Amines and polymers
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
If its a primary amine what does it look like?
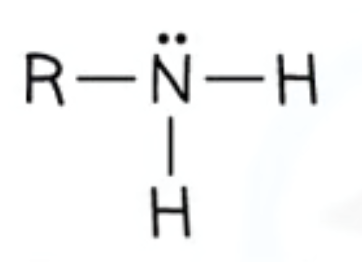
How to name amines?
-amine
e.g. methylamine
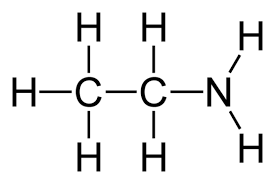
What is the name?
ethylamine
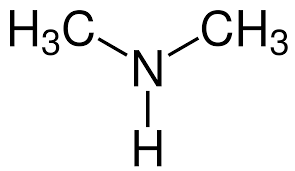
What is the name?
dimethlyamine
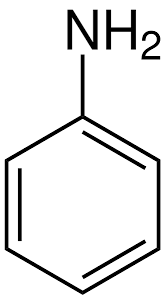
What is the name?
phenylamine
What does the nitrogen atom in amines accept?
proton H
What do amines therefore act as?
Bases in aq solutions as they donate lone pair of electrons to proton in form of dative bond
e.g. of ammonia + HCl
NH3 +HCl —> NH4+Cl-
e.g. of how amine (C2H5NH2) react with HCl and what forms?
C2H5NH2 + HCl —> C2H5NH3+Cl-
amine salts e.g. ethylammonium chloride
What is the solubility of amine salts?
soluble ionic compound
when alkyl group is small they are water soluble but become less so as carbon chain increases
What are the ways amines can be prepared:
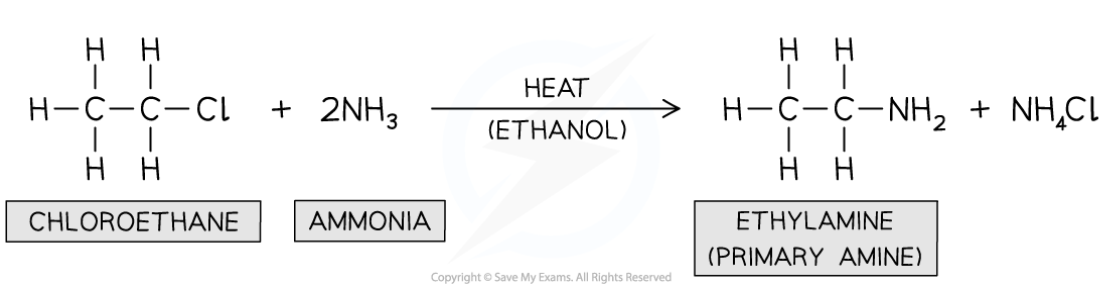
Reaction between hallogenoalkanes with ammonia
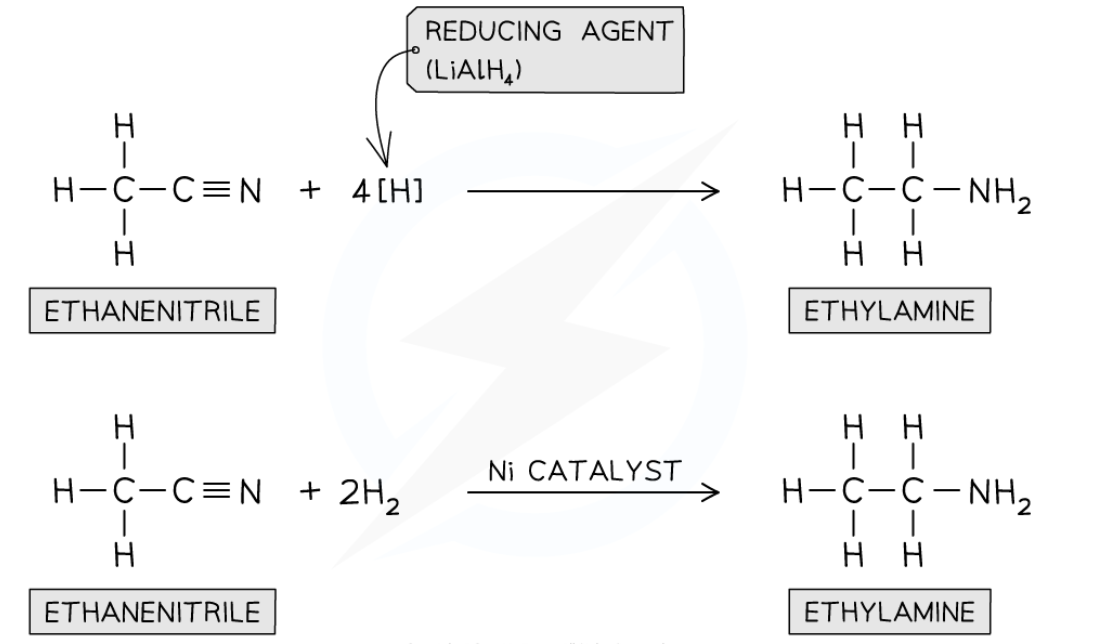
Reduction of nitriles
What type of reaction is halogenoalkanes with ammonia?
