
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
compared to sodium, we expect that oxygen would be…
about the same electronegativity
compared to magnesium, we expect that calcium would have an ionic radius that is…
larger (because it has more electron shells, leading to a greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons)
Silicon tends to form…
4 bonds
We expect the oxygens in O2 (oxygen gas) to form…
nonpolar covalent bonds
We expect that an O ion would have a charge of…
-2, because
We expect that a Li ion would have a charge of…
1+, because it’s in group 1
We expect that chromium would form…
cations, because it’s a transition metal which tends to lose electrons
The air around us is a good example of a…
relatively homogenous mixture
How many valence electrons does aluminum have?
3
water (H2O) is a…
molecule and compound
How many neutrons are in oxygen-18 (18 O)?
10, because mass # is 18 and atomic # is 8, 18-8=10
How many moles of calcium are in two moles of hydroxyapatite, which has a chemical formula of Ca₅(PO₄)₃OH?
10
What is the total number of electrons that can be held in a d subshell?
10
Chlorpyrifos (CPS) is an organophosphate pesticide that is used in agriculture and around homes to kill insects and worms. Exposure to this pesticide is harmful to aquatic life, bees, and also humans. What is the molar mass of CPS, which has a chemical formula of C 9 H 11 Cl 3 NO 3 PS?
349 g/mol
Children consume the most CPS (as pesticide residue on food) on a per unit of body weight basis. If toddlers consume, on average, 0.025 micrograms (μg) of CPS per kg body weight per day, how many g of CPS would a 12 kg toddler consumer per day? Please write your answer in scientific notation.
3.0×10^-7 g
How many g of CPS would this same toddler consume in one year? Assume their body weight doesn’t change (average weight of 12 kg across the whole year).
1.095×10^-4 g/yr
Copper-containing fungicides are commonly used in organic agriculture. How many moles of copper are in 4.5 kg of copper(II) sulfate (CuSO 4), one of
the commonly used copper fungicides?
28.30 mol Cu
Copper sulfate is also used to treat toxic algal species in water management systems, with a maximum application rate of 68.5 g CuSO 4 per m 3 water. What is the maximum application rate of copper per m3 water?
27.4 g per m³
Please calculate the density of a cylinder of soil with a radius of 3 cm, a height of 10 cm, and a mass of 310 g
1.0964 g/cm³
Why do transition metals not follow the same predictable patterns as s- and p-block elements when it comes to electron configurations and valence electrons?
Electron configurations become more complex as elements get larger and electrons begin filling d- and f-orbitals. Electron are trying to achieve low energy states, which involves balancing being close to the nucleus and far from other electrons. For transition metal electrons, this means determining if a higher energy, more complex orbital (d or f) that is closer to protons in the nucleus is lower energy than moving up to another main shell further from the nucleus but also from other e- (these are often only very slightly different in energy levels). This also affects which electrons engage in bonding -- how close are they to the outside of the electron cloud? (Unfilled f orbitals typically do not engage in bonding.)
How many neutrons are in 234 U?
142 neutrons
What element does 234 U become when it experiences alpha decay?
thorium
What is the atomic mass of this new element? Using information from your knowledge of the radioactive decay process, not the average atomic mass on the periodic table, which includes all isotopes.)
230 amu
Please write the complete electron configuration for
calcium.
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2
What is the correct formula for chromium oxide, a mineral composed only of chromium (III) and oxygen?
Cr2O3
Why is oxygen more electronegative than sulfur and lithium? (For credit, your answer must provide separate reasoning for both sulfur vs. oxygen and lithium vs. oxygen.)
S = larger = more e- shielding (e- can't "see" protons in nucleus as well); Li = same main level but fewer protons (less positive pull on e-), wants to form a cation (donate e-) to have a full outer shell, not gain them like O
A tree absorbs about 25 kg of CO2 per year. Assuming all of the carbon in the CO2 is converted into cellulose (C6H10O5)n, what mass of carbon (in kg) is added to the tree
each year?
