Clin Path - Exam 2 w/ Assignments
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
You centrifuge a urine sample that is reddish-brown. After centrifugation, the supernatant loses its reddish-brown color. The sediment is still reddish-brown. What is most likely present in this urine sample?
Intact RBCs (hematuria)
You are viewing a typed print background through a urine sample in a clear, transparent tube. You cannot see any of the typed print when looking through the sample, and there are visible particles floating in the sample. How will you record this result on your UA report?
Turbid & Flocculent
You centrifuge a urine sample that is reddish-brown. After centrifugation, the supernatant and the sediment are both still reddish-brown. What could most likely be present in this urine sample based on these results?
Heme proteins from RBCs (hemoglobinuria) & heme proteins from muscle cells (myoglobinuria)
What is the range for Urine Specific Gravity (USG) for a patient that is 'isosthenuric'?
1.008 - 1.012
What urine biochemical tests detects protein in the urine?
SSA turbidity test
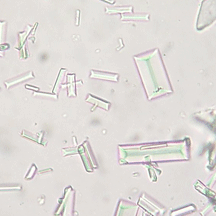
What are the structures in the image shown?
Struvite crystals

What are the structures in the image shown?
Calcium oxalate dehydrate crystals
What factors play a role in the formation and observation of crystals in the urine?
Urine pH, animal’s diet, concentration of the elements that form crystals present in the urine, & urine temperature
What cell types is the largest cell type found in the urine sediment?
Squamous epithelial cells
When you evaluate urine sediment, which magnification should you use to identify and quantify any cells that are present?
40X
What types of inflammation would be mostly composed of neutrophils?
Suppurative
When bacteria are present inside of a WBC, the cell is:
Septic
What tissue cell types is most commonly observed on the normal healthy ear swab or skin scrape cytology from a dog or cat?
Epithelial cells
What pieces of information can you obtain by performing histology?
Arrangement of cells in relation to neighboring cells, number and type of cells present, criteria of malignancy of cells if present, & characteristics of the cytoplasm and nucleus of cells
How many signs of malignancy must be present for a cytology to be called 'malignant'?
At least 3
What type of inflammation would be mostly composed of neutrophils?
Suppurative/Purulent
If pyogranulomatous inflammation is present, which WBCs would you expect to find increased on cytology examination of the sample?
Neutrophils & lymphocytes
When bacteria are present inside of a cell, the cell is described as:
Septic
If a cytology sample is classified as malignant, what conditions must be met?
3 or more signs of malignancy are present
What pieces of information can histology provide that cytology cannot?
Arrangment of cells according to their arrangement in the body
If you are using the wet mount to evaluate urine sediment, you should report your findings using what rules?
Report results only from the unstained sample. Use the stained sample only to confirm the identification of structures.
If you want to confirm the presence of WBCs in an animal's urine, what should you do?
Make a slide and evaluate the urine sediment looking for the presence of WBCs.
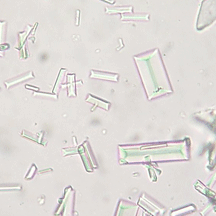
This structure is observed in a urine sediment from a dog on 40X. What is the structure?
Struvite crystals

This structure is observed in a urine sediment from a dog on 40X. What is the structure?
Calcium oxalate dehydrate crystals
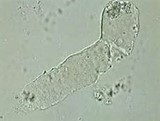
This structure is observed in a urine sediment from a dog on 10X. This structure is formed in the renal tubules of the kidneys and appears colorless, transparent, and has rounded ends. It is primarily composed of protein. What is the structure?
Hyaline cast
If visible particles are observed floating within the urine sample, you would describe this using which term?
Flocculent
What cell is the largest found in the urine sediment?
Squamous epithelial cells

Which of the urine samples shown in the image is likely to have a lower Urine Specific Gravity?
A
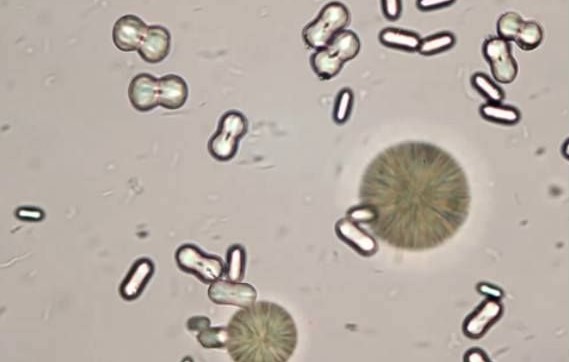
These structures were found in the urine of a horse observed on 40X. What are the structures?
Calcium carbonate crystals
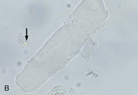
This structure is observed in the urine sediment of a cat on 10X. This structure is formed in the renal tubules of the kidneys and has squared ends and a dull, colorless to gray appearance. Ignore the arrow in this image. What is the large structure?
