Disorders of Oropharynx
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
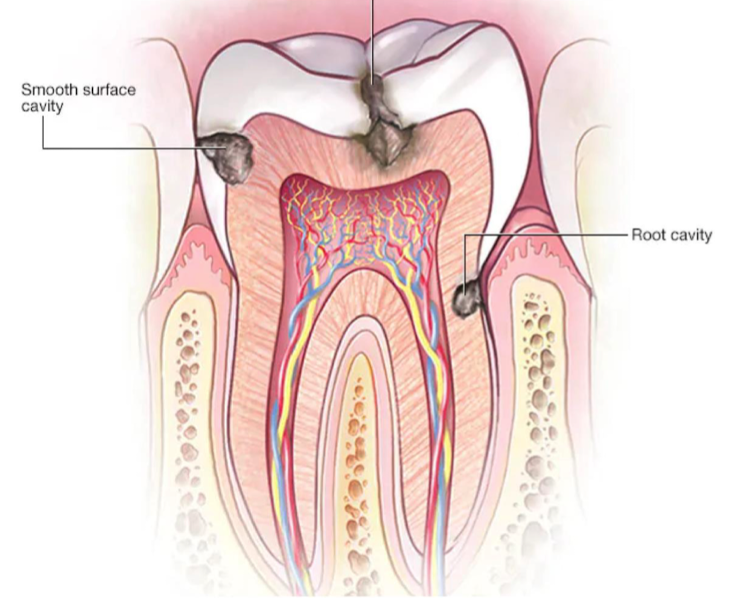
Dental caries clinical features?
Painless discoloration, may progress to painful tooth erosion with irritates the nerve and leads to temperature sensitivity & tenderness with percussion.
AKA cavities.
Dental caries tx?
Good oral hygiene
Dental referral
Pain management in acute setting: dental wax, NSAIDs, dental blocks
Dental caries cause?
Erosion of enamel due to bacterial activity.
Gingivitis causes?
Inflamed gingival tissue caused by bacterial plaques at gum line.
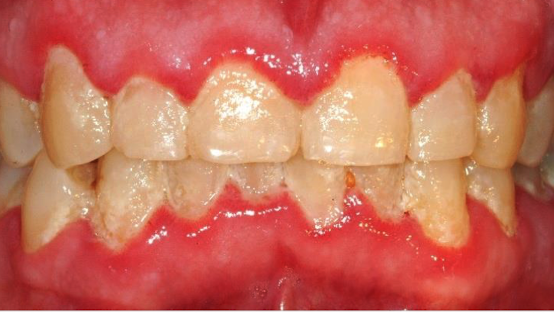
Gingivitis clinical features?
redness/swelling of gums
bleeding with light touch and brushing
gum recession, exposed roots
Gingivitis tx?
Oral hygiene
Dental referral
Mouthwash with bactericidal properties and/or antibiotic rinse
Chlorohexidine
Closys (chlorine dioxide)
Xerostomia clinical features?
Very dry mouth (mucosa/tongue), halitosis and difficulty speaking.
Xerostomia tx?
usually caused as a side effect of medication, so search for medication.
Artificial saliva (biotene)
Referral to ENT, Rheumatology, or Endocrinology to rule out autoimmune disorders.

Antibiotic-associated dental disease clinical features?
permanent tooth discoloration for children < 8 years
crosses placenta - permanent discoloration from utero exposure & long tubular bones with growth inhbition
Effects are less likely with doxycycline.
Antibiotic-associated dental disease tx?
Cease long-term use of tetracyclines
Only use in severe infection cases like Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
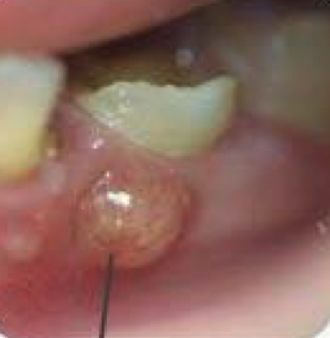
Dental infections clinical features?
Redness/swelling of gums or face
Pain with mastication
Common bacterial causes:
Strep Viridans
Bacteroides
Peptostreptococcus
Dental infections types of absesses (2)?
Periapical (apex of tooth) absess, peridontal abscess (periodontal soft tissues)
Dental infections tx?
I&D
Broad-spectrum ABs: Clindamycin, Augmentin (amoxicillin-clavulnate)
Dental referral
Root canal
Septic cavernous sinus thrombosis
When infection spreads via the pterygoid venus plexus, typically S. aureus or MRSA.
Septic cavernous sinus thrombosis clinical features?
HA, fever, proptosis (eye bulging), chemosis (sclera swelling), periorbital swelling, and cranial nerve palsies, extra ocular muscle weakness.
Septic cavernous sinus thrombosis imaging?
Preferred imaging is MRI venogram and MRI w/ contrast; can do CT w/ contrast
Septic cavnernous sinus thrombosis tx?
Broad-spectrum ABs: Vancomycin, Ceftriaxone and Cefepime; and anti-coagulation (heparin infusion)
Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ)?
