Neuro - Clinical Neuroscience Techniques (Test 3)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What are the 5 most common used techniques we will focus on?
computerized tomography (CT)
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
electroencephalogram (EEG)/ event related potentials (ERP)
positron emission tomography (PET)
functional MRI (fMRI)
What 2 techniques are related to structure?
computerized tomography (CT)
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
What 3 techniques are related to function?
electroencephalogram (EEG)/ event related potentials (ERP)
positron emission tomography (PET)
functional MRI (fMRI)
Which technique is most widely used?
computerized tomography (CT)
CT was developed in ____ and is also called a sophisticated _____
1970
x-ray
CT provides ____ anatomical images of the brain
static
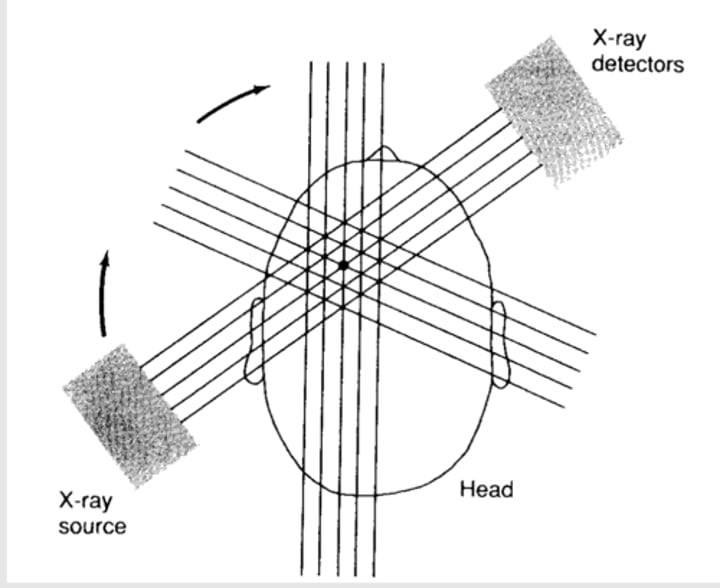
How does the x-ray portion of a CT work?
x-ray source emits a series of narrow x-ray beams and rotates around the head
How is a CT obtained?
information from many positions is taken and reconstructed as a 3D image of the brain using mathematical techniques
How is the image produce for CT?
produced because different substances absorb different amounts of X-rays
Dense tissues absorbs ____ of rays, therefore they show up on as ______ image
a lot, light (white)
What shows up as a lighter image (white)? (i.e. dense tissue)
bones
acute blood (spilled blood in brain)
Soft tissue absorbs ____ rays, therefore they show up as _____ image
fewer, dark
What shows up as a darker image? (i.e. soft tissue) `
CSF
Brain tissue
infarct
Cysts - fluid filled
How does density of brain tissue impact CTs?
density of gray matter is lighter, white matter is darker
Why do we sometimes use intravenous injection of dye for CT?
used to increase contrast
may allow blood vessels and tumors to be seen
Most CT images are from the perspective of the patients _____, so we see what?
feet
left & right sides of brain are opposite
What are 4 advantages of CT?
- provides structural imagine of brain in vivo (in vivo means in a live organ)
- can be used in healthy and clinical subjects
- indicates areas of brain abnormality
- relatively non-invasive
What are 3 disadvantages of CT?
- poor spatial resolution
- provides measure of structure, not ongoing activity (no function)
- expensive and requires highly trained specialist staff
What does spatial resolution prevent us from?
localizing things precisely
also makes it hard to see small things
How is MRI similar to CT? How is it different?
like CT, MRI provides static "slice" images of the brain, but in even greater anatomical detail
How much detail does an MRI provide?
down to 1-2mm in size
How are MRI images obtained?
images result from effects of changing strong magnetic fields applied to brain tissue (brain tissue responds differently to magnets)
What do nuclei do when the subject is placed in the magnetic field?
