Evidence-Based Medicine, Reviews, and Confidence Intervals (Exam 2)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What does this refer to
Limitations
Collection of high-quality evidence was limited by bias and lack of blinding as MDs made observations about interventions and outcomes of their own patients.
Difficulty with carrying forward
Scurvy
Handwashing
Early pioneers of EBM
Drs Sackett, Guyatt, Chalmers, Feinstein, and Cochrane
History of Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM)
What does this refer to
Ask a clinical question
Search For evidence
Evaluating the evidence
Applying the evidence
Evaluation of the process
Process of evidence-based medicine
What step of evidence-based medicine is the following
PICO
Population or patient
Intervention
Comparison
Outcome
Step 1 Ask a clinical question
What step of evidence-based medicine is the following
Starts with identifying the type of evidence of interest
Filtered
Unfiltered
Use keyword search narrowing for relevancy through Systematic Review
Lump and critique by similarities if applicable
Step 2. Search for evidence
What does this refer to
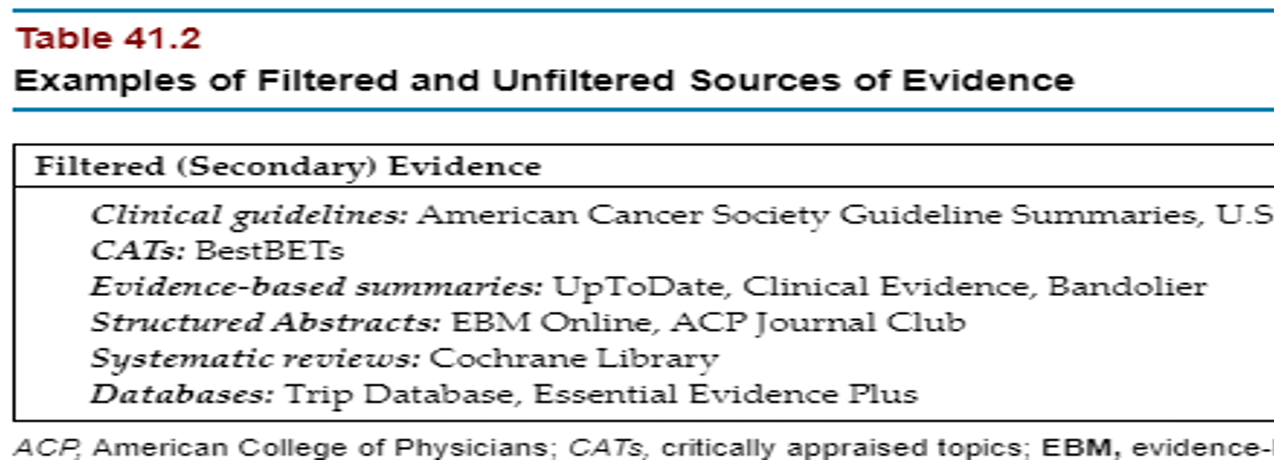
_____-has already been reviewed and synthesized by experts.
UpToDate, CATs, etc… Full list on pg 121 table 11.2 in “A Guide to Clinical Practice…” textbook.
Filtered
What does this refer to
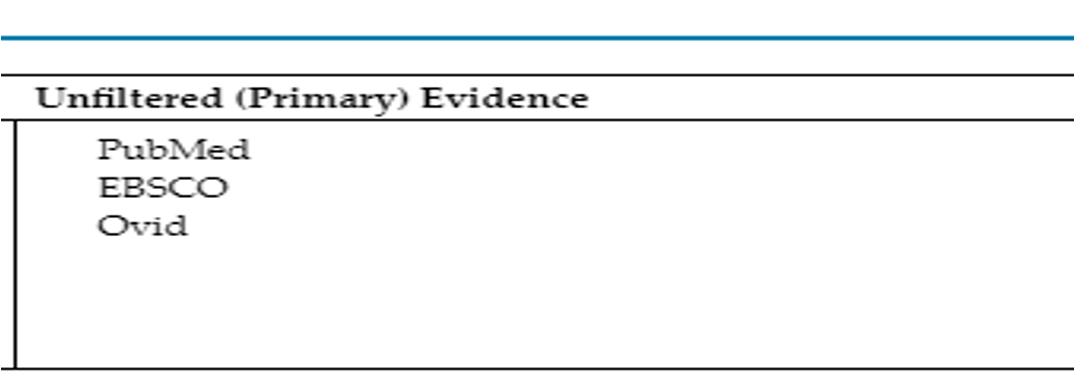
________-primary evidence original research articles. Same table for full examples.
Unfiltered
What step of evidence-based medicine is the following
Consider the outcome measurement
Validity
Bias, confounding error, Loss to follow up
Step 3 Evaluating the evidence
What does this refer to
Cohort
Case-Control
Cross-sectional
Observational study designs
What does this refer to
Identify the best evidence
Combine it with clinical judgement
Discuss with the patient for informed consent
Step 4 Applying the evidence
What does this refer to
Consider the outcome of the patients in your practice
Was the treatment effective for them, better or worse than expected or informed
Continuous process.
