Titrations and Titration curves
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
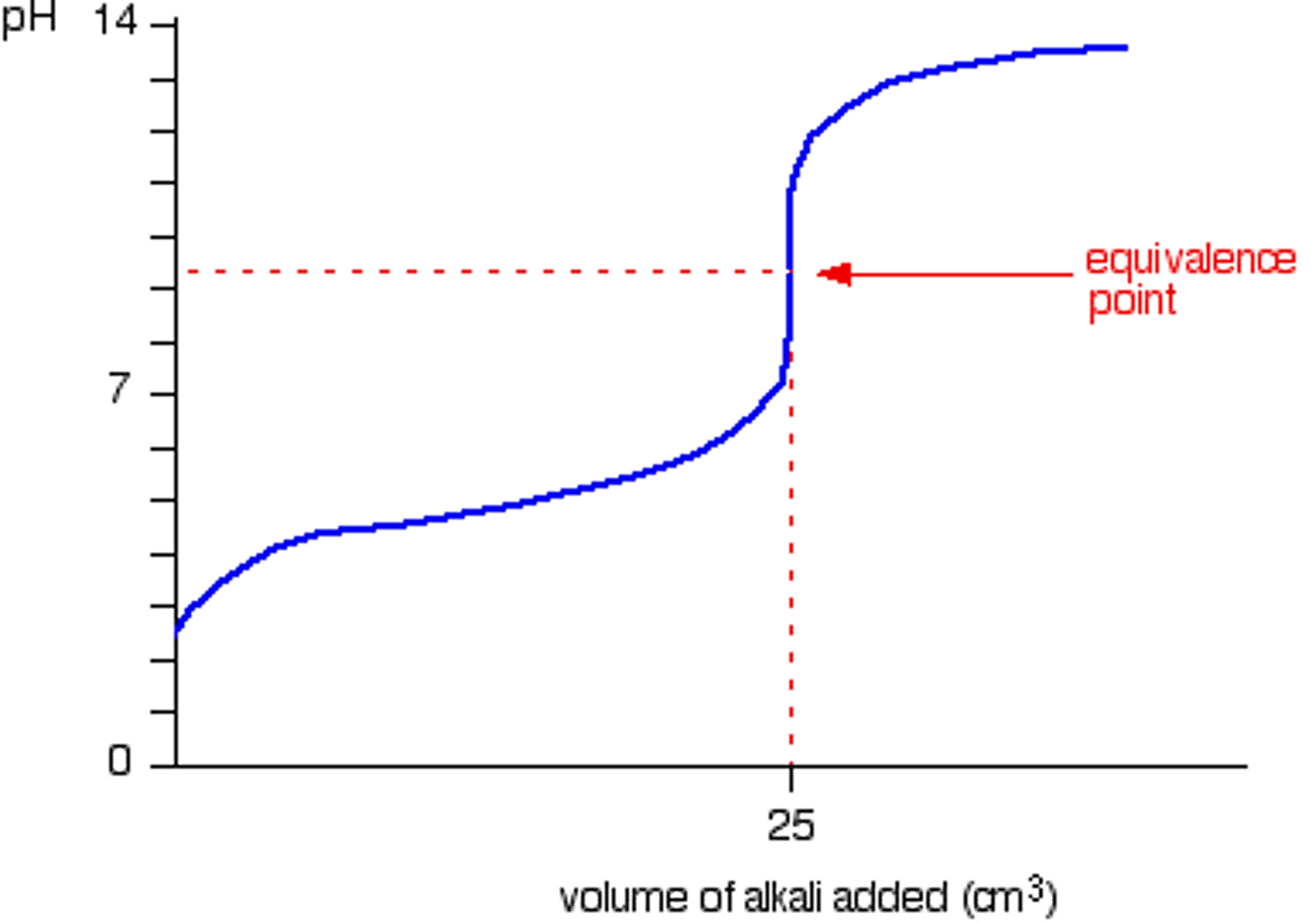
