DSA10 - Pathology of the Eye
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
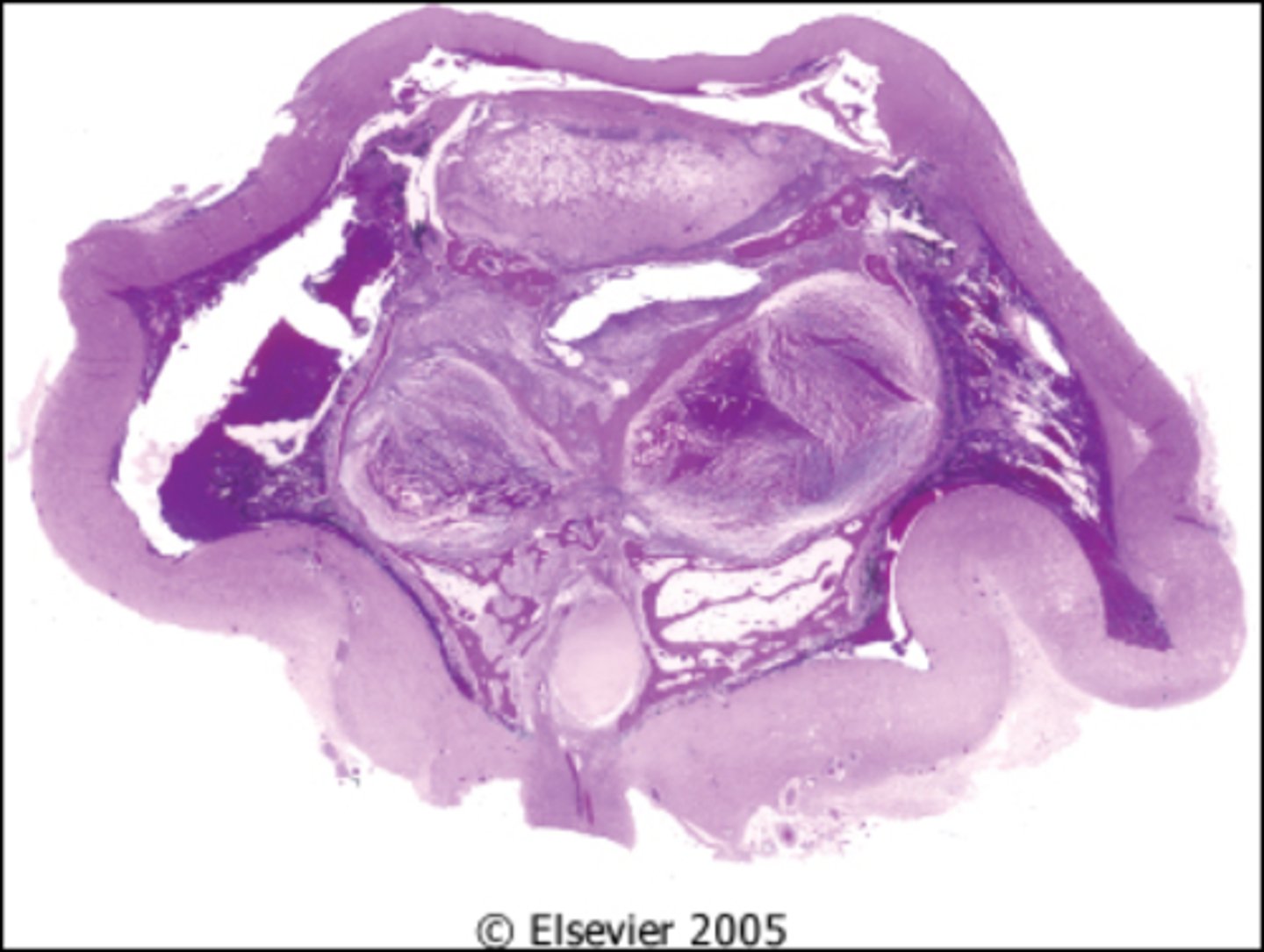
Proptosis
Information for Symptom:
bulging or protruding of one or both eyes from the orbit due to forward displacement
Thyroid Ophthalmopathy (Graves Disease)
Information for Condition:
Autoimmune disease which can affect the thyroid --> enlarged rectus muscles due to Hyaluronic acid deposition, the orbit and the skin; eye is forced to protrude forward (exophthalmos)
May not regress w/ Tx for Hyperthyroidism
Lacrimal Gland Neoplasm
Information for Condition:
Mass on major lacrimal gland (which sits superior and lateral to eye globe) that pushes eye inferior and medial (towards the nose) --> proptosis
Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation
Information for Condition:
Inflammation of orbit (may lead to Proptosis) due to inflammatoy pseudotumor, IgG4 disease, or infectious mass.
Commonly bilateral with episodic recurrence
Sx: Decrease vision, diplopia, red eye, headache painful presentation in children - resembles orbital cellulitis. can have constitutional symptoms
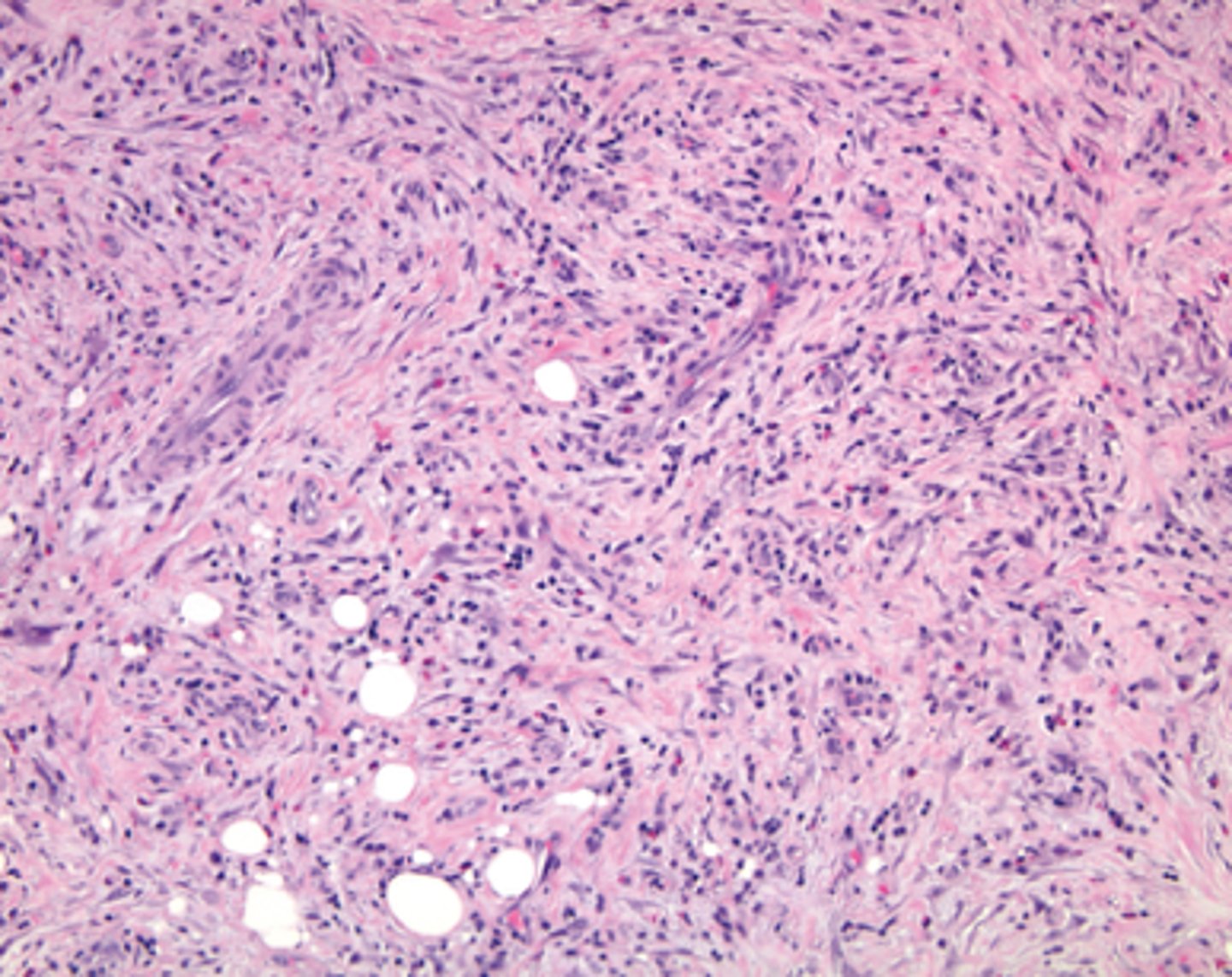
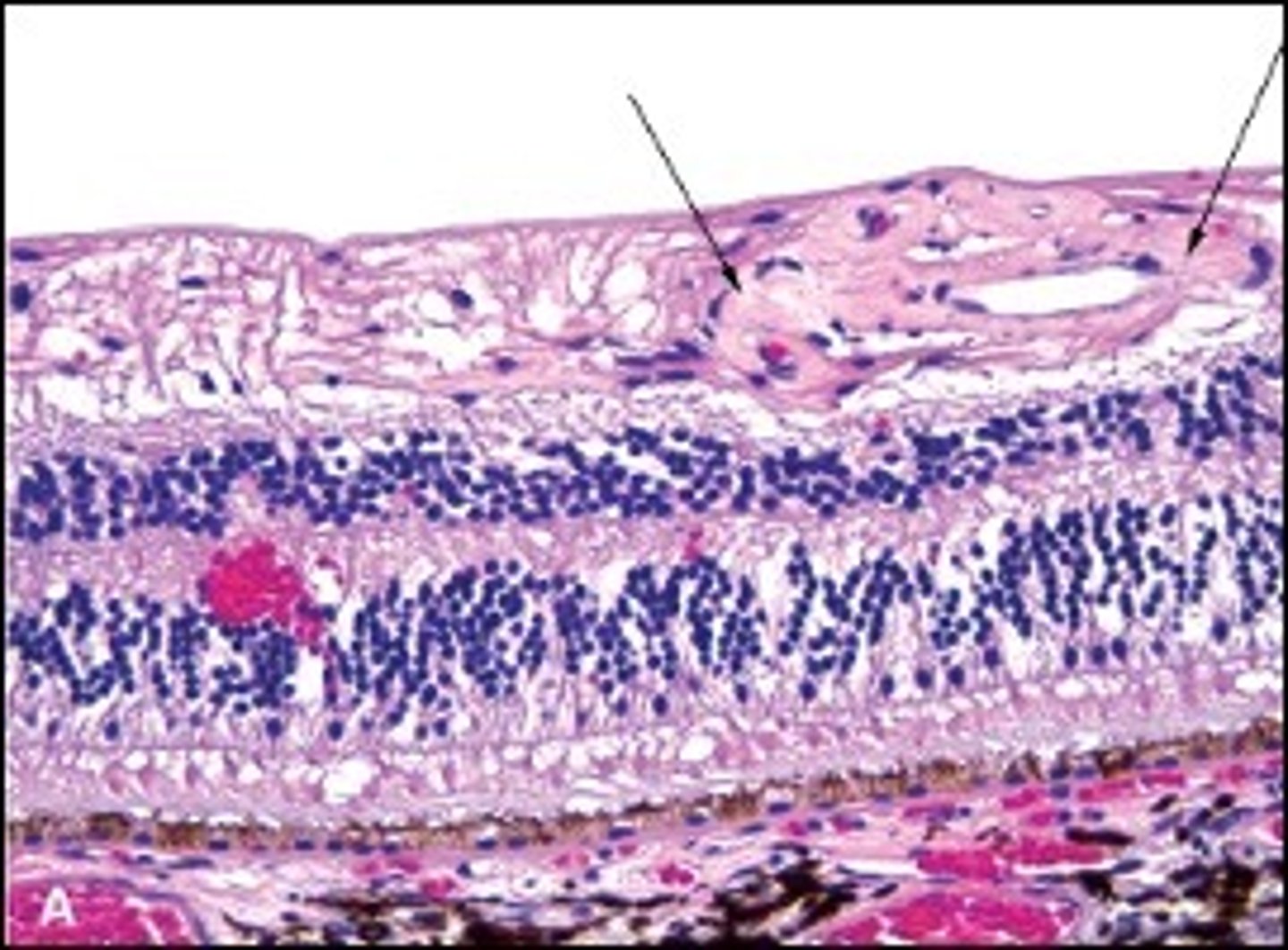
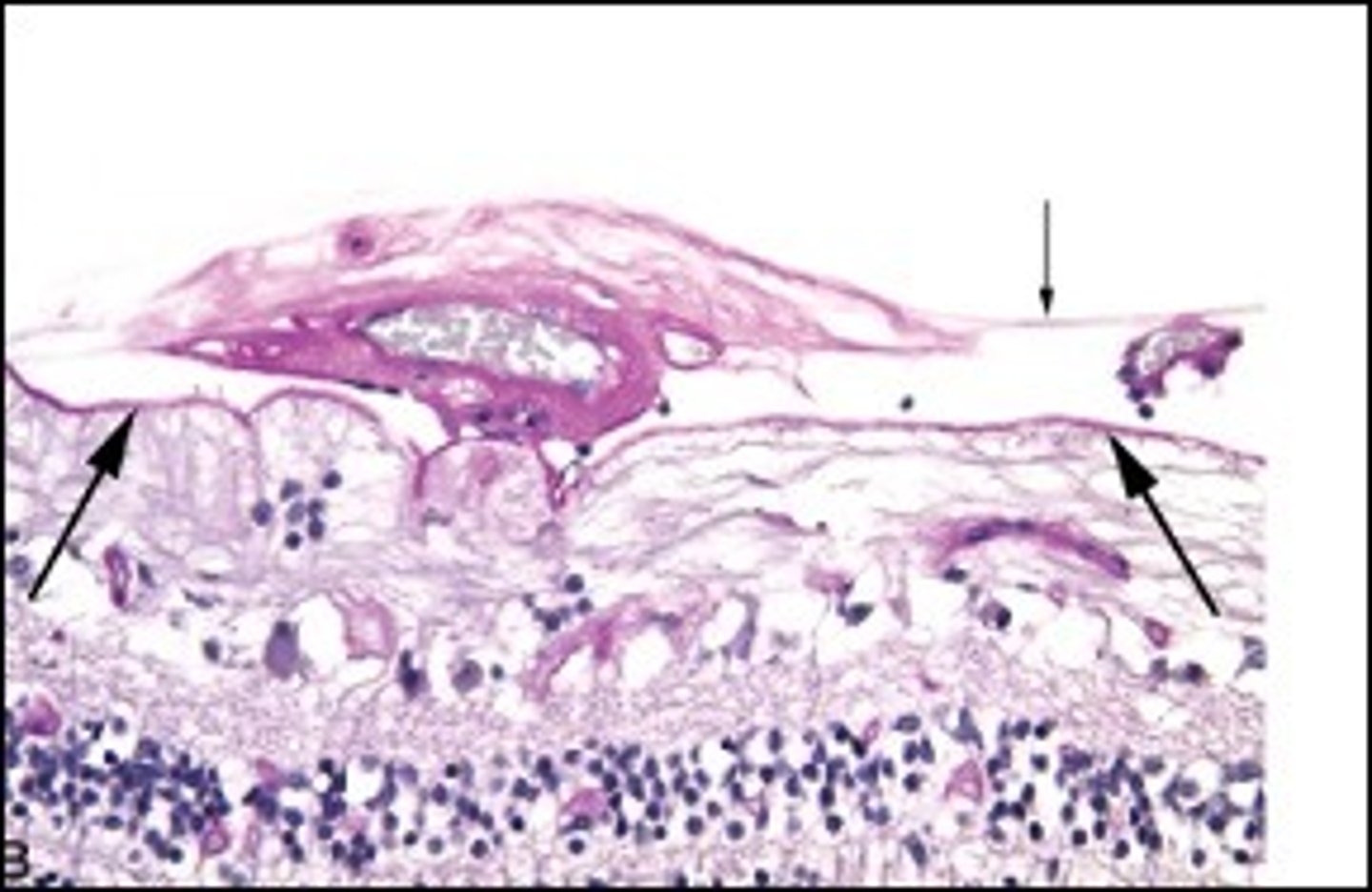
Inflammatory pseudotumor:
-Mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate with fibrosis - can cause Idiopathic Orbital Inflammation
*may be idiopathic or IgG4 disease
What is shown here?
