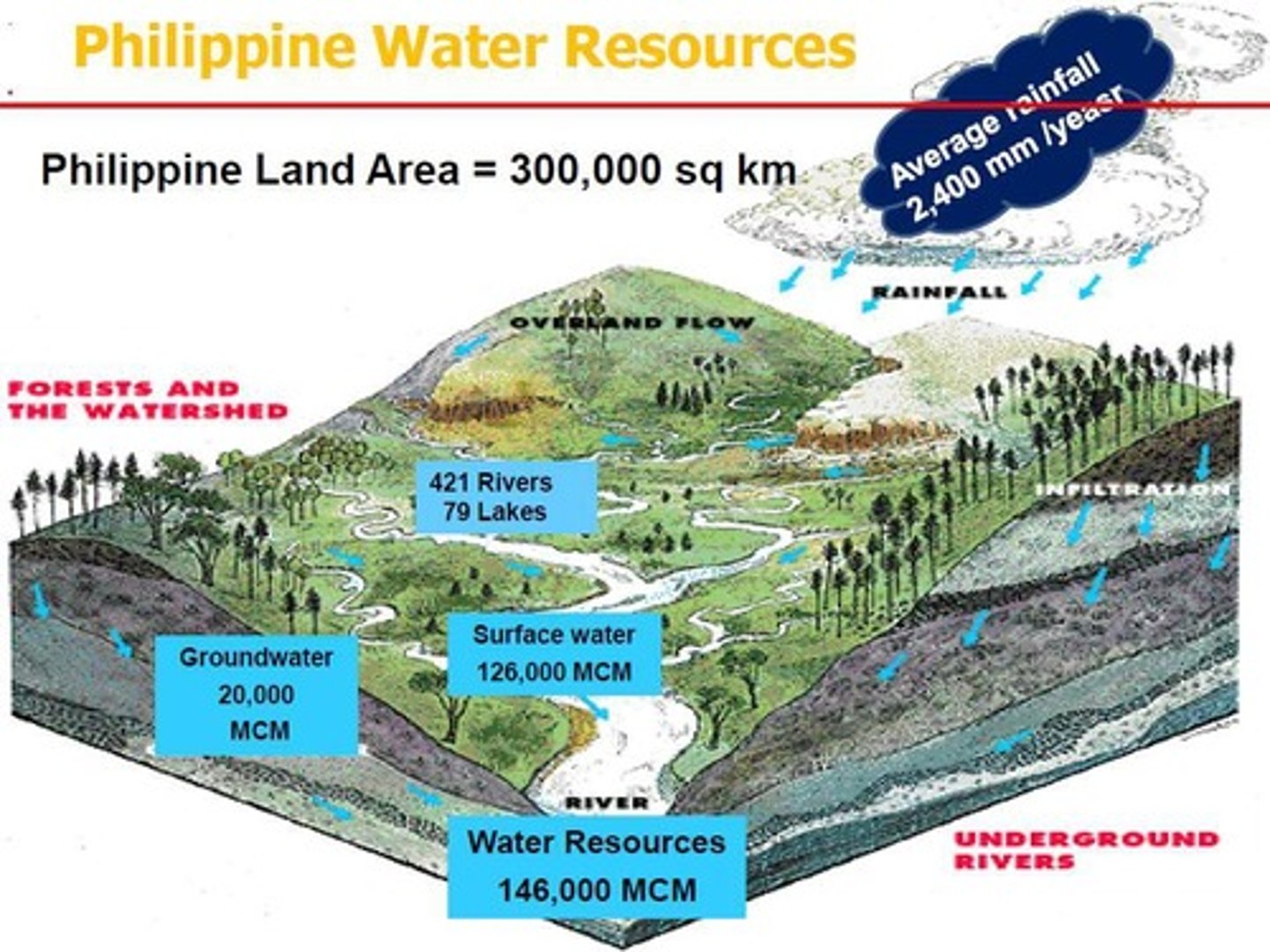
Water Resources Planning: Levels, Cycle, and Philippine Case Study
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is water resources planning?
A disciplined process to meet water needs efficiently, equitably, and sustainably, anchored on hydrologic reality, societal priorities, and institutional feasibility.
What are the three pillars of water resources planning?
Hydrologic reality, societal priorities, and institutional feasibility.
What are the multi-objective aspects of water resources planning?
Supply reliability, flood risk reduction, water quality, environment, energy, navigation, recreation, and livelihoods.
What are the three levels of water resources planning?
National level, basin level, and project level.
What decisions are made at the national level of water resources planning?
National policies, investment programs, water allocation frameworks, and drought/flood strategies.
Who are the typical actors involved at the national level of planning?
NWRB-type agencies, environment and public works departments, economic planning bodies, and finance.
What decisions are made at the basin level of water resources planning?
River basin plans, multipurpose storage rules, environmental flow allocation, and floodplain zoning.
Who are the typical actors involved at the basin level of planning?
Basin organizations, local government units (LGUs), utilities, irrigation authorities, and communities.
What decisions are made at the project level of water resources planning?
Project scopes, siting, design standards, operation and maintenance plans, and cost recovery.
What is the first stage of the project development cycle?
Identification, which includes need or opportunity statement, preliminary objectives, and early stakeholders.
What activities are involved in the pre-feasibility stage of the project development cycle?
