Chapter 22: The Respiratory System Overview
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Respiratory System Functions
Obtains O2, removes CO2, regulates blood pH.
Respiration Processes
Four distinct processes: ventilation, exchange, transport, tissue.
Pulmonary Ventilation
Air movement into and out of lungs.
External Pulmonary Exchange
Gas exchange between lungs and blood.
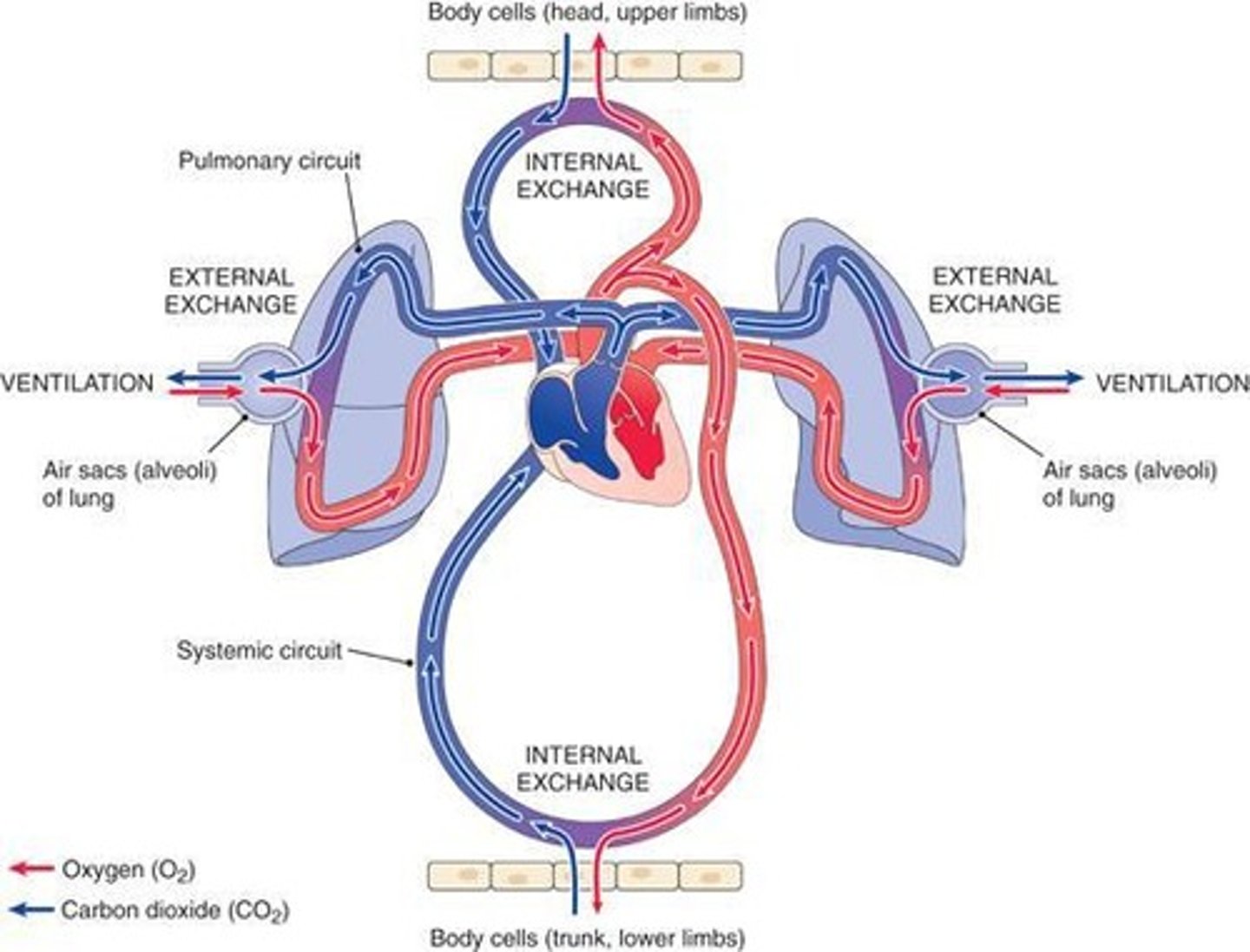
Transport
O2 and CO2 movement via blood.
Internal Tissue Exchange
Gas exchange between blood and tissues.
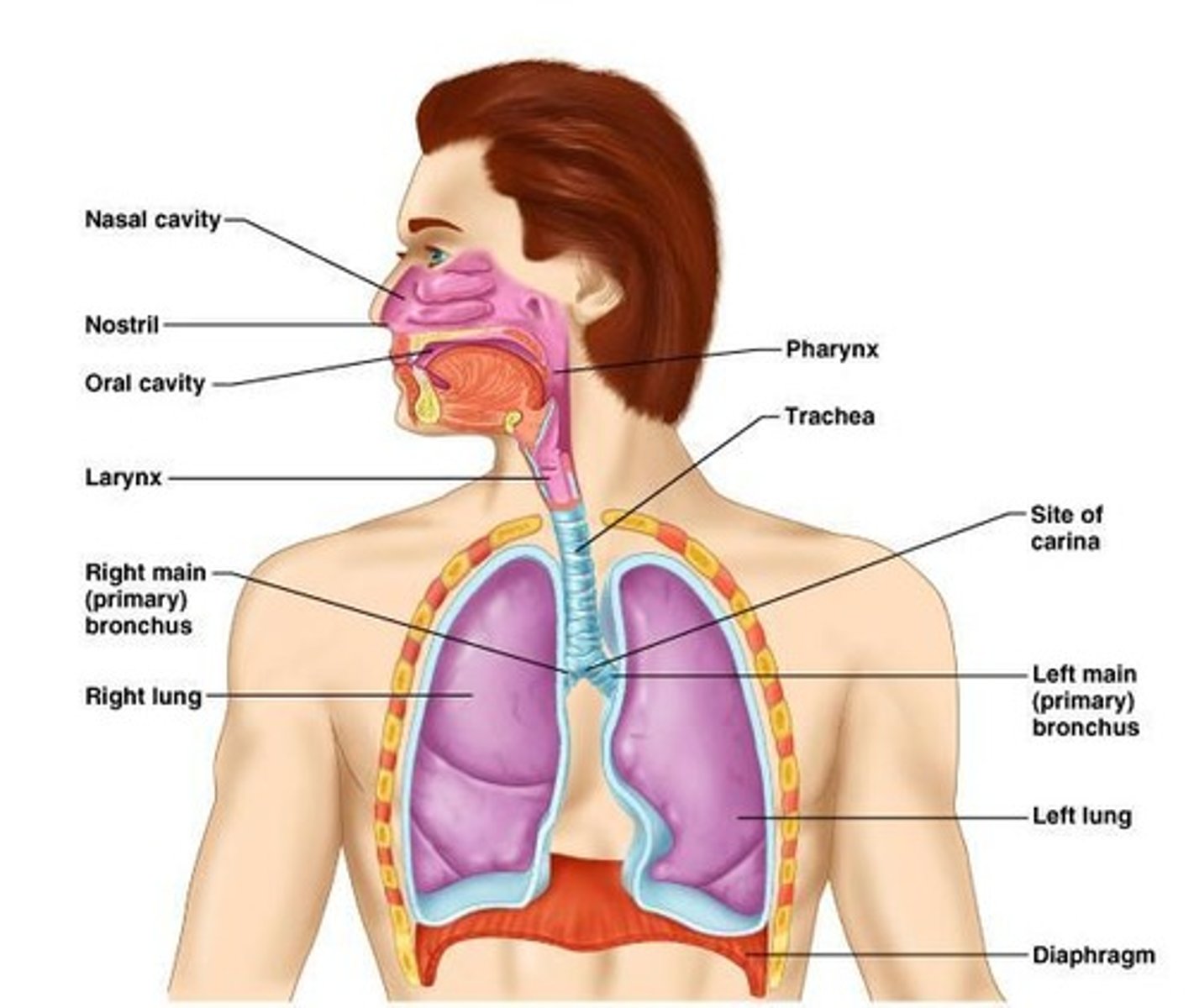
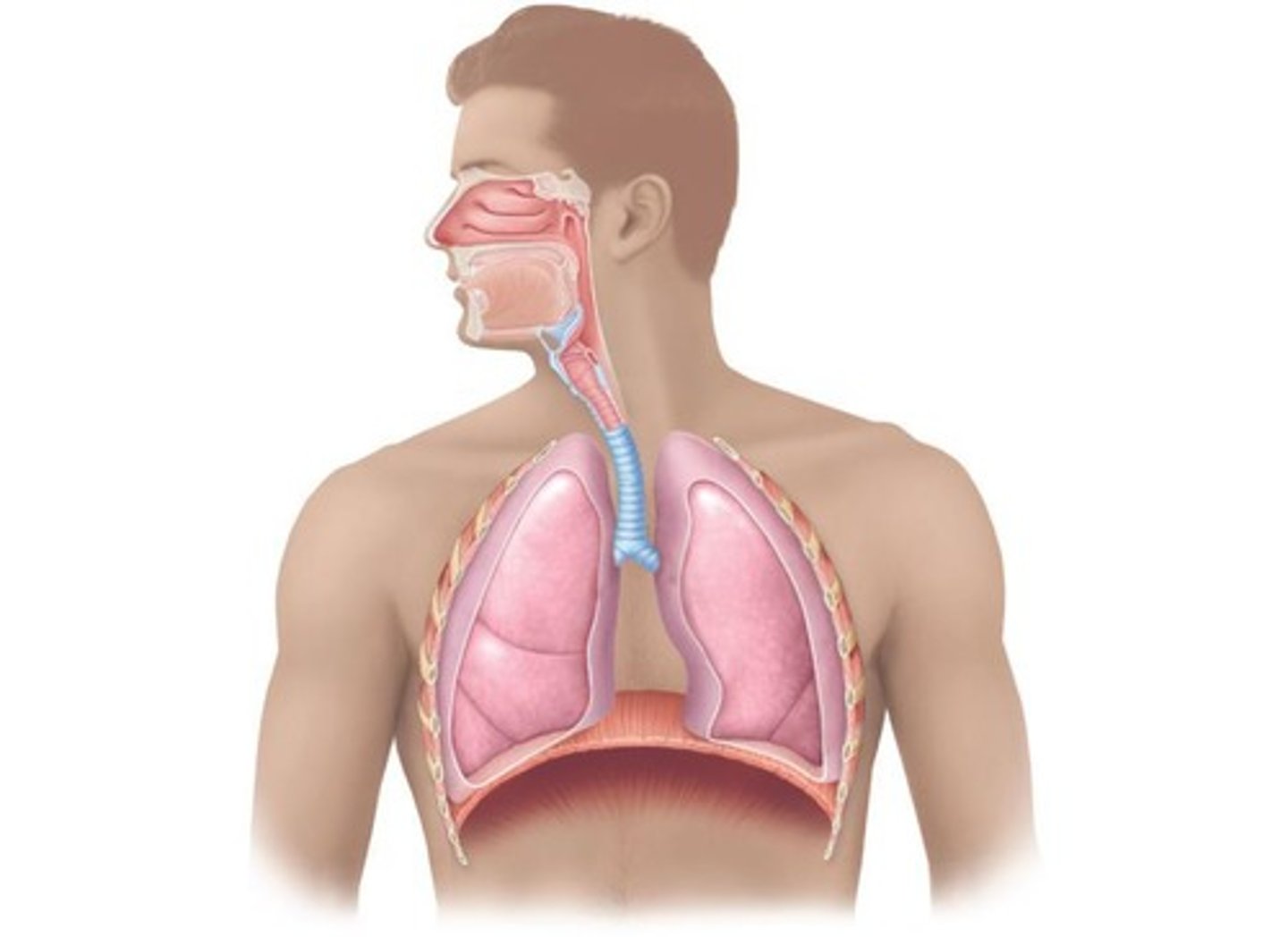
Nose
Primary air passageway; resonance chamber for speech.
Larynx
Voice box; sound production and airway protection.