Sjogren syndrome
Information for Condition:
Autoimmune lymphocytic attack on lacrimal and salivary glands --> can lead to Proptosis; may progress to lymphoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Information for Condition:
Common
Involves sun-exposed areas
Usually involves lower eyelid rim and medial canthus
Blepharitis
Information for Condition:
Eyelid inflammation
Chalazion
Information for Condition:
Ducts for sebaceous glands under the palpebral conjunctive become blocked --> lipogranulomas form due to gland rupture
Sebaceous carcinoma
Information for Condition:
Aggressive condition
May show Pagetoid spreading of carcinoma in-situ cells (Atypical epithelium w/ cytoplasmic lipid) to overlying mucosa
May develop lymph node metastases
(esp intraparotid & submandibular LNs esp)
*Mortality Rate = 22%*
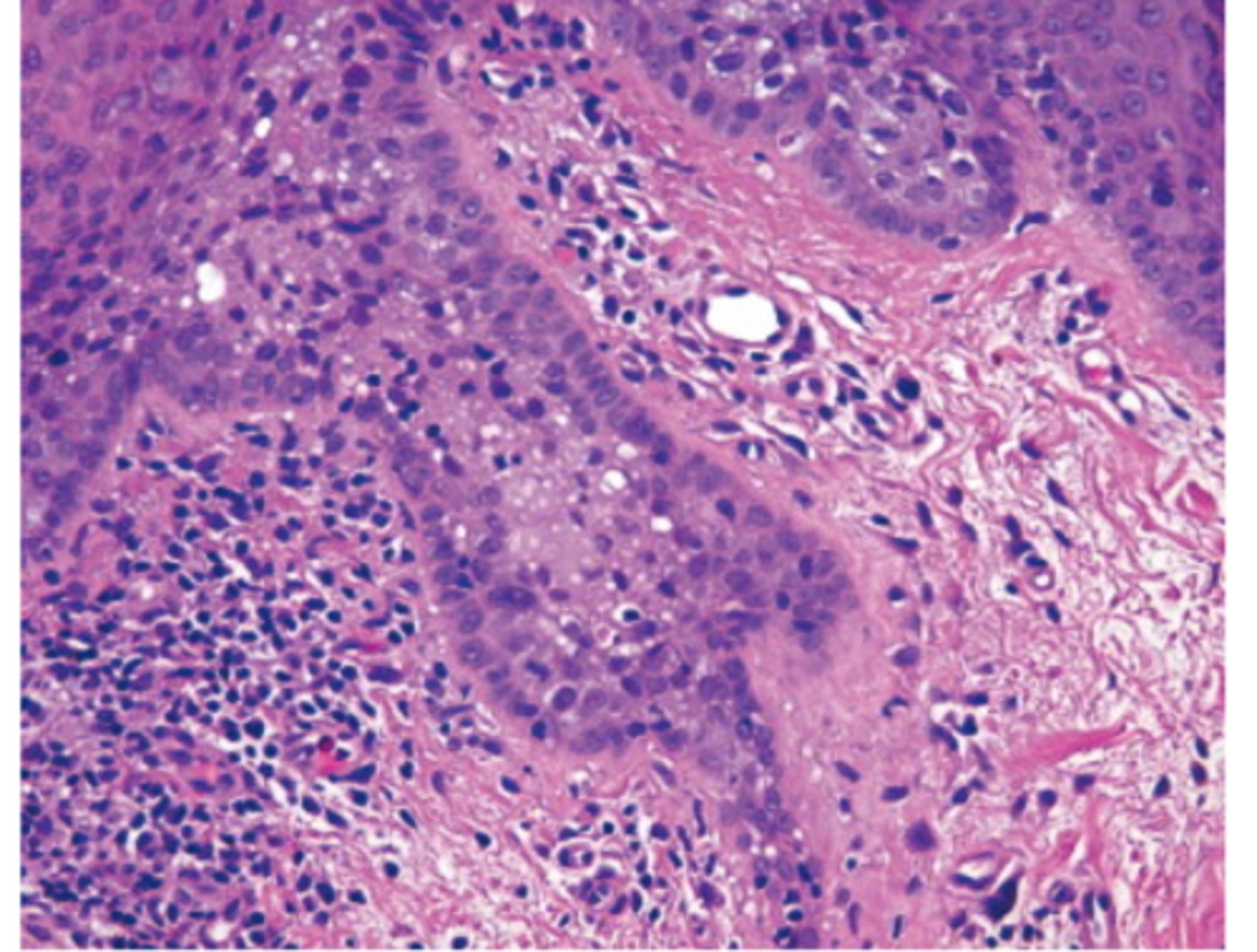
neutrophils; lymphocytes
Bacterial conjunctivitis involves a surge of (neutrophils/lymphocytes), while viral and allergic conjunctivitis involve a surge of (neutrophils/lymphocytes)
Chlamydia trachomatis (trachoma)
Information for Condition:
-Gram-negative bacteria; intracellular cause
-Highly contagious, endemic in low-income counteries
-Scarring inverts upper eyelids --> lashes damage cornea = most common cause of blindness worldwide
-Caustic alkali injury
-Cicatricial pemphigoid
What other conditions can cause Conjunctival Scarring?
Pinguecula
Information for Condition:
-Raised yellowish white mass within the bulbar conjunctiva, adjacent to the cornea
-See solar elastosis & neovascularizaiton
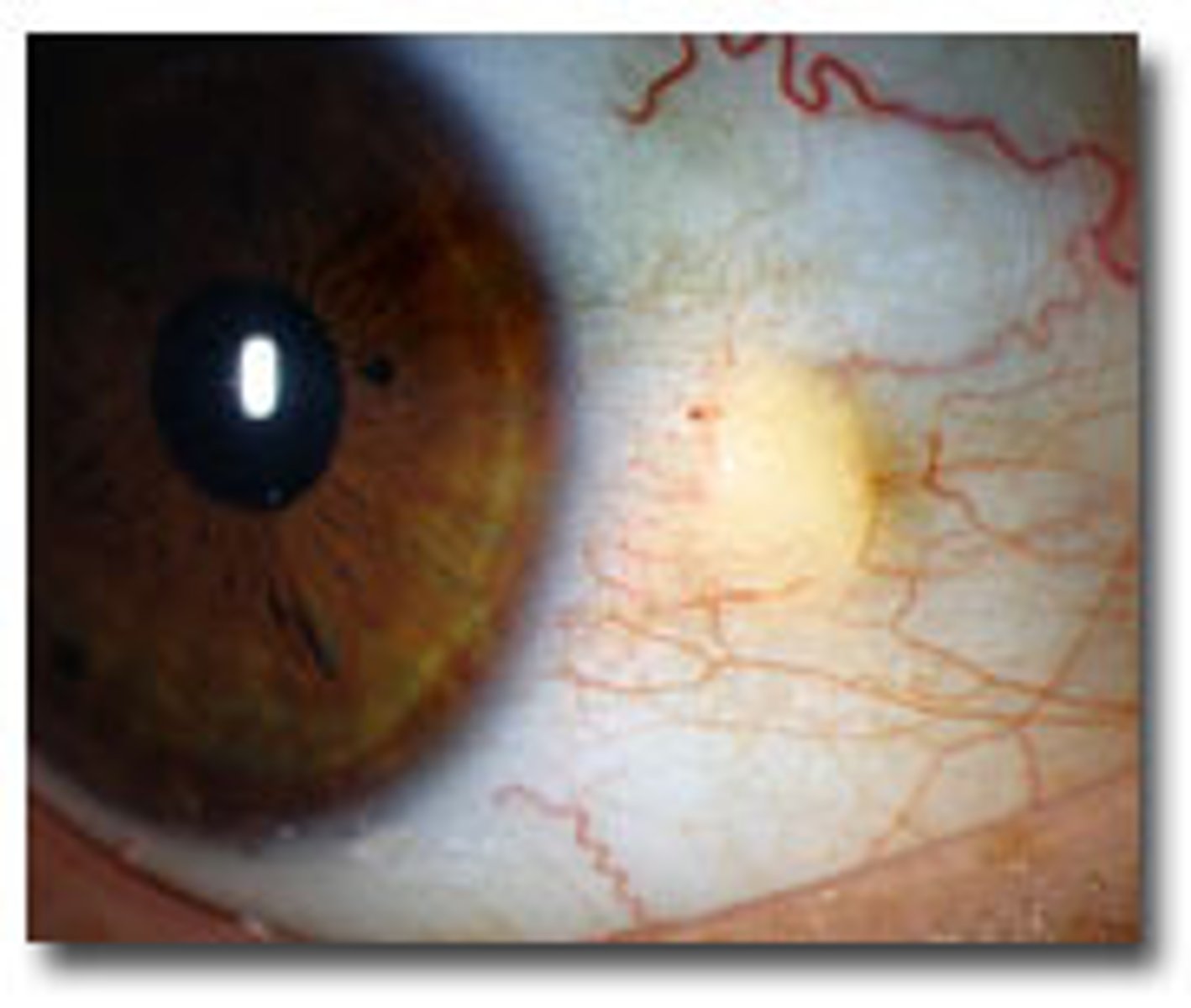
Pterygium
Information for Condition:
-Fleshy triangular growth of bulbar conjunctiva
-See solar elastosis & neovascularizaiton
-Extends onto cornea from limbus, and may be biopsied to evaluate for Squamous Carcinoma
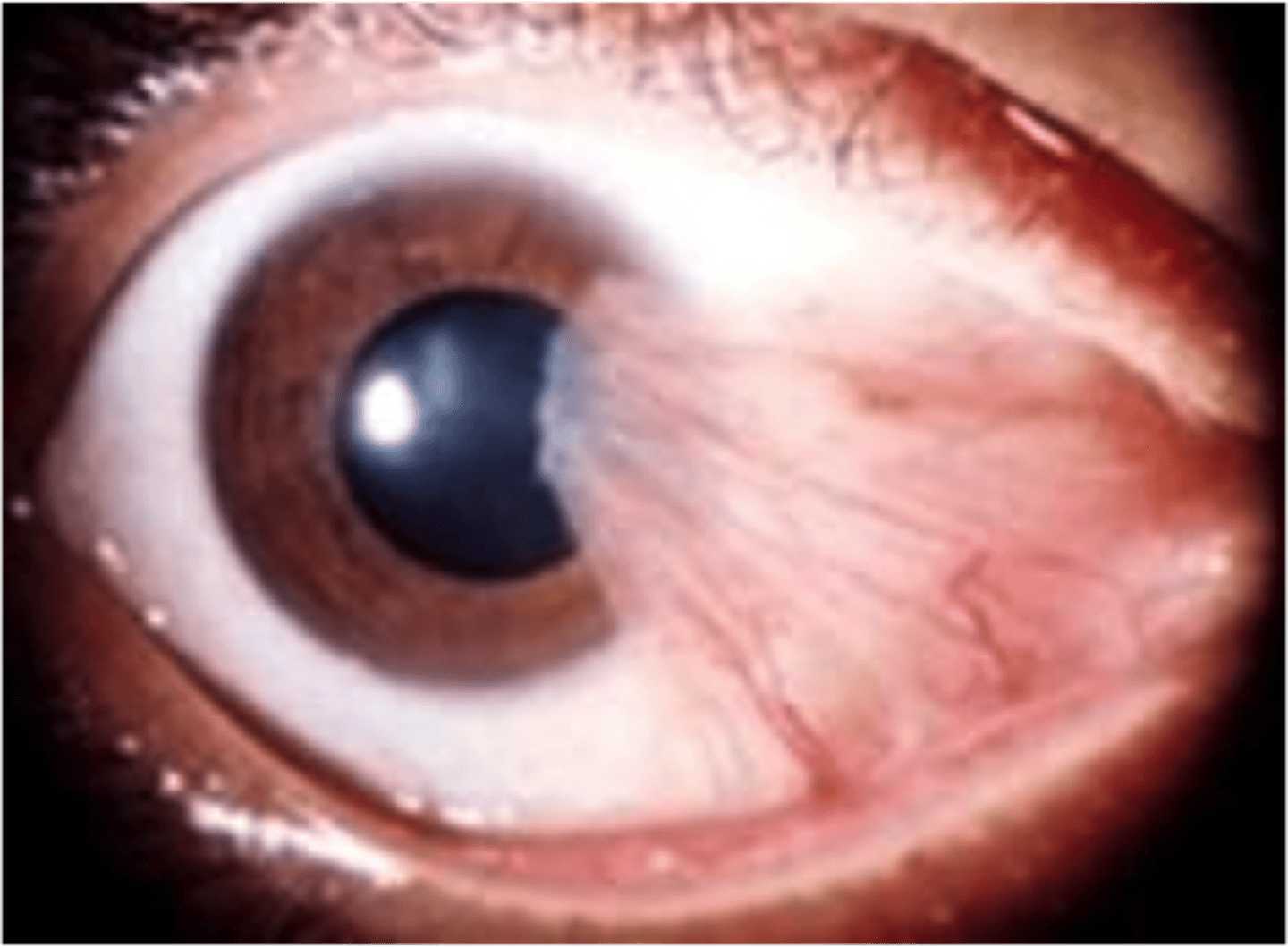
-Squamous papilloma (HPV 16 & 18-associated)
-Squamous carcinoma and carcinoma-in-situ
-Nevi (common, bulbar conjunct, with cysts)
-Melanomas (from primary acquired melanosis with atypia (like lentigo maligna), BRAF in 40%, 25% aggressive)
What neoplasms are associated with the Conjunctiva?