Pain within the TMJ potentially caused by:
Injury
Poor head/neck (posture muscular attachments)
Physiological manifestation of stress
Jaw clenching and grinding
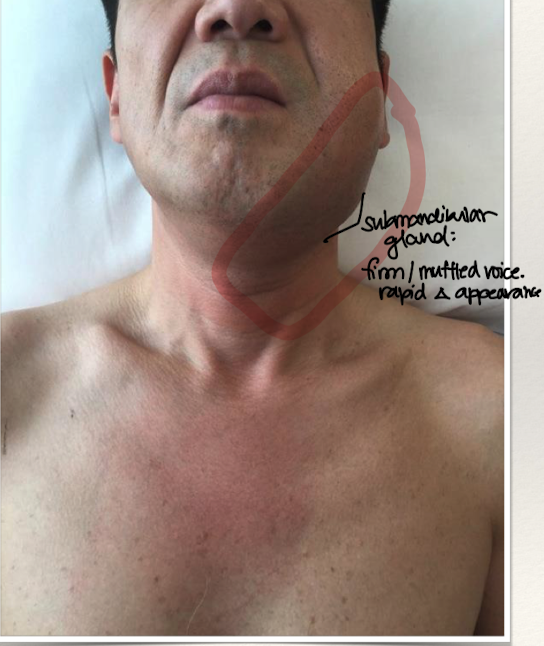
Ludwig’s Angina caused by?
Submandibular space infection: rapidly spreading cellulitis. Typically a bilateral infection of two compartments in the floor of the mouth (sublingual or submylohyoid)
Caused by Streptococcus Viridans & Bacteroides
Ludwig’s Angina clinical features?
Fever/Chills/Malaise
Mouth pain and muffled voice
Swelling of jaw/neck
Airway compromise (may need trach)
Ludwig’s Angina dx?
PE findings and CT scan w/ contrast
Ludwig’s Angina tx?
I&D
IV broad spectrum antibiotics:
Ampicillin-Sulbactam
Ceftriaxone + Metronidazole
Clindamycin + Levofloxacin
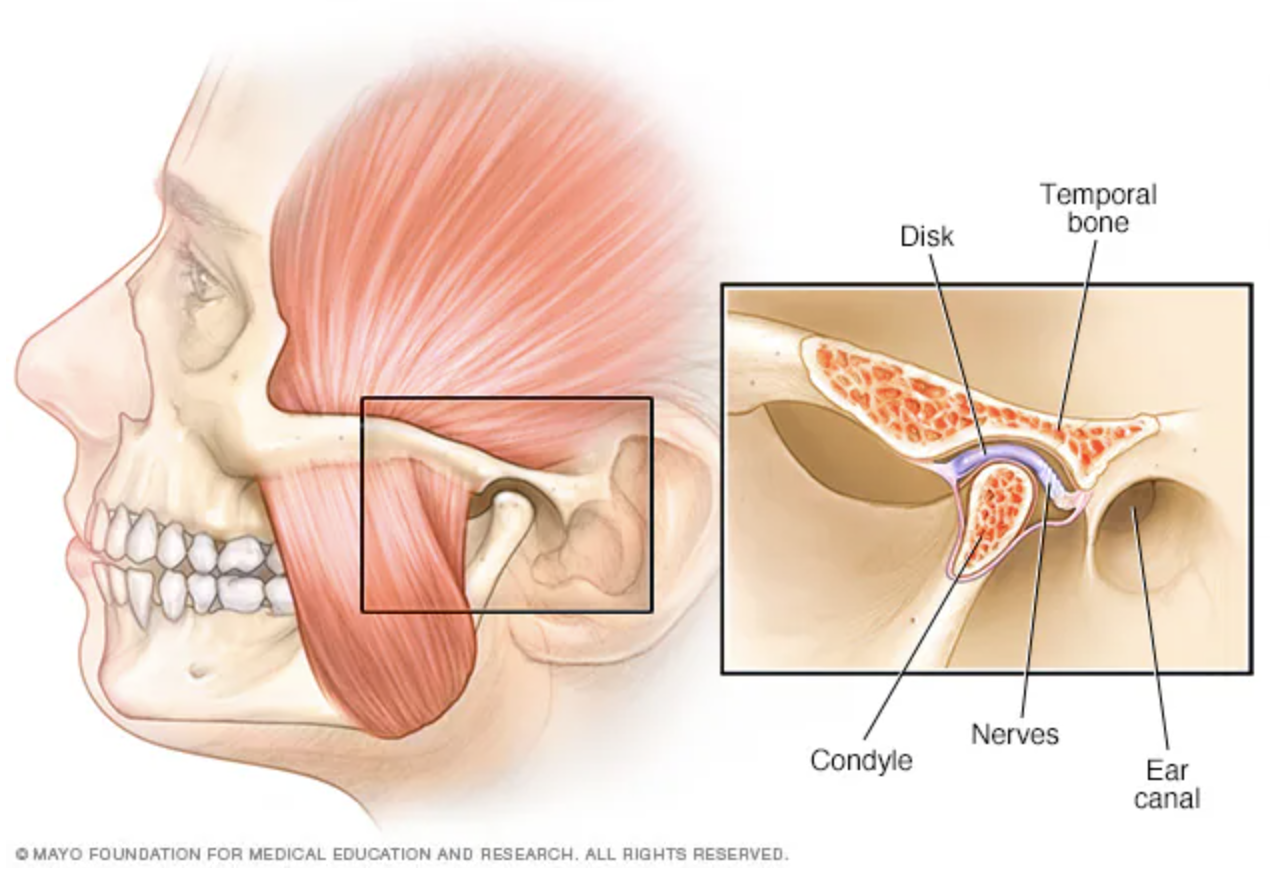
Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ) clinical features?
Pain with TMJ and while chewing, popping or clicking within the TMJ, and headaches.
Sometimes mistaken for ear pain.
Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ) tx?
NSAIDs, night guard, muscle relaxers.
Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ) anterior dislocation sx?
Extreme opening of mouth (eating, yawning, laughing, singing, vomiting, dental treatment)
TMJ ligament weak or torn, or caused by genetic predisposing factors.
