DNA Replication, Repair, and Recombination Overview
1/417
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
418 Terms
Mutation Rate
Frequency of mutations per cell generation.
Silent Mutation
Mutation that does not alter protein function.
Lactose Utilization Gene
Gene required for lactose metabolism in bacteria.

Glucose
Alternative sugar affecting mutation rate measurement.
Codon
Three-nucleotide sequence coding for an amino acid.
Amino Acid
Building blocks of proteins, specified by codons.

Bacterial Cell Generations
Cycles of bacterial reproduction, affecting mutation accumulation.
Average-sized Protein
Typically encoded by ~103 nucleotide pairs.
Germ Line Mutation Rate
Rate of mutations in reproductive cells.
C. elegans
Model organism for studying germ line mutations.
Fraction of Damaged Genes
Underestimates actual mutation rate due to silent mutations.
Nucleotide Change
Alteration in DNA sequence affecting genetic information.
Cell Survival
Impact of mutations on bacterial viability.
Energy Source
Substance used by cells for metabolic processes.
Protein Activity
Functionality of proteins affected by mutations.
Mutation Accumulation
Process of genetic changes over generations.
Repair Mechanisms
Biological processes correcting DNA mutations.
Recombination
Genetic process exchanging DNA between organisms.
Damaging Mutation
Genetic change impairing organism's function.
Bacterial Mutation
Genetic alteration occurring in bacterial DNA.
Genetic Information
Data encoded in DNA sequences.
Measurement Techniques
Methods for assessing mutation rates in organisms.
Complex Organisms
Multicellular entities with intricate genetic structures.
Glucose Presence
Condition affecting mutation rate measurement.
Codon Change
Alteration in DNA triplet coding for amino acid.
Amino Acid Change
Modification that may not affect protein activity.
1 in 10^6
Rate of mutation for average-sized proteins.
Bacterial Mutation Measurement
Determining mutation rates in bacterial populations.
Mutation Correction
Adjusting mutation rates for silent mutations.
DNA Repair
Mechanism correcting DNA damage.
Bacterial Survival
Ability of bacteria to live under stress.
Nucleotide Pairs
Building blocks of DNA sequences.
Generation Time
Time taken for one complete reproductive cycle.
Self-Fertilization
Reproductive process where an organism fertilizes itself.
Haploid Genome
Genome with a single set of chromosomes.
Cell Division
Process where a parent cell divides into daughter cells.
Germ-Line Mutation Rate
Rate of mutations occurring in germ-line cells.
Amino Acid Sequence
Order of amino acids in a protein chain.
Fibrinogen
Protein that converts to fibrin during blood clotting.
Fibrinopeptides
Peptides derived from fibrinogen, involved in clotting.
Stable Mutation
Permanent change in DNA sequence that is inherited.
Somatic Cells
Cells forming the body, not involved in reproduction.
Germ Cells
Cells that transmit genetic information to offspring.
Essential Proteins
Proteins necessary for survival and function of an organism.
Mutation Frequency
Rate at which mutations occur in a population.
Evolutionary Limitations
Constraints on complexity due to mutation rates.
DNA Sequencing
Technique to determine the nucleotide sequence of DNA.
Species Divergence
Point at which two species evolve from a common ancestor.
Indirect Estimates
Calculations based on comparative analysis rather than direct measurement.
Nucleotide Sequences
Specific order of nucleotides in a DNA strand.
Comparative Analysis
Method of comparing biological data between different species.
Deleterious Mutations
Mutations that negatively affect an organism's fitness.
400 Amino Acids
Typical length for proteins studied in mutation rate calculations.
Cancer
Uncontrolled cell proliferation due to genetic mutations.
DNA Fidelity
High accuracy in DNA replication and maintenance.
Nucleotide Change Rate
Approximately 1 change per 10 billion nucleotides.
Human Genome Size
Approximately 3 billion nucleotide pairs.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands.
Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphates
Building blocks for DNA synthesis during replication.
Base-Pairing
Specific pairing of nucleotides in DNA strands.