Nevus in Conjunctiva
Information for Condition:
Circumscribed growth in conjunctiva
Small cells w/ cystic glands
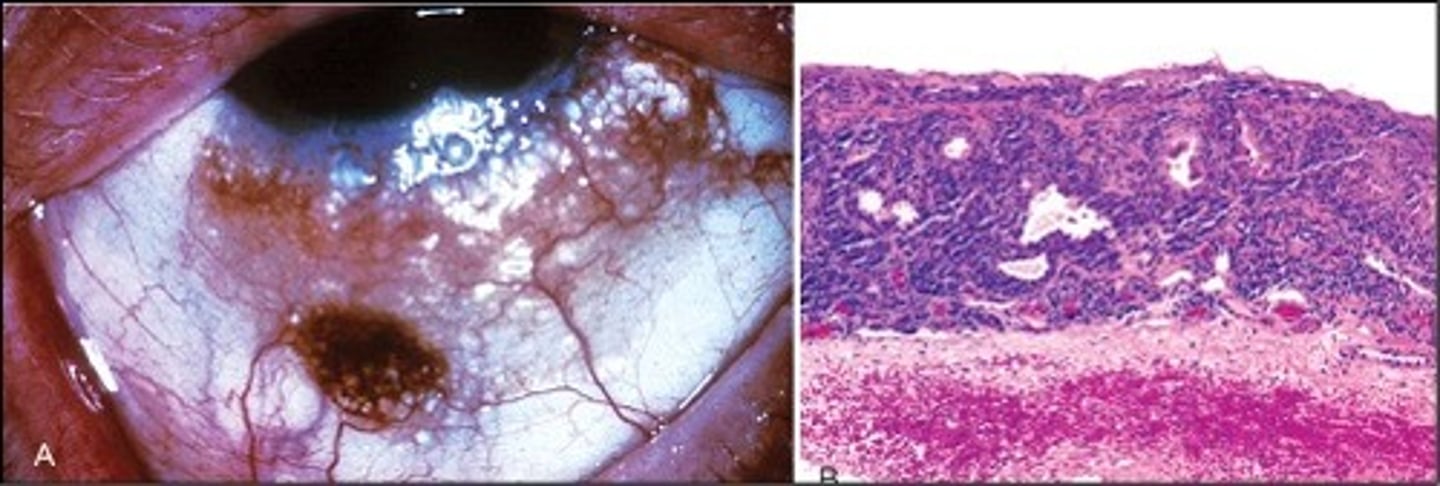
Melanoma in Conjunctiva
Information for Condition:
Irregular growth in conjunctiva
Large & atypical cells that invade stroma
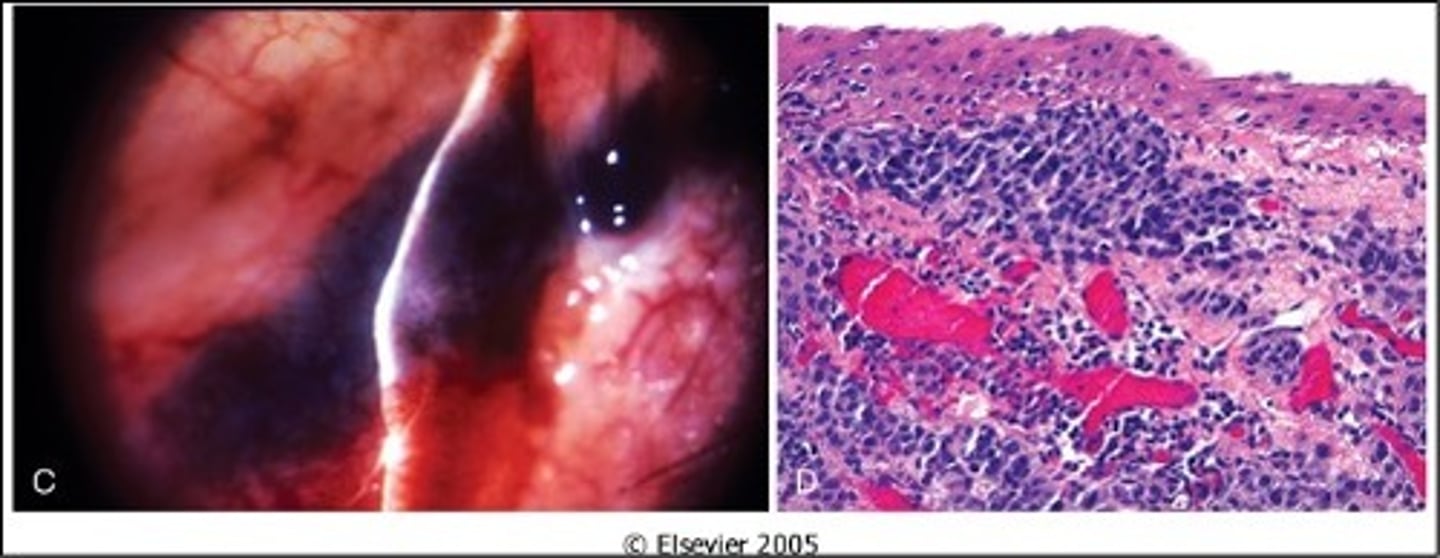
Herpes (simplex and zoster)
Information for Condition:
Virus that can cause keratitis (granulomatous inflammation centered on Descement membrane) and corneal ulcers:
-Will see scarring, neovascularization & deep granulomas
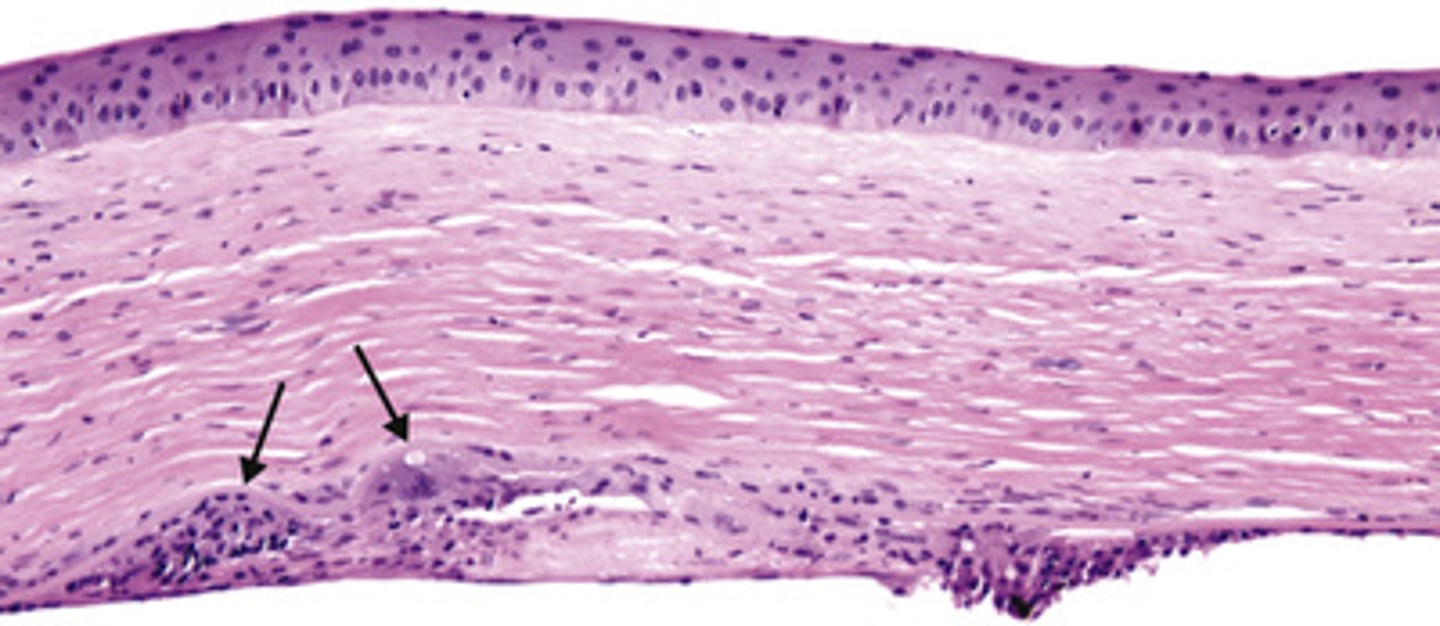
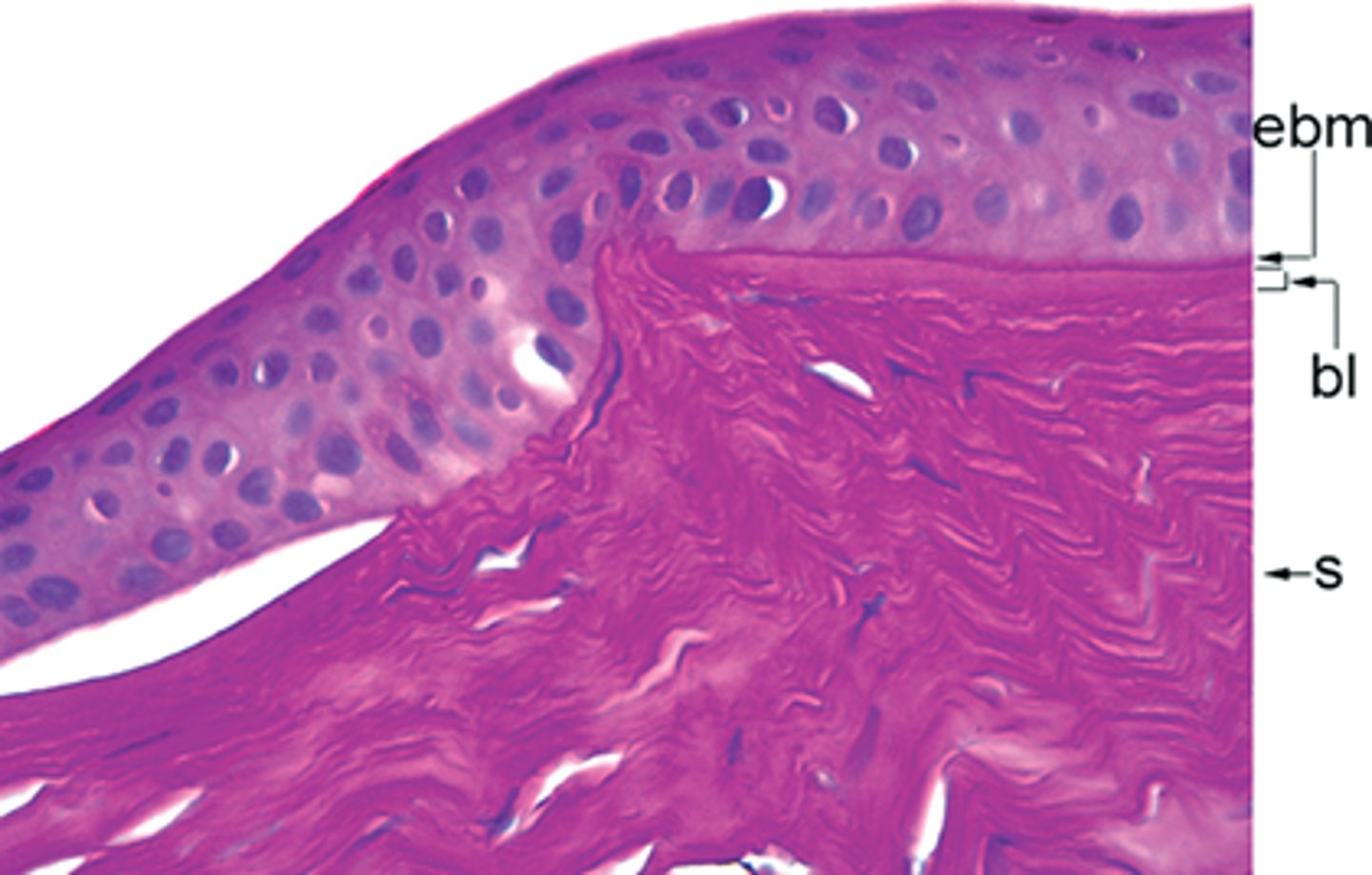
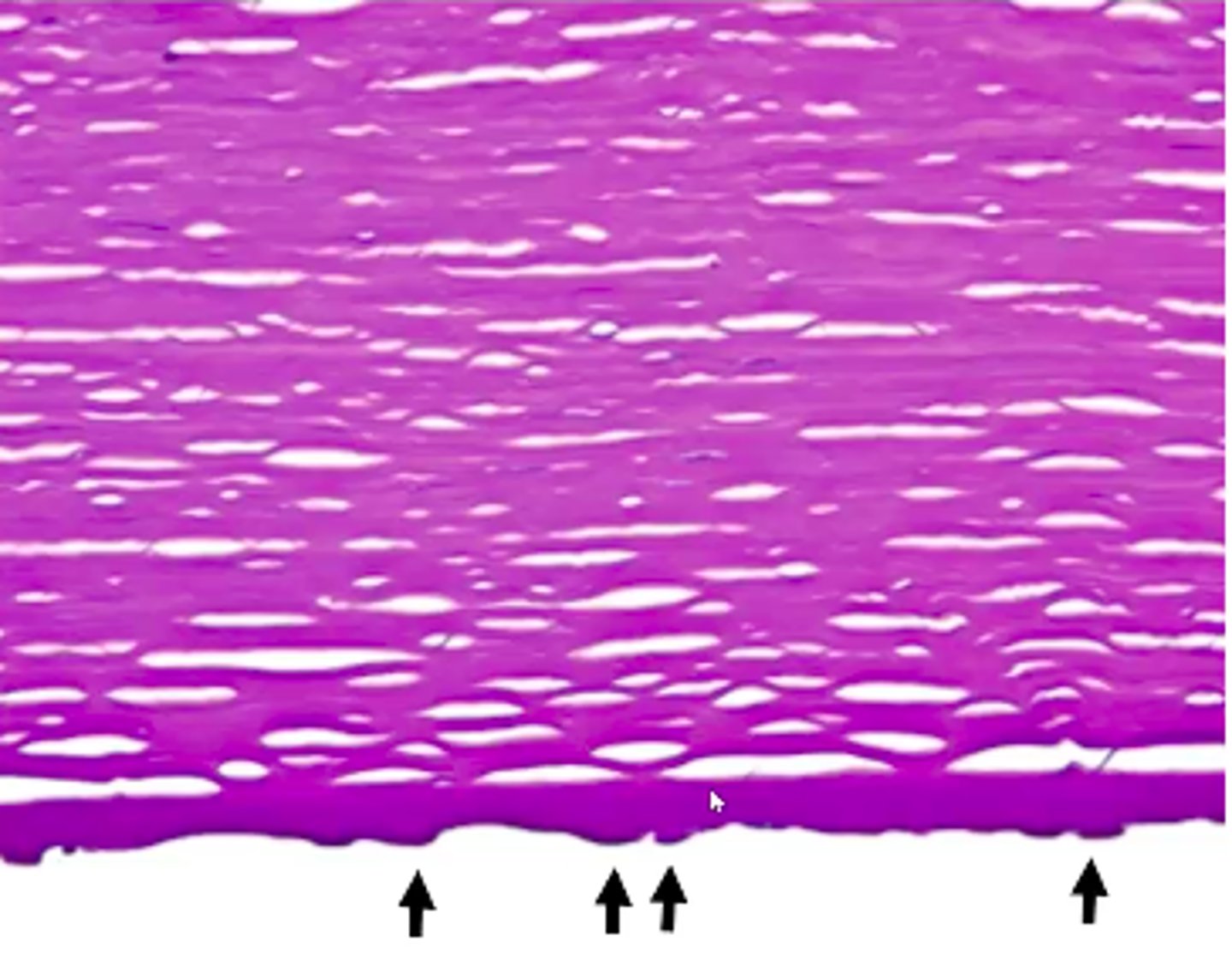
Band keratopathy
Information for Condition:
Calcium deposits in Bowman layer; metastatic calcification (may be due to hypercalcemia)
