Ecology Exam 2
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 6-11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
All life on Earth is…
Carbon based
Photosynthesis
Light energy drives a series of reactions that result in the fixation of CO2 and the release of O2.
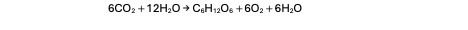
Photosynthetic pigments absorb…
Visible light
Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR)
Portion of the solar radiation spectrum.
Light-dependent reactions
Captures energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH.
Light-independent reactions
Uses that stored energy to convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrates, like glucose, without directly requiring light.
Carboxylation
is the rate-limiting reaction of carbon assimilation
is catalyzed by an enzyme; rubsico
is divided into three stages: carboxylation, reduction, and regeneration
CO2 + RuBP (5-C) + 2 3-PGA (3-C)
Plants use cellular respiration to…
convert the energy in sugars and other molecules into ATP.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Net Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis - Respiration
The amount of CO2 used in photosynthesis -minus the amount of CO2 lost in respiration =…
The availability of light directly influences…
the rate of photosynthesis
When it is dark and there is no PAR available
only respiration occurs
As available light increases…
the rate of photosynthesis increases
Light Compensation Point (LCP)
is the light level (PAR) at which… CO2 uptake photosynthesis = CO2 loss in respiration
rate of net photosyntheis is zero.
As light levels exceed the LCP…
the rate of photosynthesis increases with PAR.
Light Saturation Point
Value of PAR above which photosynthesis does not increase.
Photohibition
The rate of photosynthesis will decline as PAR exceeds the saturation point (seen in some shade-adapted plants)
Stomata
openings on the leaf surface that allow CO2 to enter; found on terrestrial plants.
Stomata are usually open when…
the concentration of CO2 inside the leaf is lower than the air around it.
Stomata are usually closed when…
photosynthesis and the demand for CO2 are reduced for any reason.
Transpiration
when the stomata are open, water vapor in the leaf diffuses out
Transpiration rates depend on…
the diffusion gradient and stomatal conduction of H2O vapor.
Turgor Pressure
the force exerted outward on a cell wall by the water inside the cell.
Plants take up water from the soil by their…
roots and transports that water to their leaves.
Water potential (ψ)
The difference in Gibbs energy between the water in the soil-plant-atmosphere continuum and pure water. expressed in terms of pressure (energy per volume) using Pascals.

Movement of water in a plant goes from areas of … potential to …. potential
higher, lower

Scaling
process of changing morphological & physiological features as a function of body size
How to transport O2
-Increase surface area but keep same volume
-Transport O2 to interior of body via tube shape
-Larger organism with more complex systems.
Herbivory
-Animals feed exclusively on plant tissue
-Plants are low in protein and high in carbohydrates
-Adaptations:
1) Lack enzyme to breakdown cellulose, depend on specialized bacteria/protists in digestive tract; ex: cows
2) Breeding times coincide with plant growth times
3) Favor N2 rich plants
Carnivory
-Feeds exclusively on the tissue of other animals
-Few problems with digesting and obtaining nutrients.
-Problem: obtaining enough food (quantity > quality)
-Many eat herbivores
Omnivory
-Feeds on tissue of plants AND animals
-Food habits may change w/ season, life cycle stage, size, and growth rate.
-Means of getting food has been a major selective agent in process of natural selection
Detritivores
Feed on dead plant and animal matter
Conformer
exterior enviro change causes internal changes in the body (conforming to their environment)
is unable to maintain consistent internal condition (ex: salinity, O2 levels/oxygen concentration)
Regulator
use various mechanisms to regulate interior enviro… changes in the external environment DOES NOT cause internal changes.
requires A LOT of energy to change in biochem, physio, morpho, and behavior.
Option 3 with when an animal experiences changes in the environment
a single species may use a different strategy under different conditions or in different activities… Ex: active girdled lizards regulate body temperature while inactive lizards do not.
Homeostasis
maintenance of relatively constant internal enviro in a varying exterior enviro
Animals extract _ energy from the organic compounds in food they eat
energy
Terrestrial atmospheric oxygen
is readily available
Aquatic oxygen
-Aquatic insects come to surface to fill tracheal system or carry air bubble.
-Marine mammals come to surface for O2 (ex: whales and dolphins)
3 ways to obtain water
Drink
Eat
Produce metabolic water during respiration
Ways to lose water
Waste (urine/feces)
Evaporation from skin
Exhaling air with vapor
Adaptation to water intake v. loss
-Cloaca: common receptacle for digestive, urinary, and reproductive tracts in birds and reptiles; water reabsorbed from cloaca to body
-Salt gland
-Mammals have kidneys that produce urine with high ion concentration
-Migration is an option
-Estivation
-Diapause
-Physiological ways to reduce respiratory water loss during dry season (Ex: some rodents lower the temperature of the air they exhale)
Estivation
Period of dormancy to avoid effects of drought, used by some animals in arid regions (physiological inactivity)
Diapause
Stage of arrested development in life cycle to emerge w/ improved conditions, used by many insects.
Thermal conductivity
ability to conduct or transmit heat
Ecthothermy
Maintains body temp by exchanging thermal energy w/ surrounding environment (heat w/o) dependent on external temperatures
Poikilotherms = cold-blooded
Endothermy
maintains body temp by generating metabolic heat
Homeotherms = warm-blooded
Heterothermy
combination of endo and ectothermy
Animals regulate body temperature through…
behavior, physiology, morphology
Poikilotherm Temp Regulation
-Performance (ex: locomotion, growth, development) varies with temp.
-Topt: temp/range of temps where performance is optimal
-Tmin/Tmax: min and max temps where performance reaches 0. Performance is optimal at Topt.
-Relies largely on behavioral thermoregulation; they seek out microclimates where enviro temps allow body temps to approach optimal value.
Insulation
keeps body heat in and keeps enviro heat out
Water loss from _ will continue as long as…
transpiration;
light energy supplies enough heat for evaporation, moisture is available in the soil, roots maintain a lower water potential than the soil, if there’s no rain- eventually gradient will be lost
Water Use Efficiency
the ratio of carbon fixed per unit of water lost
Aquatic autotrophs (plants, algae, and phytoplankton) get carbon by…
-CO2 diffuses from the atmosphere into surface waters and mixes into the water column
-Some can use bicarbonate as a carbon source using the enzyme carbonic anhydrase
Tmin
minimum temperature
(net photosynthesis near zero)
Tmax
maximum temperature
(net photosynthesis near zero)
Topt
range of temperatures over which net carbon uptake is highest
Terrestrial plants lose heat by _ and _
evaporation, convection
Aquatic plants lose heat by _
convection
Convection
transfer of heat energy through the circulation of fluids (air/water)
Conduction
transfer of heat energy from one object to another by direct contact
Boundary layer
the layer of still air or water next to the surface of each leaf