Energy Systems
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
3 primary energy systems
1, phosphagen (ATP/PCR)
2, glycolytic system
3, oxidative system
energy system used at start of exercise
phosphagen (ATP/PCR)
energy system used around 60 second mark of exercise
glycolysis system
energy system used at 120 seconds of exercise
oxidative system
metabolism
all chemical processes in living organisms require metabolism for the maintenance of life
2 phases of metabolism
anabolism and catabolism
anabolism
smaller molecules are converted to larger molecules
EX: glucose to glycogen
catabolism
larger molecules are broken down to smaller molecules
EX: triglycerides to glycerol/ fatty acids
mitochondria
found in every cell in human body except red blood cells
membrane bound structure
where krebs cycle and ETC happen
krebs cycle
series of chemical reactions that produce a larger quantity of ATP
ATP
energy currency of cells
catabolic reactions convert biochemical energy from organic molecules to ATP
cell respiration
controlled release of energy in form of ATP
Structure of ATP
triphosphate group - 4O + P
adenosine group - sugar and base
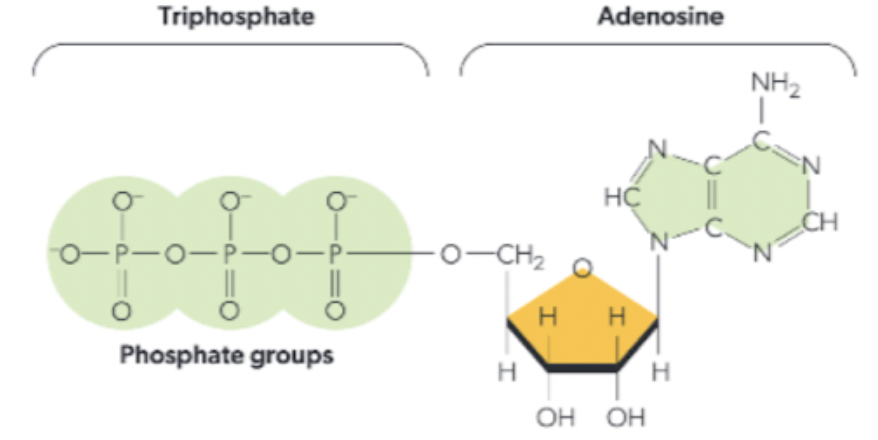
Structure of ATP info
bonds between three phosphate group are very energy rich
energy is released when ATP combined with water
energy function in sports
required for muscular contraction
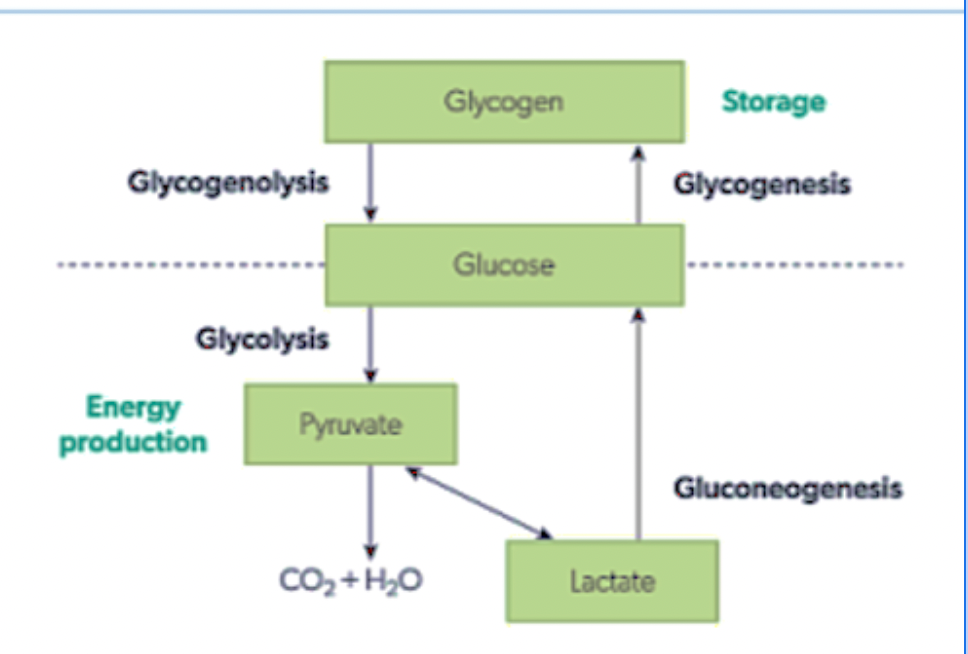
carbohydrate metabolism
the breakdown of carbohydrates into simple sugars like glucose, fructose, sucrose
glycolysis
breakdown of glucose to pyruvate
gluconeogenesis
lactase is transported back to liver when glucose is re-formed
glycogenesis
grouped together to form glycogen which can be stored in liver and muscles
glycogenolysis
process of glycogen release and breakdown to be used as glucose and glucose-6-phosphate in muscles
Carbohydrate metabolism graph
negative feedback loop
1, glucose absorbed after meal
2, pancreas responds to elevated glucose by secreting insulin
3, insulin causes liver, skeletal muscle, and other tissue to take more glucose
4, normal glucose level reached
aerobic energy systems conditions
pyruvate is decarboxylated to form Acetly-CoA which produces ATP
Oxygen and fuel not always available
anaerobic condition
pyruvate reduced to lactate which is an important source of ATP for cells without mitochondria
Pyruvate
chemical compound that is produced during the metabolism of glucose through glycolysis process
fat oxidation
1, fatty acids transported with help from enzyme carnitine
2, fatty acids broken down to Acetly-CoA
3, oxidation of fatty acids involves repeated cycle of 4 reactions where fatty acid chain reduced by 2 carbons each cycle
4, This produces energy
fat oxidation differences
the process could differ depending on
chain length of fatty acid
double or single bond
how many double bonds
body preference in fats
body prefers to use mono and poly unsaturated fats than saturated fats
unsaturated fats bonding
monounsaturated fats have 1 double bond between two carbon atoms
polyunsaturated fats have 2 or more double bonds between two carbon atoms
saturated fats bonding
all carbon atoms connected by single covalent bonds
unsaturated fats
one or more double bonds between C atoms
liquid at room temp
from plant source
saturated fats
solid at room temp
linear and compact structure
single bonds between C atoms
From animal sources
Cis - unsaturated