Strong acid into strong base
Neutral equivalence point
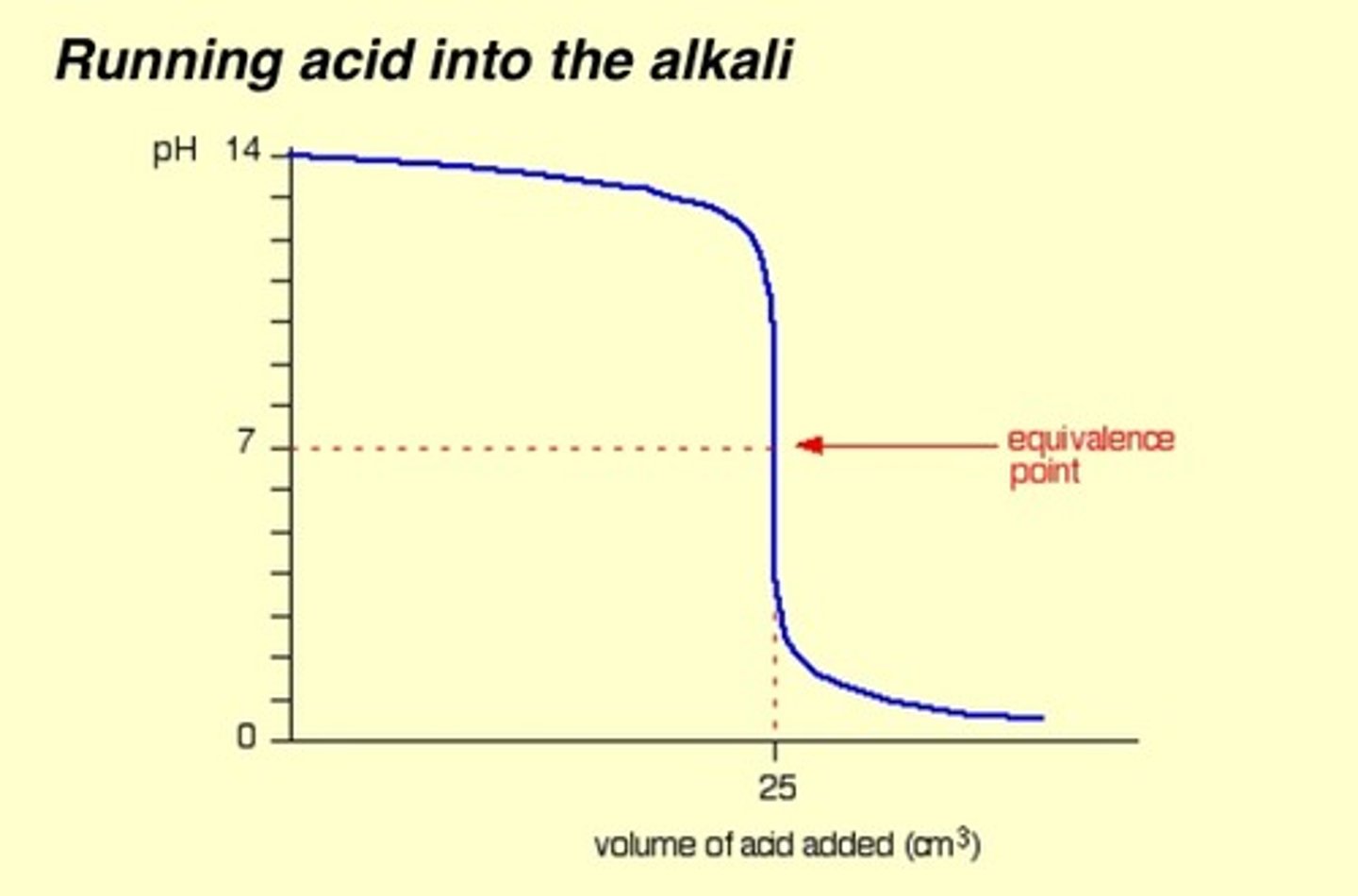