Ehlers-Danlos or Marfan syndrome (effects CT disorders)
Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ) lateral and posterior dislocation sx?
Rare, usually due to high-energy trauma.
Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ) clinical features?
Patient cannot close jaw, need to assess for fracture using CT scan or panoramic X-ray.
Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ) tx?
Reduction:
Soft food diet x 2 weeks
Avoid extreme opening of jaw x 3 weeks
Warm compress to TMJ x 24 hours
Support jaw when yawning
NSAIDS (ibuprofen)
And specialist referral.
Techniques to relocate TMJ dislocation?
Syringe technique (rolling a syringe in mouth forward and backward) or manual technique (using thumbs to push mandible down and back).
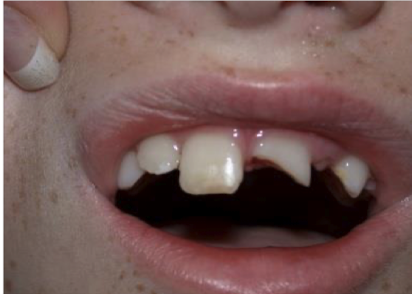
Dental crown fractures (2)
Uncomplicated: enamel or enamel + dentin; complicated: exposed pulp
Dental crown fractures clinical features?
Fractured tooth on exam, dental pain and sensitivity
Dental crown tx?
Urgent Dental referral for complicated
Routine dental followup for uncomplicated
Monitor for additional facial trauma/injuries (CT scan)
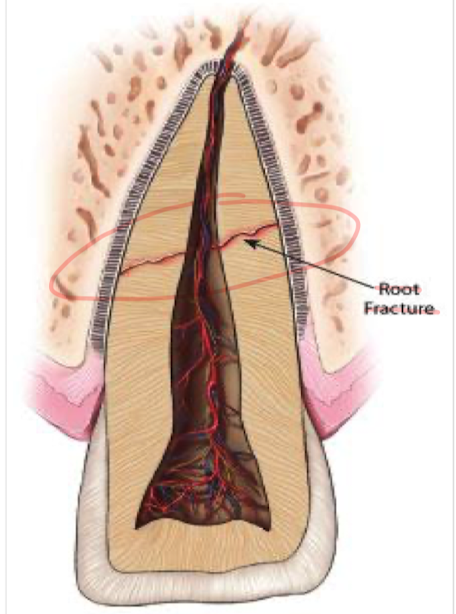
Dental root fractures?
Need x-ray to diagnose, usually mobile teeth after injury
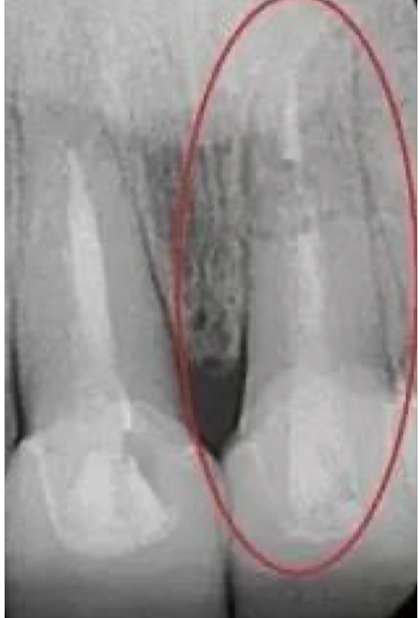
Dental root fractures clinical features?
Dental pain and wobbly tooth (tooth laxity)
Dental root fracture tx?
Dental referral
Tooth splint
Crown removal and root preservation
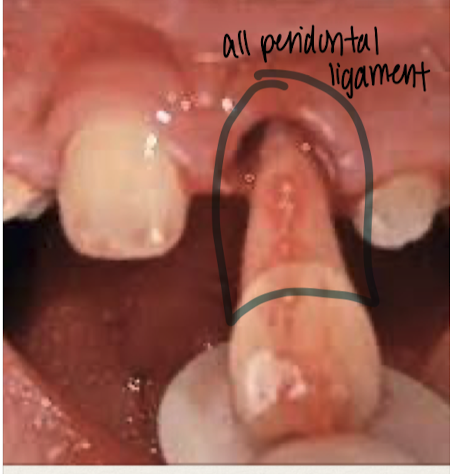
Tooth avulsion
True dental emergency, need to focus on preservation the periodontal ligament
Best practice to keep tooth clean and put back into socket
Tooth avulsion clinical features?
Avulsion of tooth, evaluate for possible alveolar injury (maxillofacial CT scan)
Tooth avulsion tx?
Immediate replanation
Don’t touch periodontal ligament
Remove debris with gentle rinse of water or saline
Manually replant tooth
Tooth culture media or cold milk if unable to replant, or saliva
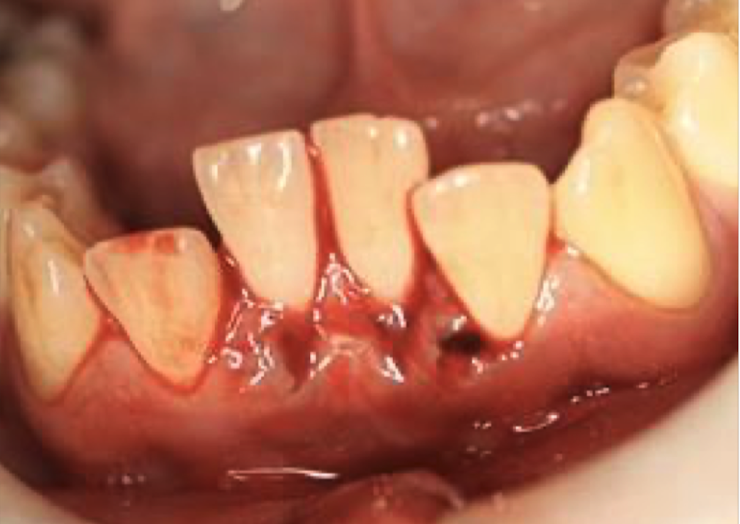
Tooth luxation
Movement of tooth out of socket, usually due to trauma or injury. Can be:
Intrusion: up into the socket
Luxation: lateral or posterior
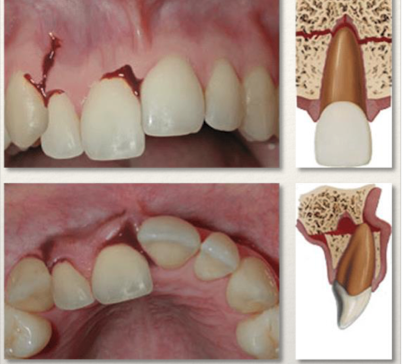
Tooth luxation clinical features?
