AQA A level Business 3.7
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What are mission statements and what are the influences on missions?
A mission statement sets out the purpose of a business existing.
Influences:
-Value of the founders
-Industry the business is in
-Views of society
-Size of business and ownerships
-Culture of business
What are corporate objectives and what are the internal and external influences affecting corporate objectives?
The corporate objectives of a business quantify the mission of a business and set specific and measurable targets for the whole population
External influences:
-Economic conditions
-Social changes
-Tech changes
Global prices
-Competitors
Internal influences:
-Poor performance
-New leadership
-Business ownership, culture and growth.
What is a strategy and tactics?
Strategy is a long term plan or approach that a business will take to achieve its objectives.
Strategies often involve a major commitment to resources.
Clear strategies guide tactical decisions.
Tactics are the day to day decisions take by middle managers, they are frequent and involve fewer resources.
What is the objectives hierarchy?
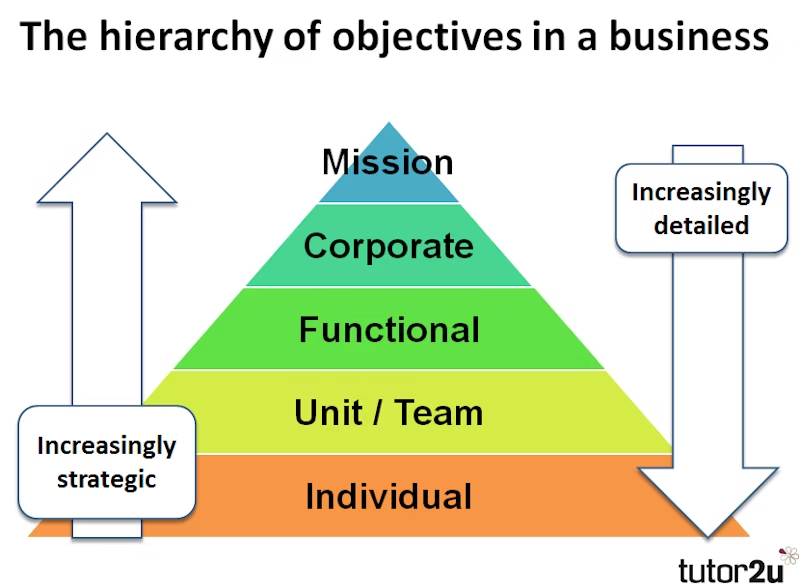
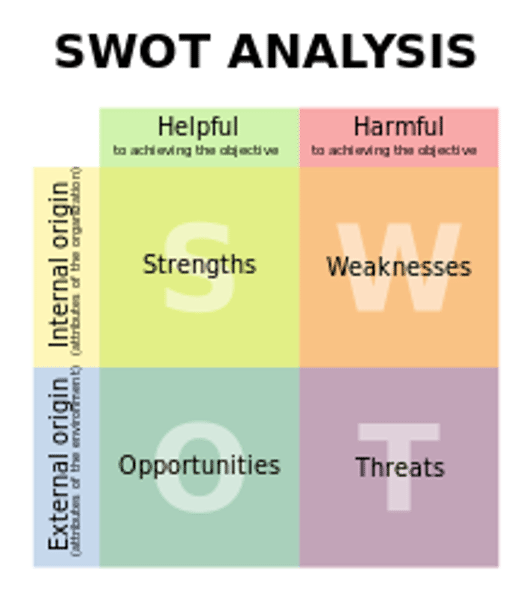
What is a SWOT analysis and what are the benefits and limitations?
A strategic tool that a business can use to analyse its current position and external factors that might affect it.
Benefits- assists strategic thinking in a structural way, low cost (simple approach) and can be combined with their decision-making models.
Limitations- subjective (depends on managers opinions), doesn't offer clear solutions and classification may depend on perspective.