6.82 kg C/yr
polar molecule
separate centers of positive and negative charge-changes melting point, boiling point, solubility
dipole
molecule with positive + negative ends; polar molecules exist as dipoles
conditions for a molecule to be polar:
it must have polar bonds
the bonds must be arranged such that a separation of charge exists
importance of water’s polarity
attracts other water’s and polar compounds, universal solvent
phospholipid bilayers have…
polar exterior and nonpolar interior
stoichiometry
the quantitative relatoinship between reactants and products in a chemical reaction (Greek words for element + measurement)
formula mass
the average mass of a “formula unit” relative to that of a carbon-12 atom; the sum of the atomic masses for all atoms in a formula
law of combining values
when all the measurements are made at the same temperature and pressure, the volumes of gaseous reactants and products are in small whole-number ratios
Avogrado’s hypothesis
when measured at the same temperature and pressure, volumes of all gases contain the same # of molecules
molar volume of a gas
one mole of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L at standard temperature and pressure (STP)
STP
defined as 1 atmosphere (atm) of pressure and a temperature of 0°C
steps in stoichiometric calculation:
write and balance the chemical equation for the reaction
determine the molar masses of the substances involved in the calculation
use the coefficients of the balanced equation to convert moles of the given substance to moles of the desired substance
use the molar mass to convert moles of the desired substance to grams of the desired substance
solution
a homogenous mixture (solid or liquid), where the major component is the “solvent” and the minor components are “solutes”; solid ex. steel, liquid ex. peroxide
CaO+H2O=Ca(OH)2
molecular relationship: 1 molecule (equation is balanced) of CaO reacts w/ 1 molecule of H2O to form 1 molecule of Ca(OH)2
molar relationship: 1 mole of H2O reacts w/ 1 mole of CaO to form 1 mole of Ca(OH)2
mass relationship: (ratio of reactant and product molecular masses)
solution concentration
amount of 486 g H2O solute in a given amount of solvent
dilute solution
contains relatively small amounts of solute in a given amount of solvent
concentrated solution
contains relatively large amounts of solute given a solvent
molarity
measuring amounts of solutes (M); moles of solute per liter of solution (M=mol/liter)
percent by volume formula
volume of solute/volume of solution x 100
percent by mass formula
mass of solute/mass of solution x 100
solids
particles have fixed position and vibrational motion
liquids
particles free to move within confines
gas
particles far apart and move randomly and rapidly
melting point
the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid
vaporization
when liquid becomes gas at boiling point
condensation
when gas becomes liquid
sublimation
when solid goes straight to gaseous state
what changes and what stays the same when 1.00 L of an aqueous solution of NaCl is diluted to 1.80 L?
-# of moles stays the same
-volume of water changes
-concentration of solution changes
ionic bonds
cation-anion attraction (strongest of forces that hold matter in the condensed state (liquids/solids))
dipole forces
attraction between polar molecules (ion-dipole forces)
hydrogen bonds
dipole force; when a hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom such as (N,O, or F); can exhibit an additional polar attraction
dispersion forces
nonpolar molecules exhibit a dynamic induced dipoles, the strength of which increases with molecular weight; temporary attraction (weakest)
in liquids, dipole forces are simultaneously…
attractive and repulsive
ions are attracted to the dipoles of…
polar molecules
hydrogen bonding in water:
strong intermolecular forces in molecules w/ very polar bonds to H; increases boiling point
strong H-bonding creates an…
open, cage-like structure of ice; makes ice less dense than water
larger, heavier molecules =
more dispersion forces (less tightly held outer electrons)
more surface area =
more dispersion forces (more area to interact w/ other molecules)
“like dissolves like”
solutions form most readily when both the solute and solvent have similar intermolecular forces
acids
-a molecular substance that ionizes in aqueous solution to form hydrogen ions (H+)
-common ex. HCl, lemon juice, sulfuric acid, vinegar
-properties: sour, proton donors, pH less than 7
bases
-a substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in aqueous solution
-common ex. sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, lithium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, and ammonia
-properties: slippery, bitter, proton acceptor, pH above 7
types of intermolecular forces
ionic (strongest)
dipole forces
H-bonding
disperion forces (weakest)
acid and base reactions drive many Earth processes such as…
regulating long-term atmospheric CO2 levels via carbonic avid reactions w/ silicate minerals
-set the conditioins for agriculture, including nutrient availability (pH as a “master variable” in soils)
-allows oceans to serve as a major carbon sink, w/ risks of ocean acidification
neutralization
when an acid reacts with a base, the properties of each are neutralized and the products are water and a salt; acid+base=water+salt
titration
the amount of acid or base in a solution can be determined by careful, quantitative neutralization
Arrhenius Theory
-defines acids as substances that dissolve in water to produce H+/protons
-bases produce OH- (hydroxide ions) in water
limitations of Arrhenius Theory
H+ ions do not exist in water solution
-does not explain the basicity of ammonia and similar compounds
-applies only to reactions in aqueous solution
Bronsted-Lowry Theory
-acids are proton donors
-bases are proton acceptors
salts
-formed from neutralization reactions of acids and bases
-ionic compounds composed of cations other than hydrogen and anions other than hydroxide
electrolytes
salts that conduct electricity when dissolved in water
salinity is measured by measuring the…
electric conductivity of water or soil in the field or lab
strong acids…
ionize completely in water solution
weak acids…
ionize only partially in water solution
pH scale
expresses the acidity or basicity of a solution; pH means power of hydrogen
which polyatomic ions have double bonds?