Tender teeth with bleeding, obvious deformity of tooth in socket, recommend advanced imaging to evaluate alveolar process.
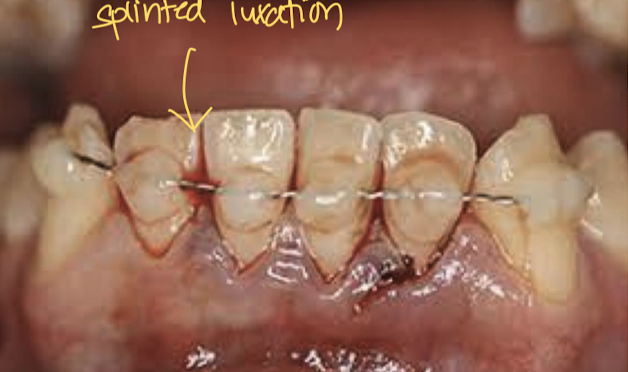
Tooth luxation tx?
Reduce teeth promptly:
May require local anestheia, splinting or gingival sutures (to save tooth)
May require root canal
Dental or oromaxillofacial surgery referral neededx
Maxilla and midline fractures
Usually occurs because of high-energy trauma
Maxilla/facial bone fractures
Potentially serious complications to the vasculature, glands, muscles, nerves
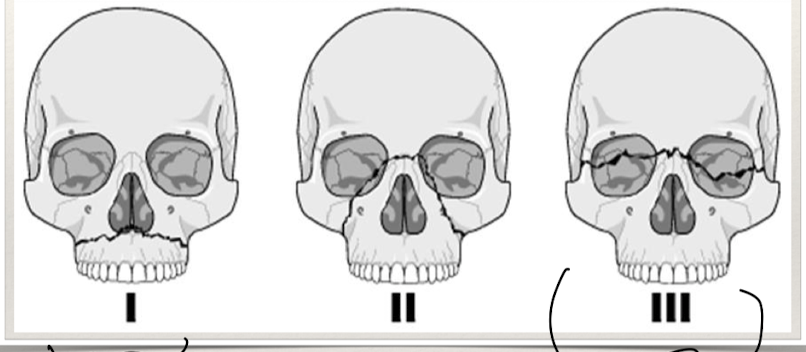
Maxilla and midline fractures clinical features?
Need to see mechanism of injury:
Contusion, ecchymosis (bruising), malocclusion, enopthalmos (sunken eyes), extraocular muscle not intact.
Bleeding
Dysphonia (abnormal voice) or edema or oropharynx
Risk of airway compromise
Nasoethmoid fractures - CSF leak (risk of meningitis)
Lefort fractures
Maxilla and facial fractures tx?
Evaluate with maxillofacial CT scan
Repair lacerations
Plastic surgery/oral maxillofacial surgery consult
Mandibular fracture imaging?
U-shape makes plain film difficult, requires panorex or CT scan.
Secondary to bone structures it is typical to see multiple fractures
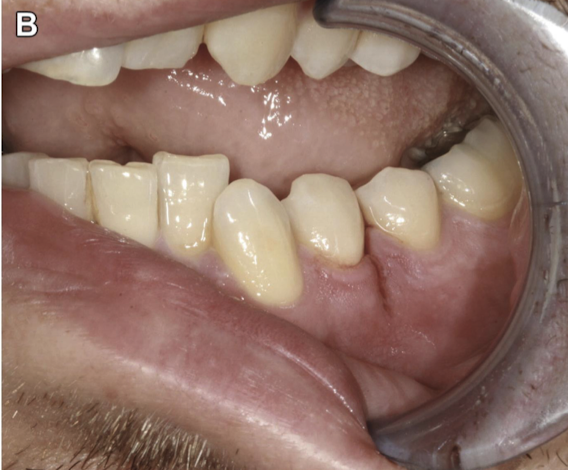
Mandibular fracture clinical features?
Malocclusion, bleeding at gums, step-off, pain with mastication.
Mandibular fractures tx?
Oral maxillofacial or plastic surgery consult, soft and pureed diet.
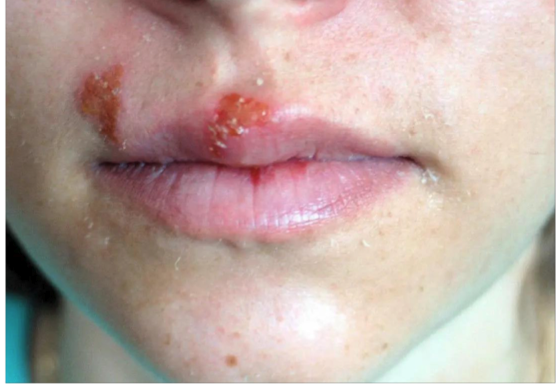
Herpes Simplex Virus infection
Recurrent vesiculoulcerative lesions around the mouth or genitals.