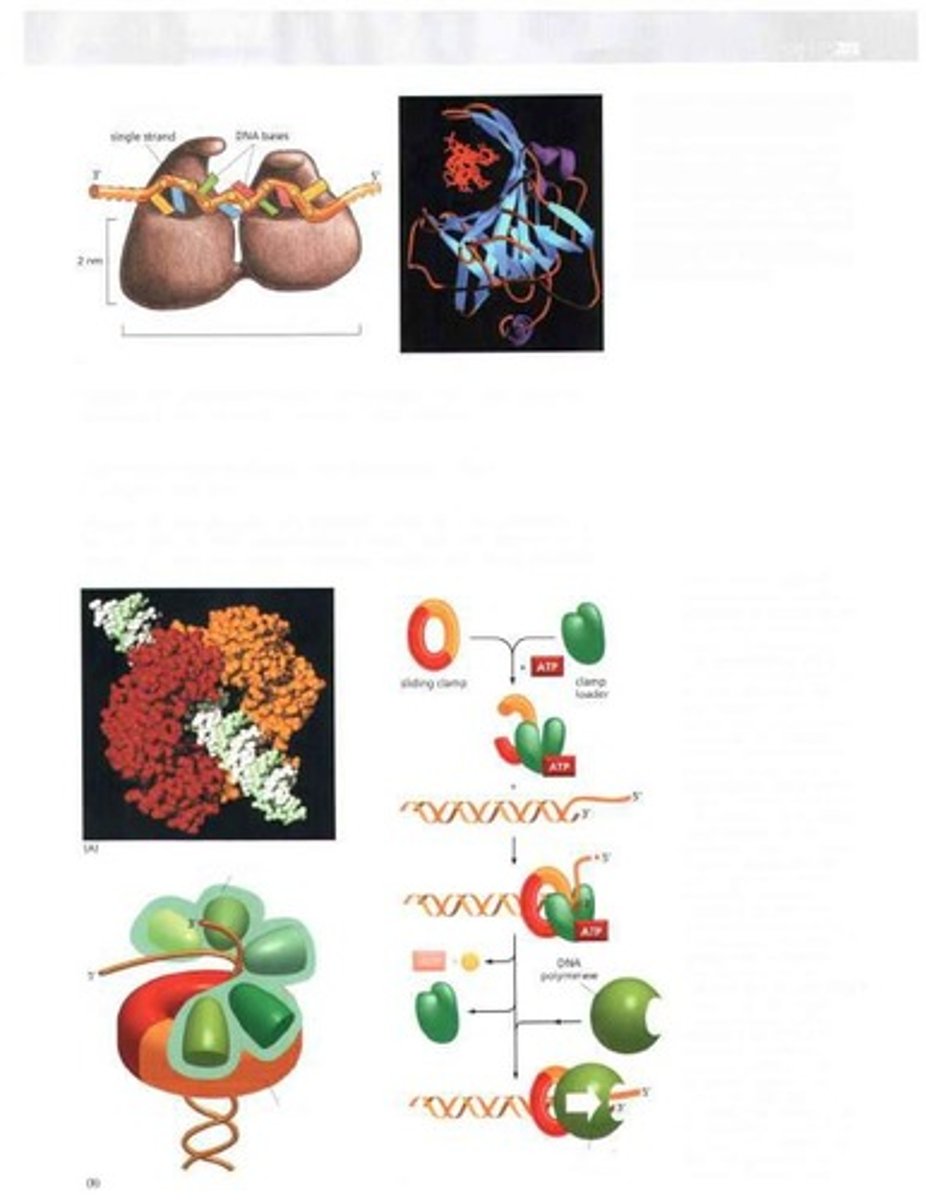
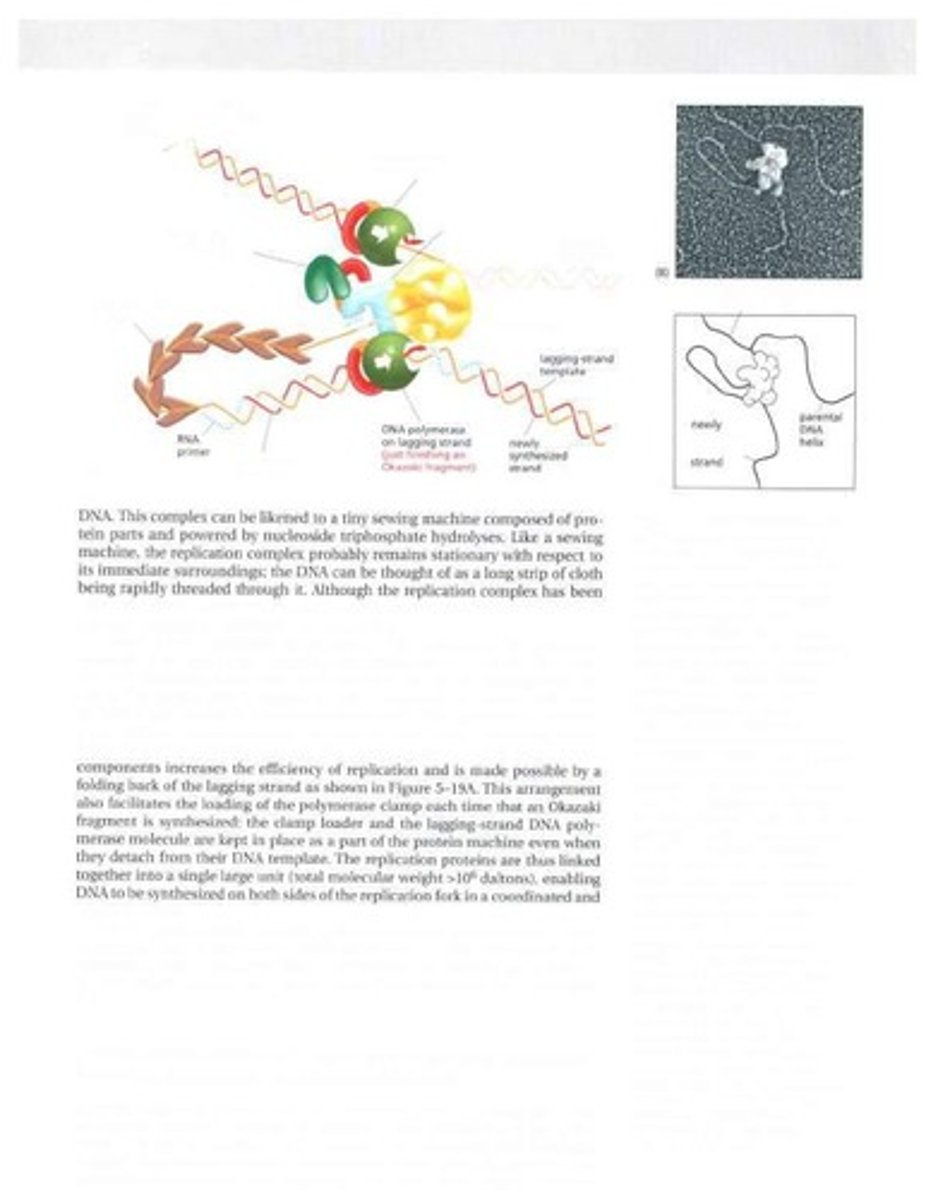
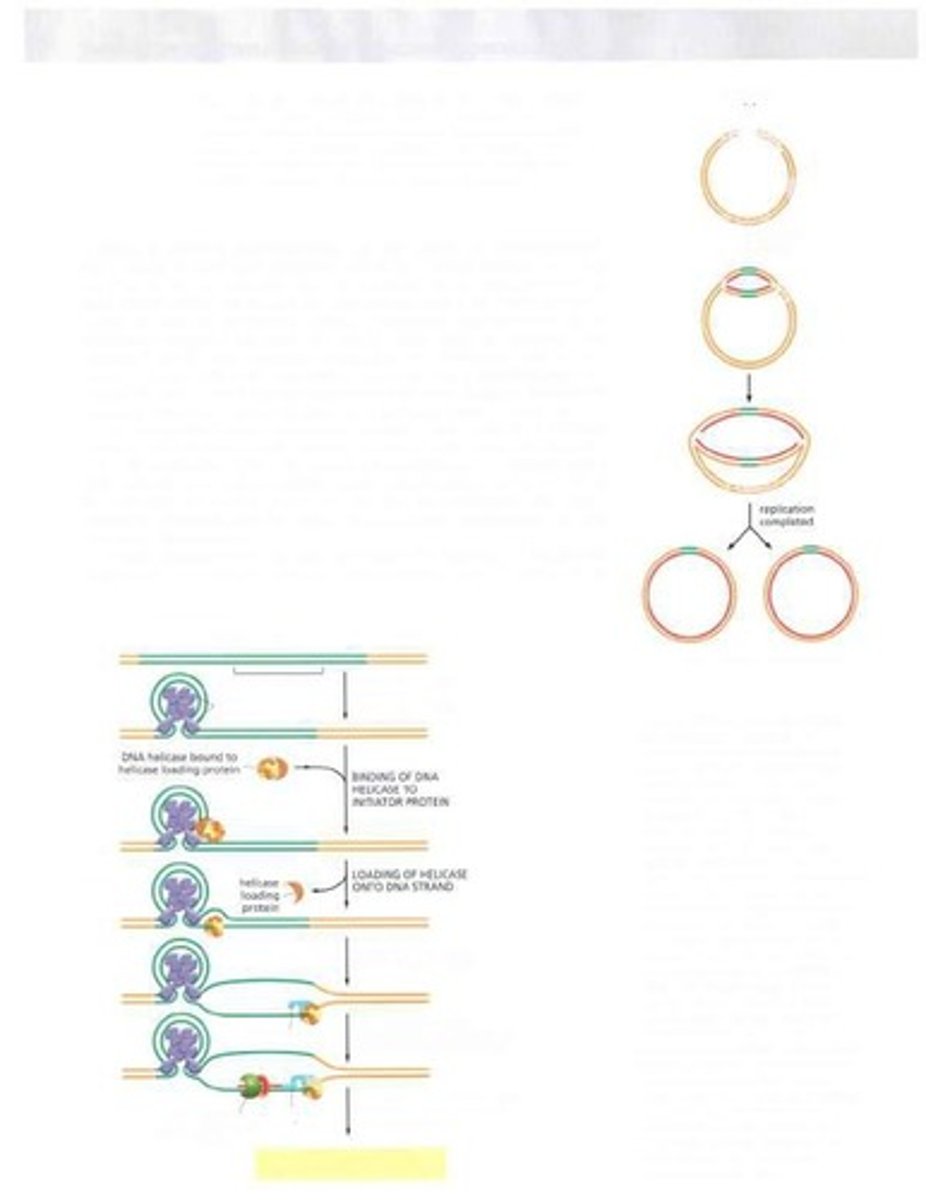
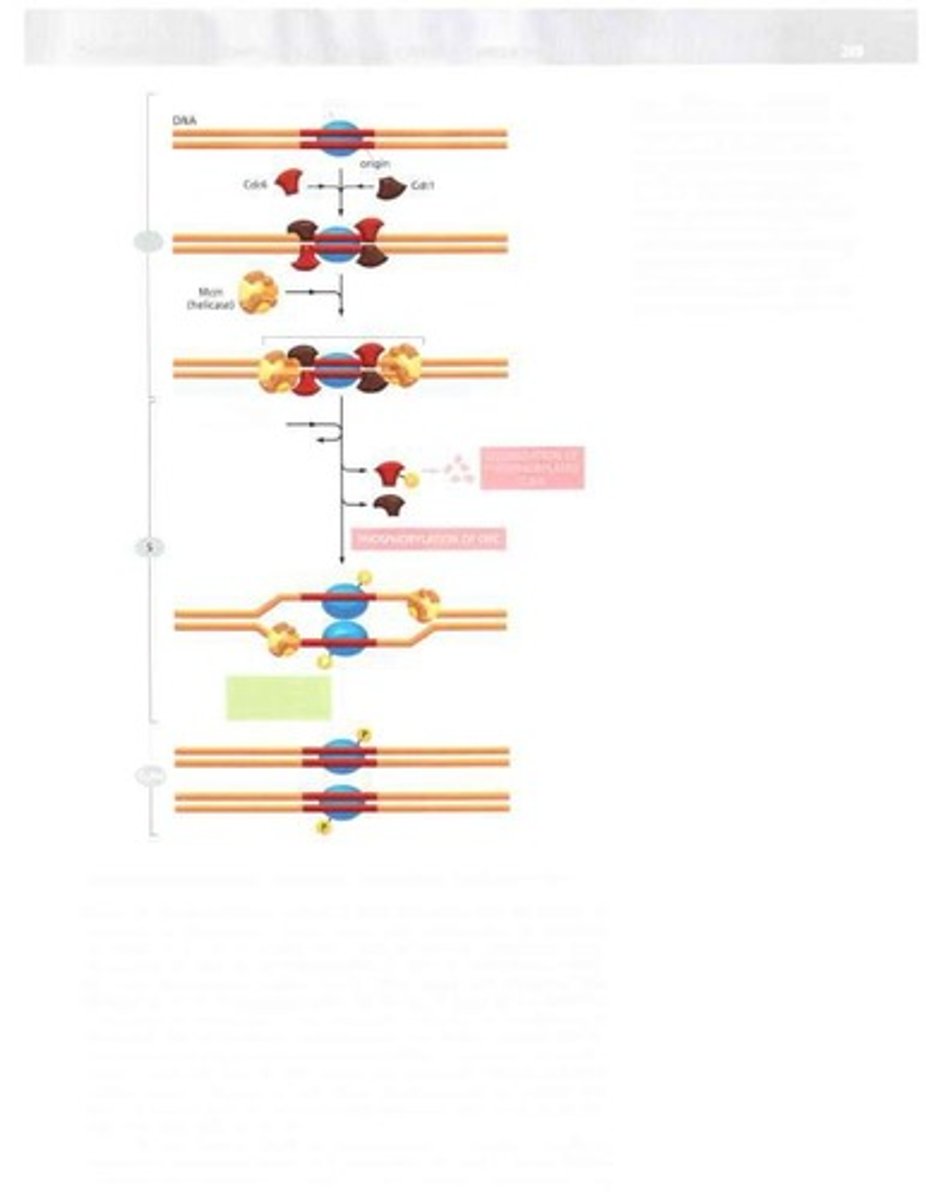
Replication Machine
Complex of proteins that ensures accurate DNA replication.
Semiconservative Replication
Each new DNA helix contains one old and one new strand.
DNA Template Strand
Original strand used to guide synthesis of new DNA.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak interactions that stabilize DNA base pairs.
