Parts of the Brain. PsYcH
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
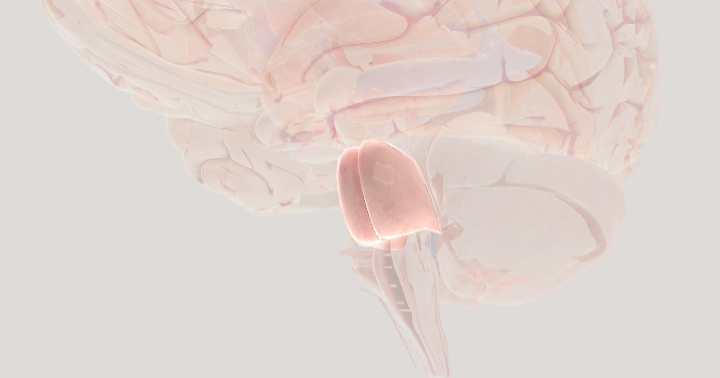
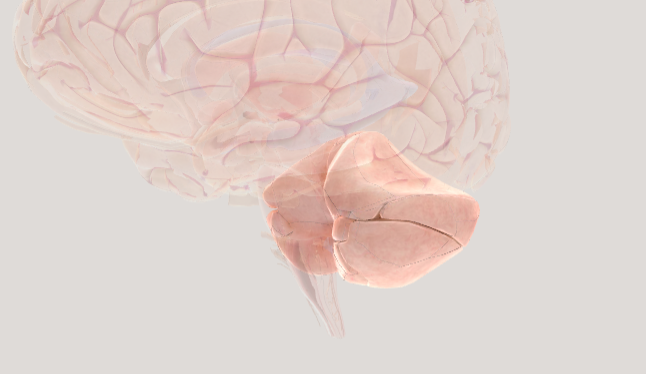
Hindbrain
responsible for essential life-supporting functions, as well as maintaining basic motor skills and coordination. Made up of Cerebellum, Pons, and Medulla oblongata
medulla
part of the brainstem at the bottom of the brain that connects to the spinal cord. It controls essential involuntary bodily functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure
Pons
helps coordinate and control various bodily functions, including breathing, sleep, and facial movements
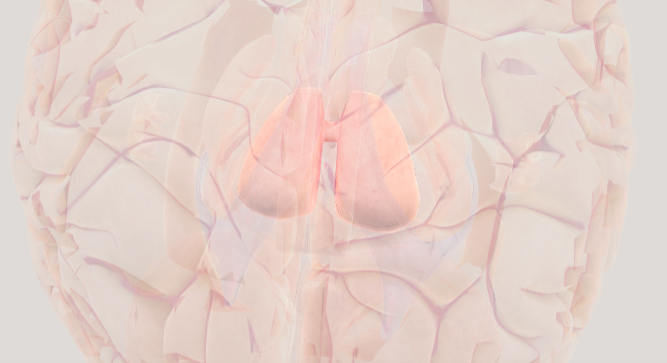
Cerebellum
the "little brain" that helps us with movement and coordination
Midbrain
crucial role in coordinating eye movements, visual and auditory processing, and controlling certain motor functions
Forebrain
It is responsible for higher-level cognitive functions, such as:
thinking, learning, memory, emotion, decision-making, planning, and consciousness
made up of Cerebrum and Diencephalon
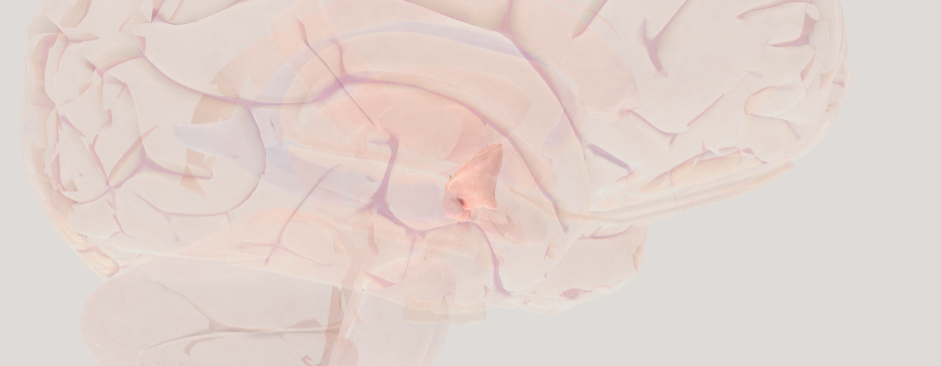
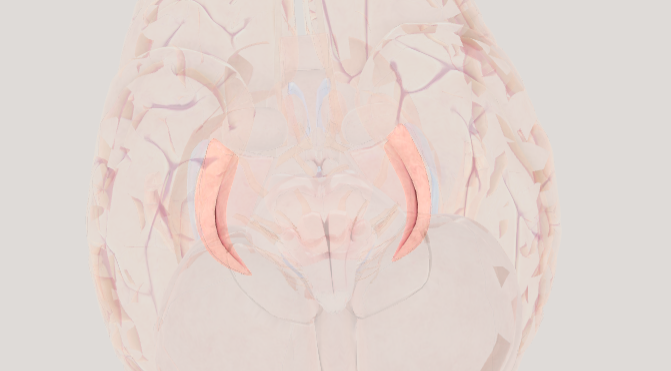
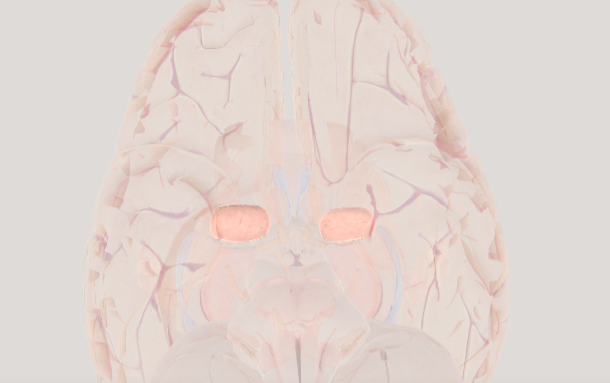
Thalamus
acts as a relay station for sensory information (except for smell)
Hypothalamus
acts as the body's control center for homeostasis, regulating essential functions like body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep
