Unit 4: Cell Communication and the Cell Cycle
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

20 Terms
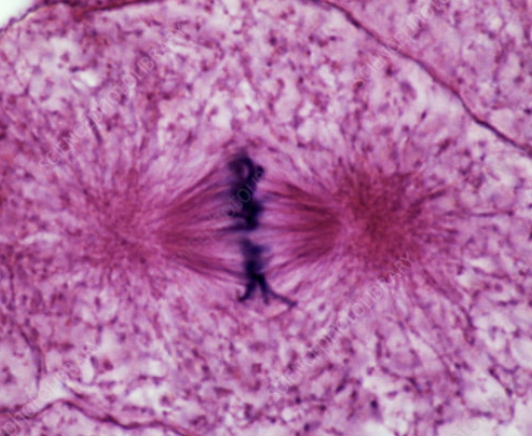
Which phase of mitosis is this? Why is it important?
Metaphase.Chromosomes line up at metaphase plate with microtubules attached at the kinetochores of the chromosomes to make sure that they can separate during the next phase of mitosis
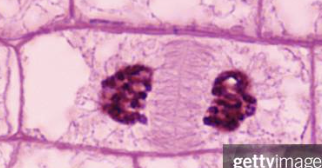
Which phase of mitosis is this? Why is it important?
Telophase. The nuclear envelope starts to develop around the two sets of nuclei, but the cell is not yet split
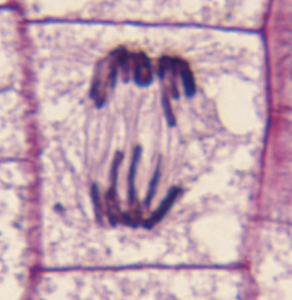
Which phase of mitosis is this? Why is it important?
Anaphase. Sister chromatids are moved towards opposite ends of the cell.
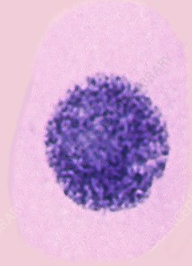
What phase of mitosis is this? Why is it important?
Prophase. The beginning of mitosis. The chromosomes start to condense and the nucleus begins to break down
Plasmodesmata
Channels between the cell walls of plant cells that allow molecules to move between cytoplasms of neighboring cells to enable communication
Ligand
A non protein molecule that binds to a receptor on a target cell, initiating a cellular response.
Long distance communication
Usually involves signals traveling in the blood vessels until it reaches its target cell
cAMP
cAMP is a secondary messenger that relays and amplifies the signal carried by the ligand in the transduction stage. It often activates protein kinases that continue to amplify the signal
What does cell signaling rely on?
Cell signaling relies on the interaction between ligands and receptors to communicate. If the ligand cannot bind to a receptor, or if a cell does not have that receptor it will not receive the message.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death. It is a controlled process that is important in organism development and regulation of the cell cycle.
Negative feedback loop
DECREASES the effect of the stimulus, often returning the organism to homeostasis
Positive feedback loops
INCREASES the effect of the stimulus. Often pushes the organism away from homeostasis and promotes further change in response to the initial stimulus.
G1 stage
The first phase of interphase where the cell is doing its normal functions but increasing its number of organelles
Why does chromosome number increase during anaphase
Chromosome number increases during anaphase because sister chromatids are pulled apart towards opposite poles of the cell, effectively doubling the number of chromosomes counted in each half of the cell.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
To distribute duplicated chromosomes to daughter nuclei
What is the purpose of cytokinesis
To divide the cell into two identical daughter cells after mitosis.
What is the purpose of microtubules during mitosis?
Microtubules help separate and move chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell, ensuring accurate distribution during cell division.
G2 checkpoint
A regulatory point in the cell cycle that ensures DNA has been correctly replicated and assesses cell size and damage before entering mitosis.
G1 checkpoint
A control mechanism that ensures cells are ready to enter the S phase. Checks for protein availability and DNA damage/mutations
M Checkpoint
A phase in the cell cycle that verifies chromosome alignment on the spindle fibers before allowing anaphase to continue