Waxy cast
If you state that the urine is clear, which characteristic of urine are you describing on your UA?
Clarity
What does it mean when you describe urine as being 'isosthenuric'?
The plasma from blood is unaltered as it passes through the kidneys meaning that the concentration of plasma and urine are the same.
Which stain is commonly used to stain cytology samples with blood contamination or high concentrations of cells?
New Methylene Blue

You are evaluating the clarity of the urine sample in the image. What would you report for the clarity of this sample?
Turbid
Which biochemical test is used to confirm the presence of bilirubin and bile pigments in the urine?
Ictotest
Which biochemical test is used to confirm the presence of protein in the urine?
SSA turbidity test
Which biochemical test is used to confirm the presence of sugars in the urine?
Clinitest
What would not be considered a component of the urine sediment?
Protein
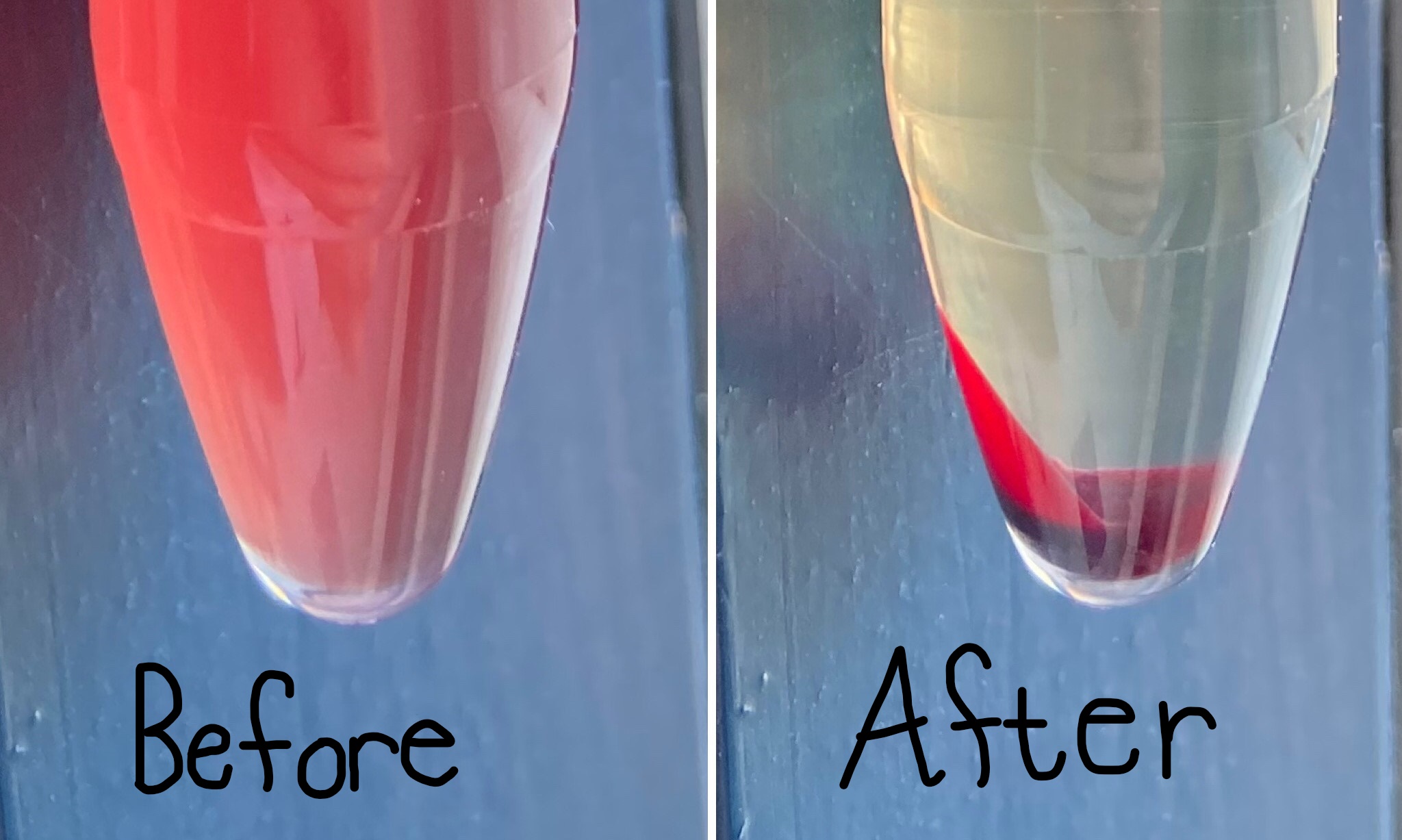
You have a urine sample that appears red in color. You centrifuge that sample and notice that the supernatant loses the red color while the sediment still appears red. What is happening?
There are intact RBCs in the sample (hematuria).