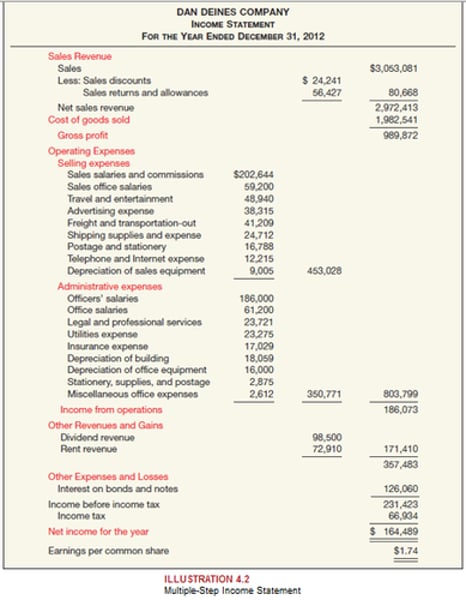
Whats an income statement?
An income statement communicates the revenue generated by a business and then its profits at various levels following expenses and incomes.
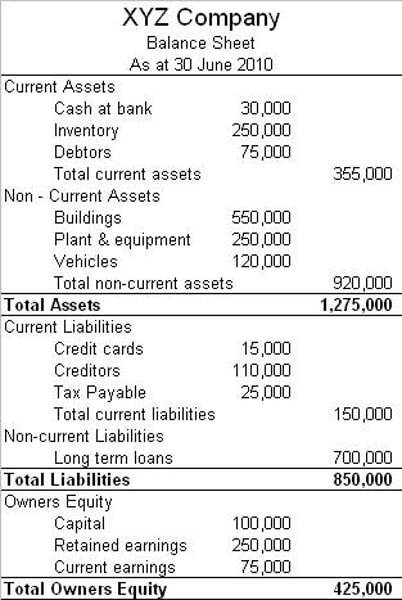
Whats the balance sheet?
A financial document that records the assets and liabilities of a business. A balance sheet gives a snap shot of the value and financial strength of a business.
What are non current assets (fixed assets)?
Used to operate business. Tangible non current assets are land and machinery. Intangible non current assets are the brands and patents.
What are current assets?
Assets that the business expects to use or sell within the year, can be converted into cash to pay off liabilities.
What are current liabilities?
Payments that are due within 1 year
What are non-current liabilities?
Debts that a business doesn't expect to pay within a year
What are net current assets?
the working capital a business has
Define financial ratios and give examples
A financial ratio compares 2 pieces of information.
Types:
-Gearing ratio- assesses the extent to which a business is based on borrowed finance
-Efficiency ratio- provides an indication of how well an aspect of a business has been managed
What are profit margins and how do you interpret them?
It is a performance ratio
Gross Profit Margin = Gross Profit/Sales Rev x 100
Op Profit Margin = Op Profit/ Sales Rev x 100
Profit margins are able to give an indication of the quality of the profit and how well the business is managing different areas of the business eg direct and indirect cost
So for gross profit margin, it allows a business to understand the way direct costs affects the level of profit and for operating profit margin it allows the business to understand how indirect costs affect the level of profit
What is ROCE and how do you interpret them?
Its a performance ratio
ROCE= Operating Profit/Capital Employed x 100
Want it to be a high number
Compares operating profit earned with the amount of capital employed by the business. Capital employed is its total equity plus any non-current liabilities.
Shows how effectively the business was able to make a profit from investments placed in the business. ROCE can be improved by increasing the operating profit or by decreasing the capital employed
What is current ratio and how do you interpret them?
It is a liquidity ratio
Current ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Want to be between 1.2 and 2.0
Compares current assets with current liabilities in doing so it works out whether or not a business has sufficient working capital to pay its short term debts
What are payables and how do you interpret it?
It's a financial efficiency ratio
recievables days = recievables /Sales x 365
calculates the time it takes to collect the debts that are owed, the shorter the period the easier the firm will find to pay their short term cash needs
What is inventory turnover and how do you interpret it?