Step 5 Evaluating your process
What does this refer to
Investigation
What does this refer to
Using a single data point as a way to describe the larger group. For example: using the sample mean x to estimate the population average.
You calculate the mean HgA1C in your clinic over a week of patients and use that exact number to estimate the average HgA1C of your entire patient panel.
Point estimate
What does this refer to
Using a range of values of which has a high probability to contain the true average of a population instead of a calculated exact number.
Interval estimate
What does this refer to
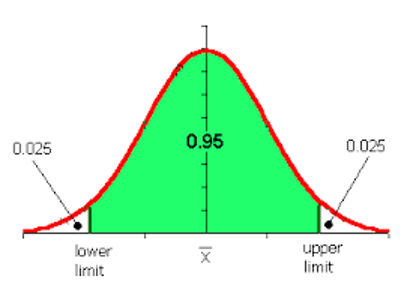
Range of numbers at a stated percentage of probability that the population average lies within.
Example 95% CI(p-1.96 X SE, p+1.96 X SE)
90%-1.645
95%-1.96
99%-2.58
Confidence Interval
What does this refer to

Calculating Confidence Interval (You want to know if offering a Saturday yoga class would be cost effective for the practice)
What does this refer to
Univariate analysis
Data is using one variable for descriptive statistical analysis.
Not looking for cause or relationship
Ways of looking at descriptive statistics’ distribution
Mean, median, quartile, skew, (looking for patterns)
Analysis
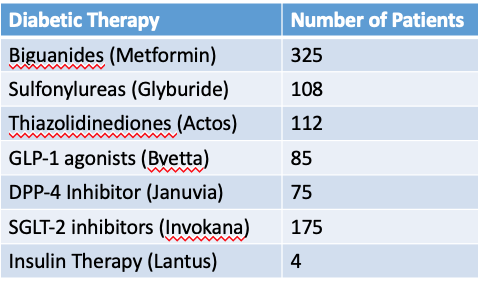
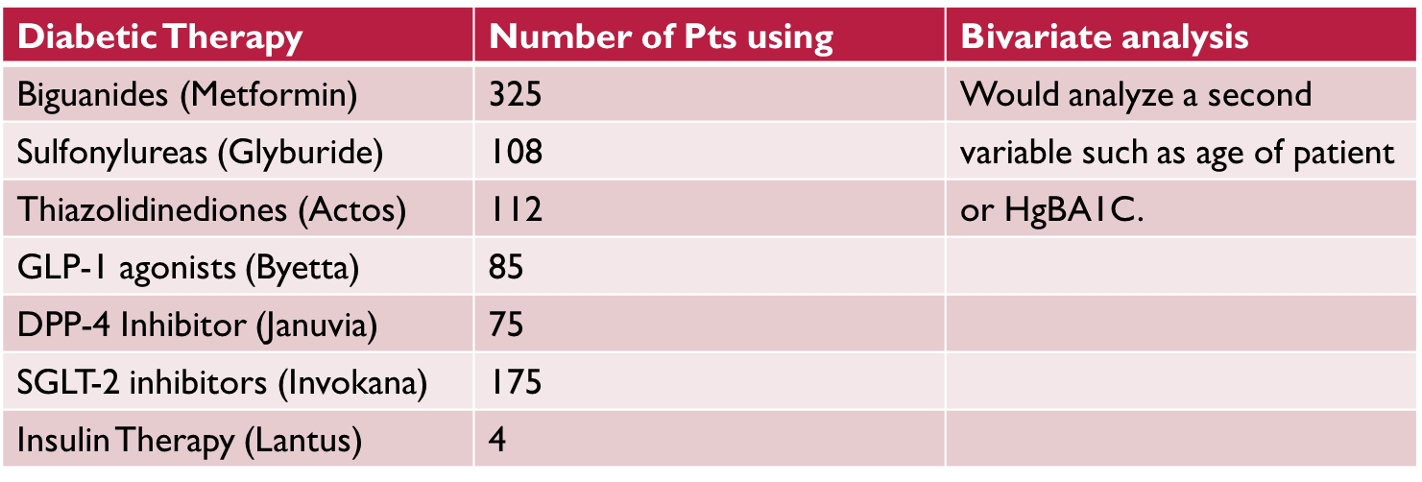
What does this refer to
Multivariate Analysis uses statistical tools to analyze more than just a single variable.
What does this refer to
____________ is a is a literature review focused on a single question that tries to identify, appraise, select and synthesize all high quality research evidence relevant to that question.
Systematic review
What does this refer to
__________ is a survey in which the results of all of the included studies are similar enough statistically that the results are combined and analyzed as if they were one study.
Meta-analysis
What does this refer to
What evidence is currently out there? What is your research question?
Who could benefit?
How could you impact public health?
Provided background information is necessary to engage the reader?
Background information
Keywords
Limitations
Introduction
What does this refer to
How can you set up research to support or reject your question?
Choose research method
Chose research design
Methods
What does this refer to
How can you set up everyday practice to deliver best care?
EBM
Going forward