Nucleophilic substitution in which lone pair in ammonia acts as nucleophile and replaces halogen in halogenoalkane
What are the conditions needed for reaction of halogenoalkanes and ammonia?
Excess, hot ethanolic ammonia under pressure
—> primary amine
e.g. of haloalkane with ammonia
What type of reaction is nitriles forming amines?
Nitriles contain a -CN group which is reduced to a -NH2
Conditions for nitrile reduction?
nitrile vapour and hydrogen gas are passed over ni cat/ LiAlH4 in dry ether
—> primary amine
e.g. of reduction of nitrile
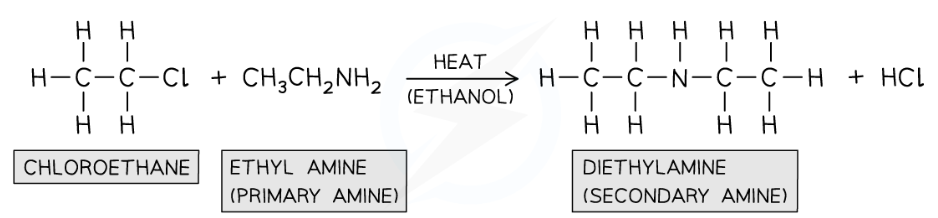
What type of reaction is halogenoalkane with primary amine?
Nucleophilic substitution reaction in which nitrogen in primary amine acts as nucleophiles and replaces the halogen in the halogenalkane
What conditions for halogenoalkanes with primary amine?
Primary amine in ethanol and heated in sealed tube under pressure a secondary amine is formed
e.g. of reaction
How are tertiary amines formed?
further reaction of secondary amine
e.g. triethylamine (CH3CH2)N
What is phenylamine?
organic compound made of benzene ring and amine (NH2) functional group
What can be reduced to pheylamine, C6H5NH2?
Nitrobenzene, C6H5NO2
Step 1:
Reduction of nitrobenzene:
Nitrobenzene, C6H5NO2, is reacted with tin and conc HCl (both act as reducing agents)
Reaction mixture is heated under reflux in boiling water bath
Phenylammonium ions, C6H5NH3+ are protonated due to the acidic conditions
Step 2:
Formation of phenylamine:
phenylammonium ions, C6H5NH3+, are deprotonated by the addition of excess sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH (aq)
Summary:
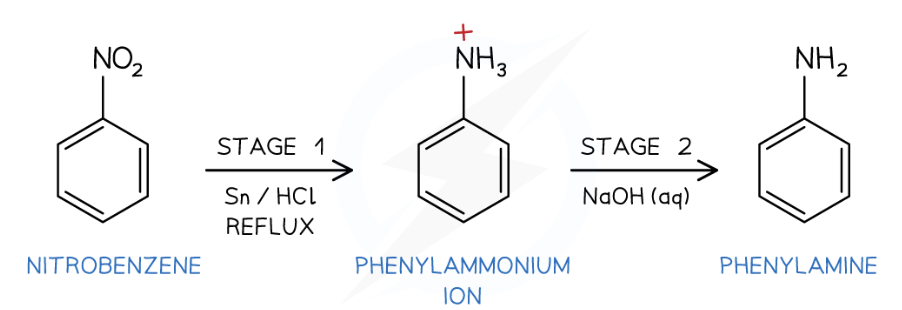
What functional group does amino acids have?
Basic amino (-NH2) group
Carboxylic acid (-COOH) group
What can amino acids act as + what is this known as?
Act as both acids and bases
Amphoteric
Amino acids make up _____
proteins
What is the arrangment of 2-aminocarboxylic acids?