It's a financial efficiency ratio
inventory turnover (rate of stock turnover)
inventory turnover = Sales /Av Stock value
Measures a businesses ability to convert inventories into revenue faster sales are generated the faster the profits are reviewed. The lower the number the more efficient the business is. Perishable goods have much faster turnovers than non-perishable goods.
What is gearing ratio and how do you interpret it?
Gearing = Loans / Capital Employed x 100
Assesses how a business has raised its long term finance it represents the proportion of a firms equity that is borrowed A highly geared business has more than 50% of its business in the form of loans it makes them more vulnerable to interest rate increases
Who uses financial accounts?
Managers- to assess performance of business
Potential investors or lenders- to assess the security and liquidity of the business
Shareholder- assesses the return they may receive on their investment.
Government- to calculate tax liability of business
What is window dressing?
Where a business manipulates its financial accounts to make them look more favourable to stakeholders eg delaying payments to a later financial period to boost short term profits
What are the measures of internal performance?
Marketing- product information (may include future sales forecast, PPA and details on market share), market research data (may include customer opinions eg brand recognitions and satisfaction levels)
HR- labour turnover and absenteeism (may give an indication of employee happiness and the motivation and effectiveness of recruitment), unit labour costs (calculates labour costs relative to output)
Operations- quality (can be difficult to measure however factors such as customer repeat purchase, product defects or satisfaction levels), capacity utilisation levels (maximum output relative to existing output)
What is a core competency?
Core competencies are the unique abilities that a business possesses that provide it with a competitive advantage. Core competencies are developed over a period of time through the learning and skills developed within a business relating to the production of its goods and services.
Benefits and drawbacks of core competencies
BENEFITS
gives a business uniqueness
adds value to a businesses product
DRAWBACKS
outsourcing areas of the business can lead to a fragmented workforce
they take time to develop- not all businesses have them, or they may not have the right ones
Give some long term measures on performance
Research and development (R&D)- investment in R&D may give an indication of the likely impact of product development and innovation in the future. However, there is no direct link between R&D spending and the level of innovation within a business.
Profit quality- firms may choose to focus on sustainable profits not on net profits as it doesn't give a good indication as exceptional items are included.
Employee engagement- high levels of employee engagement are likely to return rewards in the future and lead to greater levels of productivity and innovation.
Sustainability- sustainable approach can be conducted in the long run you can measure this through a CSR report.
Give short term measures of performance?
Cash position
Revenue
Productivity
Profit
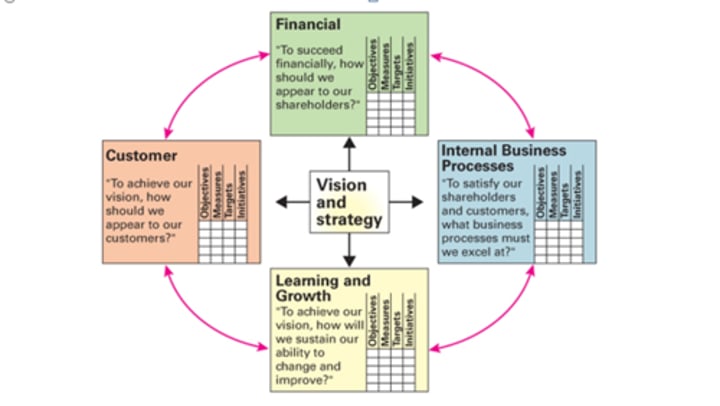
Explain Kaplan and Nortons balanced scorecard.