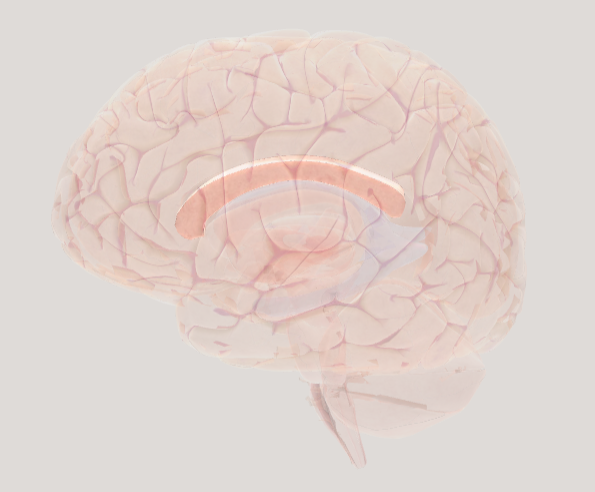
Hippocampus
plays a crucial role in memory formation, consolidation, and retrieval. The hippocampus is also involved in spatial navigation, emotional regulation, and learning
Amygdala
primarily controls emotional responses, especially fear and anger
Cerebral cortex
responsible for higher-order cognitive functions such as:
thinking, learning, memory, language, decision-making, and motor control
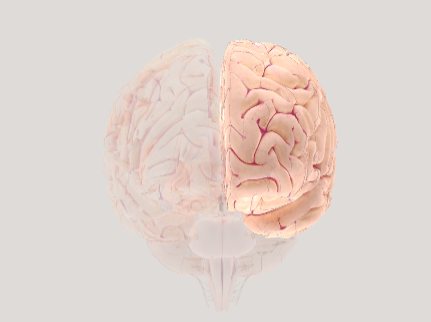
Left hemisphere
the left half of the cerebrum, generally responsible for language, logic, analytical thinking, and controlling the right side of the body
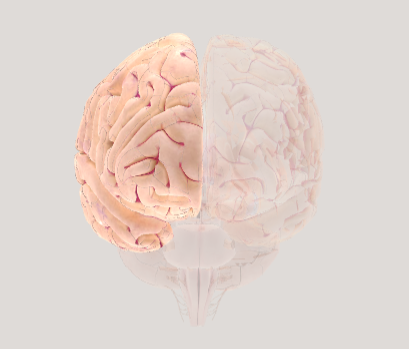
Right hemisphere
associated with creativity, intuition, spatial awareness, and processing visual information, including faces and music
Corpus callosum
large bundle of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, allowing them to communicate and share information. coordinating various brain functions such as movement, sensory processing, vision, and cognitive tasks
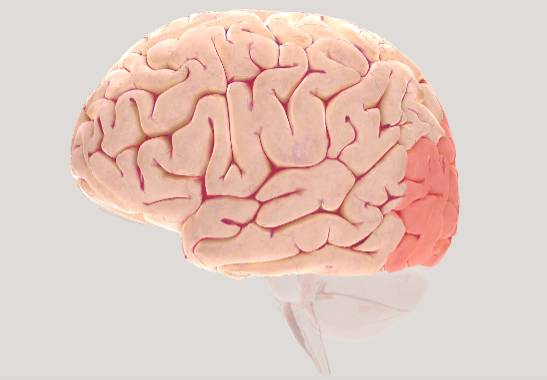
Occipital lobe
exclusively responsible for processing visual information, such as color, shape, depth, and movement
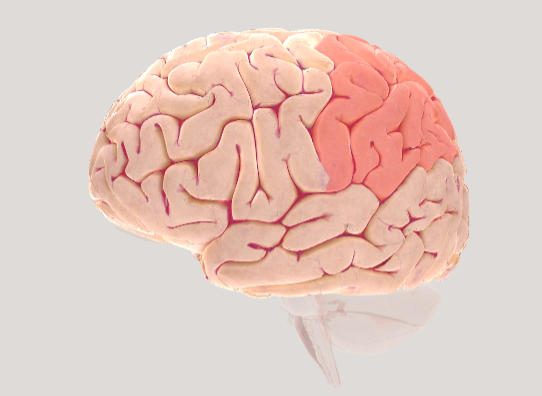
Parietal lobe
responsible for processing sensory information from the body, such as touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception (body position).