Type of amino acids in which amine (NH2) group is bonded to carbon atom next to COOH group
General strucutral formula of amino acids:
RCH(NH2)COOH
R group can be acidic, basic or neutral
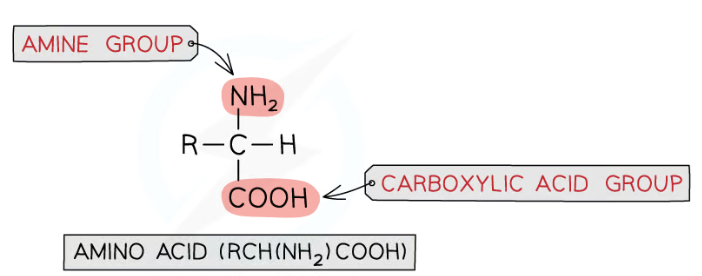
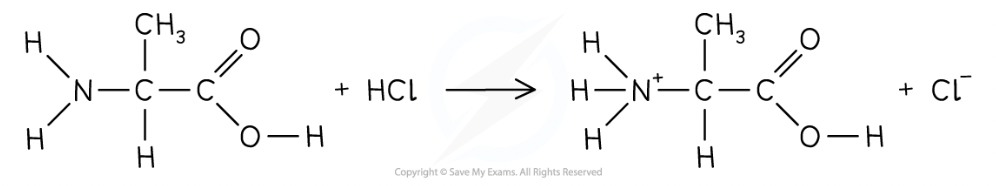
Reactions of amine group with acids- amino acids
Amine is basic and reacts with acids to make salts
e.g. amino acid reacts with HCl to form ammonium salt
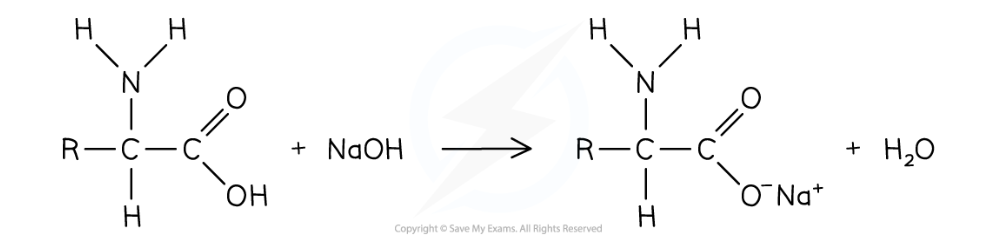
Reaction of carboxylic acid group with aqueous alkalis
Amino acid reacts with aq alkali to form salt and water
eg. general amino acid reacts with soidum hydroxide to form a sodium salt
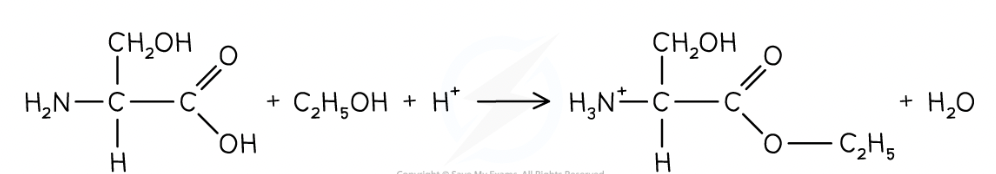
Reaction of carboxylic acid group in esterification with alcohols
conditions needed?
Amino acids are esterified by heating with alc in presence of conc sulphuric acid
Carboxylic acid group is esterified whilst basic amine group is protonated due to acidic conditions:
How are amides formed?
Condensation reaction with carboxylic acids or acyl chlorides with ammonia or amines
General structure of amides
RCONR2

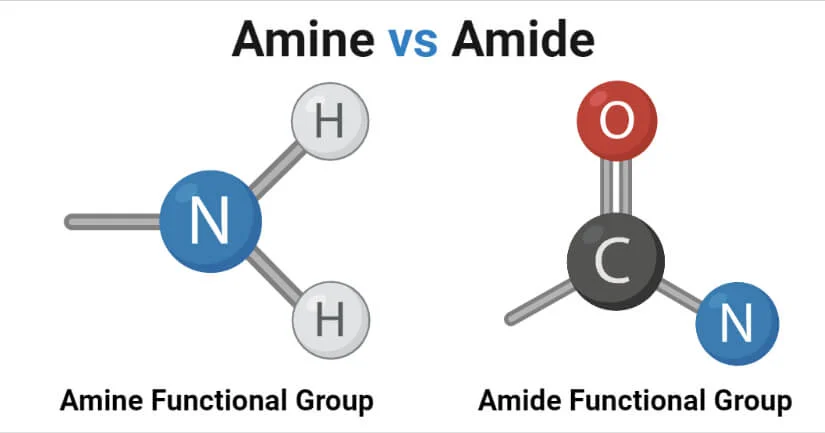