Strong base into strong acid
Neutral equivalence point
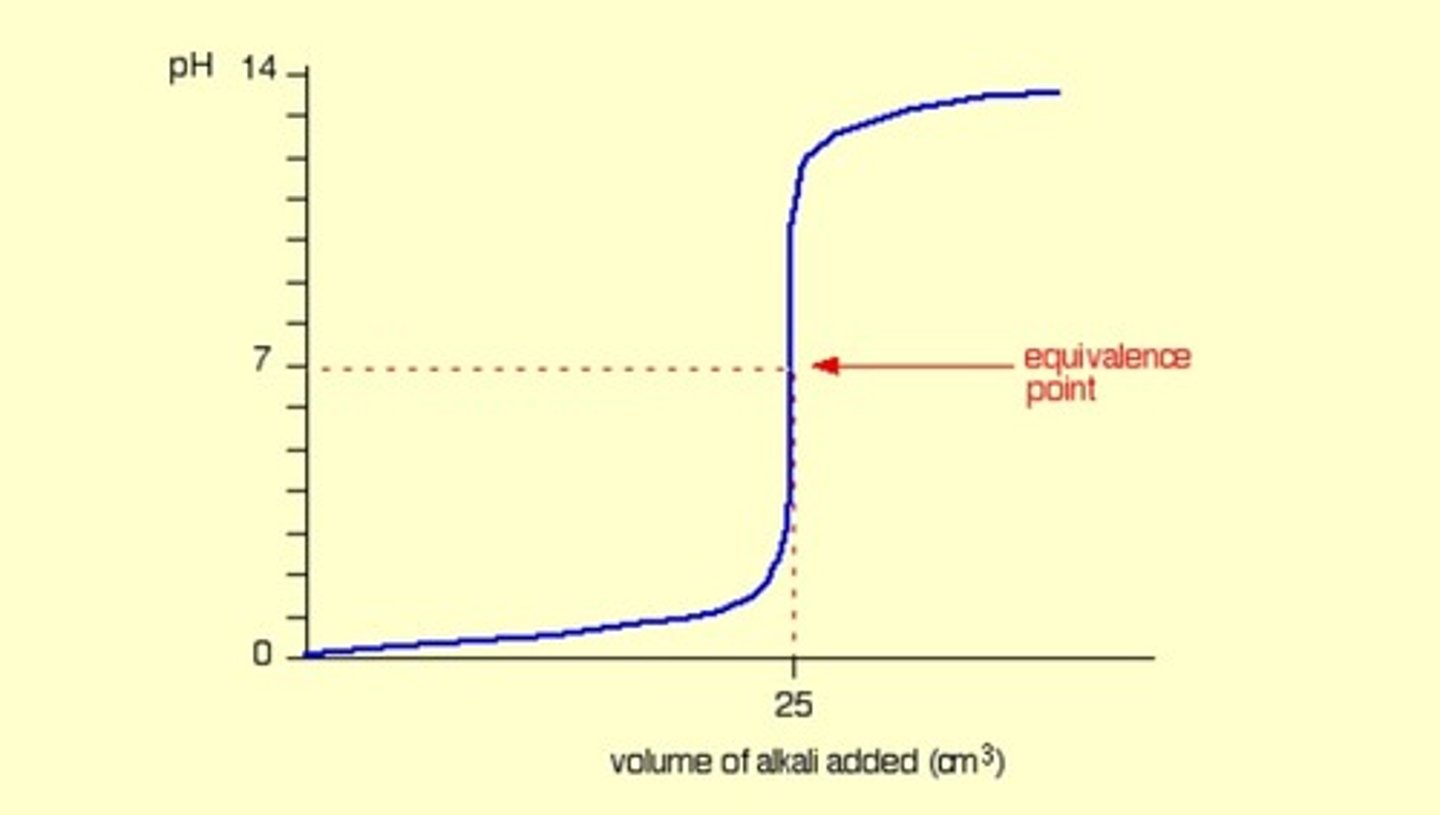
Weak acid into strong base