Usually painful vesicles or ulcers.
Typically HSV 1, but can be HSV 2
Recurrent infections are common because latency period is in the neural ganglia, factors involve: sunlight, trauma, or emotional stress, URI
Herpes Simplex Virus clinical features?
painful, itchy ulcers or lesions on the oral or genitals that become crusted lesions on the lip
gingivostomatitis
can present as ulceration within the mouth (cold sores)
fever, HA, cervical or submandibular lymphadenopathy
self-resolves in 1-2 weeks
Herpes Simplex Virus dx testing?
Viral culture & PCR swab - swab the open sore; or Tzanck smear, that shows giant multinucleate cells
Herpes Simplex Virus tx?
Usually self-resolves but can use OTC tx and some antivirals.
OTC: abreva, campho-phenique
Acyclovir or valacyclovir reserved for severe causes
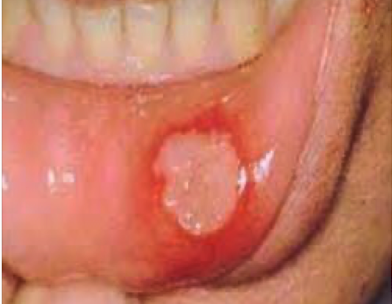
Aphthous Stomatitis aka canker sores
Present as painful ulcers in the oral mucosa and heal within 7-14 days, pathogenesis is known to be multifactoral (immune dysregulation, trauma, or associated with B12 deficiency).
Aphthous Stomatitis clinical findings
Buccal and labial mucosa that turns into a painful ulcer within 1-2 days.
Aphthous Stomatitis dx testing
Hx & PE - can search for additional causes like B12 deficiency, iron levels, skin conditions, or autoimmune diseases
Aphthous Stomatitis tx
First line tx is topical corticosteroids: dexamethasone elixir.
Reduce aggravating factors/foods
Pain control
Abx mouth rinse (chlorhexidine)
Anbesol - topical coating to encourage epithelization
Debacterol - helps to debrief ulcer and encourage epithelization
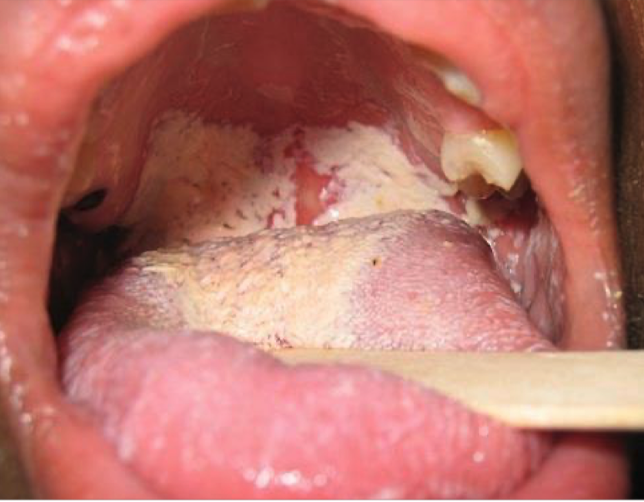
Oral candidiasis (thrush)
Typically infestatiton of Candida albicans
Oral candidiasis clinical findings
Dry mouth, pain while eating/swallowing, loss of taste
Infants/elderly are more commonly affected
Immunocompromised, dentures, antibiotics, or inhaled corticosteroids, AIDS
Oral candidiasis diagnostic studies
KOH prep slide, can see hyphae or budding yeast
Oral candidiasis tx?
Pediatrics: Nystain
Adults: Clotrimazole lozenge
Adults (severe): Fluconazole
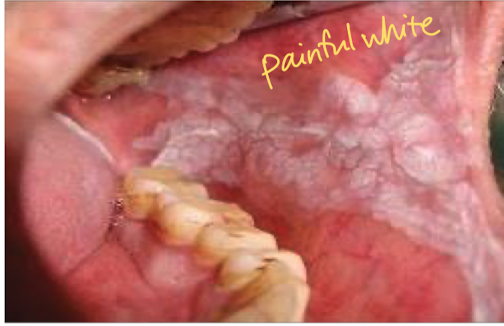
Oral leukoplakia
Painless white patches that can’t be scraped off, irregular with sharply defined borders. Considered precancerous.
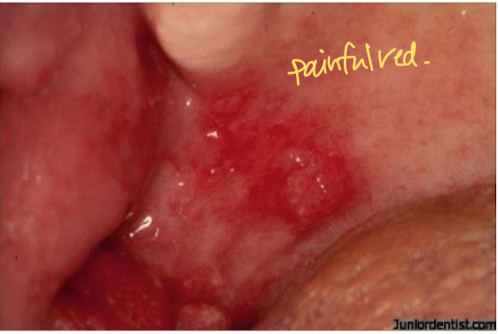
Oral erythroplakia
Potentially painful red macule or patch that is soft in texture, considered cancerous.