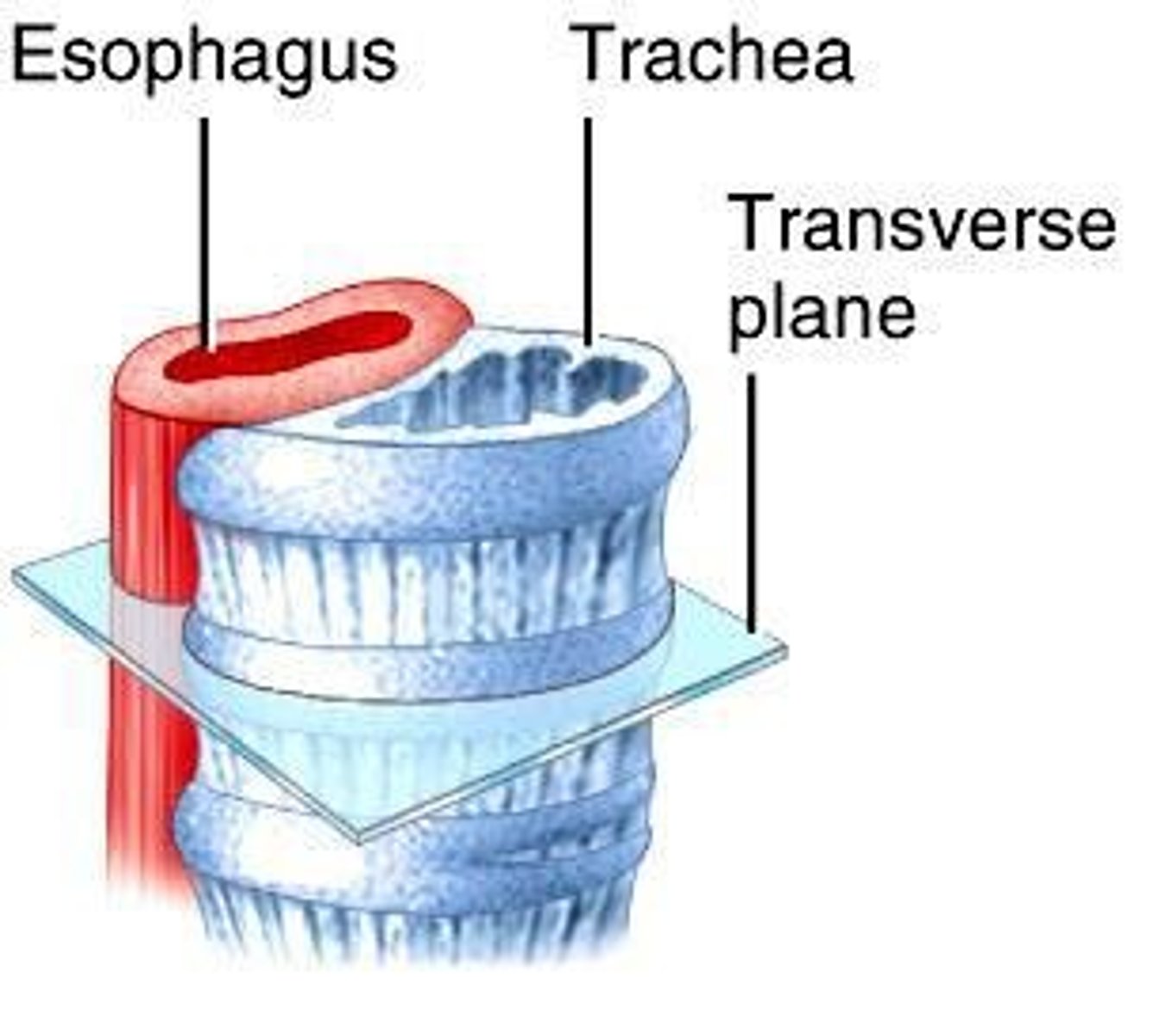
Trachea
Windpipe; conducts air to bronchi.
Bronchial Tree
Branching airways from trachea to lungs.
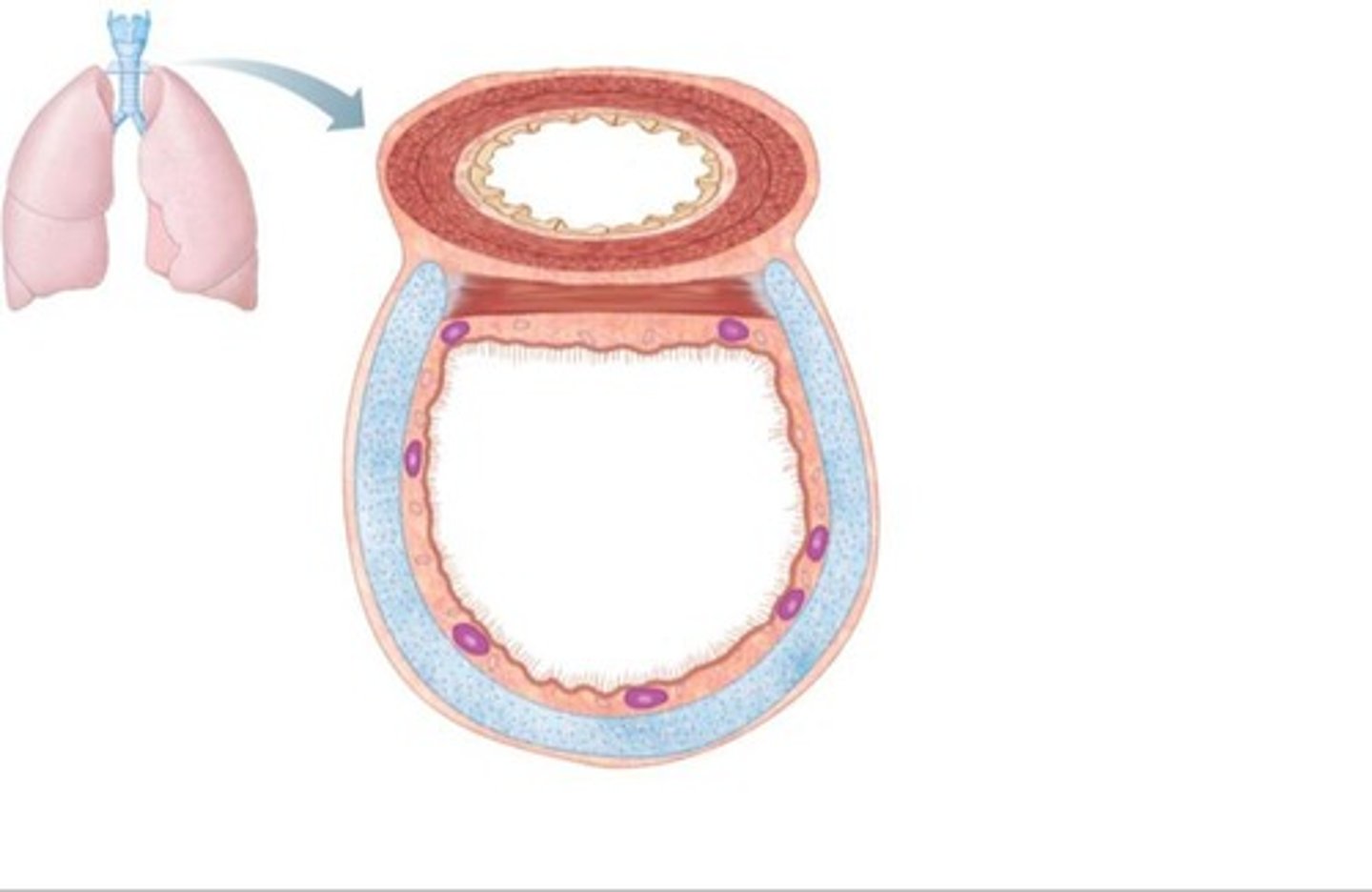
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs for gas exchange.
Goblet Cells
Secrete mucus to trap foreign particles.