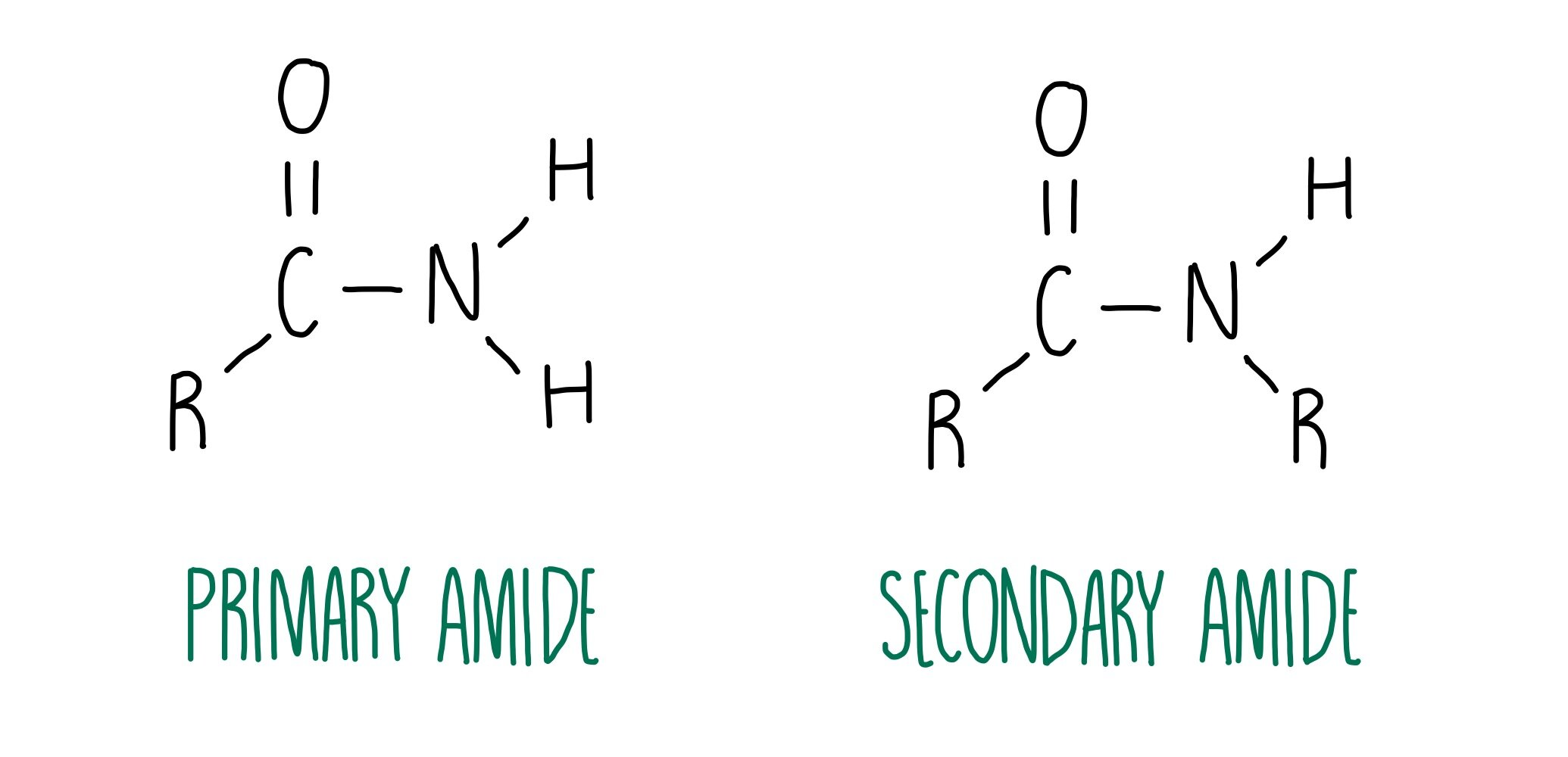
What are primary, secondary and tertiary amides?
Primary amide - one carbon bonded to the amide nitrogen
R' and R'' are both hydrogen atoms so one "ammonia" hydrogen has been substituted with the carbonyl group from the RCO portion of the molecule
Secondary amide - two carbons bonded to the amide nitrogen (one MUST be the carbonyl carbon)
Tertiary amide - three carbons bonded to the amide nitrogen (one MUST be the carbonyl carbon)
How to name primary amides?
add -amide to the stem
e.g. ethanamide
Secondary amides:
secondary amides, the alkyl chain attached to the nitrogen is added at the start of the chemical name
This alkyl chain is prefixed with N-
The chain containing the carbonyl group is named the same as a primary amide
e.g. N-propylethanamide
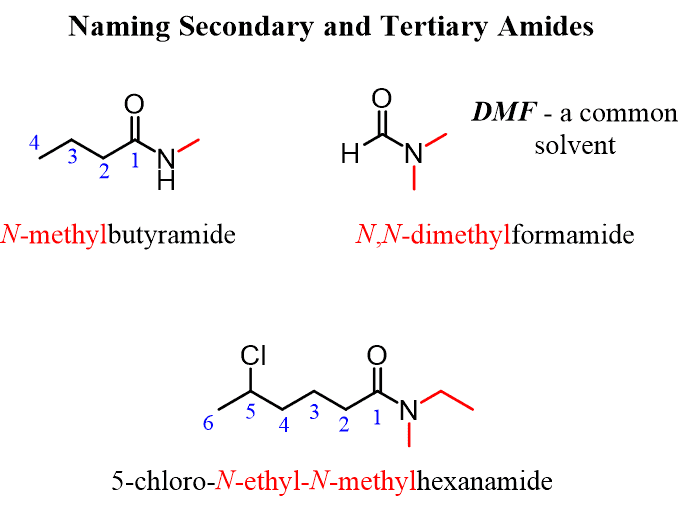
Naming tertiary amides:
naming of these chains is the same as secondary amides
As with standard nomenclature, these chains are listed in alphabetical order and the prefix 'di-' is used if necessary
N-methyl-N-propylethanamide
What type of isomer is optical and other type?