Basic equivalence point
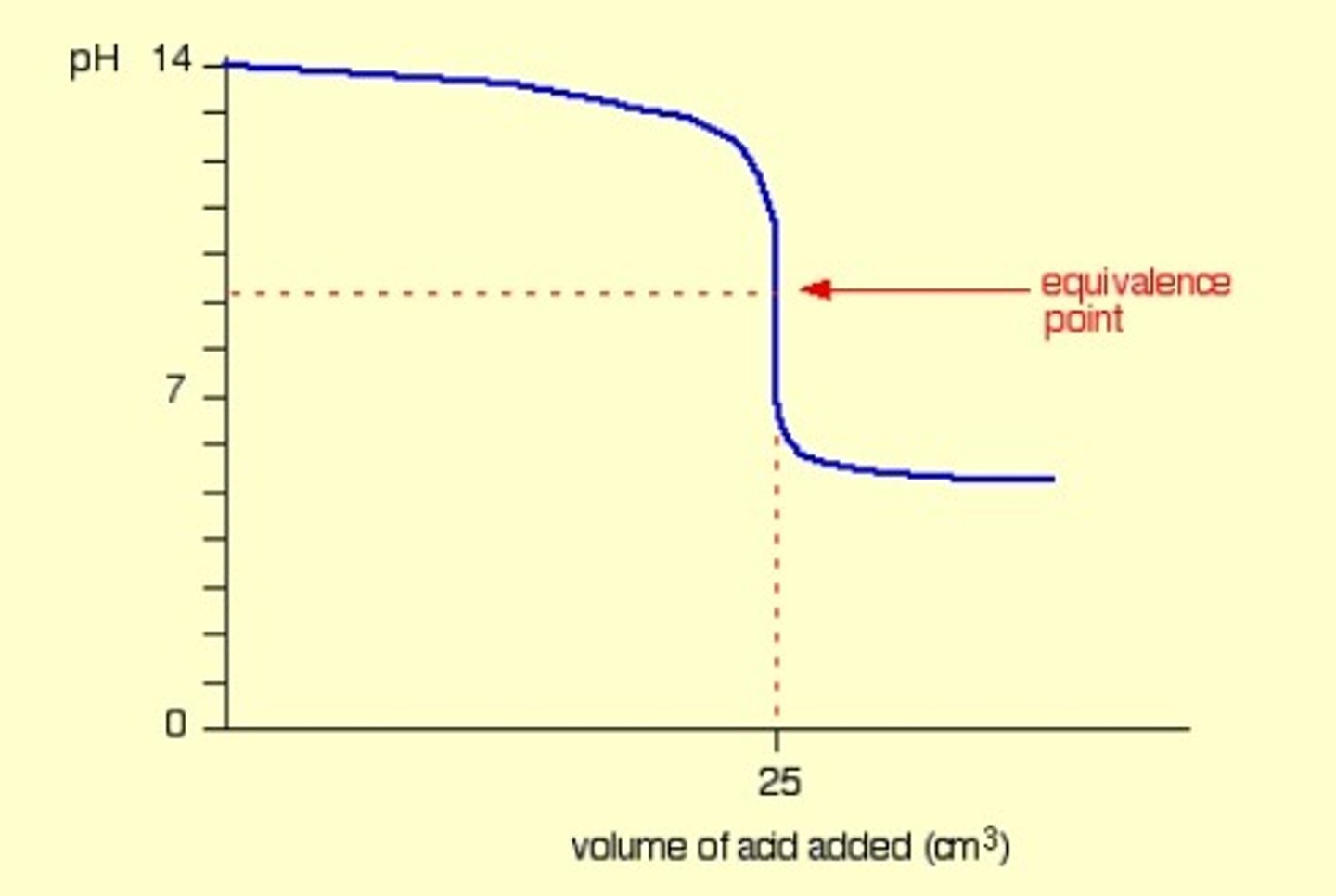
Strong base into weak acid
Basic equivalence point.