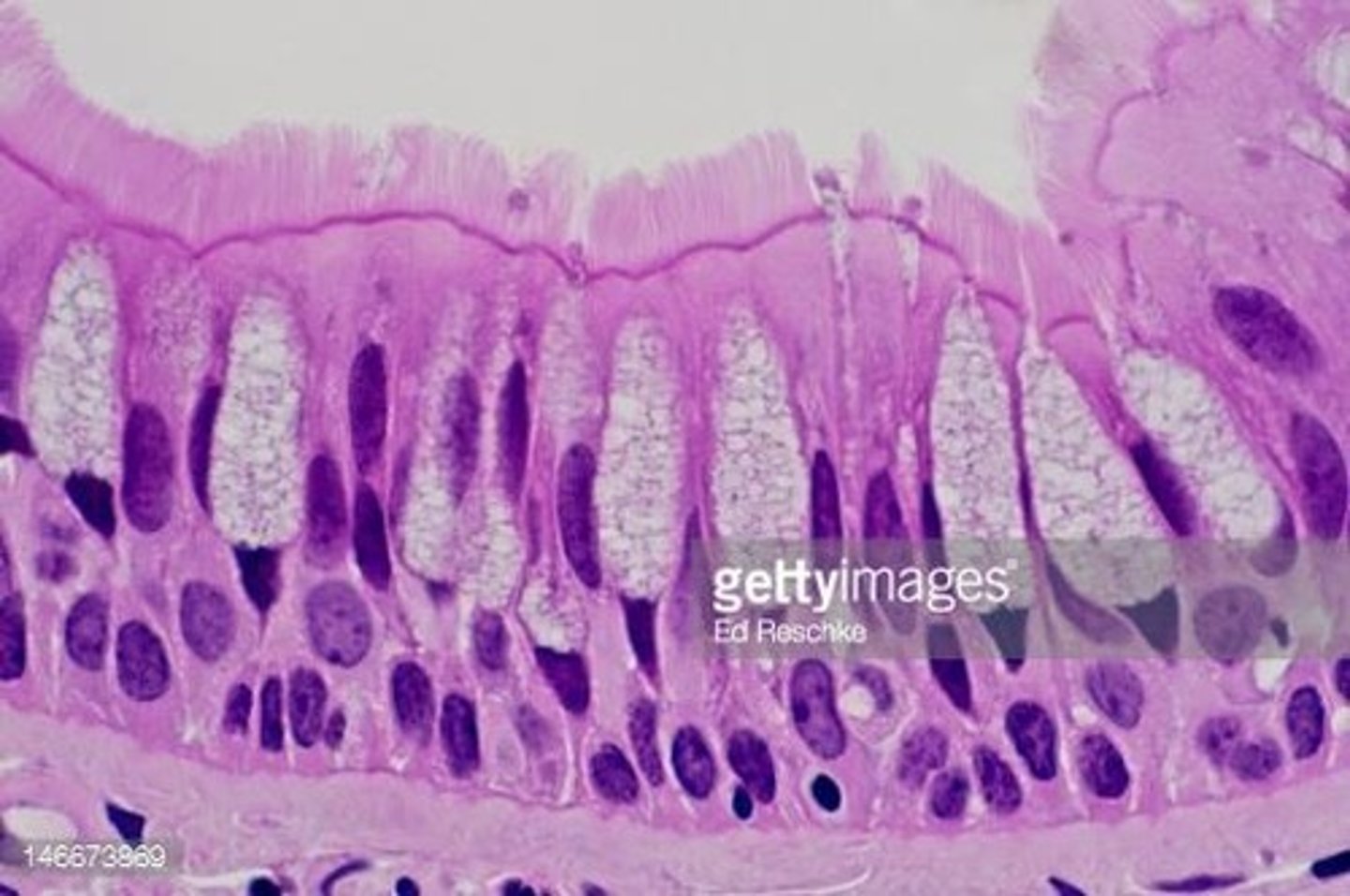
Ciliated Epithelium
Lines respiratory tract; moves impurities out.
Diaphragm
Muscle aiding in inhalation and exhalation.
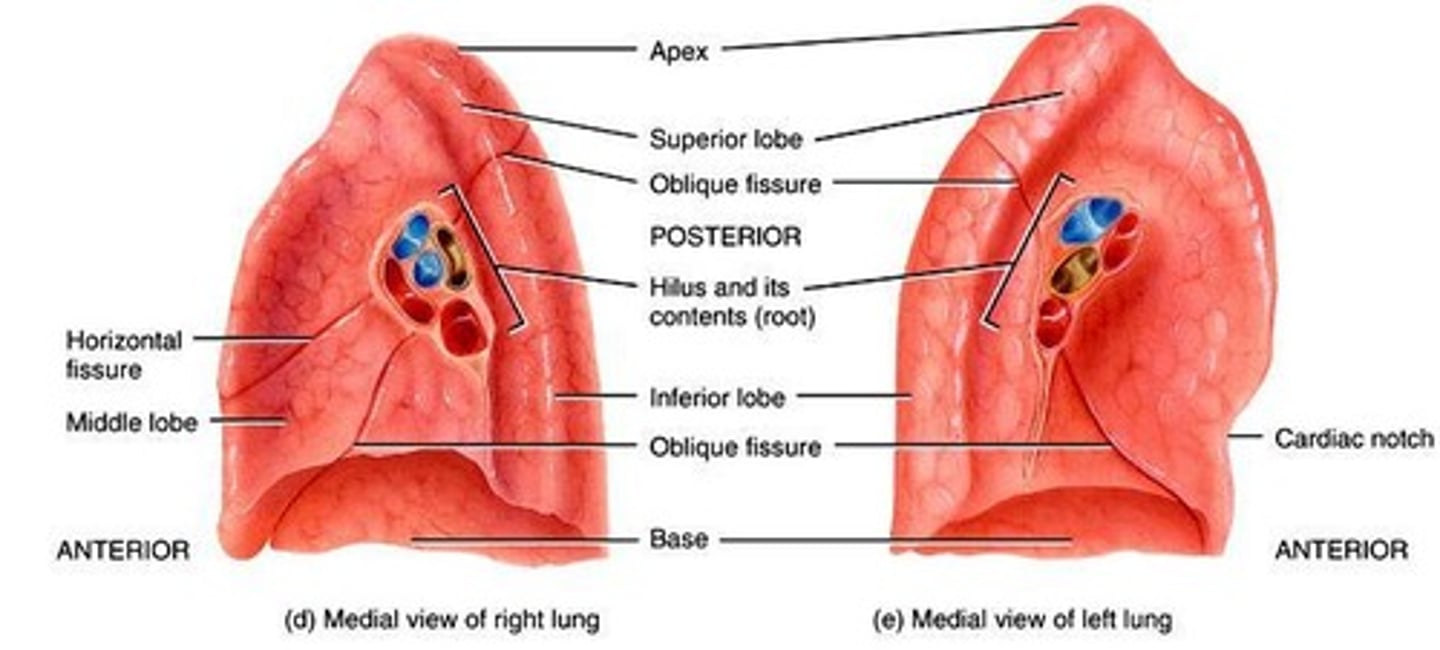
Right Lung
Three lobes; larger than left lung.
Left Lung
Two lobes; accommodates heart's position.