Stereoisomerism:
Geometrical (E/Z)
Optical
stereoisomers definition
molecules with same structural formula but atoms arranged differently in space
Compounds with a chiral centre (chiral molecules) exist as two optical isomers which are also known as _________
enantiomers
enantiomers definition
non-superimposable mirror images of each other just like your left and right hand
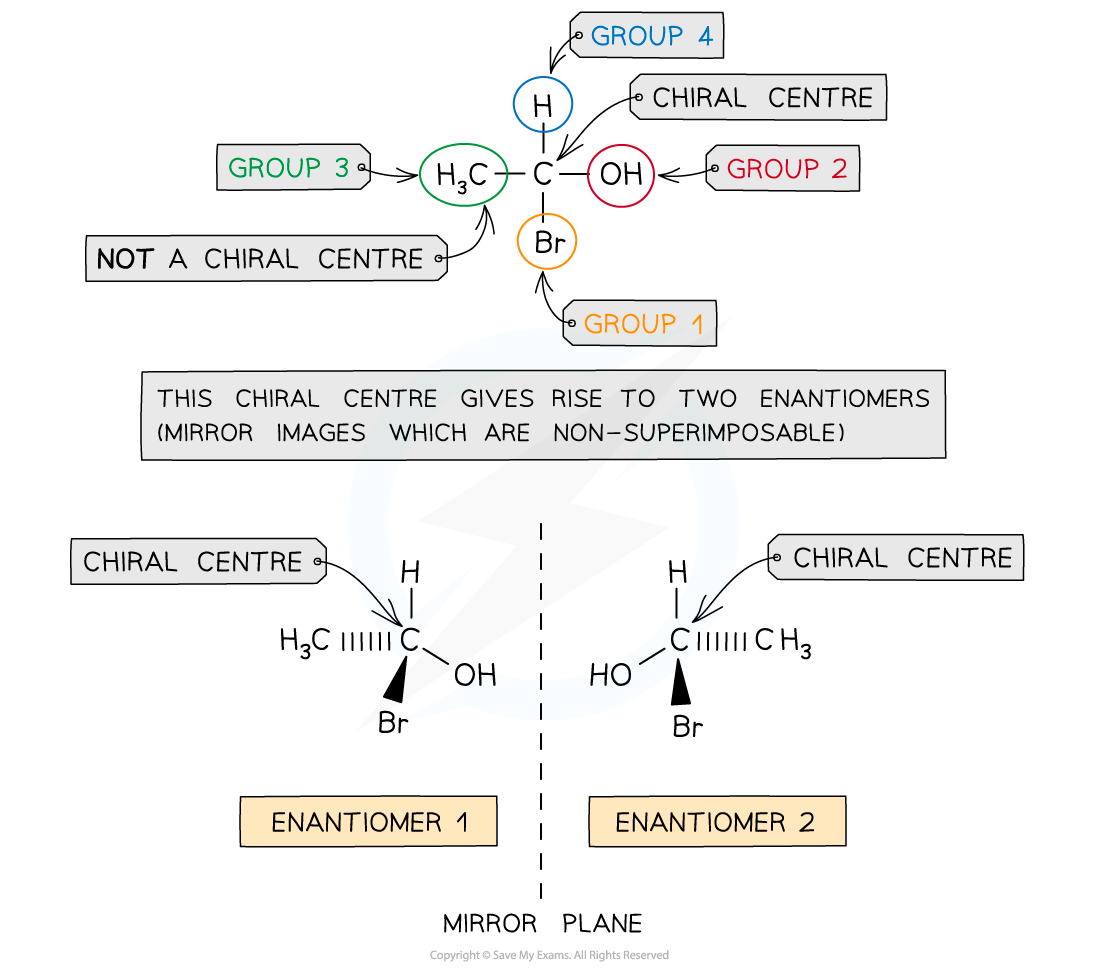
chiral:
Whether a particular carbon is bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms and therefore is chiral
Whether a particular carbon is bonded to two of the same atoms or groups of atoms and therefore cannot be chiral
What are condensation polymers?
polymer is produced by repeated condensation reactions between monomers
condensation polymerisation involves the elimination of a small molecule
Condensation polymers can be identified because the monomers are linked by _____
ester or amide bonds
Condensation polymers can be formed by:
dicarboxylic acids and diols
dicarboxylic acids and diamines
amino acids
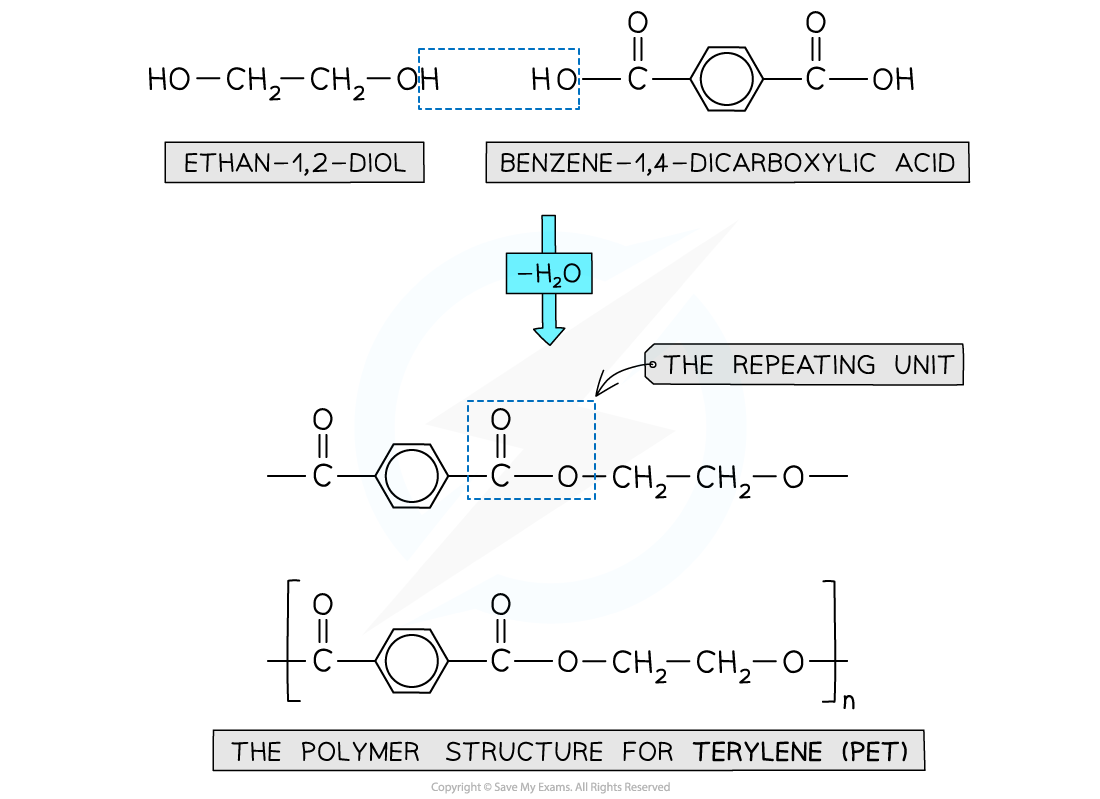
How is polyester formed + what bond forms?
