Endogenic Processes (Plate Tectonics, Igneous, and Plutonism)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Endogenic Processes
large-scale landform building and transforming processes within the Earth
Alfred Wegener
1912 German geophysicist, astronomer, and meteorologist
describes the shift in the positions of Earth’s continents
proposed the Theory of Continental Drift Theory
was not accepted by most scientists
Alfred Wegener
Proposed the Theory of Continental Drift
Enumerate the Types of Plates
Enumerate the Types of Plates
Tills
sediments carried or deposited by glaciers later cemented to form rocks
True
One of the evidences of The Continental Drift Theory is that the continents fir together like jigsaw puzzles.
Harry Hammond Hess
an American Geologist in 1962
proposes that the seafloor itself was pushing the continents apart due to convection currents
Proposed the Seafloor spreading theory
Seafloor Spreading
magma convections in the mantle cause the seafloor to spread apart
the convections create rifts of which magma comes out of and forms land
Convergent/Destructive Plate Boundaries
two plates colliding against each other
e.g. Formation of mountains
Transform/Conservative Plate Boundary
Plates slide past each other. (e.g. Earthquakes)
Divergent/Constructive Plate Boundary
Two plates moving apart or rifting
Oceanic-Continental Convergent Boundary
oceanic plate subducts due to its density and molten crust from the subducting plate forms volcanoes or mountains on the continental crust
Continental-Continental Convergent Boundary
the denser continental crust subducts slightly then bunch up forming mountains
Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent Boundary
the denser oceanic crust subducts and molten crust from the subducting plates form volcanoes or islands
Basins
depressions of water
John Tuzo Wilson
Canadian geophysicist that proposed the Wilson Cycle in 1975
75%
Percentage of volcanoes found along the Pacific Ring of Fire
Volcanism
the extrusion of molten rock from the Earth’s subsurface
creation of surface terrain features or volcanoes
Volcanic Eruption
sudden violent discharge of steam and volcanic material
volcanic bombs, lapilli, ash, and lava
Effusive or Non-Explosive Eruptions
low gas content and viscosity magmas
basaltic to andesitic
Explosive Eruptions
high gas content and viscosity magmas
andesitic to rhyolitic
Magmas
main material ejected from a volcano
composed of molten or partially molten rocks found in the upper mantle
Lava Flow
most common volcanic feature
influenced by temperature, viscosity, and gas content
Pyroclastic Flow
fast moving fluidized mass of rocks and gases
burns everything in its path and can explode and cause acid rain
Pahoehoe Lava
smooth, ropy surface with low viscosity and high temperature
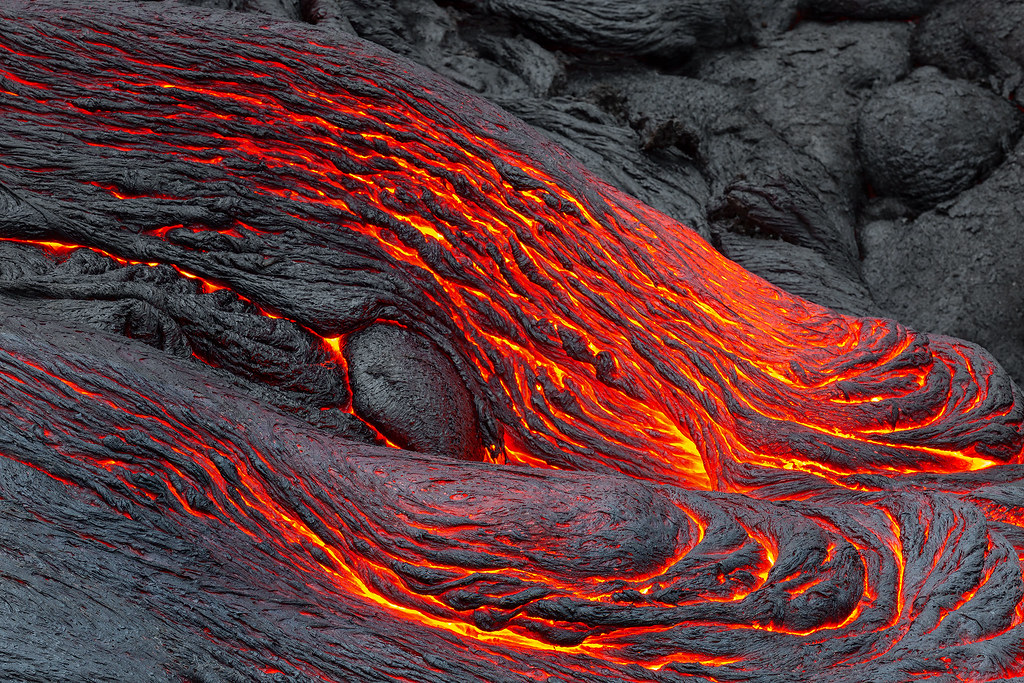
Aa Lava
rough surface and viscous but low in temperature
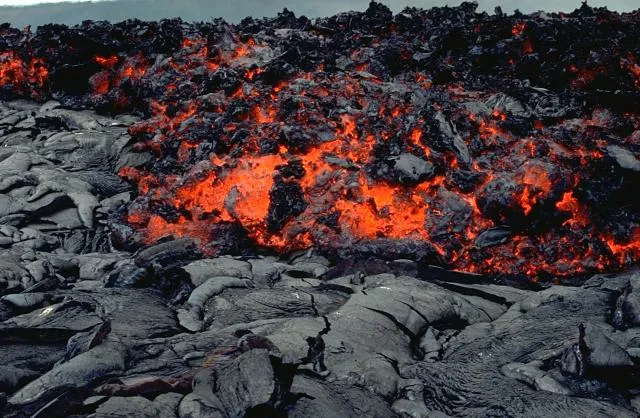

Blocky Lava
like Aa but much thicker and has a blocky surface

Pyroclasts
all broken materials from a volcano
Tephra
loose pyroclasts classified as bombs, blocks, or ash
Tuff
a rock from the cementation of tephra
Decompression Melting
upward movement of the mantle to an area of low pressure
Flux Melting
rocks melt when water or carbon dioxide is added
Heat Transfer Melting
hot liquid rock melt surrounding rocks
Partial Melting
minerals with low or high melting points
Basaltic Magma
1000-1200 Celsius
low viscosity and gas content
high in iron, magnesium, and calcium but low in potassium and sodium
Andesitic Magma
800-1000 Celsius
moderate viscosity and gas content
commonly erupts from stratovolcanoes
Rhyolitic Magma
650-800 Celsius
high viscosity and gas content
high in potassium and sodium but low in iron, magnesium, and calcium
Composite Volcanoes
steep-sided cones with explosive eruptions due to viscous lava
andesitic and rhyolitic lavas
Shield Volcanoes
broad gently sloping cone resembling a warrior’s shield with frequent less violent eruptions
basaltic lavas
Cinder Cone Volcanoes
has a bowl-shaped and are the simplest and smallest
basaltic lavas
Plutonism
formation of intrusive igneous rock
solidification of magma beneath the Earth’s surface
Fractional Magma Crystalization
when magma cools, it crystallizes in reverse order of partial melting
Phaneritic Magma Texture
crystals are visible to the eye
Aphanitic
crystals are too small to see
Porphyritic
a mixture of coarse and fine crystals
Bowen’s Reaction Series
determined the order of mineral crystallization from a magma
Norman Levi Bowen
A Canadian geologist who made the Bowen’s Reaction Series