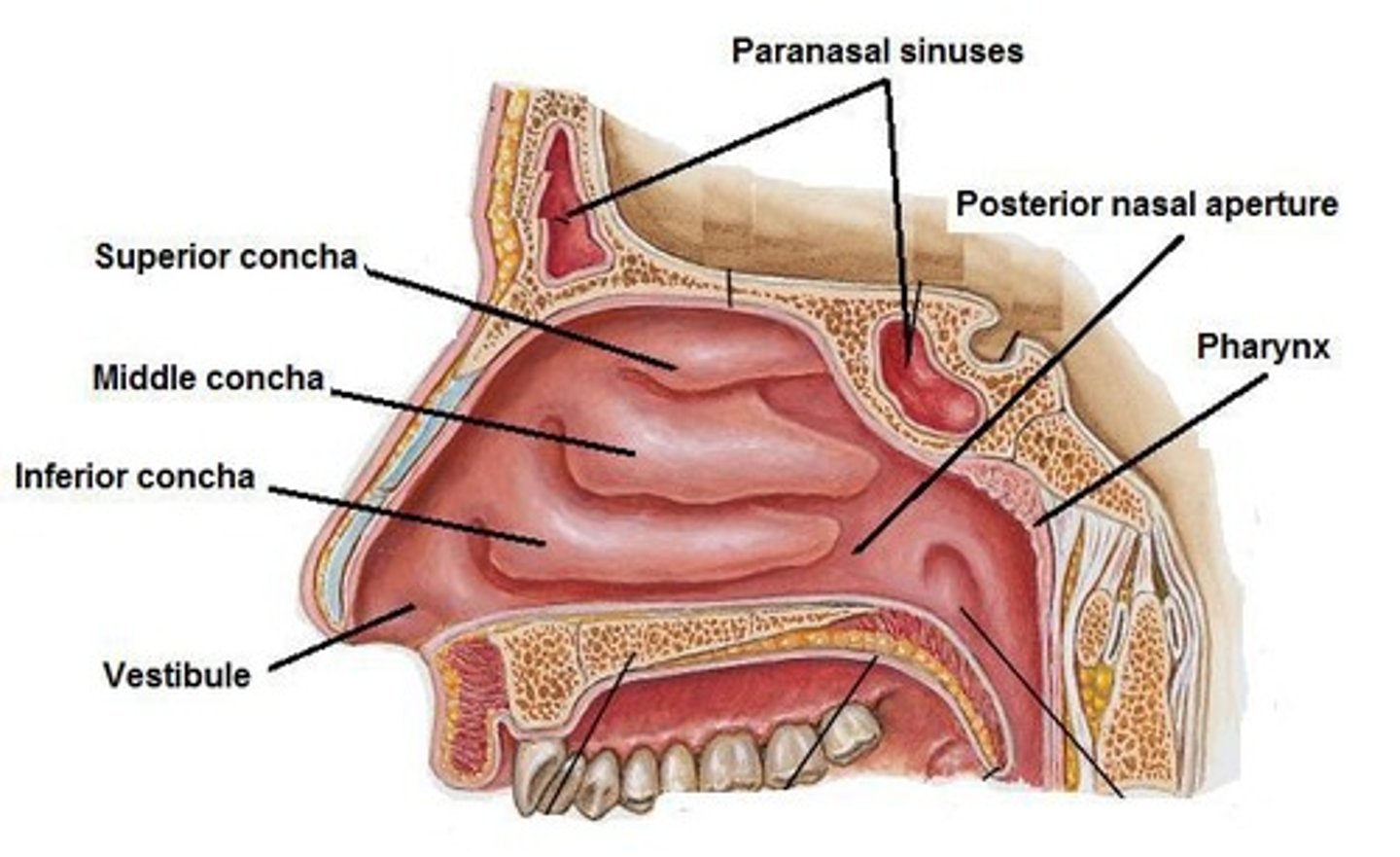
Nasal Cavity
Warms and moistens air; contains turbinates.
External Nares
Nostrils; entry points for air.
Internal Nares
Connects nasal cavity to pharynx.
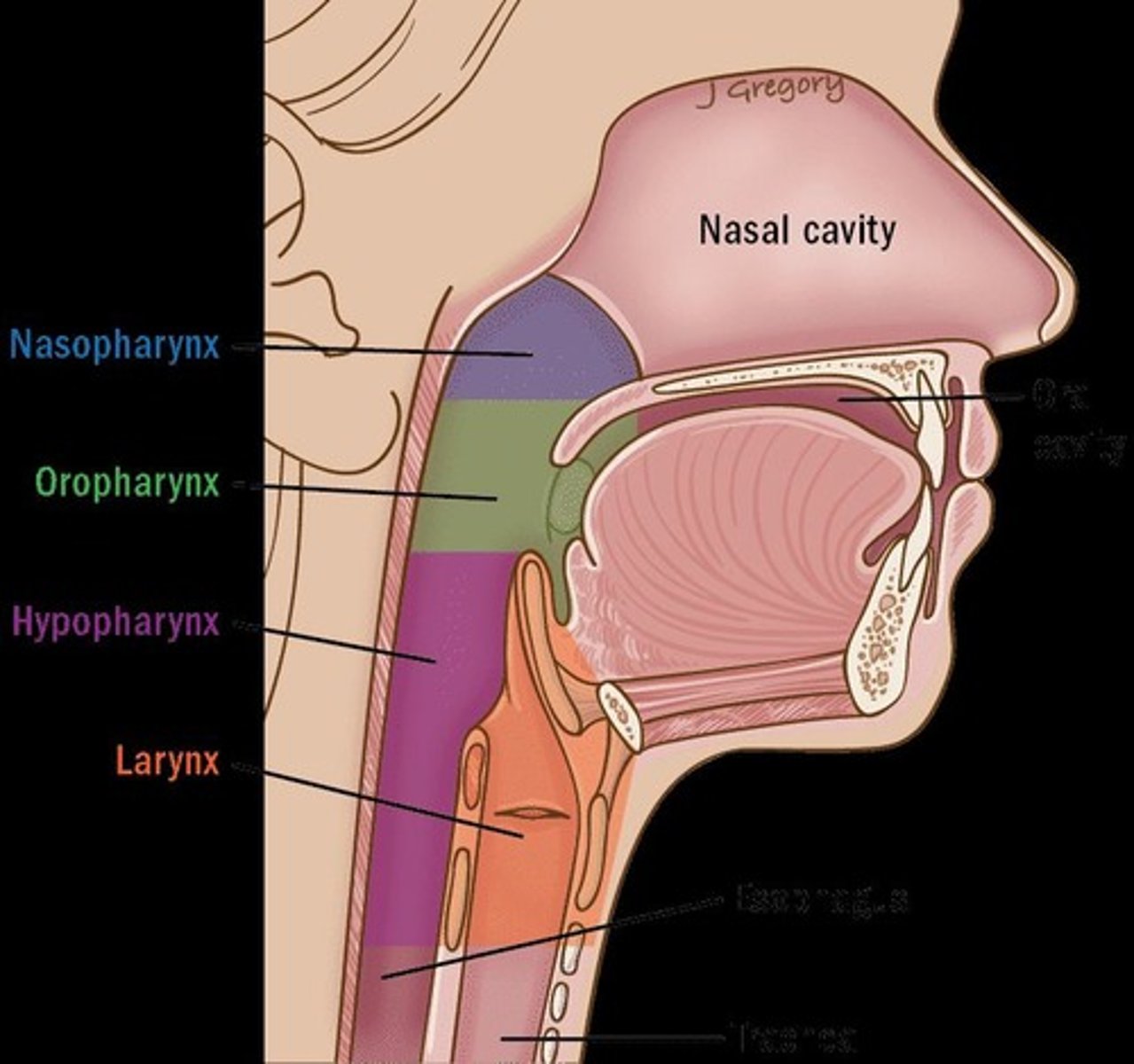
Pharynx
Passageway for air and food.