dicarboxylic acid monomers and diol monomers —> one of the -OH groups on the diol and the hydrogen atom of the -COOH are expelled as a water molecule (H2O)
ester bonds
What polyester looks like?

e.g. of polyester
poly(ethylene terephthalate) or PET/Terylene
What PET looks like
Formation of polyesters - hydroxycarboxylic acids
hydroxycarboxylic acids
They contain an alcohol group (-OH) at one end of the molecule while the other end is capped by a carboxylic acid group (-COOH)

What are polyamides?
polymers where repeating units are bonded together by amide links
formula of an amide group is -CONH
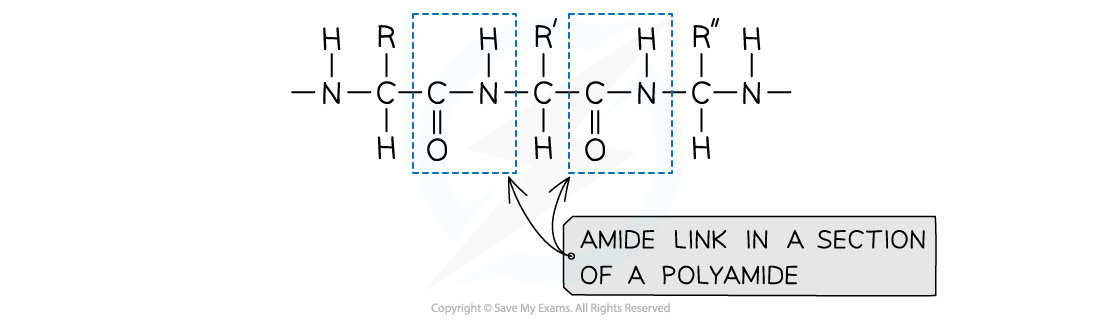
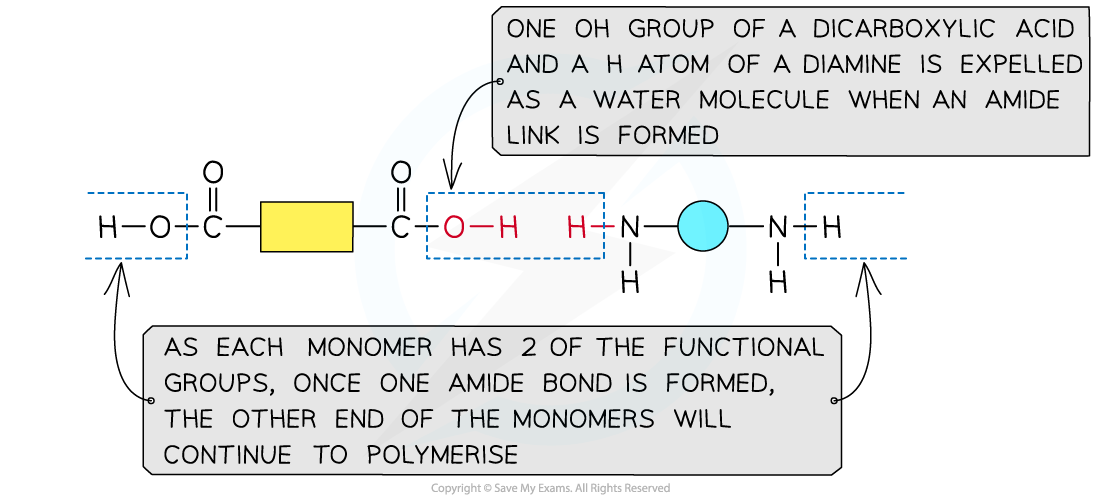
What forms polyamide?
diamine (contains 2 -NH2 groups) and a dicarboxylic acid (2 -COOH groups)
OR
Dioyl dichlorides (Contains 2 -COCl groups) instead of the acid (it is more reactive monomer but more expensive)
What polyamides look like?