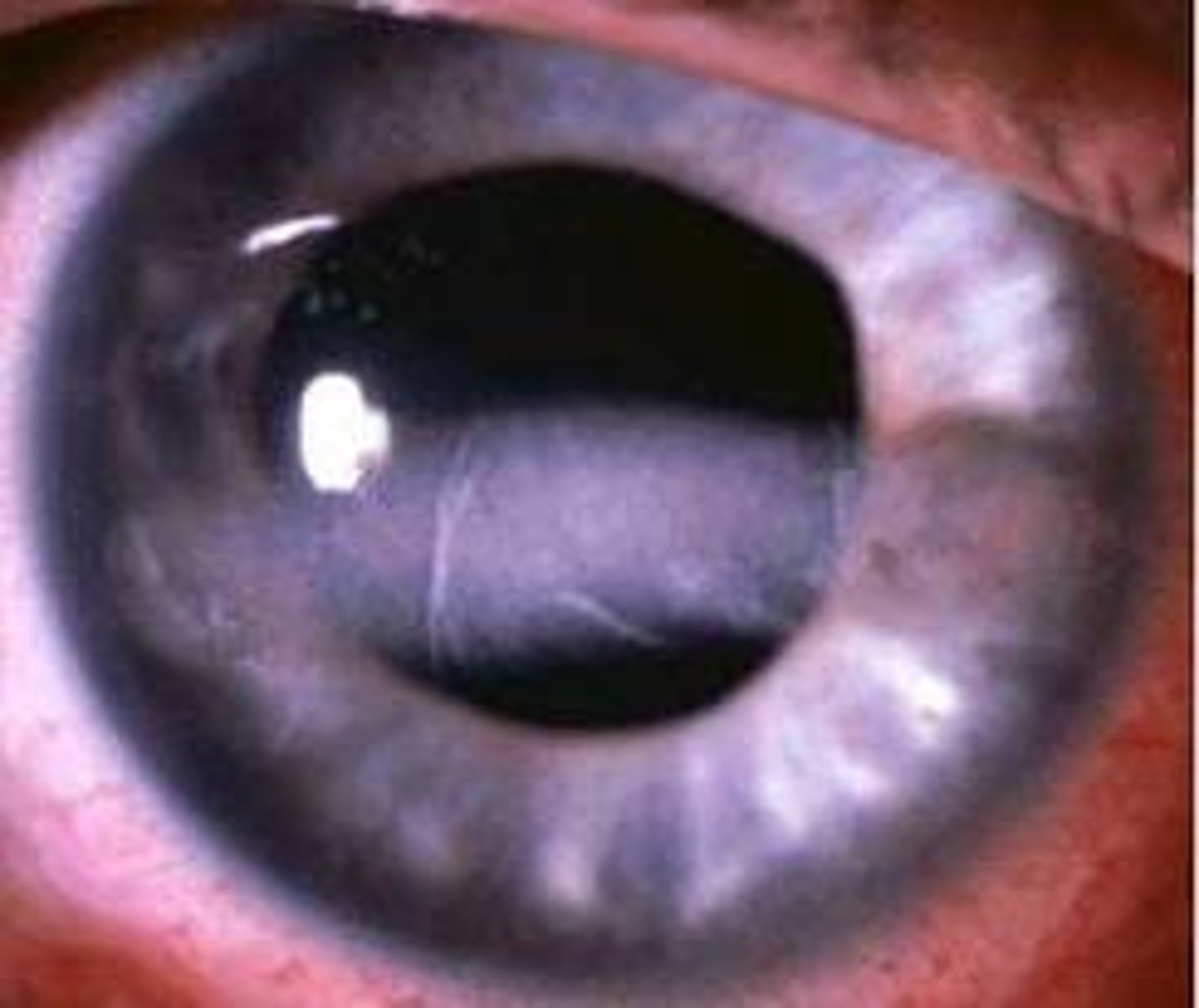
Keratoconus
Information for Condition:
Cone-shaped cornea due to Bowman layer defect --> causes discontinuity in Bowman layer --> Stroma protrudes through + deforms basement membrane
Fuchs dystrophy (bullous keratopathy)
Information for Condition:
Common endothelial dysfunction in Cornea - endothelium produces deposits (guttae) on Descemet membrane --> stromal edema --> subepithelial bullae on cornea
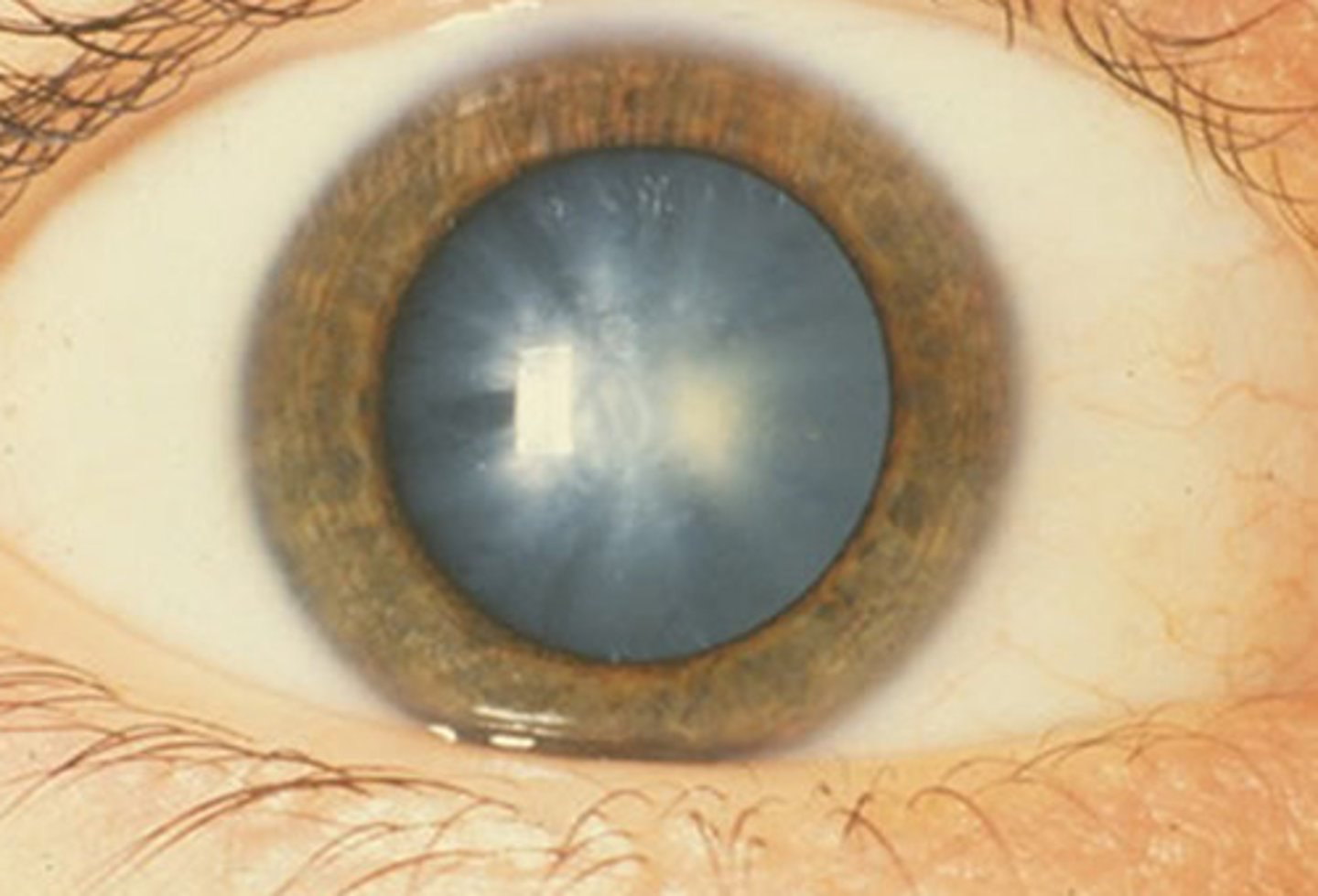
Cataracts
Information for Condition:
Lens opacity (congenital or acquired)
Pseudophakic (artificial lens) bullous keratopathy
Information for Condition:
Corneal decomposition following cataract surgery of lens
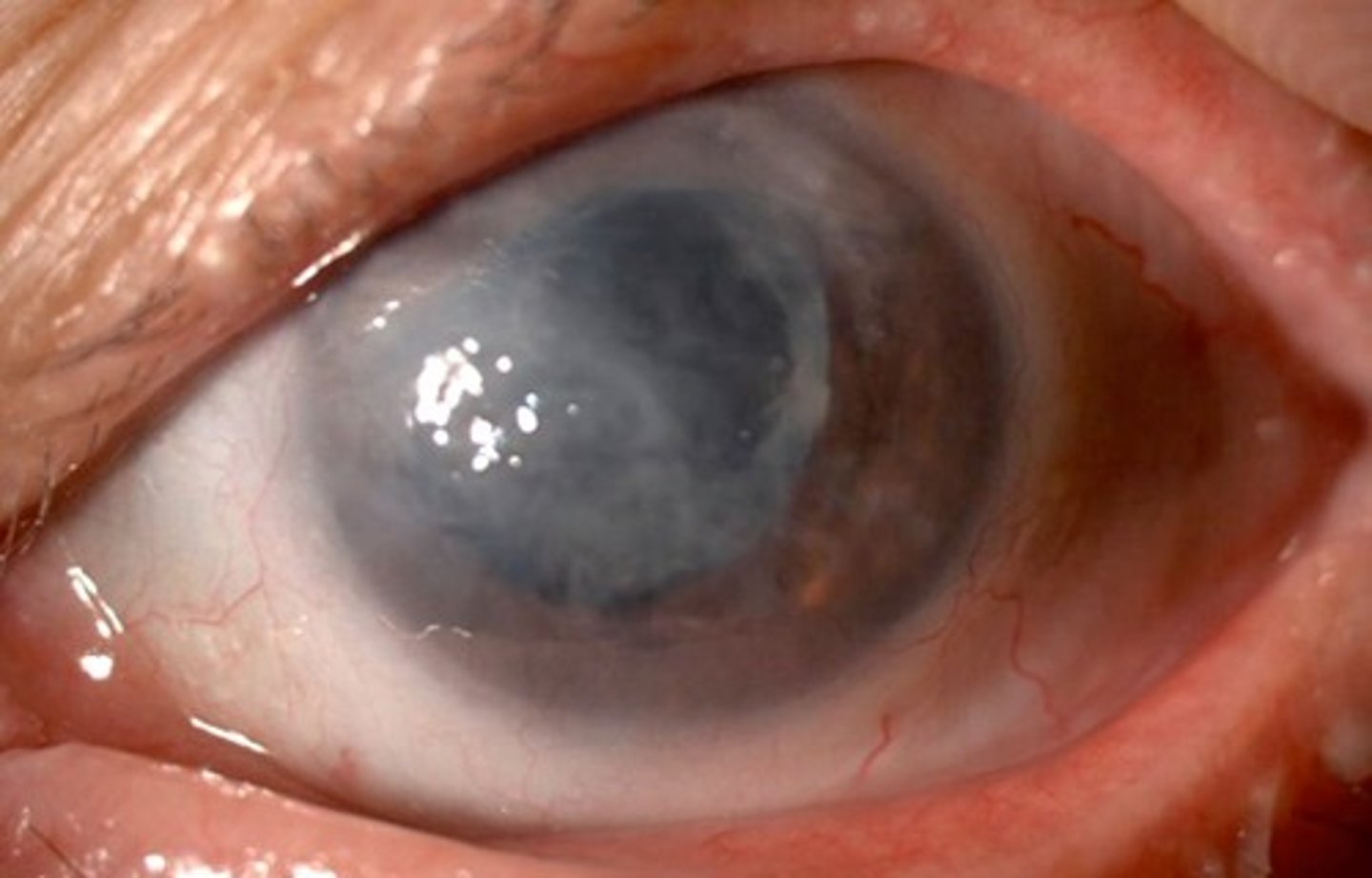
Anterior Segment Inflammation