Oral leukoplakia or erythroplakia diagnostic studies
KOH prep or biopsy (non-healing, nodularity, bleeding, rapid change/growth)
Oral leukoplakia or erythroplakia clinical features
Can lead to SCC and associated with chronic tobacco and ETOH use
Oral leukoplakia or erythroplakia tx
Monitor, cryotherapy abaltion (precancerous), surgical exision (cancerous)
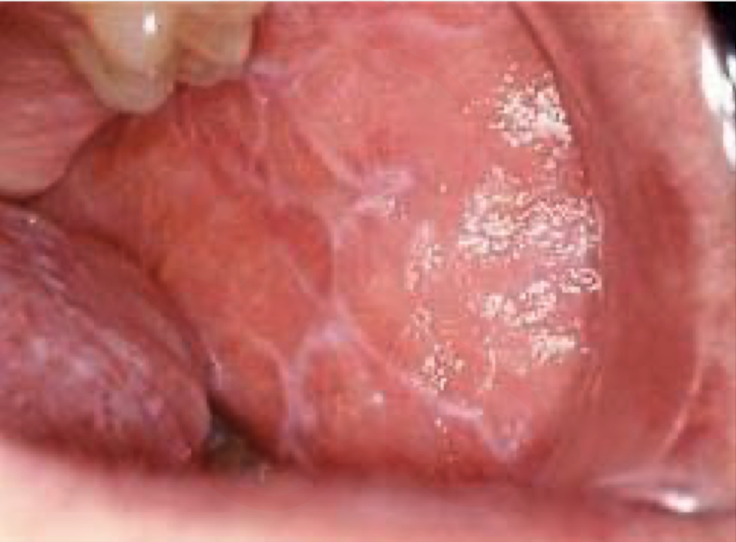
Lichen Planus
Lace-like pattern typically affecting the skin, scalp, oral cavity, genitalia, and nails. Thought to be immune-mediated by activated T-cells.
Lichen Planus clinical features?
Lace-like pattern in the mucous membrane
Erosive mucous membrane dz - painful
Loss of appetite due to pain assoc. with eating
Lichen Planus dx?
Hx & physical, need biopsy to support dx but also to rule out malignancy.
Lichen Planus tx?
First line - topical corticosteroids (Clobetasol)
No cure, just need to alleviate sx
Oral steroids for those who fail topical (Prednisone)
Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD)
Associated with a hx of transplant; results as a complication of transplant when immune cells are recognized as foriegn.
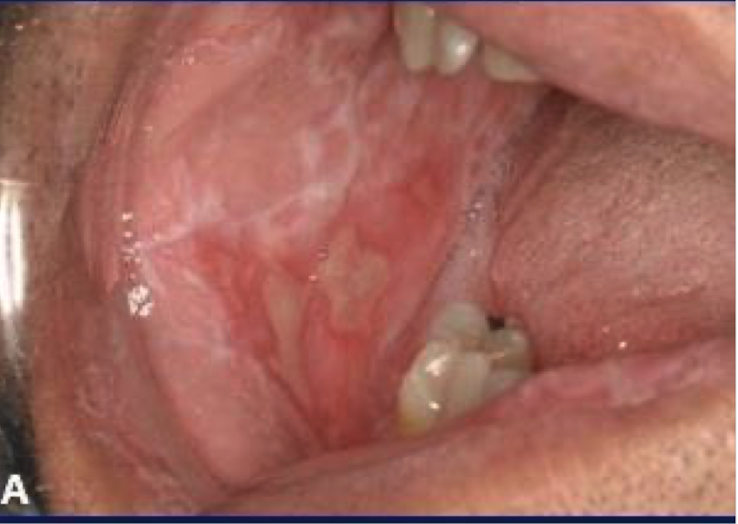
Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD) clinical features
Skin rash & painful mucosa ulcerations
Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD) tx?
Topical steroids
Topical tarcolimus (for transplant rejection)
Specialist - oncologist (stem cell transplant)
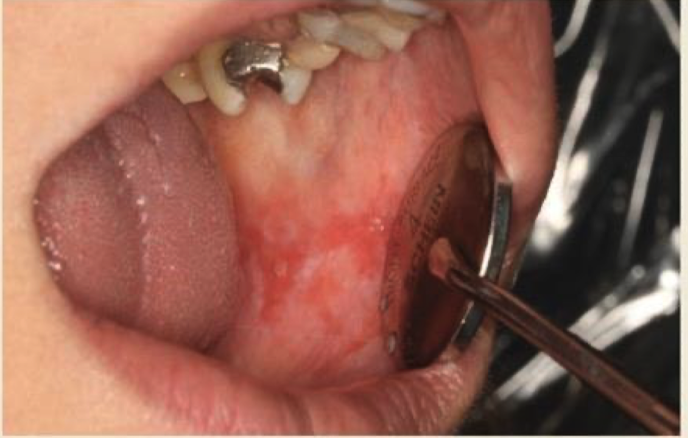
Lupus oral lesions
Chronic autoimmune dz that has multi-organ involvement; 12-45% of lupus patients develop oral lesions
Lupus oral lesions clinical features?
white or erythematous plaques, with punched out ersions/ulcers on the soft or hard palate and/or buccal mucosa.
Lupus oral lesions tx?
Topical corticosteroids
Tacrolimus 0.1% ointment
Hydroxychloroquin
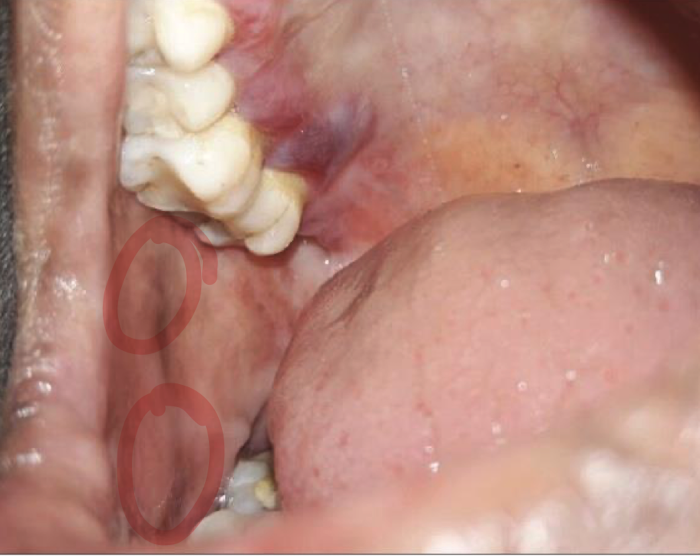
Bullous Pemphigoid
autoimmune dz, subepithelial blister formations
Bullous Pemphigoid clinical findings
Blister formation in the mouth
Bullous Pemphigoid dx?