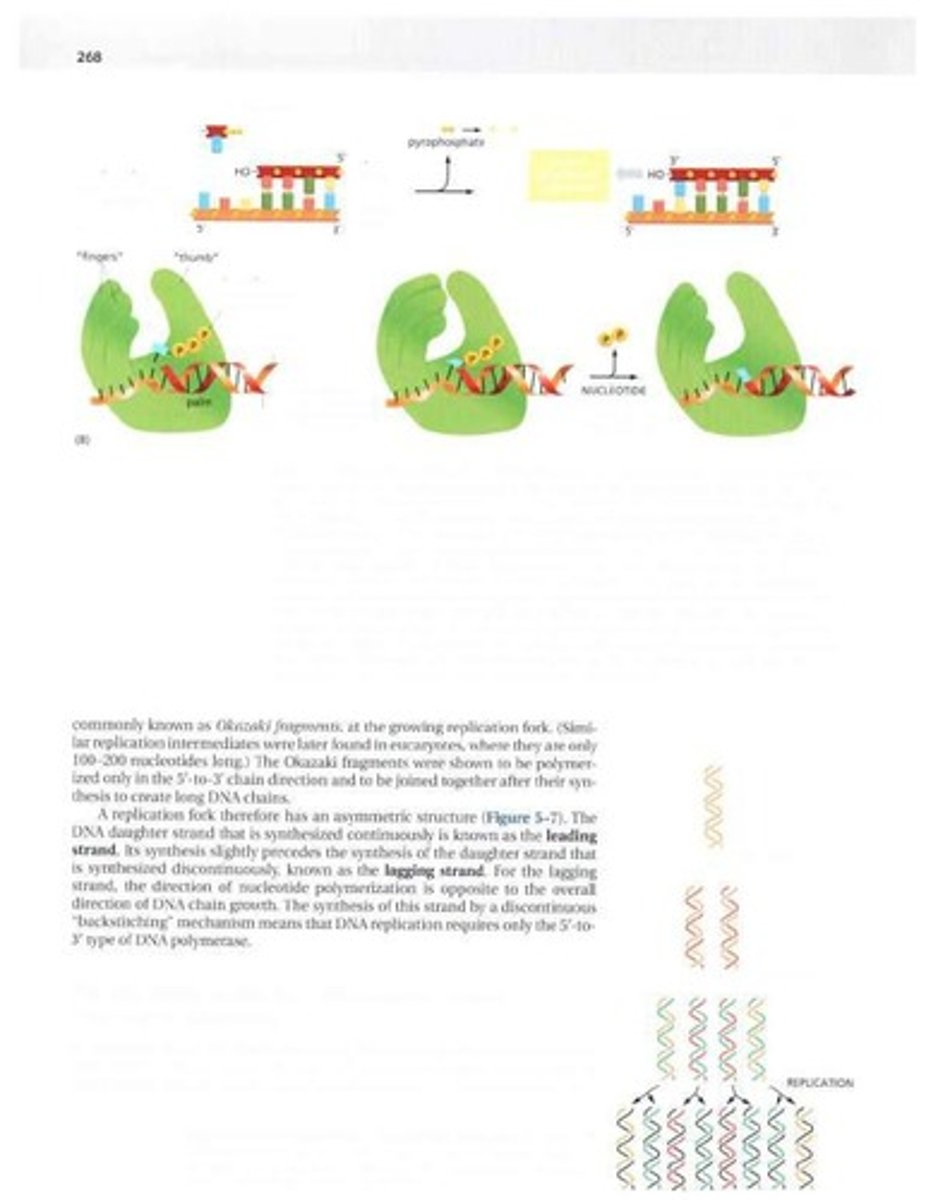
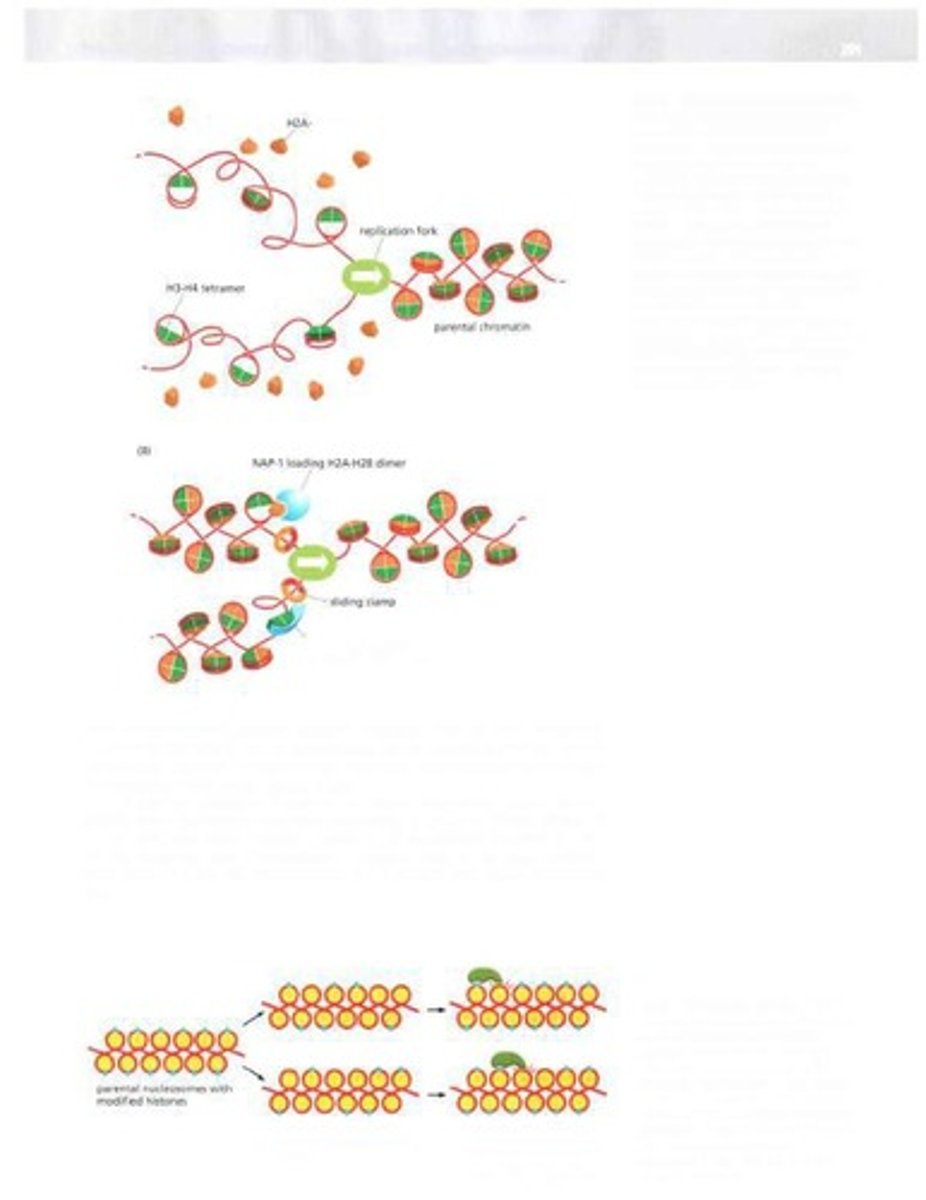
Replication Fork
Y-shaped structure where DNA strands separate for replication.
Polymers
Large molecules made of repeating subunits, like DNA.
Nucleotide
Basic unit of DNA, consisting of a base, sugar, and phosphate.
Cell Proliferation
Increase in cell numbers through division.
Natural Selection
Process where advantageous traits increase in frequency.
