Cytoskeleton, Stem Cells, and Cancer Biology Overview
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Cytoskeleton
A complex set of structures that are very dynamic.
The large network consisting of protein fibers and other molecules that gives shape and structure to cells in the body.
what does the cytoskeleton deal with
cell movement
cell shape
organelle movement
organelle orientation
Actin filaments
Also known as microfilaments, they are the smallest type of filament measuring 7-9 nm.
double helix
f-actin
Intermediate filaments
Medium size filaments measuring 10 nm
toughest filament
long, unpolarized, and less dynamic.
serves as a rope in desmosomes and nucleus
Microtubules
The largest filament
measuring 25 nm,
appears during mitosis in the metaphase plate and axons.
Deforming force
The force needed to snap the filaments.
Actin deformation
Actin had low deformation and medium deforming force.
Microtubule deformation
Microtubules had high deformation and low deforming force.
Intermediate filament strength
Intermediate filaments had the best deformation and deforming force, proving that it is the strongest.
Cytochalasin D (toxin to filaments)
A toxin that inhibits polymerization by binding to the + end.
Phalloidin (toxin to filaments)
comes from death cap mushrooms
inhibits depolymerization
there arent antibodies for filaments so we can use phalloidin for staining filaments
treatment for phalloidin consumption
eating raw meat. raw meat attacks the filaments in the meat and not your cells
Thymosin beta 4 (polymerization regulator)
A sequestering protein that regulates ATP G actin binding
works with profilin to regulate polymerization
Profilin (polymerization regulator)
An ATP/ADP exchanger that promotes swapping ADP for ATP G actin.
Cofilin (polymerization regulator)
A severing protein that severs off a chunk of F actin from the - end by adding ADP.
Capping proteins ((polymerization regulator)
Proteins that bind to F actin ends to prevent treadmilling.
Cap Z
A capping protein that binds to the + end of F actin.
Tropomodulin
A capping protein that binds to the - end of F actin.
Formin (polymerization regulator)
dimer
nucleating protein that starts nucleation.
Actin
makes up 10% of all proteins in a cell
alpha actin (actin subtypes)
contractive structures (aka filopodia)
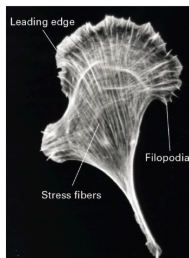
Beta actin (actin subtypes)
leading edge structures
Gamma actin (actin subtype)
stress fibers
G-actin (globular)
Globular actin that requires ATP and Mg2+.
F-actin (filament)
Filamentous actin that is decorated with myosin S1 and appears as an arrowhead on TEM imaging.
pointed end if - side
barbed end is + side
Treadmilling
A process where G actin is added and removed at either ends, resulting in no net increase or decrease in size once steady state is established.
+ end experiences treadmilling 5x faster than - end
polymerization of G actin like this forms f-actin
Critical concentration
A concentration level akin to chemical equilibrium in the context of actin polymerization.
optical traps/tweezers
uses infrared light to determine force of f actin filaments
opsonization and phagocytosis
require f actin to form the shape of the WBC phagocytosing
Listeria
A bacteria that is non-mobile until it reaches the cell
causing severe food poisoning
nucleates f actin b/c it has f actin tail
can cross placenta in pregnant women
becomes motile by binding to f actin alongside act A
types of intermediate filaments
keratin (skin)
desmin
neurofilaments
lamin
-nucleus
iimportant for karyo skeleton
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
disease caused by defective keratin filaments in basal lamina
causes susceptibility to shear stress and recurrent skin infections
dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB)
“Butterfly children” with skin as fragile as a butterfly wing
VYJUVEK
A treatment that topically transfects COL7A1 gene to code for Collagen VII to restore skin keratin.
Microtubules structure
Made up of 13 protofilaments
Building blocks of microtubules
alpha beta tubulin
-dimer
-alpha tubulin has non- exchangeable GTP
-beta tubulin has exchangeable GTP
have pigments and that is what lets animals become camoflaged
ex. flounder melanosis
MAPS
Microtubule associated proteins
MAP2
A microtubule associated protein.
Tau
Associated with Parkinson's and Alzheimer's; keeps microtubules intact.
XMAP215 and CLASP
Increases polymerization of microtubules.
Kinesin 13
Increases depolymerization of microtubules.
Katanin
Aids in synaptic pruning.
Colchicine (drug)
Promotes microtubule depolymerization; used to treat cancer and gout.
Taxol/Taxotere (drug)
Enhances polymerization of microtubules; treats cancer by inducing apoptosis.
Kinesin (molecular motor)
Used in anterograde transmission from - to + end.
Dynein (molecular motor)
Used in retrograde transmission from + to - end.
Kartagener syndrome
Defect in dynein.
STEM cell
A cell that can divide and differentiate; some can divide a certain number of times before differentiating fully.
uses for stem cells
tissue engineering
drug discovery
regenerative medicine
food production
recovery after diseases
“clean meat”
wooly mammoth DNA used to make meat
Differentiation
Cell's ability to form into a specified type of cell.