Tissue biopsy
Bullous Pemphigoid tx?
Topical corticosteroids (Clobetasol propionate)
Systemic corticosteroid (severe cases)
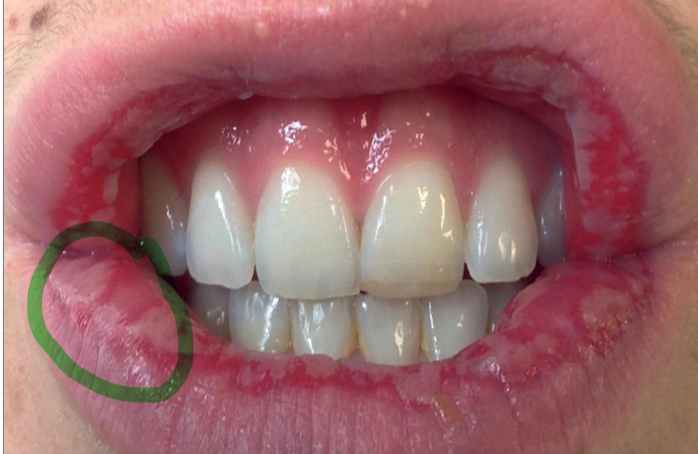
Erythema multiforme
immune-mediated condition with target-like lesions on skin and erosions in the oral mucosa.
Erythema multiforme clinical features
70% of people with erythema multiforme can develop oral lesions
Affect the vermillion lip and mucosal surfaces, gingiva and tongue
Erythema multiforme dx?
Hx + physical and recent herpes tx, biopsy
Erythema multiforme tx?
Only focus on sx relief:
Lidocaine mouthwash (lidocaine, diphenhydramine, aluminum hydroxide)
Oral glucocorticoid therapy
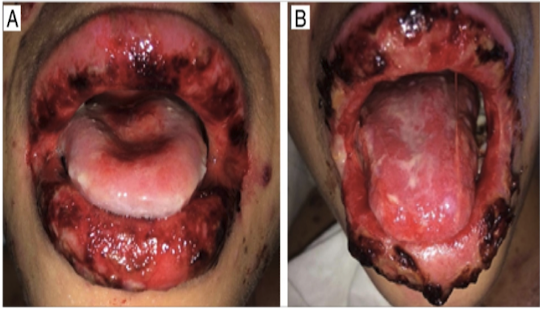
Steven Johnson’s Syndrome/Topic Epidermal Necrolysis
Severe mucocutaneous rxn
Mostly triggered by medications (ABs)
Mucuous membranes affected 90% of patients
Less severe (SJS) and more severe (TEN)
Steven Johnson’s Syndrome/Topic Epidermal Necrolysis clinical findings
painful hemorrhagic erosions
diffuse
high risk of bacterial infection (bacteremia & sepsis)
Steven Johnson’s Syndrome/Topic Epidermal Necrolysis tx?
Supportive care
Pain control
Hospitalization/burn unit/ICU
AB for secondary infection
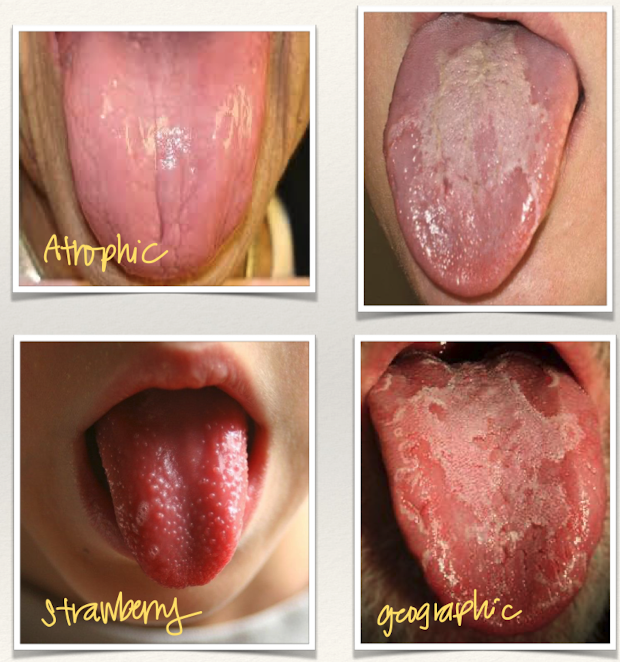
Glossitis
Inflammation of the tongue, caused by nutritional deficiencies, drug reactions and xerostomia.
Forms: geographic tongue, strawberry tongue, and atrophic tongue.