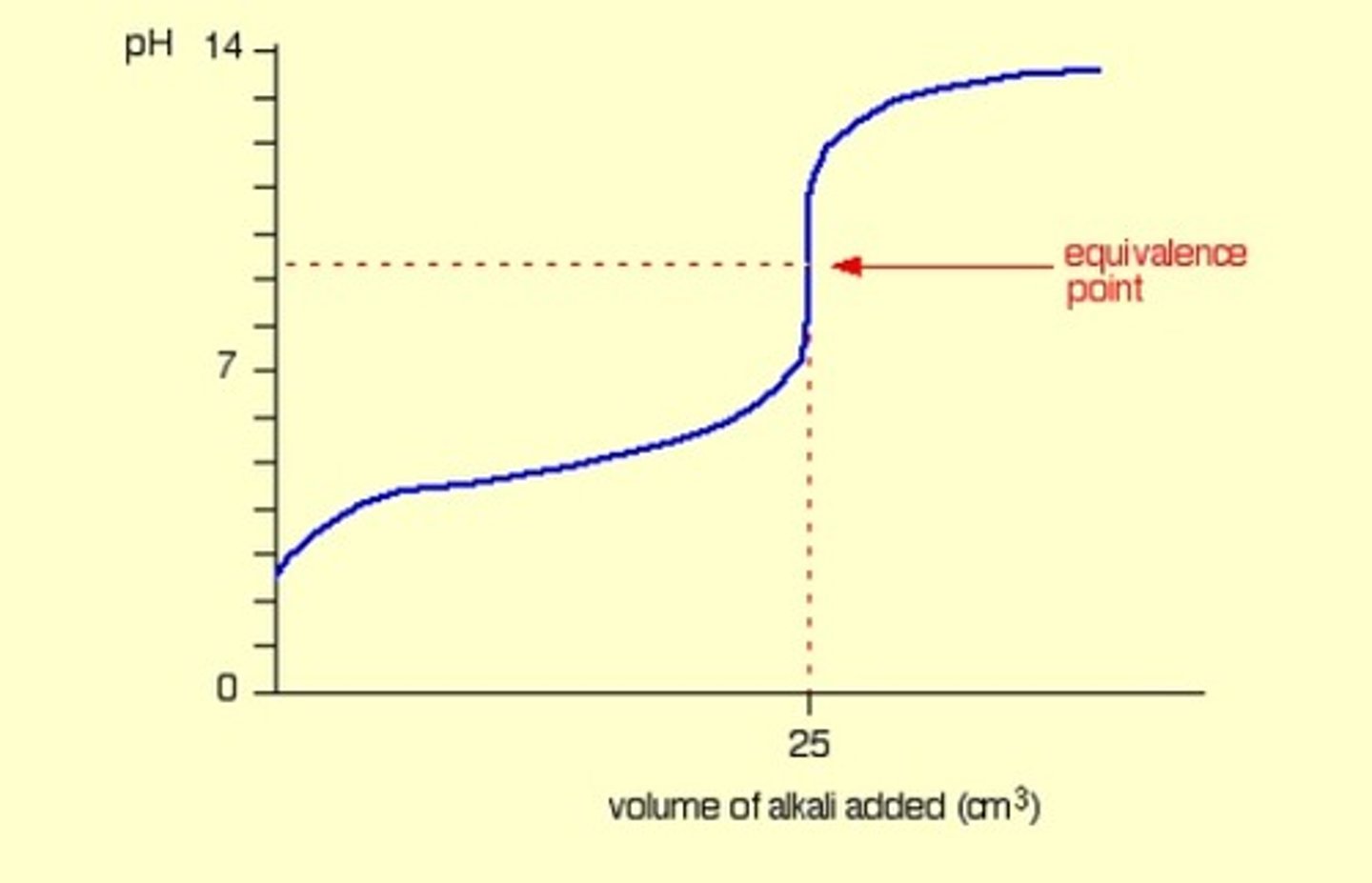
Weak base into strong acid
Acidic equivalence point