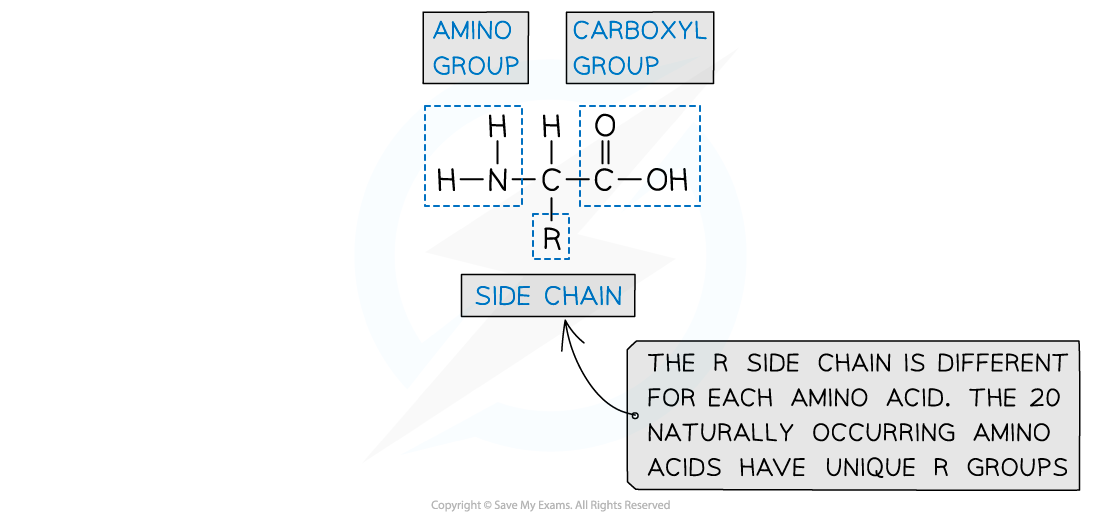
Formation of proteins- amino acids
proteins are made up from amino acid monomers
Amino acids have an aminocarboxylic acid structure
properties are governed by a branching side group - the R group
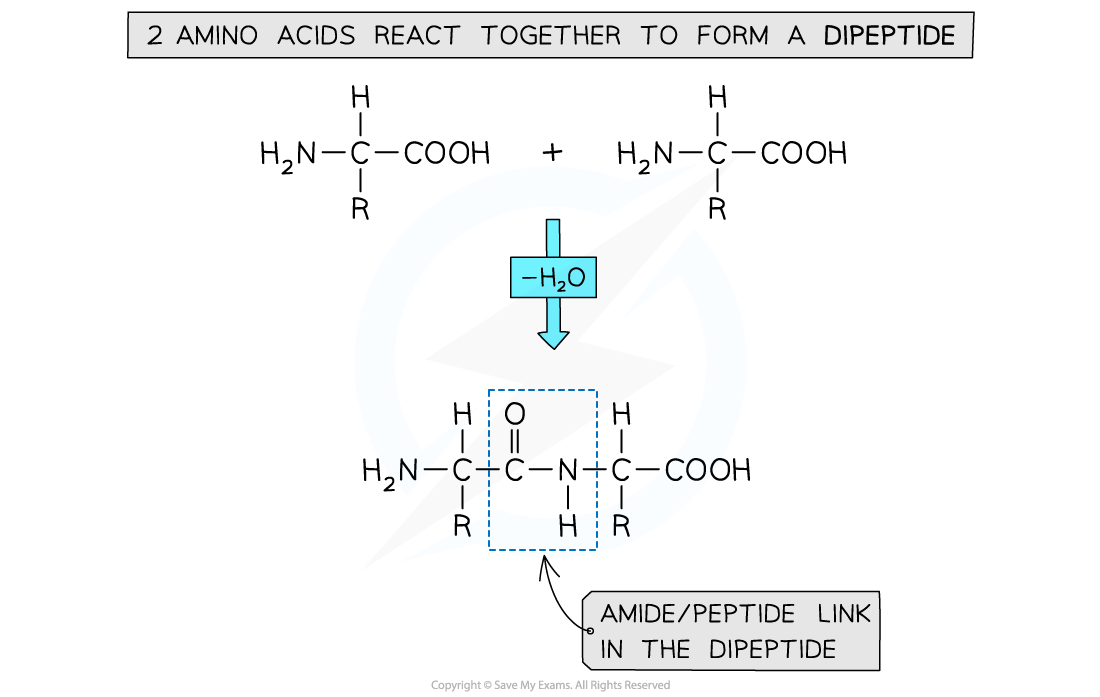
How are dipeptides formed?
polymerising 2 amino acids together
amine group (-NH2) and acid group (-COOH) of each amino acid is used to polymerise with another amino acid
How are polypeptides formed?
polymerising more than 2 amino acids together
Both polyesters and polyamides can be broken down using ____ + what is the advantage?
hydrolysis reactions- at landfill can be easily broken down and products used for other applications
advantage over polymers produced from using alkene monomers
How is acidic hydrolysis done?
an acid (such as hydrochloric acid) acts as the catalyst
Polyamides such as Kevlar are heated with dilute acid
This reaction breaks the polyamide into a dicarboxylic acid and ammonium ions
What is alkaline hydrolysis?