Glossodynia
Tongue pain (burning), can occur with glossitis.
aka “burning mouth syndrome”
tx: supportive care
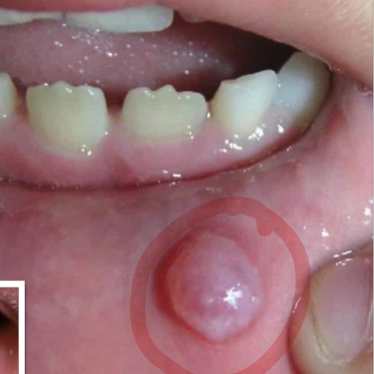
Mucocele
Caused by trauma (lip biting) disrupting the minor salivary glands.
Mucocele clinical findings
Pink/blue soft papule or nodule in varying sizes, typically found on the lower lip.
Mucocele tx?
Can pop or drain with an 18 gauge needle, but is also self-resolving.
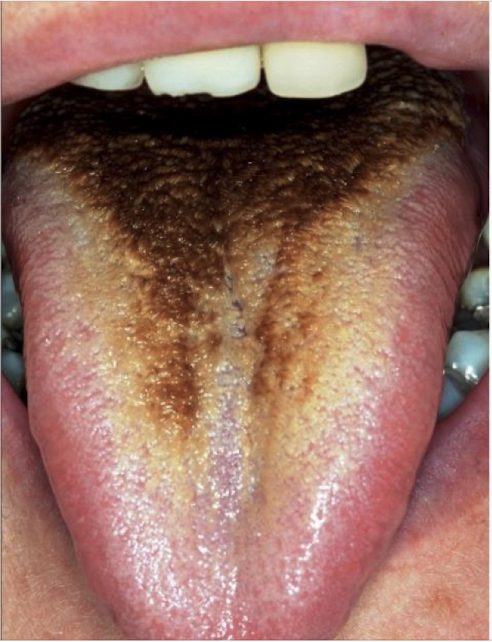
Black hairy tongue or Lingua Villosa Nigra
Elongated filiform papillae (due to inadquare desquamation), has yellowish-brown discoloration of tongue surface
Seen with smoking, AB use and poor oral hygiene
Benign and often asymptomatic.
Black hairy tongue or Lingua Villosa Nigra clinical features?
Not painful, yellowish-brown discoloration
Black hairy tongue or Lingua Villosa Nigra tx?
Brushing or scraping 2-3x daily and improved oral hygiene.
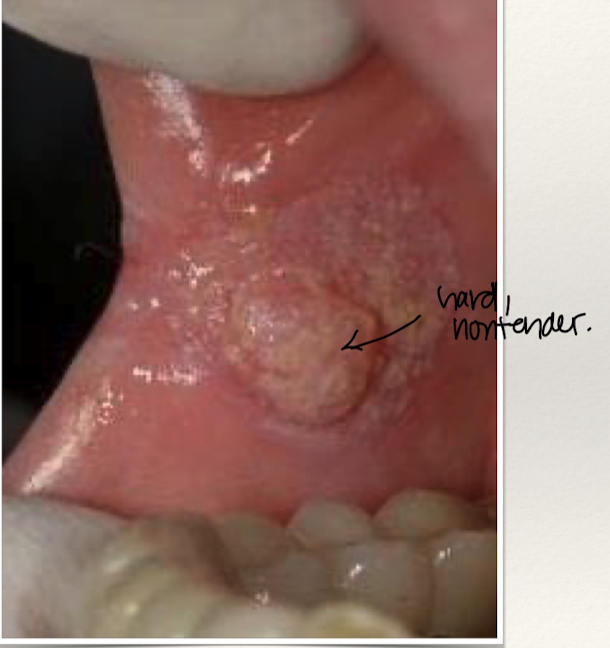
Oral cancer (squamous cell carcinoma)
90-95% of oral cavity lesions, develops through premalignant changes (leukoplakia/erythroplakia) carcinogen exposure.
Associations with:
Tobacco/ETOH
Genetic
HPV
Oral cancer SCC clinical findings
Mouth/throat cancer can be present with otalgia (ear pain)
Lesion on mucosa or tongue (hard, firm, non-healing wound)
Remove dentures to fully check for complete PE
Neck mass
Oral cancer SCC tx
surgical excision, chemo/radiation
Oncology/ENT referral
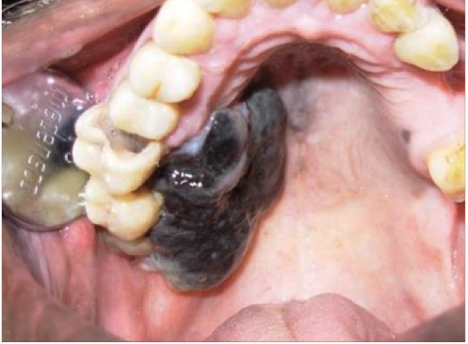
Oral cancer melanoma
Most serious form of oral cancer, mucosal has worse prognosis than cutaneous melanoma
Oral cancer melanoma clinical features
Hyperpigmented lesion within the oral cavity and mucosa
Oral cancer melanoma tx?
Wide local surgical resection, risk of morbidity with aggressive resection and balance against risk of metastatic disease
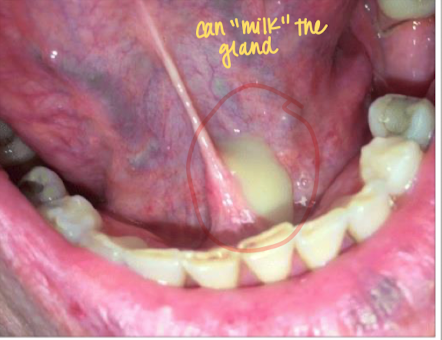
Sialoadenitis
inflammation of one of the three salivary glands: parotid, submandibular or sublingual
Sudden enlargement & pain along affected gland
Obstructive, infectious or inflamatory
Can be viral or bacterial