Information for Condition:
Inflammation causing synechia (adhesion) of iris to back of cornea; Often associated with vision loss
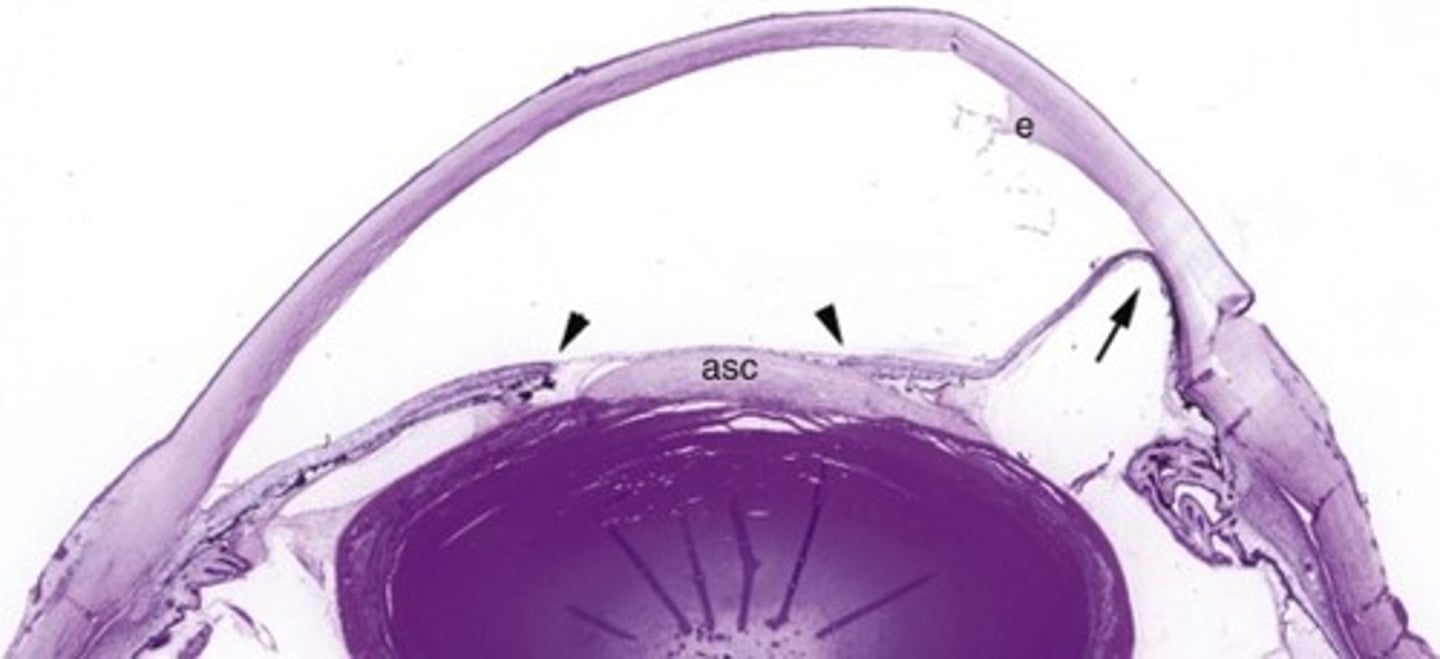
Glaucoma
Information for Condition:
-Caused by increased intraocular pressure (leads to optic nerve damage and visual field changes)
-Aqueous humor produced by ciliary body goes from posterior to anterior chamber
-Open Angle Vs Angle Closure
Can damage optic nerve (see increased cupping of disc, atrophy of ganglion cell layer of retina, aka "Glaucomatous Retinal Degeneration" & atrophy of nerve)
-Virus
-Pneumocystis
-TB
What can cause Infectious Uveitis?
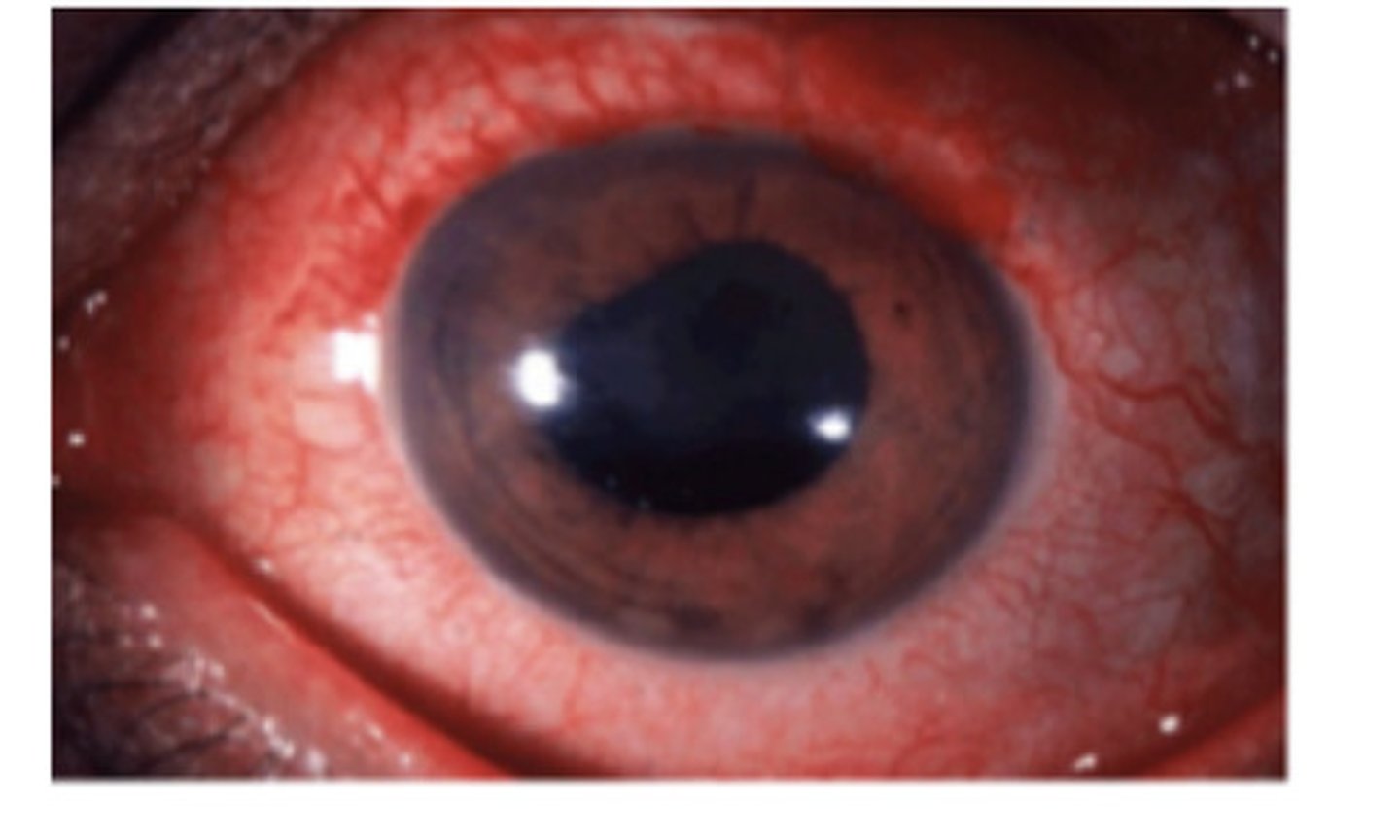
Sarcoid Uveitis or Sympathetic Ophthalmia
What Uvea condition(s) would also show granulmoas in the conjunctiva?