Sound Production
Generated by air passing through larynx.
Cellular Respiration
O2 usage and CO2 production by cells.
Regulation of Respiration
Controlled by various physiological factors.
External Nose
Leads posteriorly to the nasal cavity.
Hard Palate
Floor of the nasal cavity separating it from the mouth.
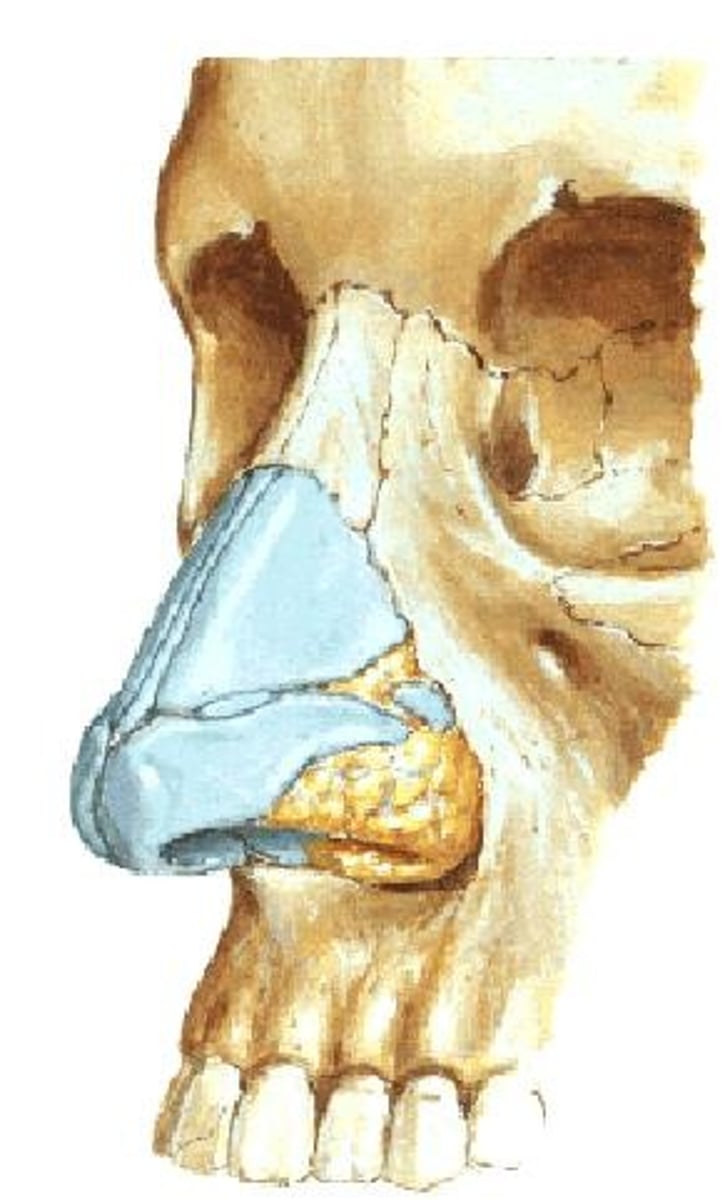
Paranasal Air Sinuses
Drain mucus into the nasal cavity.
Nasolacrimal Ducts
Drain tears into the nasal cavity.
Nasal Conchae
Three bony projections in the nasal cavity.
Mucous Membrane
Lining that secretes mucus and contains blood vessels.
Air Filtration
Dust and pathogens caught by nostril hairs.
Air Warming
Blood warms air in the vascularized mucous membrane.
Air Moistening
Liquid secretion moistens the inhaled air.
Air Turbulence
Movement between conchae increases air mixing.
Gas Exchange
Warm, moist air is essential for lung efficiency.
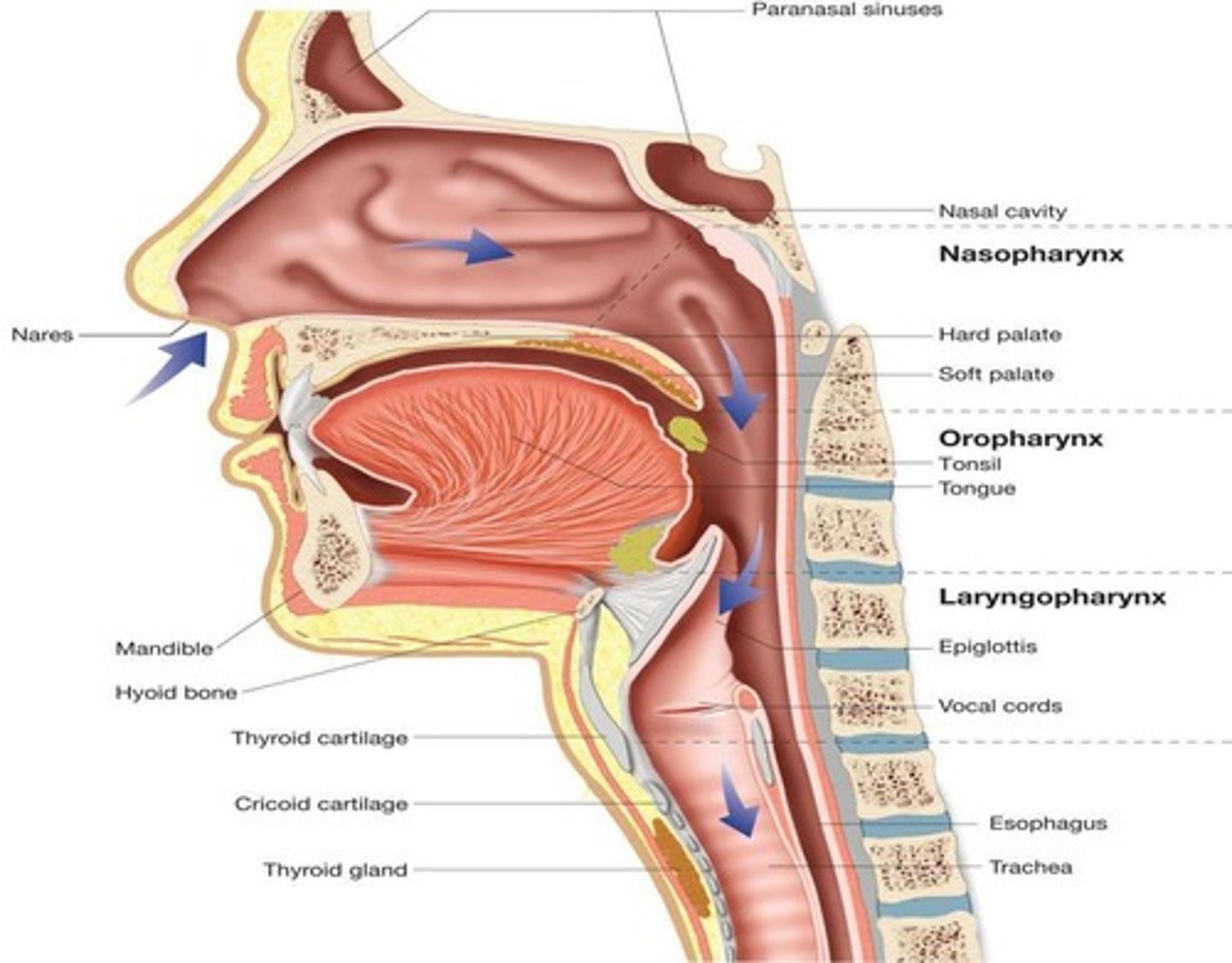
Uvula
Prevents food from entering nasopharynx during swallowing.