Replication Rate
Speed of DNA synthesis, up to 1000 nucleotides per second.
Deoxyribonucleotide
Building block of DNA, added to primer strand.
Polynucleotide chain
A sequence of nucleotides linked together.
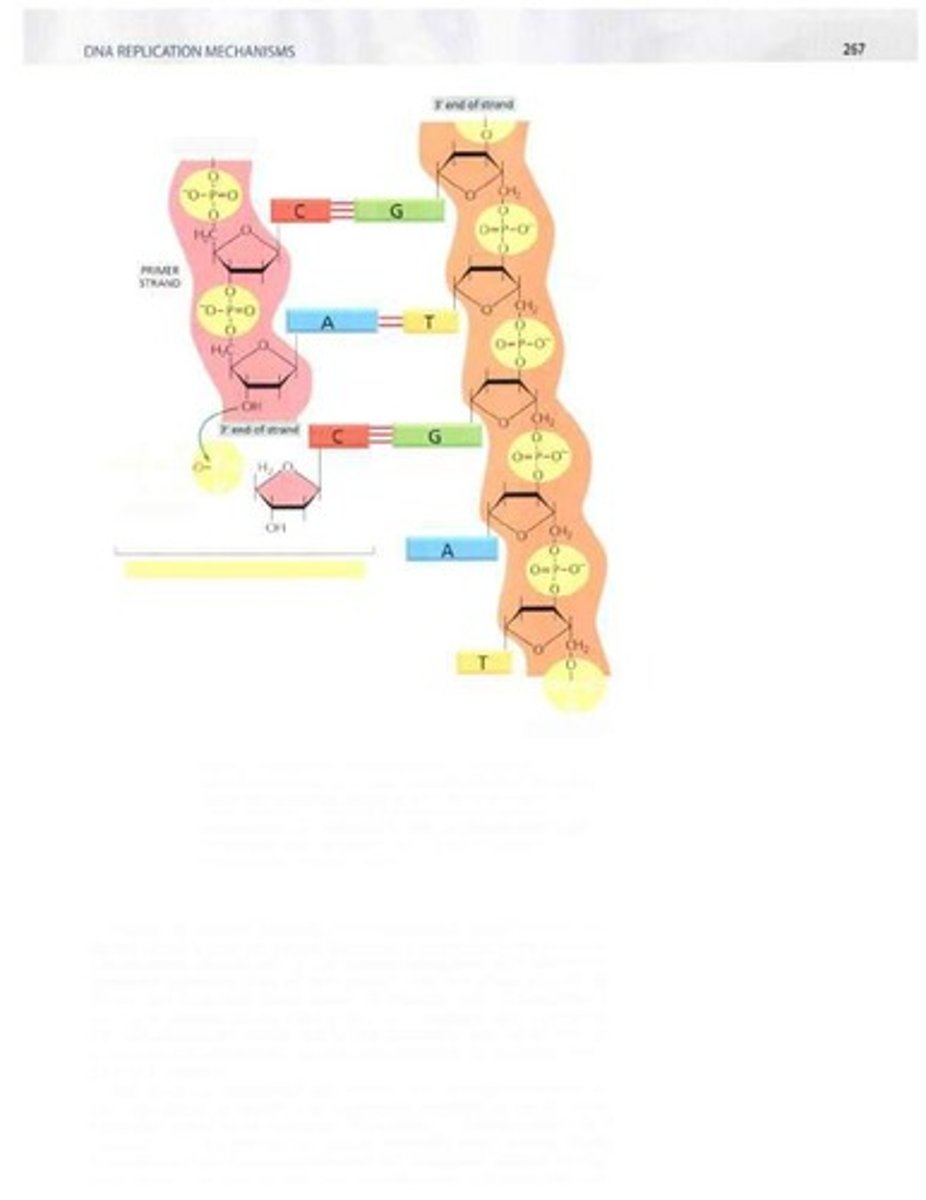
Primer strand
Initial strand that DNA synthesis builds upon.
Template strand
Existing DNA strand guiding new strand synthesis.
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate
Nucleotide precursor for DNA synthesis.
Antiparallel orientation
Opposite directional arrangement of DNA strands.
5'-to-3' direction
Direction of DNA strand growth during synthesis.
3'-to-5' direction
Direction opposite to DNA synthesis growth.
Radiolabeled DNA
DNA marked with radioactive thymidine for tracking.
Nucleotide addition reaction
Process of adding nucleotides to growing DNA strand.
Pyrophosphate
Byproduct of nucleotide addition, drives DNA synthesis.
Hydrolysis of pyrophosphate
Breakdown releasing energy for DNA synthesis.
High fidelity
Accuracy level of DNA replication, 1 mistake per 10^9 nucleotides.
Proofreading mechanisms
Systems ensuring accuracy during DNA replication.
Replication mechanisms
Processes involved in duplicating DNA strands.
Active zone of DNA replication
Region where DNA synthesis actively occurs.
Y-shaped DNA structure
Formation created by replication forks during synthesis.
Daughter DNA molecules
Newly synthesized strands resulting from replication.
Parental DNA helix
Original DNA strand serving as template.
Base Pairing
Specific hydrogen bonding between DNA bases.
Tautomeric Forms
Rare base variations affecting pairing stability.
Proofreading Mechanism
Correction process for mispaired nucleotides.
Exonucleolytic Proofreading
Error correction after nucleotide incorporation.
Okazaki Fragments
Short DNA segments synthesized on lagging strand.
3'-OH End
Required for DNA polymerase to elongate strands.
Energetically Favorable Pairing
Correct base pairing has higher binding affinity.
Conformational Change
Structural adjustment of polymerase during nucleotide binding.
Mismatch Incorporation
Incorrect nucleotide added to growing DNA chain.
Nucleotide Affinity
Correct nucleotides bind more strongly to polymerase.
Micrograph
Photographic representation of microscopic structures.