polyamide is heated with a species containing hydroxide ions (eg. sodium hydroxide)
This breaks the polymer into the sodium salts of its monomers (dicarboxylic acid salt and diamines)

Hydrolysis of polyesters:
Ester linkages can also be degraded through hydrolysis reactions
The acidic and alkaline hydrolysis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is shown below
Acid hydrolysis forms the diol and dicarboxylic acid that were used to form the polyesters
Alkaline hydrolysis forms the diol and dicarboxylic acid salt

haloalkane —> amine ( primary)
haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution with ethanoic ammonia to form primary amine:
RX + NH3 —> RNH2 + HX
How do you reduce unwanted side reactions:
excess ammonia
as it deacreases probability of amine reacting with haloalkane rather than ammonia
RX + 2NH3 —> RNH2 +NH4X
How is secondary amine formed?
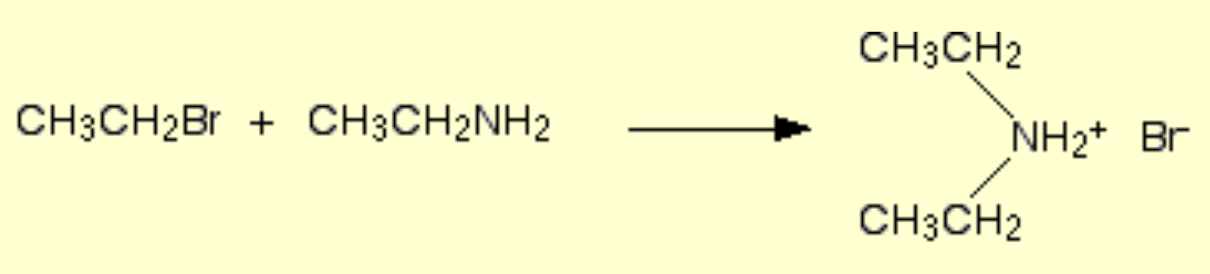
What is another way to form amines?
reduction of nitriles
H2 + Ni cat
What is a nitrile?
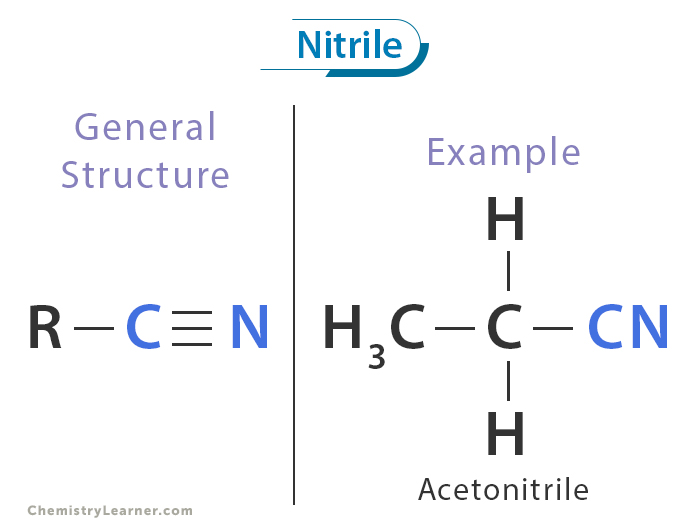
how to make aromatic amines
reduction of aromatic nitro- compound
using tin and conc HCl + reflux
equation is + 6(H) —> H20
As phenylamine is basic what will happen
react with acid to produce ammonium ion can be converted to phenyl-amine by treatment with alkali
C6H5NH3 + OH- —> C6H5NH2 + H20
How amines behave like bases
accept proton
lone pait on N donates a pair forming ammonium salt via datice cov bond
RNH2 + HNO3- —> RH3+ + NO3-
What is alpha amino acid?
NH2 is attached to second carbon atom
2-AMINO ACIDS
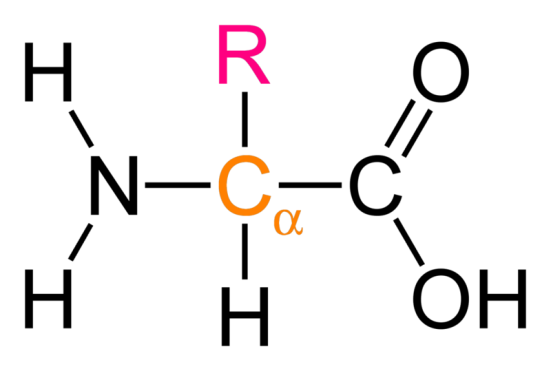
Amino acid acting as acid in aq
H2NCHRCOOH + OH- —> H2NCHROO- + H20
Amino acid acting as base in aq
H2NCHRCOOH + H+ —> H3N+CHRCOOH
acidic condition for esterfication of amino acids are needed to ____
protonate amino group
properties of enantiomers
identical chemical properties and same b.p and solubilities
have different biochemical reactions (react with enantiomers of other substance)
rotate the plane of polarisation of plane polarised light
ammonium ion shape
tetrahedral
ammonia shape
pyramidal