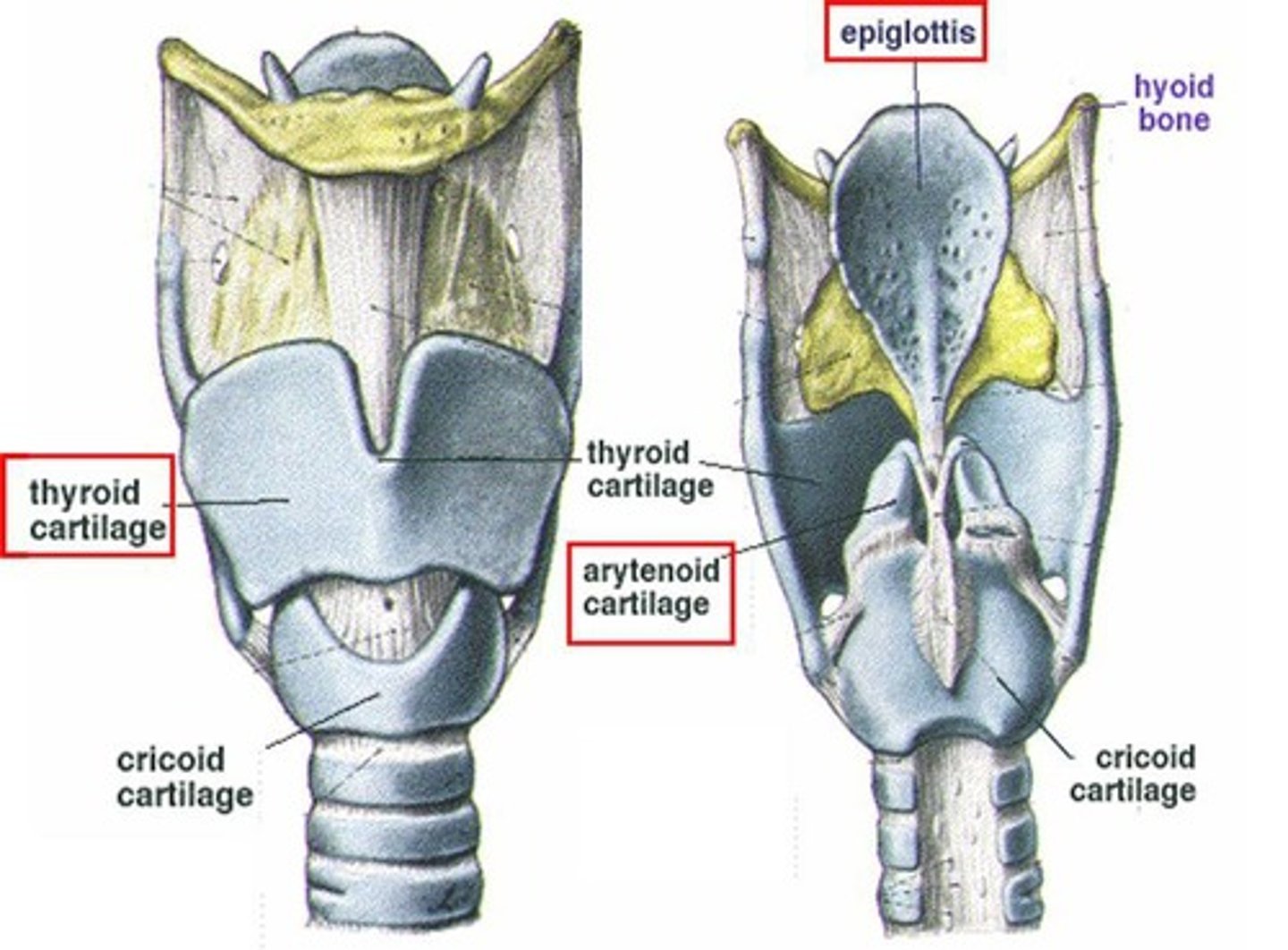
Epiglottis
Closes larynx to prevent food entering airway.
Laryngeal Prominence
Adam's apple, larger in men than women.
Thyroid Cartilage
Middle cartilage forming the larynx framework.
Cricoid Cartilage
Most inferior cartilage, ring-shaped in structure.
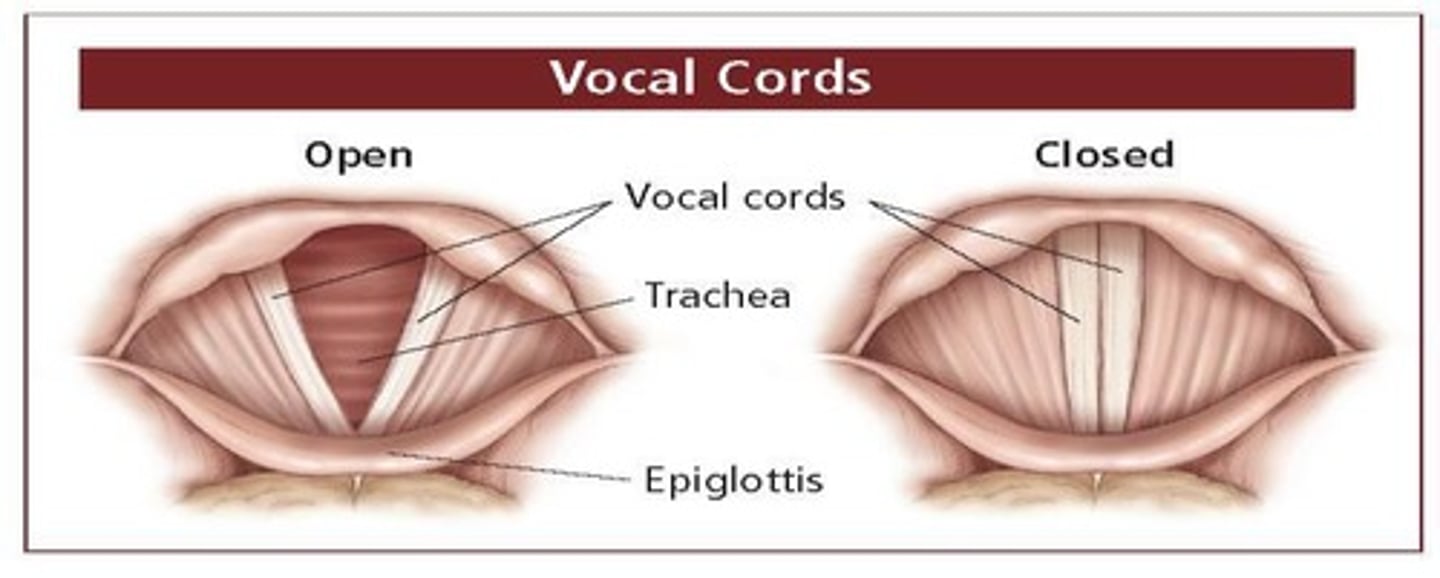
Vocal Cords
Ligaments in larynx responsible for sound production.
