C724: Information Systems Management
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are at least three major new information system trends?
IT Innovations, New Business Models, and E-Commerce Expansion (others include management changes and changes in firms and organizations).
IT Innovations (IS Trend)
are enabling firms to create new products and services, develop new business models, and change the day-to-day operations of business and include cloud computing and the growth of mobile digital business platforms for smartphones, etc.
New Business Models (IS Trend)
describes new ways that a company produces, delivers, and sells products/ services. For example: the launch of online video services like Netflix, has changed the way movies and TV shows are distributed and created.
E-Commerce Expansion (IS Trend)
has reinvented how firms design, produce, and deliver their products and has increasingly included services, not just physical products. I.S. and I.T. are the foundation of services-based e-commerce.
Management Changes (IS Trend)
allows managers to go mobile using smartphones, high speed WIFI, and remote workers. Managers are now in direct contact with these remote employees and have instant access to the needed information to make good decisions in a timely manner.
Changes in Firms and Organizations (IS Trend)
have seen business firms put less emphasis on hierarchy and structure and more on employees taking on multiple roles and tasks and working with others in a team.
What are the characteristics of a “digital firm”?
Almost all of the important relationships are enabled and mediated digitally.
Core business processes are digital.
Key corporate assets are managed digitally and available anytime, anywhere.
More responsive and flexible than traditional firms.
What are some challenges/ opportunities that are found in globalization?
Challenges: Competing for jobs, markets, resources, and ideas in foreign low-wage areas (outsourcing) so businesses can cut costs.
Opportunities: Creation of jobs in I.S. and other occupations. Outsourcing has accelerated the development of new systems in the US and worldwide by reducing costs to build and maintain them.
What are 6 reasons why I.S. are important for business today?
Operational Excellence
New Products, Services, Business Models
Customer/ Supplier Intimacy
Improved Decision Making
Competitive Advantage
Survival
Operational Excellence
businesses are constantly looking for ways to improve efficiency of their operations to achieve high profitability at a low cost.
New Products, Services, and Business Models
I.S. and I.T. are major tools that enable firms to create new products/ services as well as new business models.
Customer/ Supplier Intimacy
When a business knows its customers and serves them well, they come back (raises revenues); when a business engages more with suppliers, suppliers provide vital input (lowers costs).
Improved Decision Making
I.S. and I.T. have made it possible for managers to use real-time data, to make better decisions.
Competitive Advantage
Doing things better than other firms makes for better sales and profit.
Survival
I.S. and I.T. are a necessity for doing business, sometimes these “necessities” are driven by industry changes or by federal/ state statutes and regulations that require a digital record.
When building information systems what do managers base them on?
The organization’s needs and interests.
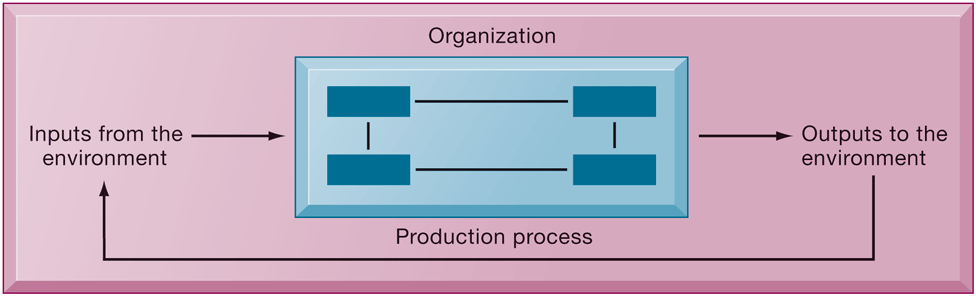
What is an organization and how does it relate to information systems technology?
An organization is a stable, formal structure that takes resources from the environment and processes them to produce outputs. Three elements define it:
Capital & Labor - primary production factors provided by the environment.
The Firm transforms inputs into outputs.
The environment consumes products/ services, inputs are received, and the cycle begins again.
Organizations are more stable than informal groups in terms of…
longevity and routineness and must abide by laws. They are social structures.
The behavioral definition of an organization is
the collection of rights, privileges, obligations, and responsibilities that are balanced over a period of time via conflict and conflict resolution.
Which features of organizations do managers need to know about to build and use information systems successfully?
The routines (daily SOPs) and business processes (collection of routines) of the firm and its politics, culture, environment, and structure are all essential for managers to know so that information systems can be created and used successfully.
Firm Politics
Political resistance is the biggest obstacle in bringing about change due to differing positional specialties, concerns, and perspectives. This often causes divergent opinions on how resources, rewards, and punishments should be given out.
Firm Culture
Organizational culture is built around a set of core assumptions that are accepted without question by its members. This culture guides in decision-making related to products/ services provided, how they are provided, the target audience, etc. It can be both a powerful unifying force and a restraint on changes within the organization.
Firm Environment
Organizations and their environments share a mutual relationship. Organizations are influenced by and rely on the surrounding social and physical environments, while they can also impact these environments. Environments tend to change faster than the organization.
Firm Structure
All organizations have a structure, these are described by Mintzberg’s Classification which identifies five basic types of organizational structure: Entrepreneurial Structure, Machine Bureaucracy, Divisionalized Bureaucracy, Professional Bureaucracy, and Adhocracy.
Mintzberg’s Classification
Entrepreneurial Structure - Young, small firm in a fast-changing environment. Simple structure, managed by one CEO (i.e. small start-up business).
Machine Bureaucracy - Large bureaucracy with a slowly changing environment. Produces standard products. Centralized management team (i.e. midsize manufacturing firm).
Divisionalized Bureaucracy - Combination of multiple machine bureaucracies, each producing a different product or service. One central headquarters (i.e. Fortune 500 firms).
Professional Bureaucracy - Knowledge-based organization where goods and services depend on the expertise and knowledge of professionals. Department Heads with weak centralized authority (i.e. law firms and schools).
Adhocracy - Task force organization that must respond to rapidly changing environments. Consists of large groups of specialists organized into short-lived multidisciplinary teams and has weak central management (i.e. consulting firms).