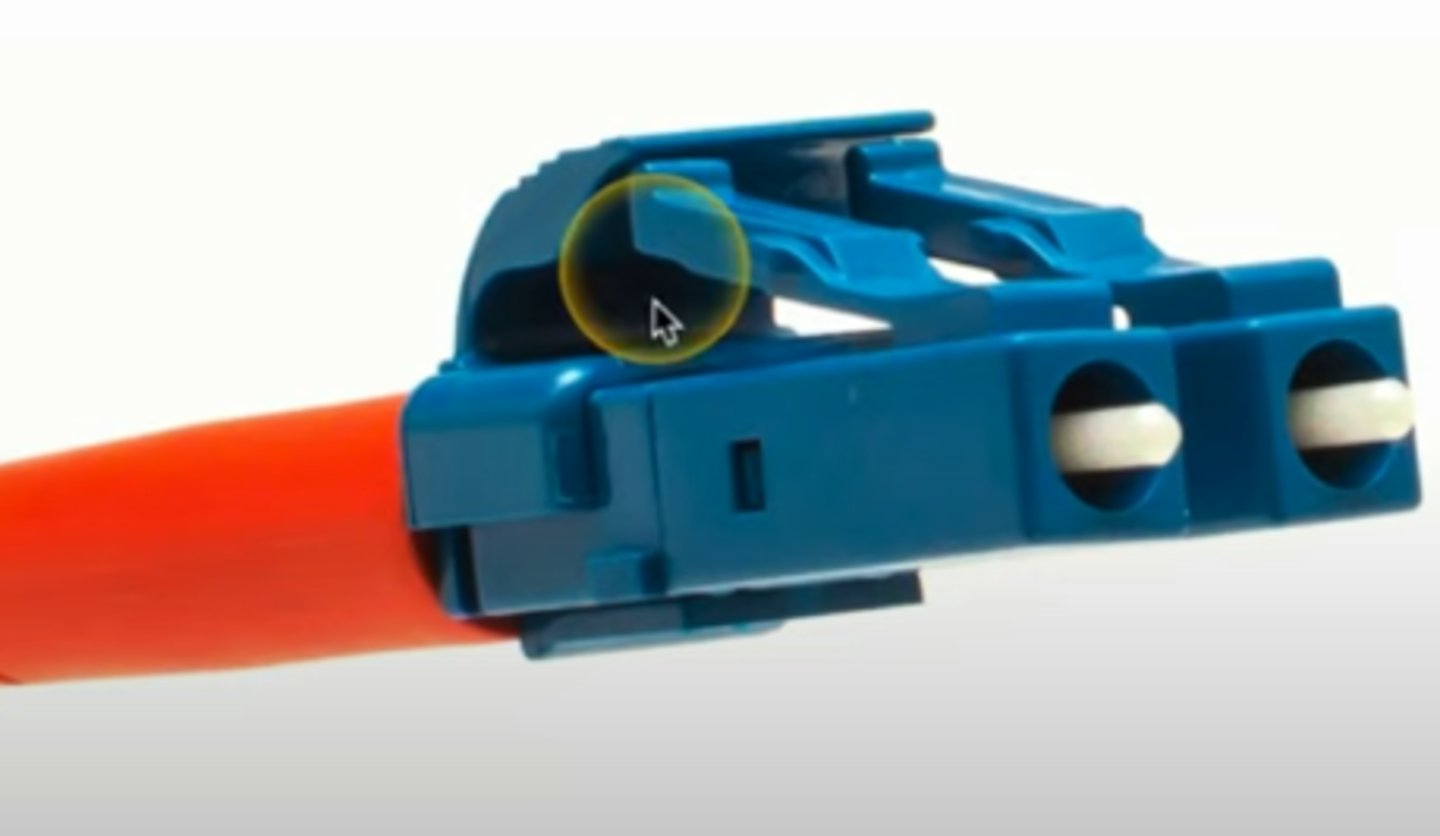
LC (Local Connector)
A type of Fiber connector.
A single interface with two separate fiber connections.