This is a planning and management tool used to match a businesses activities to its vision and strategy. It aims to improve internal and external communications and monitor organisation performance against strategic goals
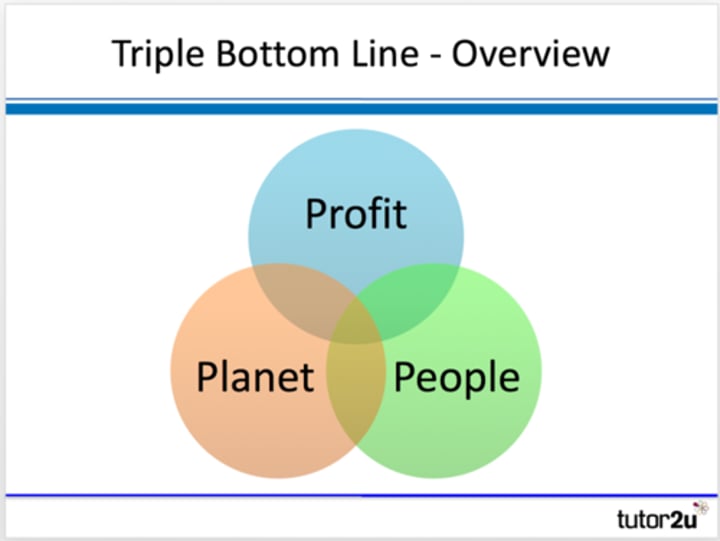
Explain Elkingtons triple bottom line
The triple bottom line looks at the impact of a business against 3 key areas.
What are factors that are influenced by the political environment?
Regulating markets
Enterprise
Environmental issues
International trade
National infrastructure
How are enterprises encouraged?
-Making finance accessible for small businesses
-Providing funding for research and development
-Support on establishing new businesses
-Guidance on running a business
How will enterprise benefit from the government spending on infrastructure?
-Speeding up communication
-Making transportation of goods faster and cheaper
-Allowing access to new markets
-Attracting new business to the UK
What are regulators?
Regulators aim to support businesses with compliance and conducting business in an appropriate way. They focus on:
-Promoting free competition between businesses
-Regulation of specific industries
-Regulators of privatised monopolies
What is the international trade and give examples?
Where governments implements policies to support their exporters as it brings in revenue and employment opportunities. Some initiatives include:
- UK trade and investment
- World trade organisation
- Open to export initiative
What are the factors influenced by the legal environment?
-Environment
-Labour
-Competition
What is competition legislation?
Competition legislation is put together to protect the interests of consumers and businesses. In particular legislation aims to control:
-Cartel activity- businesses working together to manipulate the market and limit competition.
-Abuse of market power- such as imposing unfair conditions on small suppliers
-Anti competitive practices- such as anti competitive merger and acquisitions
What is the labour market?
Labour laws aim to prevent exploitation level and at a collective level. They legislate for issues such as pay, working conditions and grievances. Legislations also governs the powers of trade unions and has diminished those powers over the past 30 years. Consequently, trade union membership has fallen considerably eg equality act 2010, trade unions act 1984 etc
Explain environment legislation?
Environmental legislation aims to internalise any negative externalities associated with business activity. Therefore, businesses are made to pay for the full cost of production eg costs to clean up or repair damage caused by pollution eg environmental act 1995
What is the political and legal impact on business decision making?
Can impose costly changes to adapt products or services to meet legal standards. If a business fails to do this this could limit businesses competitiveness as reputation is damages.
What is GDP and the business cycle?
Gross domestic product is a measure of a countries total output on goods and services over a period of time, changes over time and is represented by the business cycle.
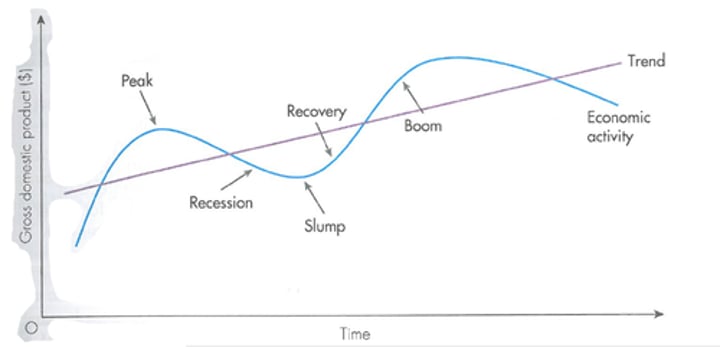
What is a boom, what are its features and its impact on a businesses strategic and functional decisions?