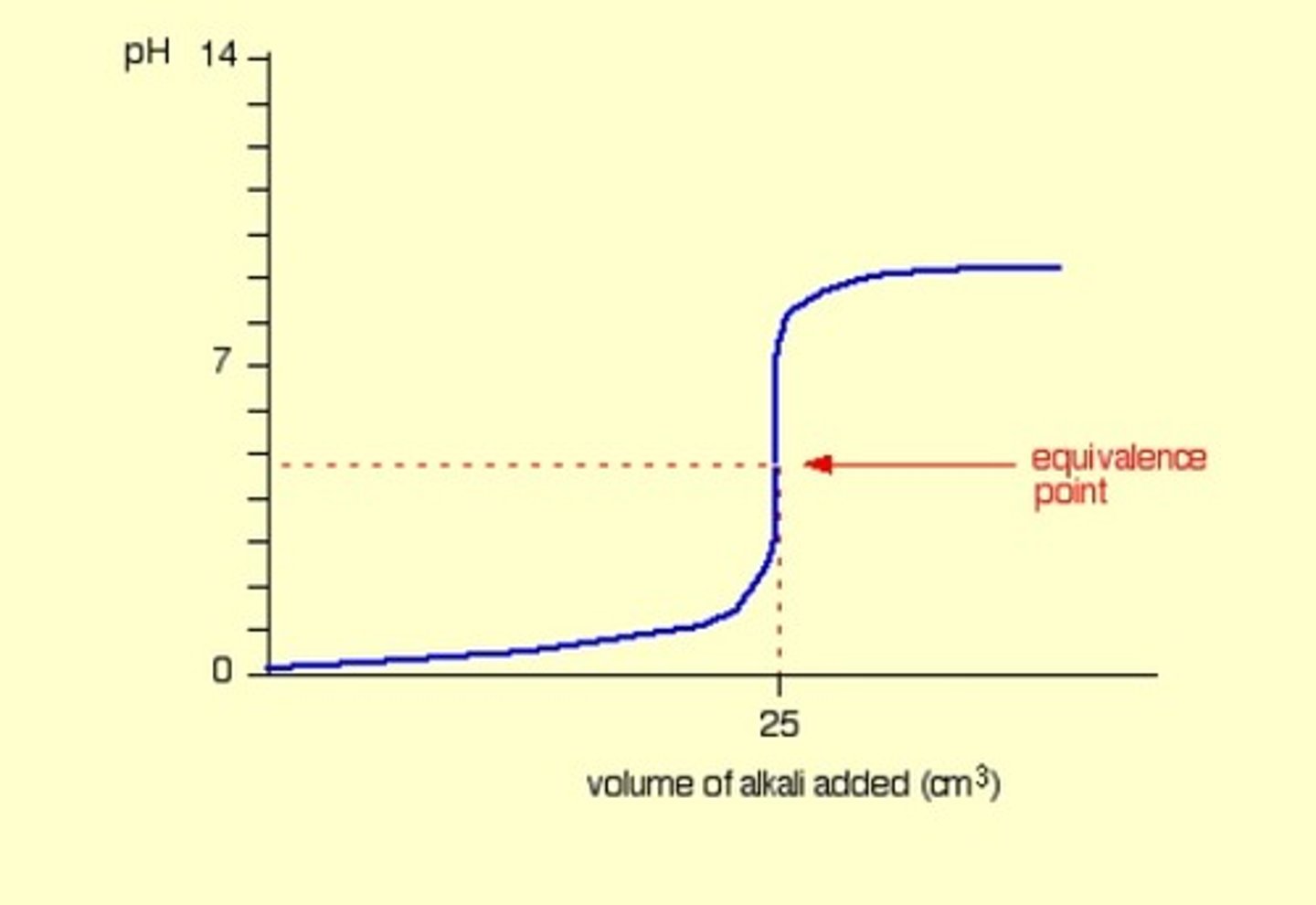
Strong acid into weak base
Acidic equivalence point.