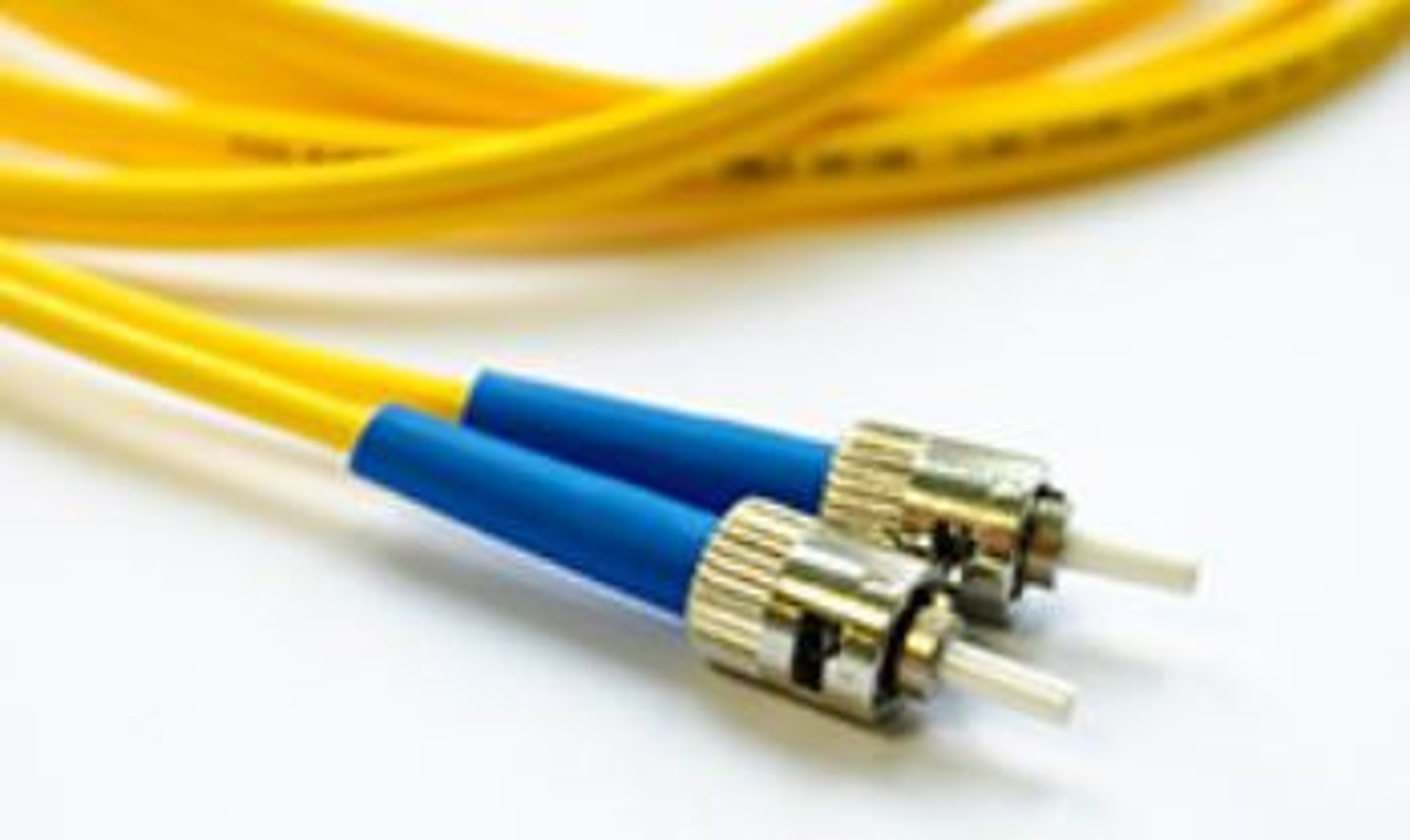
ST (Straight Tip)
A type of Fiber connector.
The end of the connector has a "bayonet" connection, which locks in with a quarter turn.