nuclei of certain atoms in brain tissue (usually hydrogen) align themselves in orientation of field
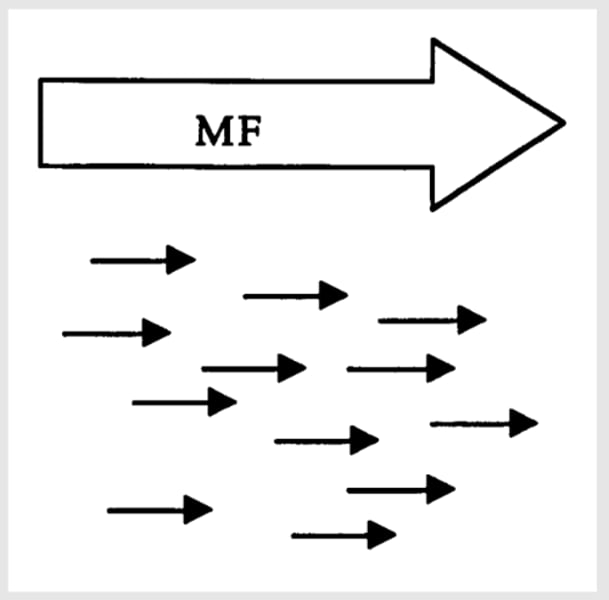
What happens to the nuclei after the introduction of specific radio frequency (RF) pulse into the field? (MRI)
this pulse causes hydrogen atoms to resonate and change axis of alignment
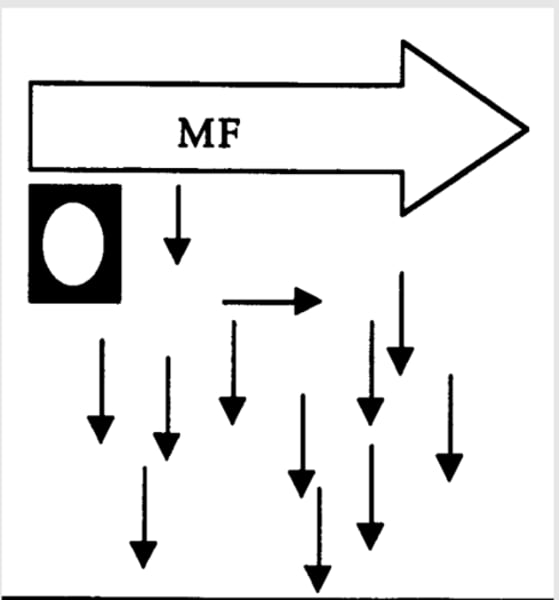
What happens when the RF pulse is removed? (MRI)
when RF pulse is removed, hydrogen atoms "relax" and return to original alignment
What is actually measured in an MRI?
discharged energy
- when hydrogen atoms relax, they discharge energy (discharged energy is what is measure)
How does the discharged energy from MRI help to produce an image?
- during realignment, hydrogen atoms discharge the RF energy that they had absorbed
- because hydrogen composition of different brain structure varies, the RF energy given off is distinct for different structures
- computer analyses construct 3D image of brain based on differential energy emissions
What is the rate at which hydrogen atoms realign and return to a lower energy state called in MRI?
relaxation
How many types of relaxation are there in MRI? What are they?
2
T1, T2
What are T1 images like? What are they similar to?
dark CSF, light tissue
similar to CT but with more detail
What are T2 images like?
light CSF, dark tissue
What do pathologies typically show up like on MRI?
behave like CSF so dark on T1, bright on T2
What are 4 advantages to MRI?
- excellent spatial resolution (about 1mm; determined mainly by magnet strength)
- brain can be visualized in any plane
- no X-rays or radioactive material used
- safe, painless, non-invasive
What are 4 disadvantages to MRI?
- even more expensive than CT
- special housing required for magnetic field
- cannot be used in patients with metallic devices (ex: pacemakers, vessel clips)
- provides measure of structure, not ongoing activity (no function)
What does EEG do (Electroencephalogram)?
records electrical activity of brain by electrodes placed on scalp
What is the focus of EEG? What is it not good for?
- focus is function
- not good for location --> picks up a pattern of activity
What is the EEG signal generated by?
post synaptic activity (activity of dendrites) of millions of pyramidal cells
How is the signal of EEG seen?
the signal is amplified and seen as waveforms
How do waveforms of EEG vary?
in frequency and amplitude
What do the waveforms of EEG depend on?
mental state (no external stimulus)
What is EEG used to diagnose?
used to diagnose epilepsy and other brain abnormalities
What is event-related potential (ERP)?
electrical potential in response to an event (event/external stimuli)
event or evoked potential
What does an ERP show?
change in EEG signal in response to sensory or cognitive stimulus
What makes EEG/ERP unique?
no other technique is as precise in timing of events as EEG/ERP
What is EEG/ERP used for?
- used in infant newborn screening test to detect early hearing loss
What are 5 advantages to EEG?
- non-invasive
- excellent temporal resolution (on a m/s scale)
- can be used to record brain electrical activity in real time
- can be used to measure brain's response to a number of sensory or cognitive variables
- relatively cheap (compared to MRI scanner)
What are 4 disadvantages of EEG?
- poor at localizing function
- activity is recorded from millions of groups of neurons (doesn't tell you where abnormality is coming from)
- brain activity may fluctuate unpredictably
- susceptible to movement artifact (ex: baby moving impacts EEG so we do these when they are asleep)
What does positron emission tomography (PET) provide?
images of brain function
What happens in a PET scan?
- subject injected with radioactive substance (ex: 2-deoxyglucose)
- glucose is transported by blood to brain
- metabolically-active areas will use more glucose and become more radioactive
What do radioactive particles emit? (PET)
positrons
What happens when positrons collide with electrons?
they form gamma rays
What is measured in a PET scan?