A boom is a high rate of economic growth and production.
Its features are high profits, low unemployment, high inflation and shortages in supply.
Its impact are that firms make strategic decisions to expand into new markets through market developments, functional decisions to expand workforce or increase recruitment, and business may seek opportunities for efficiencies and cost reductions due to economies of scale
What is a recession, what are its features and how does it impact on strategic and functional decisions?
Recession is when output starts to fall and growth declines, its features are when production declines as demand falls, governments use policies to stimulate growth, consumer confidence falls. Its impacts are that expansion plans are put on the back-burner, market penetration becomes more attractive as lower risk, business stockpile products, functions try to increase efficiency and cut costs.
What is a slump, what are its features and what is its impact on strategic and functional decisions?
It is a prolonged period of economic decline. Its features are high levels of unemployment, high rates of business failures and closures, low interest rates and low levels of spending and investment. Its impacts include redundancies, scales down of production and reduction in capacity, businesses reduce prices and focus of their most profitable product, businesses my leave certain markets.
What is recovery, what are its features and what is its impacts on strategic and functional decisions?
Recovery is where the economy starts to pick up after a period of decline. Its features include an increase in consumer confidence, businesses start to invest or take on new employees, spare capacity is used up. Its impacts include new business start ups emerge, investments increase, increase in employees to keep up with demand, functional decisions focus on ways to increase productivity.
What is inflation and deflation?
Inflation= general rise in prices over time measured by consumer price index. Low inflation rate can be managed by businesses but a high inflation rate can cause an increase in costs and reduce demand.
Deflation= fall in prices as measured by consumer price index, deflation is relatively rare in UK, short term falls can boost sales for businesses, prolonged deflation may mean that consumers postpone purchases whilst waiting for prices to fall further.
How might high, low inflation and deflation affect businesses?
High inflation may cause businesses to increase prices to pass costs onto consumers, business will look to decrease internal costs and if they increase prices this can lead to further inflation.
Low inflation may mean that businesses are more confident in a stable economic environment, businesses may also look to invest and grow.
Deflation may mean businesses struggle to pay debt- assets may have to be sold off to pay of debts, low demand may lead to redundancies.
What are exchange rates?
The exchange rate is the price of one currency expressed in terms of another. UK businesses purchase foreign currency to purchase foreign products. Exchange rates change due to fluctuations in demand for a currency.
If the pound increases in value against other currencies it is said to strengthen and if pound decreases in value against other currencies it is said to have weakened
How do exchange rates and decision making affect businesses?
Businesses will try to avoid uncertainty when exchange rates are volatile so firms may set an agreed rate for future transactions. Also a business may choose to target a specific international market or economy when the exchange rate is favourable.
Importers may switch international suppliers when the exchange rate is less favourable and may stockpile raw materials and products when currency is strong.
Exporters may lower prices to limit the impact of a strong currency and increase promotion in foreign markets when currency weak
What is monetary policy?
This adjusts the amount of money in circulation and therefore influence spending and economic activity. Main form of monetary policy is interest rates (cost of borrowing and reward for saving), other forms of this are influencing interest rates.
What is fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy involves government spending and taxation as a means of controlling economic activity. The difference between government income and expenditure in a fiscal year is known as the budget balance.
What is expansionary fiscal policy?
It reduces direct and indirect tax to increase disposable income this therefore increases spending in areas such as health and education therefore stimulating demand for businesses and creates jobs.
What is contractionary fiscal policy?
Reduces spending in areas such as health and education so pressure on inflation slows, therefore increases in direct and indirect taxes to slow down growth.
What is the impact of the interest rate on business activity?
High interest rates- consumer and business spending falls, stronger pound.
Low interest rates- consumer and business spending rises, inflation may rise and pound becomes weaker.
What are supply side policies?