Glottis
Cavity of larynx between vocal cords.
Resonating Chambers
Mouth and sinuses amplify sound quality.
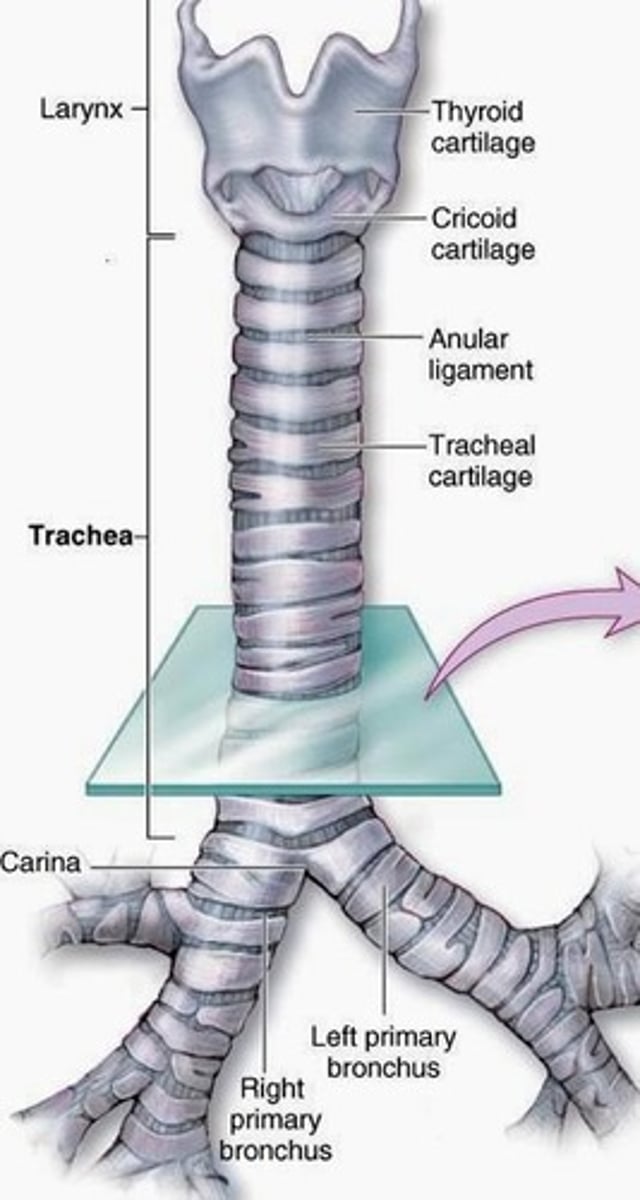
Right Bronchus
Shorter, wider bronchus, more foreign object prone.
Left Bronchus
Longer, narrower bronchus, less foreign object prone.
Tracheal Cartilages
C-shaped rings maintaining tracheal structure.
Trachealis Muscle
Smooth muscle allowing esophageal expansion.
Lumen of Trachea
Airway passage within the trachea.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Ciliated epithelial tissue lining the trachea.
Hyaline Cartilage
Type of cartilage forming tracheal rings.
Pulmonary Artery
Carries deoxygenated blood to lungs.
Pulmonary Veins
Carry oxygenated blood from lungs to heart.
Bronchus
Main passageway into the lungs.
Pleural Membrane
Protective layer surrounding the lungs.
Apex of Lung
Superior tip of the lung.
Base of Lung
Inferior surface resting on diaphragm.
Hilum
Entry/exit point for vessels and bronchi.
Oblique Fissure
Divides left lung into superior and inferior lobes.
Horizontal Fissure
Divides right lung into middle and inferior lobes.
Cardiac Notch
Indentation in left lung for heart accommodation.
Bronchopulmonary Segments
Ten segments in each lung lobe.
Lung Shape
Conical structure facilitating gas exchange.
Primary Bronchi
First division of trachea into lungs.
Secondary Bronchi
Branches into lobes; 3 on right, 2 on left.
Tertiary Bronchi
Supply bronchopulmonary segments; 10 on each side.
Alveolar Duct
Ducts leading to clusters of alveoli.
Terminal Bronchioles
Smallest bronchioles leading to alveolar ducts.
Surfactant
Substance preventing alveolar collapse during respiration.
Type I Alveolar Cells
Simple squamous cells for gas exchange.
Type II Alveolar Cells
Secrete surfactant; reduce alveolar collapse.
Alveolar Macrophages
Cells that remove debris from alveoli.
Respiratory Membrane
Thin membrane for gas exchange in lungs.
Elastic Fibers
Allow lung expansion and return to shape.
NRDS
Newborn respiratory distress syndrome due to surfactant deficiency.
Capillaries
Blood vessels surrounding alveoli for gas exchange.
Inspiration
Drawing air into the lungs.
Expiration
Expulsion of air from the lungs.
Pressure-Volume Relationship
Pressure inversely proportional to volume in containers.
Atmospheric Pressure
Pressure exerted by the weight of air.
Intrapulmonary Pressure
Pressure inside the lungs during breathing.
Thoracic Cavity
Space containing the lungs and heart.
External Intercostal Muscles
Muscles elevating ribs during inhalation.
Internal Intercostal Muscles
Muscles lowering ribs during forced expiration.
Normal Breathing Rate
Typically 12-20 breaths per minute.
Forced Inspiration
Increased air intake using neck muscles.
Passive Expiration
Air expulsion without muscle contraction.
Elastic Lung Tissues
Tissues that help lungs return to size.
Intrathoracic Volume
Volume of the thoracic cavity during breathing.
Transverse Diameter
Width of the thoracic cavity.
Anteroposterior Diameter
Depth of the thoracic cavity.
Forced Expiration
Active process using abdominal and intercostal muscles.
Airflow Direction
Air moves from high to low pressure.
Volume Increase
Occurs during inhalation to lower pressure.
Volume Decrease
Occurs during exhalation to raise pressure.
Rib Elevation
Increases thoracic cavity space during inhalation.
Diaphragm Contraction
Increases vertical diameter of thoracic cavity.
External respiration
Gas exchange between alveoli and blood capillaries.
Internal respiration
Gas exchange between blood and tissue cells.
Oxygen transport
Oxygen carried primarily by hemoglobin in blood.
Oxy-hemoglobin
Hemoglobin combined with oxygen for transport.
Oxygen saturation
Percentage of hemoglobin bound with oxygen.