naturally occuring
H atoms same side as C=C bond
causes kink in fatty acid chain
Tran-unsaturated fats
result of food processing
H atoms on opposite side of C=C bond
Causes straighter fatty acid chain
adipose tissue
just below skin fat
cell that stores fats in form of tryglycerides
functions: store energy and heat insulation
overconsumption of fat
body will store fat in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle
lypolysis
process of releasing triglycerides from body’s fat storage
Krebs cycle and ETC
Stages of aerobic metabolism which produce ATP with oxygen and fuel available
ETC
happens in mitochondrial matrix and uses NADH and FADH which are 2 molecules created during krebs cycle and glycolysis
ETC creates proton gradient leading to ATP production
Stages of cell respiration
1, glycolysis
2, oxidative decarboxylation
3, krebs cycle
4, ETC
5, oxidative phosphorylation
anaerobic energy systems
phosphagen system
glycolytic system
phosphagen system
creates ATP
cannot be used to drive muscle contraction
formula = PCr + ADP = ATP + Cr
glycolytic system
pyrvuate converted to lactate
makes small amount of ATP
process occurs quickly
suitable for exercise lasting 20 seconds to a few minutes
Formula = Glucose = 2ATP + 2Pyruvate = 2lactate + 2Hpositive
hormones in energy metabolism
insulin
glucagon
epinephrine
cortisol
growth hormones
insulin response (after eating)
1, facilitates glucose intake into skeletal muscle and liver cells
2, promotes glycogen synthesis
3, inhibits glycogen breakdown
4, supports protein synthesis
Glycagon and epinephrine response (during fasting/exercise)
when blood glucose levels drop then pancreas releases glucagon which
stimulates glycogen breakdown
promotes glucose synthesis
encourages fat breakdown
enhances protein breakdown
Epinephrine enhancing effects ensuring a continued energy supply
Lactate inflection point
the point where blood lactate begins to substantially accumulate above resting concentrations during exercise of increasing intensity
Lactic acid
once exercise exceeds the rate of maximal oxygen consumption then an oxygen debt occurs and metabolism switches from aerobic to anaerobic which leads to increase in blood lactate levels
increase in blood lactate impairs muscle contraction and leads to fatique and exhaustion
Critical power threshold
measure of the maximum power output that a person can sustain for a prolonged period of time without becoming exhausted
Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption
when the body gets into an oxygen deficit because oxygen need and oxygen supply does not match in the first moment of exercise
during recovery from exercise, oxygen utilisation continues at greater rate than needed at rest
Two components of excess post-exercise oxygen consumption
fast component which represents oxygen required to rebuild the ATP and PCr used during the initial stages of exercise
Slow component which represents the result of the removal of lactate from the muscle tissues, either by conversion to glycogen or oxidation to CO2 and H2O which provide energy required to restore glycogen stores
Reasons why oxygen consumption remains elevated during recovery from exercise
oxygen is required to rebuild the ATP and PCr stores
respiration remains elevated to help clear out any excess CO2 from tissues
oxygen must be replenished to haemoglobin and myoglobin which was taken during exercise