They are a range of measures intended to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of free markets. Policies include:
-Manipulating the labour market- training, free movement of labour, tax cuts for low incomes.
-Privatisation- transferring organisations to state ownership to encourage competition
-Reducing red tape and regulations- making it easier for businesses to operate.
What is protectionism?
Involves protecting domestic business and home industries against foreign competition and limiting number of imports into a country. Open trade can benefit all countries by creating opportunities for growth and economic prosperity. Free trade encourages specialism, leading to greater efficiencies and lower prices (it is a key factor in reducing poverty in some countries).
Protectionism is therefore sometimes criticised.
What are the factors that affect exports in terms of protectionism?
Soft loans- as generous loan agreements offered to exporting businesses to help them compete in foreign markets.
Subsidies- grants given to support exporting businesses so that they can lower their prices in order to compete internationally
State procurement- favouring domestic businesses as suppliers over foreign goods
What are the factors that affect imports in terms of protectionism?
Technical barriers- such as rules and regulations governing the standard of products entering the country
Quotas- physical limit set on the number of units that can be imported into a country
Tariffs- tax on imports increases price of imported goods. Raises government income and makes domestic businesses more competitive.
What is globalisation?
Globalisation is the process by which the world is becoming increasingly interconnected as a result of massively increased trade and cultural exchange. Globalisation involves the movement towards worldwide markets.
What are the reasons for greater globalisation?
The process of globalisation allows businesses to enter new markets, access new skills, resources and the expertise, technology and experience of international businesses and industries. The benefits of greater globalisation are:
Support/encouragement by governments
Lower costs of transportation and better infrastructure
Improved communications technology
Society becoming more culturally aware
Reduction in trading barriers
Growth in international trading blocs.
What are the opportunities and threats to globalisation.
Opportunities:
-New markets
-Cheaper resources
-Cheaper labour
-Economies of scale
Threats:
-Competition
-Pressure on pricing
-Threat of takeovers
-Economic risks
-Political risk
State 4 strategies for global markets
Effective use of CSR- avoid damaging local cultures and traditions
Strategic alliances- look for partnerships with international businesses that have experience operating in foreign markets.
Strategic takeovers- acquire brands and businesses that international customer trust
Global vs local- standardise the product to gain economies of scale
What are emerging markets?
Low income countries that are experiencing high rates of growth. They hold significant potential for UK and European businesses in terms or resources, labour and market growth.
What is social change?
Relates to the changing demands of society for different goods and services. It also includes the way society spends money eg increased spending on luxury products and accesses products and services. All businesses must keep up with changing demands of society if they want to remain competitive.
What is demography?
It is the study of the human population, there are a number of demographic trends that businesses are having to adapt to, these create new challenges and opportunities
Give some key demographic factors?
Age- general population is getting older
Migration- growing number of UK population are migrants
Urbanisation- a growing trend in developed countries of people moving from rural areas to towns and cities
Growth- populations are growing at a considerable rate increasing demand for products and goods.
What type of lifestyle changes do consumers go through?
Technology- more consumers using tech to access products and services eg online shopping
Single occupancy- more people are living on their own then before
Time- consumers now want products and services that help them save precious time
On demand culture- consumers are accessing products and services instantly or at a time that suits them eg TV shows
Luxuries- people spend a greater proportion of income on luxuries
Health and well being- consumers more health conscious then ever
How does e-commerce affect business?
More opportunities for small businesses- little capital is required to start up an online business
Reduces business overheads
Growth of direct delivery
Fraudsters
Access to global markets
Cuts out retail- lowers prices
State some key technological changes?
3D printing
Smartphones
Renewable energies
VR
Personalisation of online experience
Cloud computing
What are the opportunities and risks of technology to businesses?
Opportunities:
Innovating new products
Access to new markets
Improving internal efficiencies
Streamlining operations
Risks:
Businesses have to keep up with a fast changing technological environment
New tech make some products obsolete
What is corporate social responsibility?