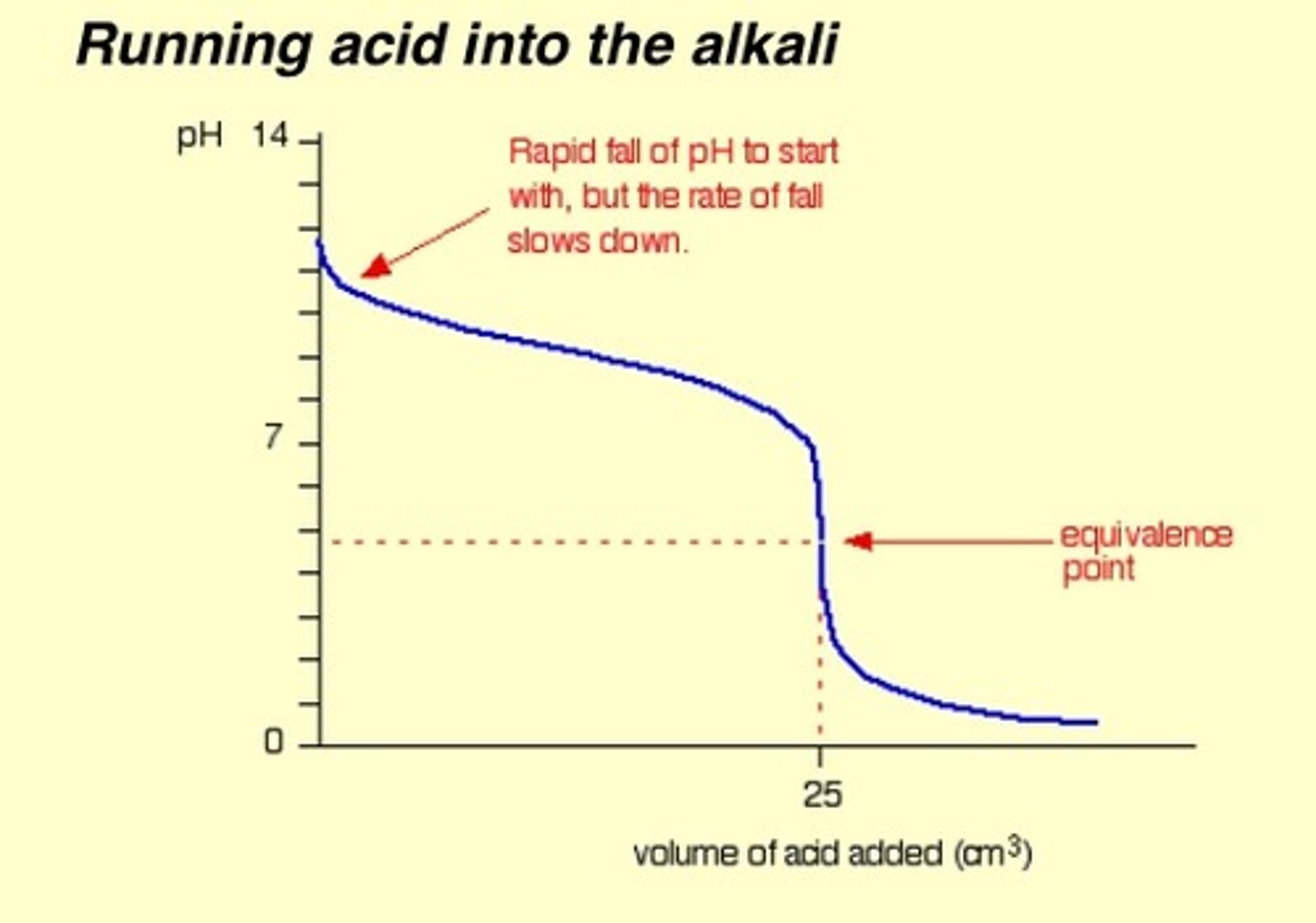
Weak acid pH
3
Weak base pH
9
Strong acid pH
1
Strong base pH
13
titration
is a method of determining the concentration of a solution by reacting a known volume of that solution with a solution of known concentration
titrant
the solution of known concentration that is added to the burette
Burette
measuring instrument consisting of a graduated glass tube with a tap at the bottom

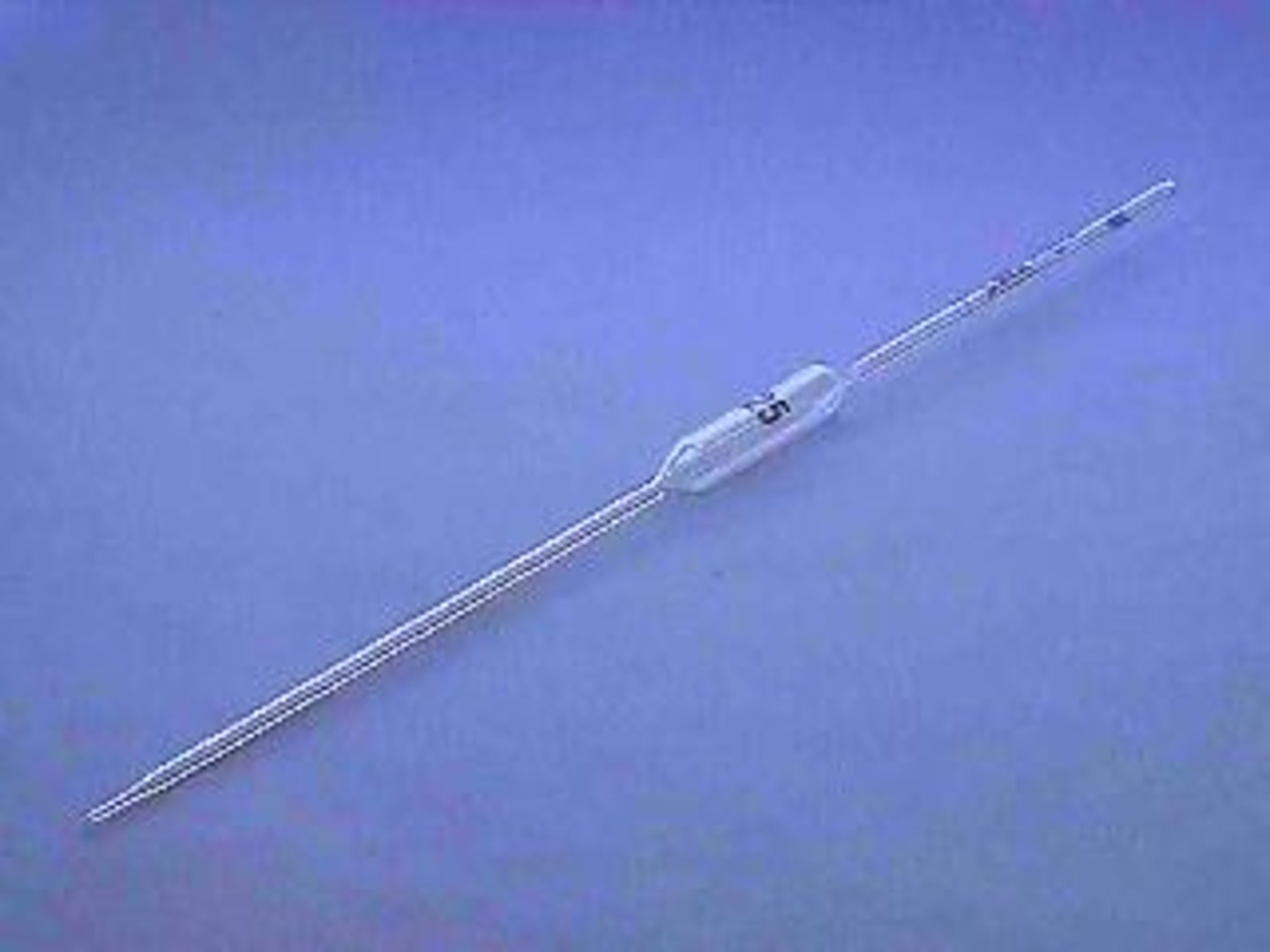
Pipette
A glass or transparent plastic tube used to accurately measure small amounts of liquid

hydronium ion
H₃O⁺
hydrogen ion
H⁺
hydroxide ion
OH⁻
Neutralisation reaction
an acid and a base in an aqueous solution react to produce a salt and water
Neutralisation ionic equation
H⁺ (aq) + OH⁻ (aq) ⇌ H₂O (l)
salt
an ionic compound made up of a cation from a base and an anion from an acid
Neutral salt
results from reaction of strong acid and strong base
Acidic salt
results from reaction of strong acid and weak base
Basic salt
results from reaction of weak acid and strong base
Acid-base indicator
a compound whose colour is sensitive to pH
Equivalence point
the point at which moles of hydrogen ions from the acid equal the moles of hydroxide ions from the base
End point
the point at which the indicator that is used in titration changes colour
Phenolphthalein
acid/neutral = colourless; basic = pink
concurrent
agreeing or consistent
Acid + Base
salt + water
Acid + Metal
salt + hydrogen gas
Acid + metal carbonate
salt + water + carbon dioxide
neutralisation complete equation
acid + base ⇌ salt + water
titration curve
A graph of pH vs volume of titrant added.