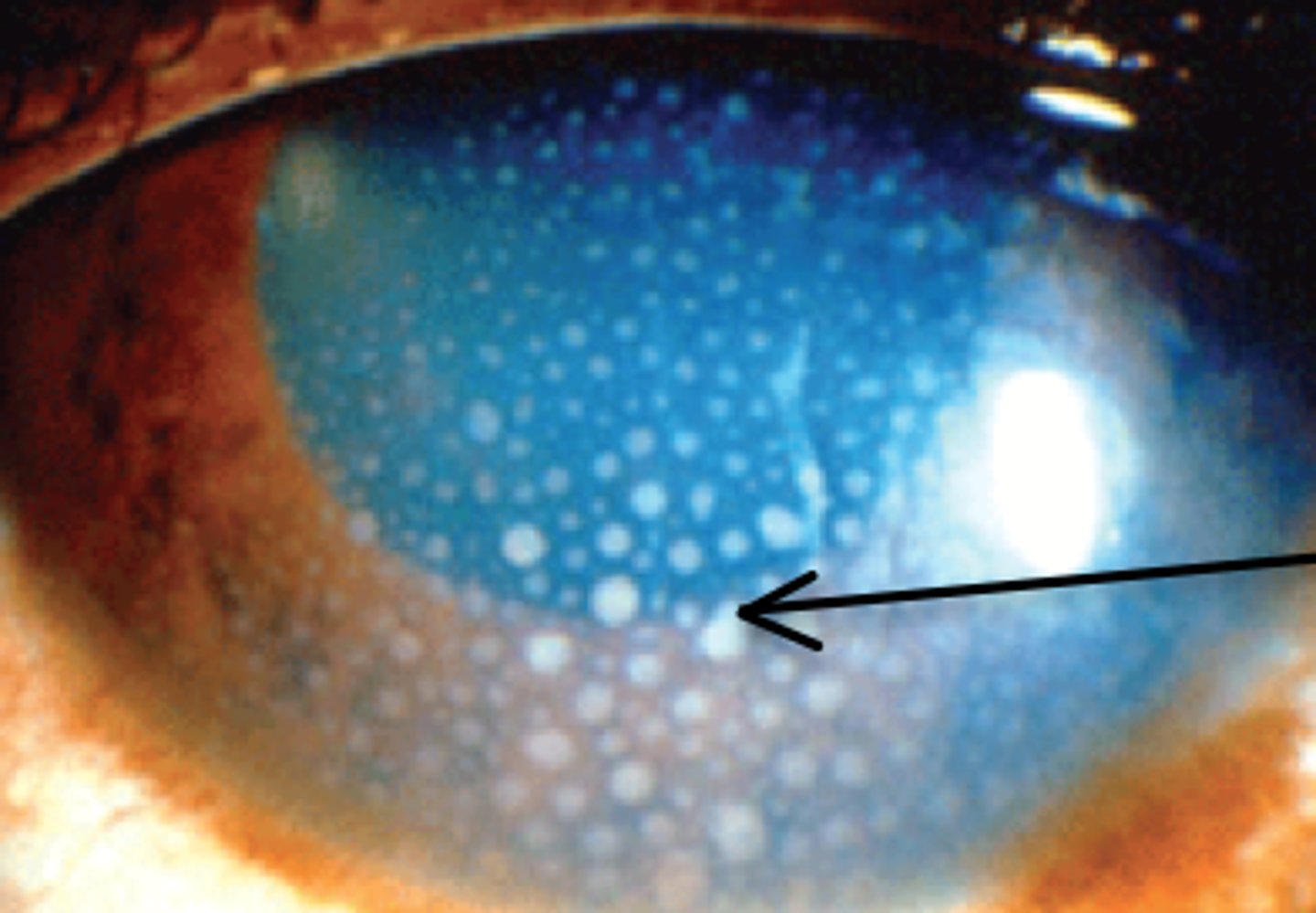
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
Information on Condition:
Characterized by immune mediated damage (uveitis) against one eye after a penetrating injury to the OTHER eye.
It is due to an immunologic mechanism involving the recognition of "hidden" antigens
May see granulomas
Nevi in Uvea
Information on Condition:
Growth in common in choroid of uvea
More circumscribed
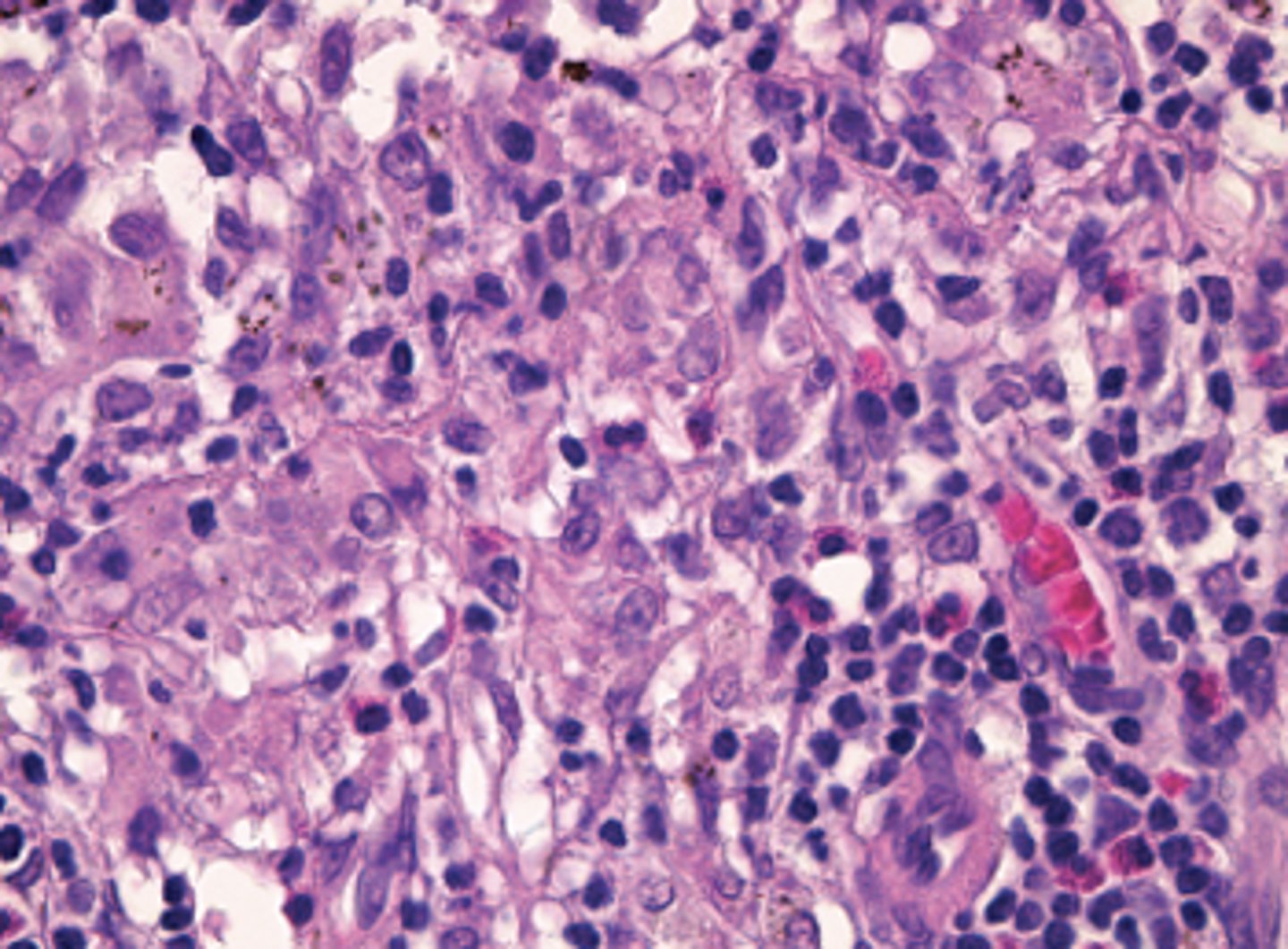
Melanoma in Uvea
Information on Condition:
Growth in the uvea; NOT related to UV exposure
"Mushroom shape/polygonal shape, epithelioid tumor cells"
Genetics = G-protein activation (not BRAF), also loss of chromosome 3 (BAP1 loss)
Prognosis = related to size, mitotic rate, type (Spindle cell is BETTER, while epithelioid is WORSE)
Can spread to liver (hematogenously), but not via lymphatics
Mortality = 20% at 5 y, 40% at 10 y, then 1% per year
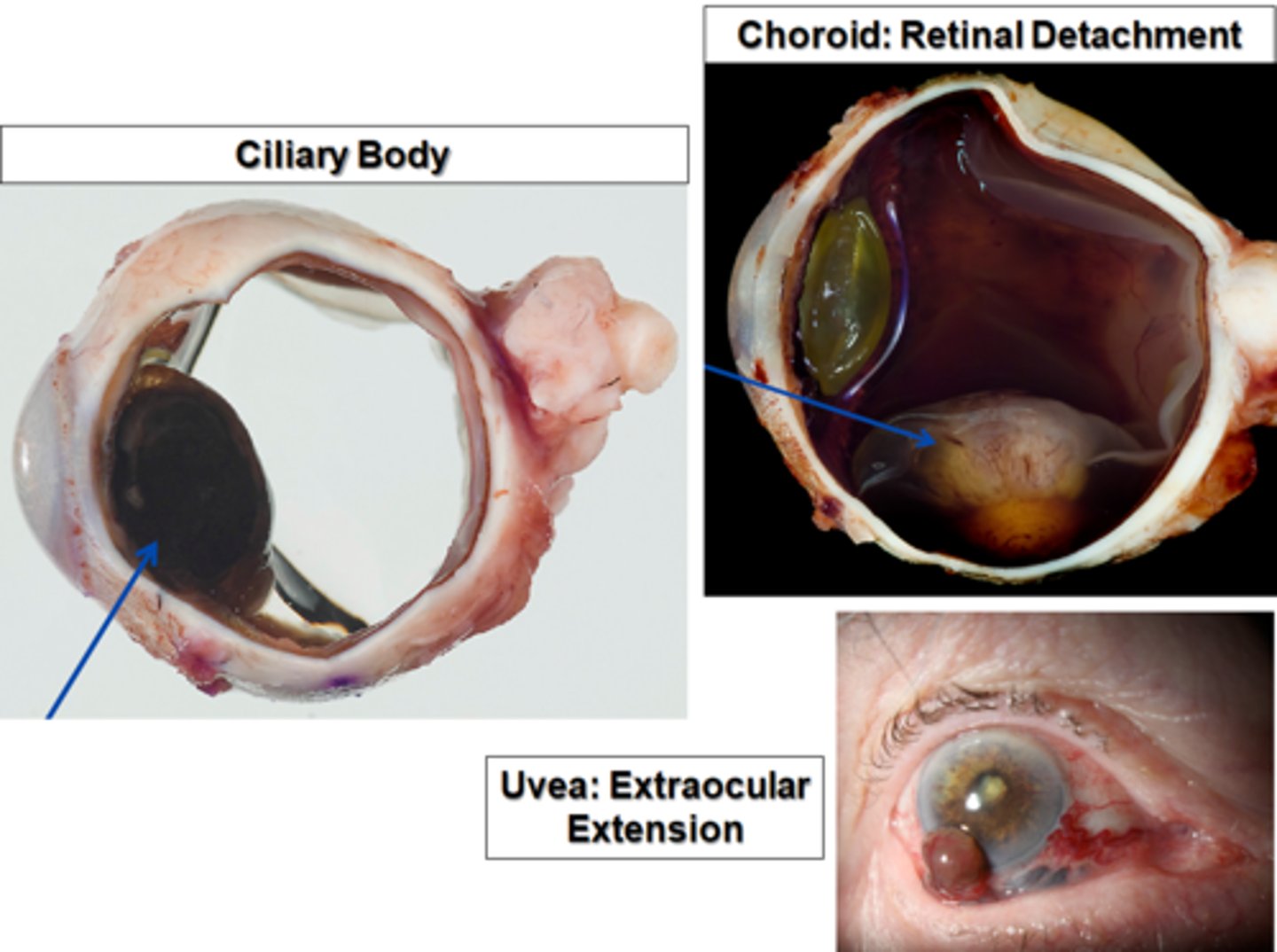
Retinal detachment
Information of Condition
two layers of the retina separate from each other - can lead to vision loss; If traumatic, it's called "rhegmatogenous"
Can cause blood vessels in retina to lose lumen thickness, while their walls become hypertrophic --> vein lumen can become nicked --> Nerve Fiber Layer Infarct downstream ==> Gliosis (scarring - "cotton wool spot")
Describe how Hypertension can negatively affect Retinal Function
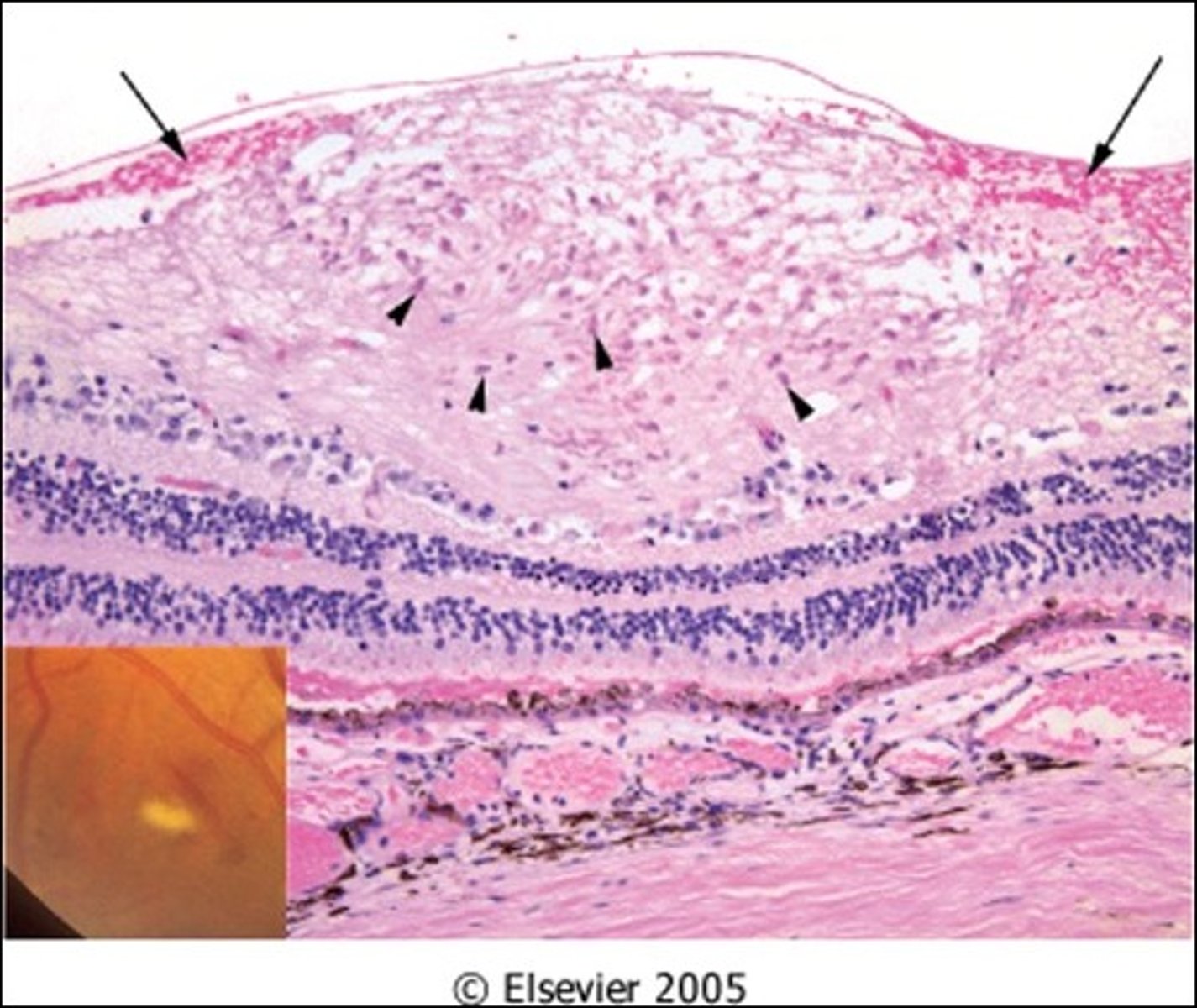
Damaged capillaries leak blood---> lipids, fluid seep into retina---> hemorrhage, macular edema, exudates & microangiopathy
Describe Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Previous occlusion of retinal blood vessels leads to growth of new fragile retinal blood vessels (neovascularization) that bleed easily (microaneurysms) and obscure vision; occurs on vitreous layer & iris
Describe Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Retinal infarct & cherry red fovea
Retinal arterial occlusion can lead to what issues?