The belief that a business should act responsibly and protect the interests of all its stakeholders. Going beyond following rules and regulations, CSR dictates that a business should operate in a way that benefits society and the environment.
Customers want a fair price, transparency and good customer service
Employee want fair pay, good working conditions and job security
Suppliers want fair prices and frequent and regular orders
Local community want employment opportunities, investment in infrastructure and minimal negative externalities
What are strategic decisions?
Strategic decisions of businesses shift in order to keep up with the constant change in technology and social change.
What are the functional decisions?
Marketing- technology gives businesses new ways of communicating with its customers
Finance- as technology improves businesses must be more wise in where they want to invest their money eg online retail means less investments in premises
Operations- growing trend of instant access to products mean businesses have to adapt to these needs by being more efficient.
HR- flexible working conditions means employees no longer need to operate from a single place of work.
What is the shareholder concept?
The belief that a businesses prime function should be to satisfy its shareholders meaning profit maximisation.
What is stakeholder concept?
Where businesses cater for the needs of all stakeholders not just shareholders, in doing so businesses create long term prosperity and avoid unsustainable practices.
What is the CSR pyramid?
Carrols CSR pyramid sets out 4 responsibilities that all businesses should meet in order to be socially responsible. Businesses should go from the bottom to the top in stages.
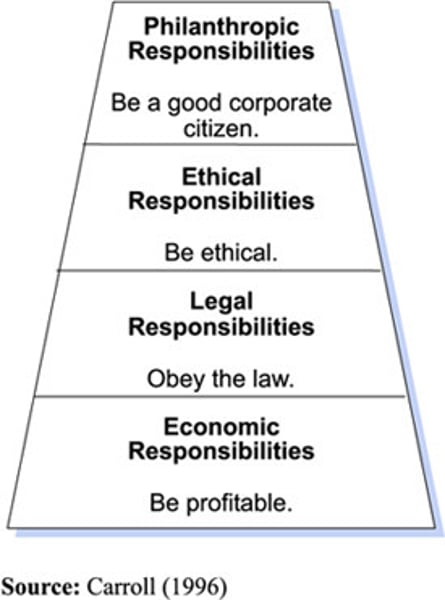
What is the issues with CSR?
Sometimes there is a short term contradiction between the first step of the pyramid and the following three. The pressures for a business to be legally, ethically and philanthropically responsible can require financial investment therefore having an impact on short term profitability
What are the pressures for effective CSR?
Can have a significant impact on businesses competitiveness:
Bad publicity can be shared through social media
Ethically orientated customers may choose a business base on its CSR record
Good CSR may attract better employees
Can support long term sustainability
What is the 5 forces model?
Used to analyse the key issues facing a business and how that business might respond to these competitive forces.
5 competitive forces are:
Competitive rivalry
Bargaining power of suppliers
Bargaining power of buyers
Threats of substitutes
Threat of new entrants
Explain in depth rivalry within the market?
This is the level of competition and aggressive rivalry between businesses within the market. As markets grow and become more attractive, new businesses may enter the market increasing competitive rivalry.
The competition is fierce if market has easy entry, easy for customers to switch, little differentiation with products and little growth of decline in market. These can all lead to a squeeze in profit margins.
Businesses would have to lower costs of production and prices to compete, develop a basis for differentiation or takeover/merge with other businesses
Explain in depth the bargaining power of suppliers
This is the power suppliers have to negotiate terms and prices, may change if the supply is a commodity eg wheat fluctuates
Supplier power is high if there are fewer suppliers, suppliers products are essential for production, supplier is able to integrate vertically forward and sell directly to businesses customers, low availability of viable substitutes
However high production costs and unfavourable terms of supply are key problems
Businesses should consider building strong relationships with suppliers, agree long term contracts of supply with favourable conditions and backwards vertical integration
Explain in depth buyer powers influence in the competitive environment?
This is the power buyers have to negotiate terms and prices. This might change as consumers gain greater access to information and greater choices between rival businesses.