Gamma rays
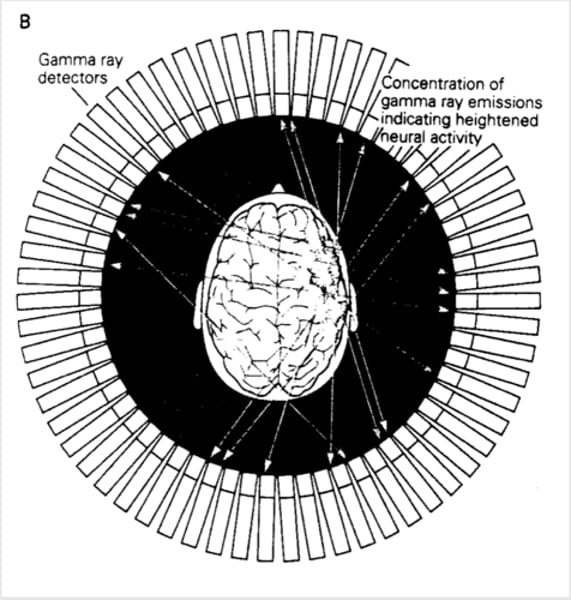
How is gamma radiation represented?
amount of gamma radiation is represented in colour-coded images which indicate those regions which are high or low in metabolism
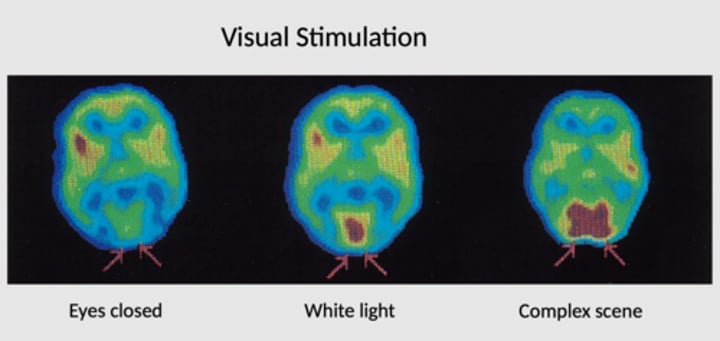
What does PET look like when eyes are closed vs. white light vs. complex scene?
What is the subtraction method?
brain is always active so we need subtract normal background activity (this is the control) from activity measured during task (this is the stimulation)
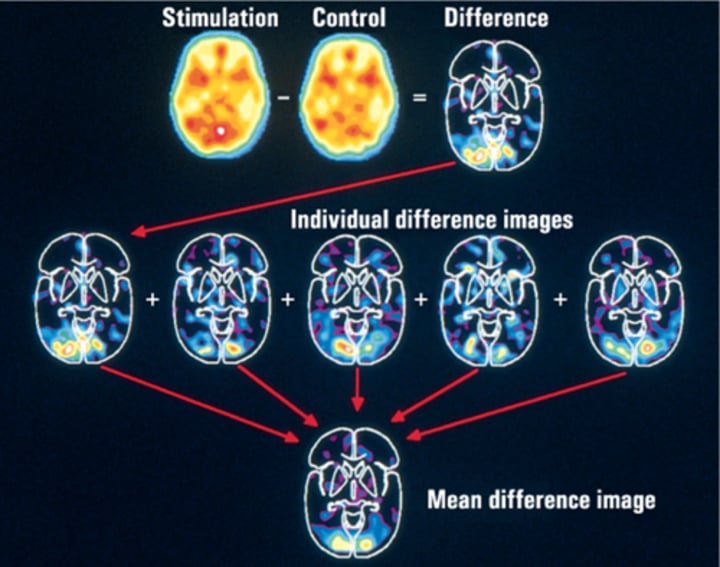
What is the subtraction method used in?
used in PET and other functional techniques
What are 3 advantages of PET?
- measure of regional brain activity in vivo
- can be used to measure brain activity during task performance
- relatively good spatial resolution (3-8mm)
What are 4 disadvantages of PET?
- invasive
- poor temporal resolution (blood flow is slower than neural transmission)
- tasks must take longer than 1 minute
- expensive
How does fMRI differ from MRI?
uses MRI technology, but measures brain activity
How does fMRI work in relation to oxygen?
- active brain areas receive more oxygenated blood than inactive areas
- concentration of oxygen blood affects its magnetic properties
- thus, MRI can detect functionally induced changes in blood oxygenation
Compared to PET, fMRI has better ____ and ____ resolution (but it has poorer _____ resolution than EEG)
fMRI has better spatial and temporal resolution
poorer temporal resolution than EEG
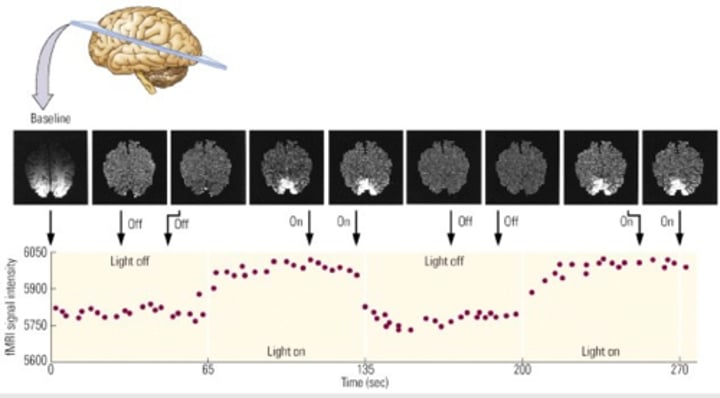
Image of fMRI
light is being turned on and off (simple stimulus)