What magnification would you use to report casts?
10X
What magnification would you use to report crystals?
40X
What magnification would you use to report cells?
40X
What magnification would you use to report bacteria?
40X
What would provide the most accurate measurement of urine specific gravity (USG)?
USG measurement of fresh urine using the refractometer
If urine has a distinctly fruity odor, what does this mean?
The urine contains ketones
When you evaluate the clarity of a urine sample, you gain information about what?
Amount of sediment present
What do you learn about your patient's health status by measuring the urine specific gravity (USG)?
Hydration status and kidney function
What is classified as a Romanowsky-type stain that is commonly used in veterinary practice?
Diff Quik
What conditions of crystal formation in the urine can be altered when the sample is refrigerated?
Temperature of the urine
What is the average urine specific gravity (USG) for a horse?
1.035
What is the average urine specific gravity (USG) for cattle?
1.015
What is the average urine specific gravity (USG) for sheep?
1.030
What is the average urine specific gravity (USG) for a dog?
1.025
What is the average urine specific gravity (USG) for a cat?
1.030
If an inflammatory fluid contains increased numbers of macrophages on cytological examination, which type of inflammation is present?
Granulomatous
Cells observed on a urine sediment exam should be reported as:
Average number of cells per number of microscopic fields examined.
You collect a sample from a mass on the liver of a dog using ulstrasound guided biopsy techniques. You make a slide, stain it, and observe mesenchymal cells on cytology. The cells are all of the same type, size, shape, and appearance. The pathology report comes back from the lab stating that the cytology sample is benign. What does this mean?
No signs of malignancy are present
How many RBCs can be present in the voided urine of an animal but still be considered normal?
No more than 2-3 RBC’s per HPF
Why are renal and transitional epithelial cells reported as non-squamous epithelial cells when observed during examination of urine sediment?
They are not easy to differentiate from one another but are easy to differentiate from squamous epithelial cells cytologically in urine.
Which type of inflammatory fluid has the highest concentration of cells and protein?
Exudate
This cell has bright red to pink to orange granules in the cytoplasm. These cells are often increased when parasitic infections and certain neoplastic conditions are present. What is the name of this WBC?
Eosinophil
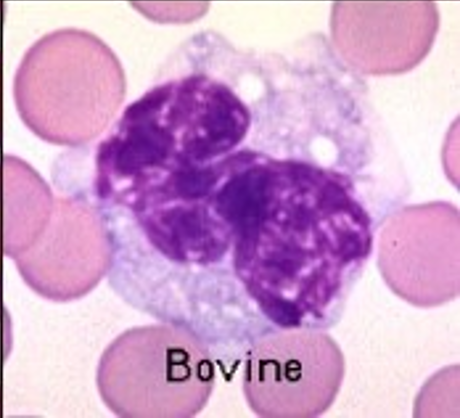
This cell has nonstaining areas within its cytoplasm that are called vacuoles. This is the largest of the WBCs and is usually increased when parasitic or fungal infections are present. What is the name of this WBC?
Macrophage
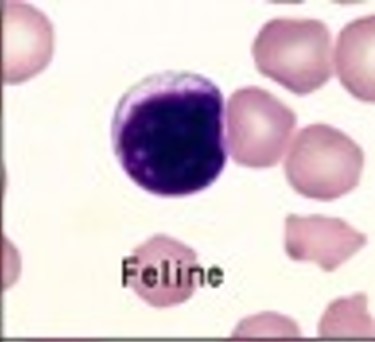
This cell has a small amount of blue cytoplasm and a large nucleus that almost completely fills the cell. This is the smallest of the WBCs. What is the name of this WBC?
Lymphocyte
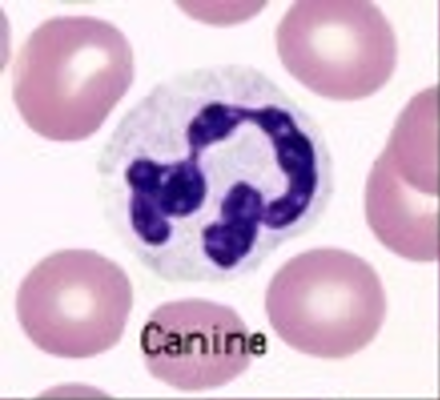
This cell has pale blue cytoplasm and a nucleus with 3 to 5 lobes. This cell is the first to respond during any inflammatory response.
Neutrophil
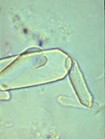
This structure is often present in increased amounts when ethylene glycol toxicity is suspected; however, this structure can also be present in small numbers in healthy animals due to their diet. What is this structure found in the urine sediment of a cat?
Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals
Which of the following biochemical tests are ignored on chem strips when analyzing urine from animals in veterinary medicine?
Urobilinogen
What are the signs of malignancy?
Pleomorphism, anisokaryosis, & increased mitotic activity