Narrowing options using desk studies, rough costs, and basic hydrologic checks.
What is included in the feasibility stage of the project development cycle?
Full technical studies, hydrologic modeling, demand and yield analysis, environmental and social assessment, and risk analysis.
What key activities occur during the design and procurement stage?
Detailed engineering, specifications, contracts, and permits.
What happens during the implementation stage of the project development cycle?
Construction, quality assurance, and environmental management plans.
What is involved in the operation and maintenance stage?
Standard operating procedures, reservoir rules, asset management, and monitoring.
What is the purpose of monitoring and evaluation in the project development cycle?
To review performance against targets, ensure compliance, and gather lessons for future upgrades.
What are some issues in water resources planning?
Water scarcity, climate variability, water quality degradation, environmental sustainability, institutional challenges, and data limitations.
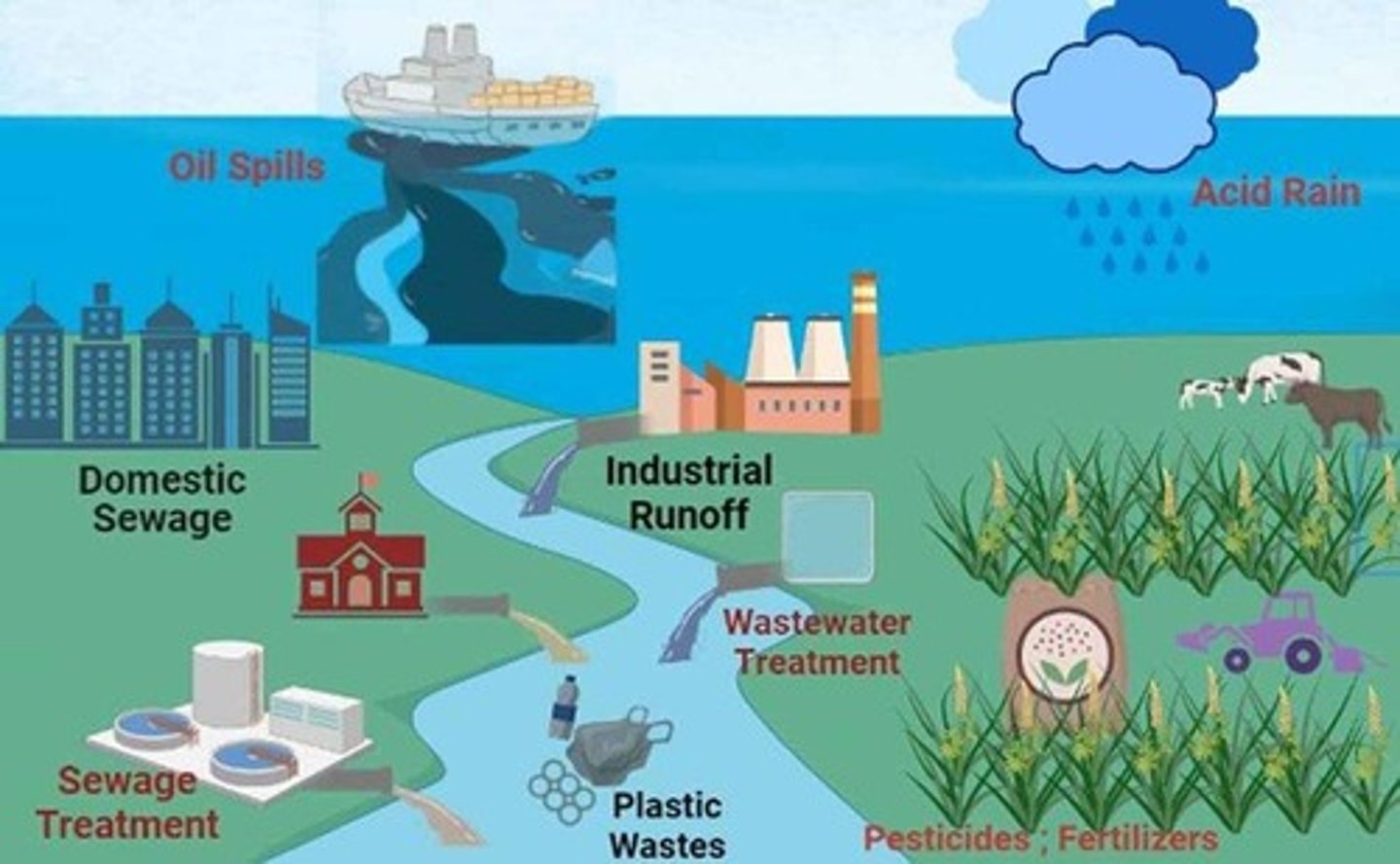
How does rapid urbanization affect water resources planning?
It increases domestic and industrial water needs, leading to competition for water resources.
What is a significant environmental issue in water resources planning?
Water quality degradation due to pollution from domestic wastewater, agriculture, and industries.
What are the consequences of poor water resources planning?
Overextraction can harm ecosystems, lead to habitat loss, and cause salinity intrusion.

What challenges arise from fragmented water management agencies?
Inconsistent enforcement of laws and policies can hinder effective water resources planning.
What data limitations affect water resources planning?
Lack of long-term, high-quality hydrological records and gaps in socio-economic and environmental data.