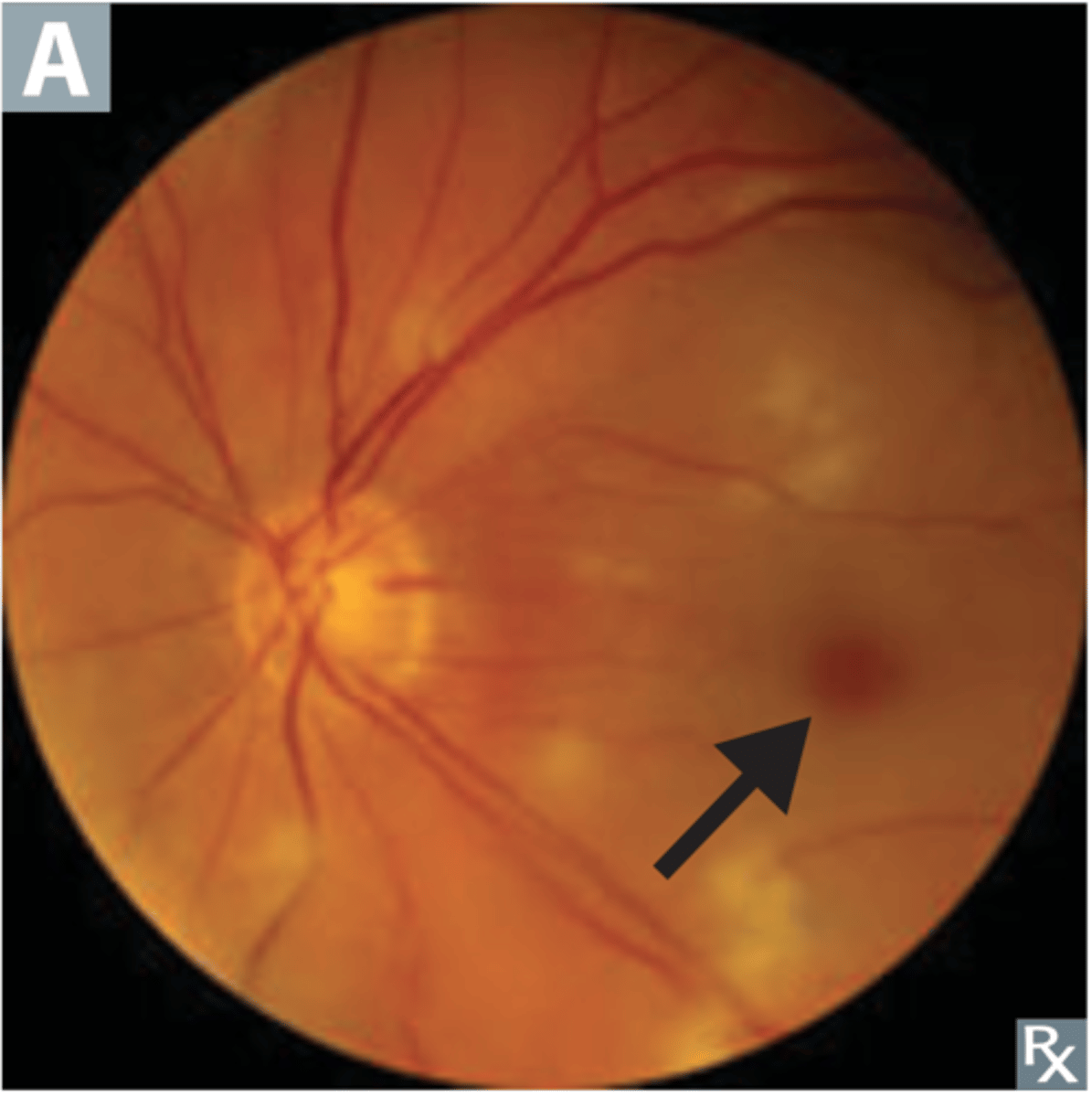
Deposits of material within macula (Bruch membrane deposits), causing possible atrophy of retina/RPE and gradual loss of central vision
Define Dry Age-related macular degeneration
Proliferation of abnormal blood vessels that leak blood and fluid/exudates into macula causing central & more severe vision loss
Progresses more quickly than dry AMD
Define Wet Age-related macular degeneration
Retinitis pigmentosa
Information for Disorder Group:
-Non-inflammatory
-Genetic condition
-Due to mutations affecting photoreceptor cells (rods & cones) or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) - usually apoptotic loss of rods & cones
-Loss of rods = night blindness & constricted visual fields
-Loss of cones = less central visual acuity
-Pigment from damaged RPE accumulates at vessels
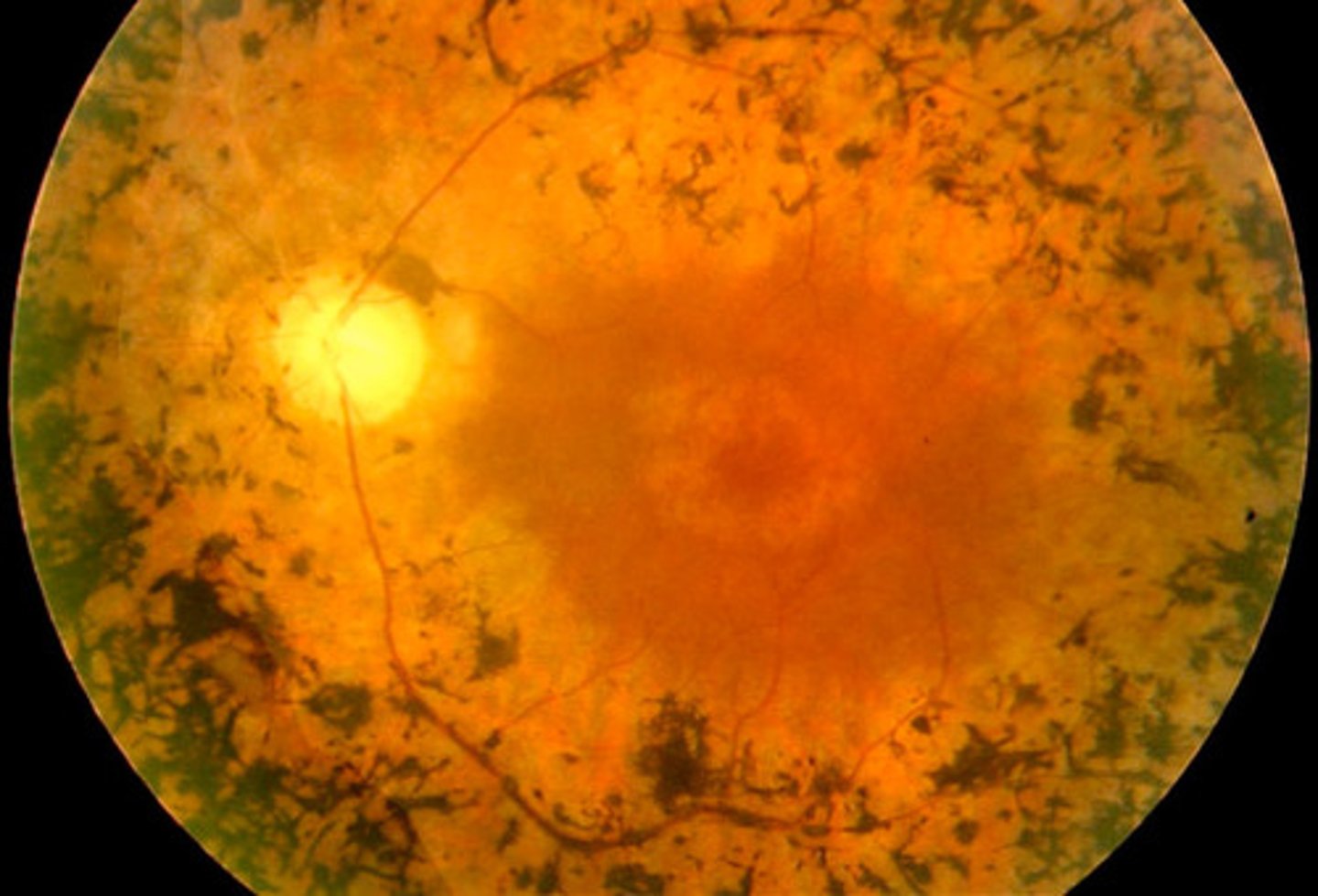
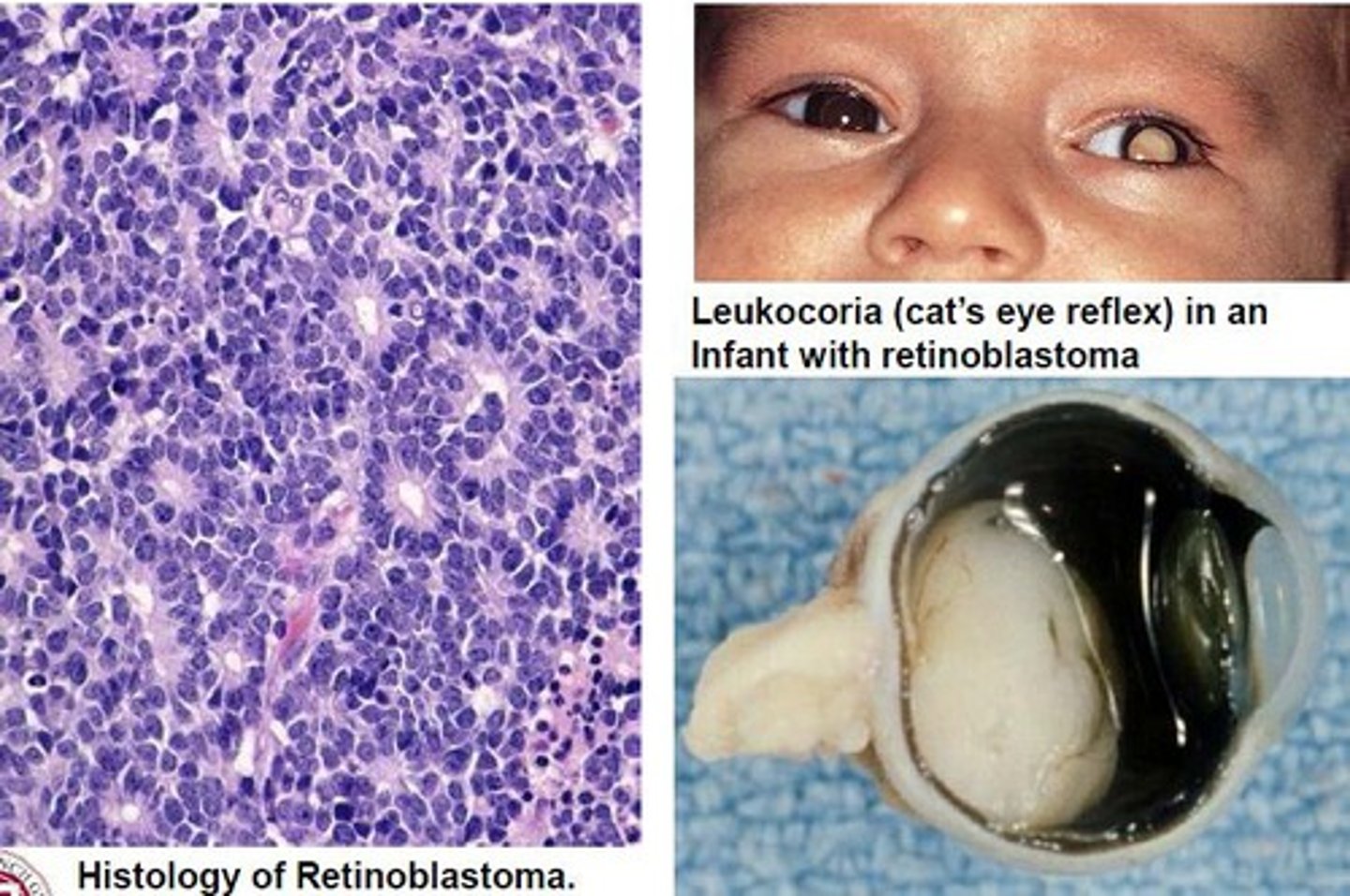
Retinoblastoma
Information for Condition:
-Hereditary & sporadic forms of cancer (40%) = mutation of RB tumor suppressor gene (normally brake on cell cycle & responsible for primitive neuronal differentiation)