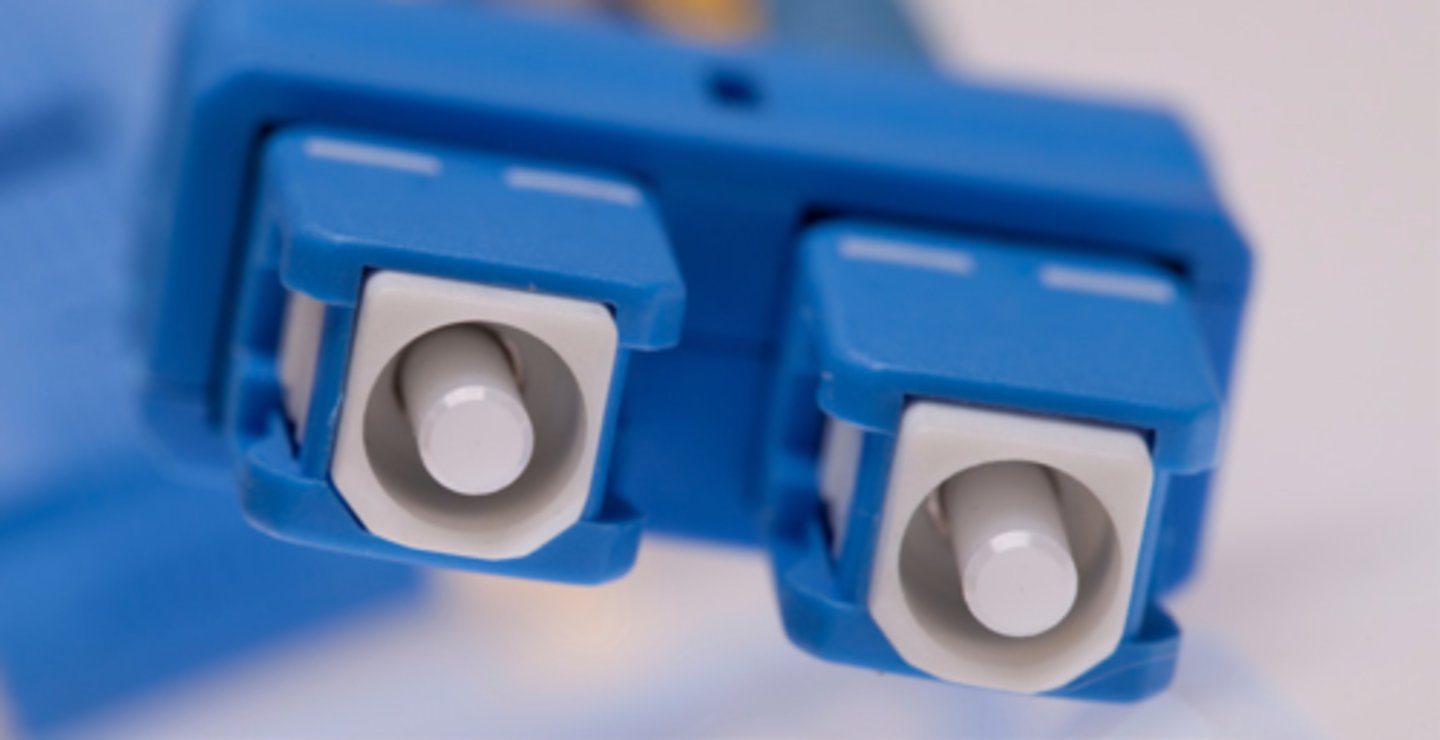
SC (Subscriber/"Square" Connector)
A type of Fiber connector.
Named after it's square appearance.
Can be broken apart and used as two separate connectors, or clipped together for one single connector.

USB 1 Speed
12Mbps
USB 2 Speed
480Mbps
USB 3.1 Gen 1 Speed
5Gbps
USB 3.1 Gen 2 Speed
10Gbps
19 Pin Type A Connector
HDMI Connector
3-row, 15 Pin Data Connector
VGA Connector
15 Pin Power Connector
SATA Power Connector
7 Pin Data Connector
SATA Data Connector
40 Pin Connector
PATA Connector