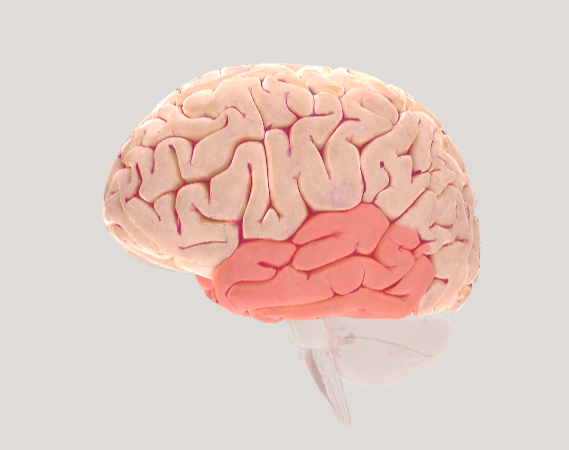
Temporal lobe
crucial for understanding speech, recognizing faces and objects, learning new information, and managing feelings.
Frontal lobe
controls personality, behavior, decision-making, problem-solving, and voluntary movement. It acts as the brain's emotional control center
Prefrontal cortex
responsible for executive functions, personality, and behavior. It allows you to plan, make decisions, control your impulses and emotions, and manage your attention
Phineas Gage
the frontal lobe of a railroad foreman who, in 1848, survived an injury where an iron rod pierced his skull and damaged his frontal lobe
Somatic nervous system
send voluntary commands to muscles for movement and to receive sensory information from the body's senses (like touch, sight, and hearing)
Autonomic nervous system
the part of the nervous system that controls automatic, involuntary bodily functions like breathing, digestion, heart rate, and sweating
Sympathetic nervous system
the "fight or flight" division of the autonomic nervous system, controlled by the brain, that prepares the body for intense physical activity by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and alertness, and diverting blood to muscles and vital organs
Parasympathetic nervous system
the "rest and digest" part of the autonomic nervous system, which controls your body's functions when you are relaxed