-Tumor = Lobulated retinal tumor
-See small blue cells, rosettes, necrosis & calcifications
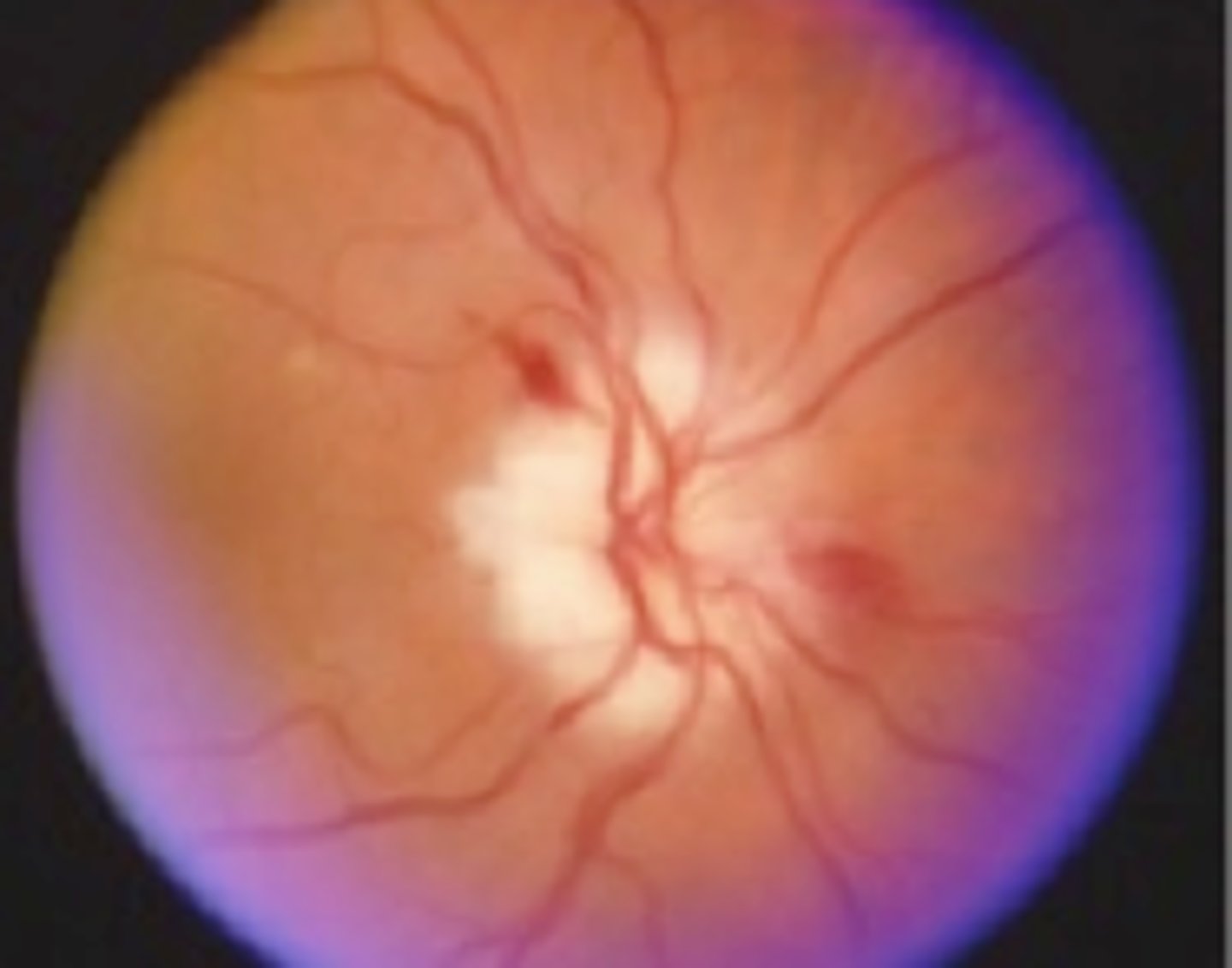
Anterior Ischemic optic neuropathy
Information for Condition:
Optic nerve ischemia due to overcrowding of nerve fibers and compromised vascular supply at the nerve head
Can be caused by Arteritis (Temporal Arteritis), embolus or thrombus
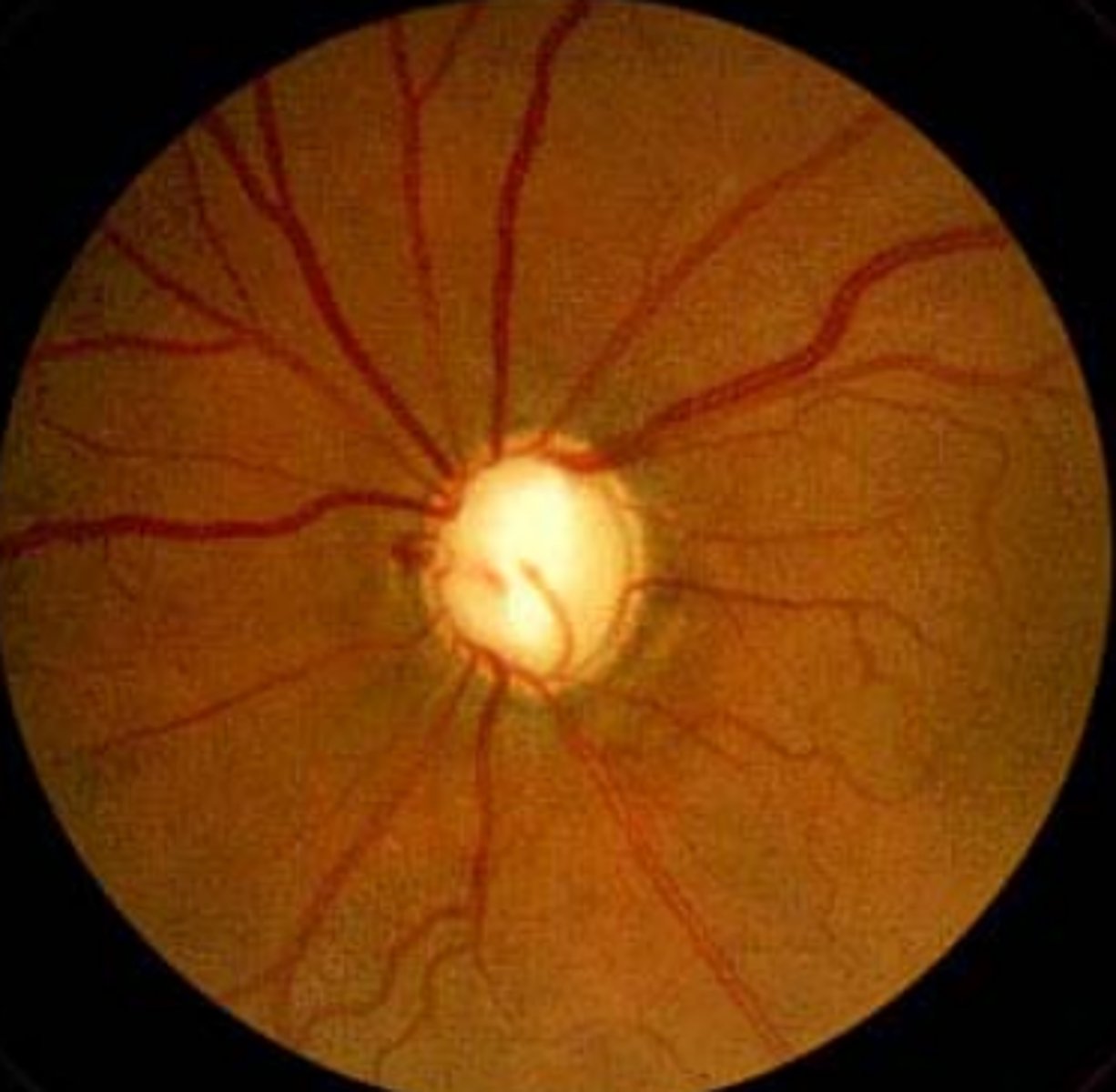
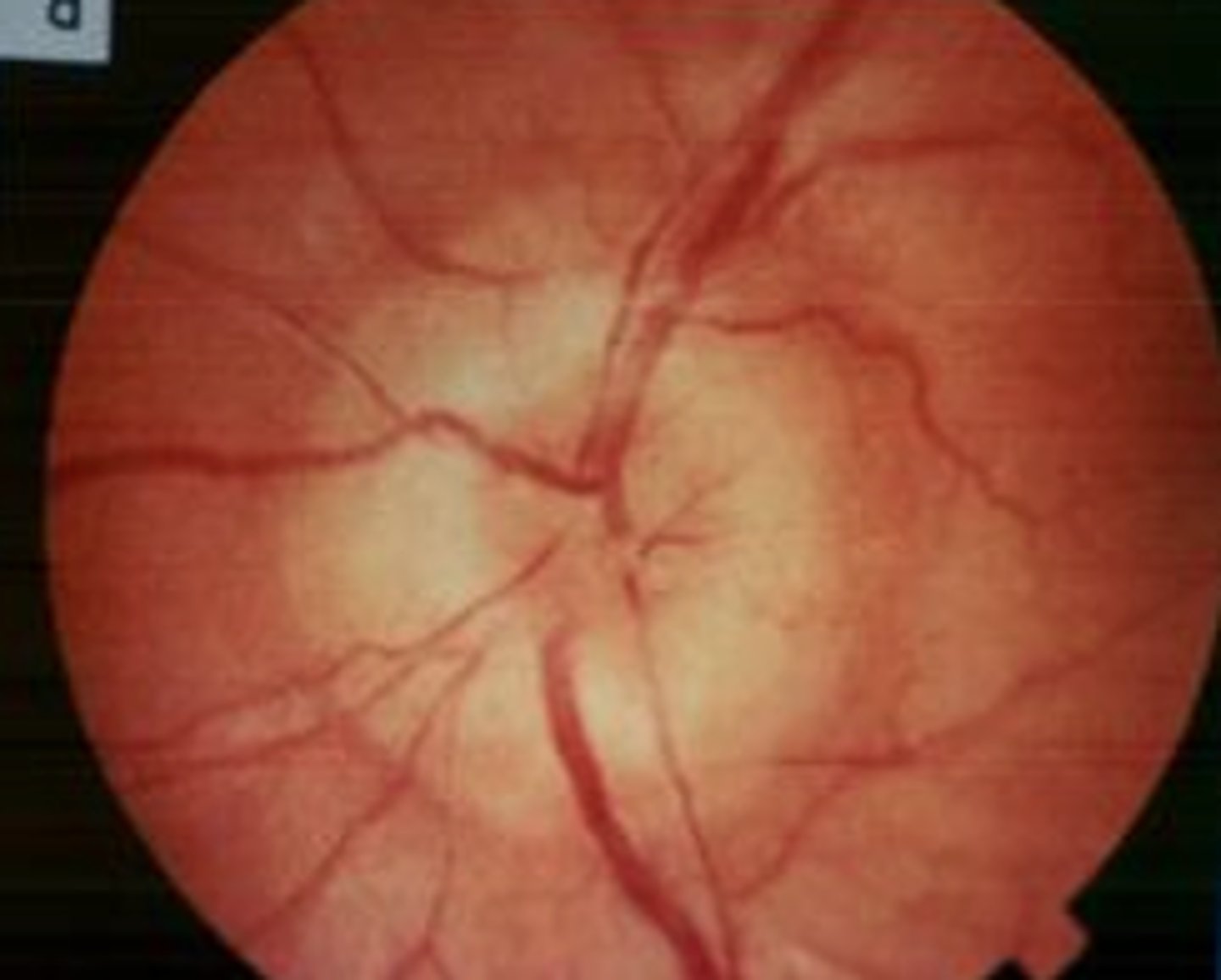
Papilledema
Information for Symptom:
Swelling and inflammation of the optic nerve at the point of entrance into the eye through the optic disk
-May be due to nerve compression (unilateral), high CSF pressure (bilateral), compromised vein outflow, or axoplasmic transport
*NOT associated with visual loss*
Optic neuritis
Information for Condition:
Inflammation of the optic nerve, causing a decrease in visual acuity and changes in color perception
-May be due to Multiple Sclerosis
Phthisis bulbi
Information for Condition:
Diseased/damaged/atrophied eyeball that has lost function and shrunk; Pt also has blindness in eye
Can be from any cause