Buyer power is high if there is little difference between product offered by competitors, products are price sensitive, customers buy in large quantities on a regular basis, it is easy for buyers to switch between competitors. A key problem is that prices are forced down and credit terms demanded so there is pressure on cash flow.
Businesses to combat this may develop a USP, lower prices to attract customers.
Explain in depth the threat of substitutes influence in the competitive environment?
A substitute is an alternative product that may deliver the same benefits to the customer. The threat of substitues may change with social trends eg the health trend for consumers to use coconut oil as a health alternative instead of olive oil when cooking.
Threat of substitues is high is alternative products exist, alternative prices fall or a customer can easily switch to a substitute.
Key problems include buyers having higher bargaining power, competition exists outside the market.
Some options to consider for the business is to develop a USP, lower prices to attract/keep customers, promote benefits in comparison to substitutes
Explain in depth barriers to entry influence in the competitive environment?
A barrier to entry is a physical, technological and intellectual factor that makes it difficult for a rival business to enter the market. The existence of large companies can create barriers to entry as they dominate resources and networks. However, disruptive technology and innovation can give small businesses leverage to enter a market.
Barriers exist when capital investment to enter market is high, customers are brand loyal to existing businesses, levels of specialist knowledge and expertise in the industry are very high.
A key problem is that is few barriers exist it is easy for new competitors to enter the market and increase competitive rivalry.
Some options for businesses to consider are: innovation as continuous development of new products can keep the business ahead of any new competition, building strong relationships with buyers, economies of scale.
What is investment appraisal?
A series of techniques designed to assist businesses in judging the desirability of investing in particular projects, may use a range of techniques eg financial and non financial methods. Can aid businesses in making decision when investing in non current assets, launching new products, new tech, expansion and
infrastructure.
What are the financial methods for investment appraisal?
-Payback- calculate the length of time it takes for an investment to recoup its original cost
-Average rate of return- calculate the annual average return over the life of an investment with other alternatives
-Net present value- can be used alongside other techniques and considers the future value of an investment by discounting the decreased future value of money.
What is payback?
It is a quick and simple investment appraisal tool. It simply focuses on the time taken to recoup the initial investment and considers the cash inflows over a number of years. It is useful for firms who need a quick return and may be facing liquidity problems.
What is average rate of return?
APR is useful because it measures the profit acheived on an investment over time, which can then be compared to other investments or the zerp risk strategy of leaving money in a bank account. However, profits may fluctuate considerably over the life of a project and this is not taken into account.
APR=average annual profit/assets initial cost
What are the 3 steps to calculating APR?
1. Total income from investment-cost of investment= total profit from investment
2. Total profit from investment/expected lifespan of asset= average annual profit
3. Average annual profit/cost of investment X 100%= APR
What is net present value?
NPV takes into account the future value of money by discounting cash flows. NPV considers time in an investment and follows the principle that the value of money depreciates over time.
What are some investment criteria?
Financial investment criteria:
-The rate of interest- using current rate of interest as a benchmark to judge investments against
-ROCE- is there an expected minimum % return on the investment.
-Cost- can the firm finance the investment?
Non financial investment criteria:
-Corporate objectives- does the investment support business strategy?
-Ethics- does the investment support CSR policy?
-Industrial relations- what will be the impact on employees
What is risk and uncertainty of an investment?
Risk is the chance of an adverse outcome and the impact it might have. The following might determine the level of risk associated with a particular investment:
-Timescale of the investment
-Knowledge/expertise of the business in the investment
-If the investment is in a new market
-Stability of the external environment
What is sensitivity analysis?
Sensitivity analysis involves using variations in forecasting to allow for a range of outcomes. It allows a businesses to ask 'what is' questions and put in place plans to deal with these scenarios. Examples might include:
-Comparing NVP using a variety of discount factors
-Allowing for a 20% fluctuation in sales and costs
-Building in contingency for unforeseen expenses