-nitrate (NO3)
-carbonate (CO3^-2)
-chlorate (ClO3-)
why does atomic radii decrease across a period (left to right), and increase down a group on the periodic table?
increasing effective nuclear charge, which pulls electrons closer to the nucleus, and increases down a group (top to bottom) due to the addition of electron shells, which increase the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
cation are always…
smaller than their neutral atoms because they have lost electrons, leading to a greater attraction of remaining electrons to the nucleus
anions are always…
larger than their neutral counterparts due to gaining electrons, which increases electron-electron repulsion and causes the electron cloud to expand
does Na or Cl have a larger atomic radius and why?
Sodium (Na) has a larger atomic radius than chlorine (Cl) because sodium has fewer protons, resulting in a weaker effective nuclear charge that holds the outer electrons less tightly, leading to a larger overall atomic size
weak acids
-acetic acid (CH3COOH)
-hydrofluoric acid (HF)
-phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
strong bases
-potassium hydroxide (KOH)
-barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2)
-most substances that end w hydroxide
strong acids
-hydrochloric acid (HCl)
-sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
-nitric acid (HNO3)
weak bases
-ammonia (NH3)
-aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3)
-zinc hydroxide (Zn(OH)2)
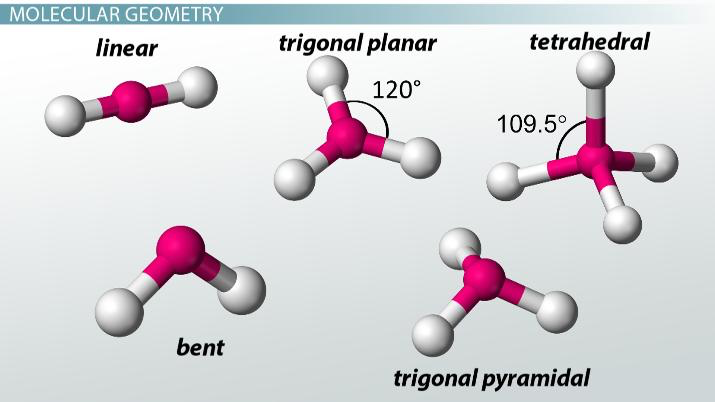
compare & contrast the molecular shapes of two nitrogen species commonly used in fertilizers:
ammonia (NH3 ) and ammonium (NH4+ )
-ammonium has a tetrahedral shape because of its 4 electron sets and 0 lone pairs (4 hydrogens bonded to the central N)
-while ammonia also has 4 electron sets, it has a trigonal pyramidal shape because of its bonds to 3 hydrogens plus one lone pair of
electrons
which elements are capable of forming expanded octets?
phosphorus, sulfure, chlorine and elements further down in their columns
why does water’s shape contribute to its polarity?
the bent shape allows a separation of charge to exist (one of the criteria for polar molecules). The lone pairs (more negative & take up more space) are on one side of the molecule, while the more positive hydrogens are pushed closer together on the far side
why is the polarity of water important for life on Earth?
-water is very polar, largely because O is so electronegative and greedy for e- that it pulls the electrons away from H in their polar covalent bonds, making the hydrogens more position and the O more negative.
-this strong polarity allows water to dissolve many different substances, even those with strong ionic bonds like NaCl.
-this polarity allows for uptake and movement of polar substances in cells and means that nonpolar regions of organic molecules can be used to block transport and movement of polar substances
how would 2H2 2Na (s) + Cl2 (g) = 2NaCl (s) be said in a sentence?
Two moles of solid sodium react with one mole of chlorine gas to form two moles of solid sodium chloride.
how much is 1 mole of gas at STP?
22.4 L
VSEPR Theory
solute
substance being dissolved
solvent
material that does the dissolving and is present in large amounts
because log scale: each pH unit change =
10x change in concentration of protons