Progenitor cells
Restricted lineage cells
can only differentiate into 1-2 specific types of cells.
Totipotent
STEM cells that can differentiate into ANY specific cell type.
Chimera test
used to see if stem cells from a given sample are totipotent or not
Pluripotent
Can differentiate into MANY cell types.
Multipotent
Differentiates into LESS cell types.
Unipotent
Differentiates into only ONE cell type.
Transdifferentiation “DIRECT REPROGRAMMING”
When a differentiated cell differentiates into another cell type without first reverting to an embryonic step
happens in the prescence of transcription factors
Dedifferentiation
When a differentiated cell turns into an embryo-like cell
can be induced by chemicals like reversine.
Redifferentiation
When embryo-like cells differentiate into a new cell type
this is how lizards and newts can regenerate limbs and eye lenses.
STEM cell niche
STEM cell microenvironment critical to control cell division and differentiation.
what is a stem cell niche composed of
neighboring cells
extracellular matrix
growth factors
environmental factors (pH, oxygen, tension, pressure)
Blastocyst
Early stage fertilized egg where hESCs are derived from.
Homing
STEM cells knowing where to go
ex. damaged tissues release factors for endogenous MSCs to home.
iPSCs (Induced pluripotent STEM cells;)
iPSC reprogramming factors introduced to somatic cells to bring them to embryonic like stage.
Fusogenic
STEM cells can randomly fuse together to form tetraploid STEM cells
can lead to cancer.
stem cells can undergo fusion when injected into human due to the stress of putting them into human
Bioethics
Moral code on bio research that vary country by country.
Therapeutic cloning
Embryonic cloning to use the cells for therapeutic purposes.
-diabetes
-alzheimers
-injury
embryo developed in vitro (lab)
Reproductive cloning
Making genetically identical organisms
in vivo
Adult STEM cells
Found in adipose.
adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells
Fetal STEM cells
Stem cells derived from fetal tissues.
amniotic
umbilical
placental
Embryonic stem cells
Stem cells derived from embryos, also known as hESCs and hPSCs.
Induced pluripotent STEM cells
Stem cells that are reprogrammed from adult cells, not used for research in the US but used in Japan and Australia.
SCID mice
Mice with Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, used to test if a candidate STEM cell can differentiate in vivo.
Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)
A method of generating STEM cells in vitro
somatic cell nucleus from chronically sick person placed into embryo to differentiate, cells removed and placed back into the person
Pro of somatic nuclear transfer
autologous stem cell therapy
-donor is the receiver
Con of somatic cell nuclear transfer
ethics?
low success rate
Sir Ian wilmut (successful clones)
dolly the sheep
John Gurdon
cloned frogs before wilmut
nobel prize winner
little Nicky (2004) (successful clones)
cloned cat
first successful cloning of primates
2018
Parthenogenesis
A reproductive process where no sperm is needed for pregnancy.
happens in sea urchins and starfish
hPSCs
Cells that arise from parthenogenesis.
pros/cons of hPSCs
pro: if we did this it would only take 200-300 eggs to be able to get hPSCs for anyone on earth
con: all alleles would be homozygous b/c of no sperm=higher chance of expressing mutation
induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
master genes
adding 4 of them to a human adult cell makes an iPSCs
they reverse the age of genes
discovered by Shinya Kamanaka and James Thomason
(HOX, Oct3/4, Sox2, Nanog)
Tumorigenicity
The potential of STEM cells to form tumors, specifically teratocarcinomas
stem cells have long telomeres
Immunogenicity
potential for activation of immune response
more frequent stem cell injections raises the chance of anaphylaxis (allergic reaction)
Inappropriate differentiation
The risk of STEM cells differentiating into the wrong cell type.
ex. woman got stem cells near her eye for tissue replacement and stem cells differentiated into bone instead
C. Elegans
A multicellular roundworm that serves as a model organism
simple anatomy
short life cycle
well mapped genome
mass reproduction
Benefits of using C. Elegans
Easy to grow on agar, non-pathogenic, and useful for discovering RNAi and apoptotic genes.
Anucleate cells
Cells that do not have a nucleus.
Skin cells
Only basal lamina cells have a nucleus; the rest serve as a barrier so there is no need for nucleus
Lens fibers
Type of fiber cell that is anucleate.
RBCs enucleate
Red blood cells remove their nuclei.
Nuclear envelope
Outer part of the nucleus
made up of 50% nuclear pores
-Allow diffusion for proteins less than 62kDa.
Nucleoplasmin
Pentameres with each subunit being 33kDa; total of 165kDa.
Functions of Nucleoplasmin
First chaperone protein discovered
nucleosome assembly
genome stability
transcription regulation.
Lamin
Intermediate filaments found in the nucleus only
interconnect chromatin to form nuclear skeleton
Types of Lamin
Three main types: A, B, and C.