MGKT 2080 Chapter 14 McGraw Hill Connect
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
price
the overall sacrifice a consumer is willing to make to acquire a specific product or service
instead of generating costs, price generates _____
revenue
____ is the most challenging of the four P's
price
What are the 5 C's of pricing?
company objectives
customers
costs
competition
channel members
profit orientation
a company objective that can be implemented by focusing on target profit pricing, maximizing profits, or target return pricing
target profit pricing
- pricing strat
- profit goal is overriding concern
- uses price to stimulate certain level of sales at a certain profit per unit
maximizing profits
- profit strat
- relies primarily on economic theory
- analyze mathematical model that predicts sales and profits
target return pricing
- pricing strat
- more concerned with rate of generated profit
- designed to produce a specific return or investment
sales orientation
based on the belief that increasing sales will help the firm more than will increasing profits
premium pricing
- a competitor-based pricing method
- firm deliberately prices a product above other to capture consumers who always shop for the best and price doesn't matter
competitor orientation
firm strategizes according to the premise that they should measure themselves primarily against their competition
competitive parity
a firm's strategy of setting prices that are similar to those of major competitors
status quo pricing
charging a price identical to or very close to the competition's price
customer orientation
based on the premise that firm should measure itself primarily according to whether it meets its customer's need
customers
- the second C
- lays the foundation of economic theory
- explain how prices are related to demand
a ______ ______ shows how many units of a product or service consumers will demand during a specific time at different prices
demand curve
a demand curve can be either curved or...
straight
the horizontal axis
measures quantity demanded and plots it against the vertical axis
the vertical axis
measures the various price possibilities
point
represents quantity demanded at specific price
prestige product and service
consumers purchase for their status rather than their functionality
price elasticity of demand
measures how changes in a price affect the quantity of the product demanded
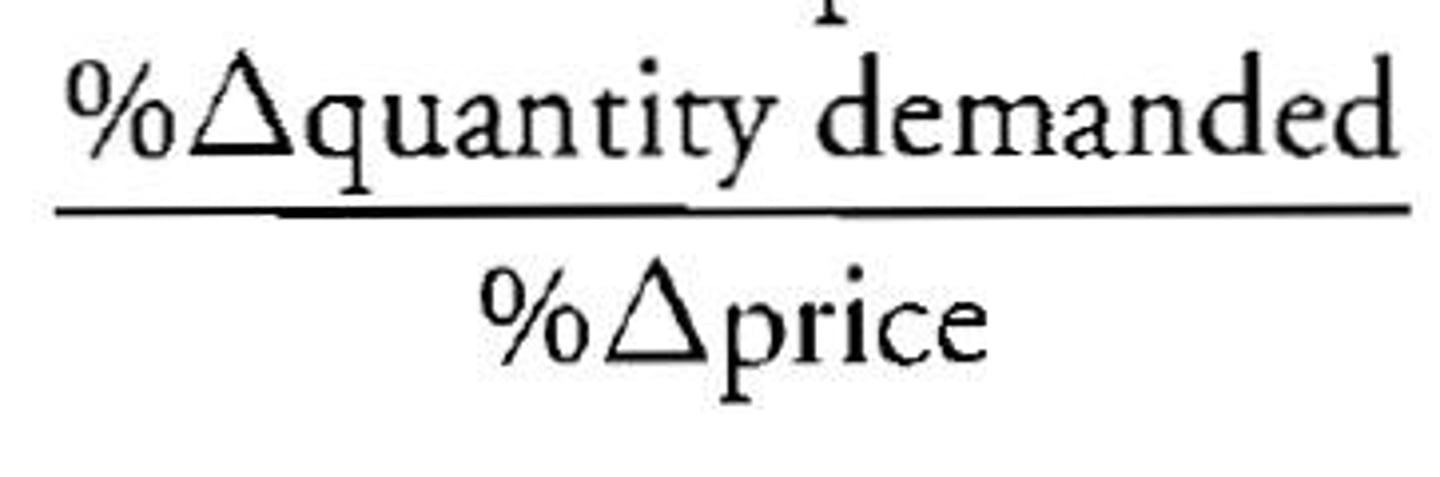
elastic
describes demand that is very sensitive to a change in price (less than -1)
inelastic
Describes demand that is not very sensitive to a change in price (greater than 1)
dynamic pricing/individualized pricing
the process of charging different prices for goods or services based on the type of customer, time of the day, week, or even season, and level of demand
what are the factors influencing price elasticity of demand?
- income effect
- substitution effect
- cross-price elasticity
income effect
the change in the quantity of a product demanded by consumers due to changes in their incomes
substitution effect
refers to consumers' ability to substitute other products for the focal brand, thus increasing the price elasticity of demand for the focal brand
cross-price elasticity
the percentage change in the quantity of Product A demanded compared with the percentage change in price in Product B
complementary products
products whose demand curves are positively related, such that they rise or fall together
substitute products
changes in their demand are negatively related
costs
- the third C
- prices should NOT be based on this
variable costs
- primarily labor and materials
- vary with production volue
- per-unit basis
- far mor e complex in service industry
- tend to change depending on the quantity produced
fixed costs
- remain essentially at the same level, regardless of changes in the volume of product
- ex. rent, utilities, insurance, etc.
total cost
the sum of fixed and variable costs
break-even analysis
technique that enables managers to examine the relationships among cost, price, revenue, and profit over different levels of production and sales
break-even point
the point at which the costs of producing a product equal the revenue made from selling the product
total revenue =
price x quantity sold
what are the 3 curves in the break-even analysis graph?
- fixed costs (horizontal straight line)
- total costs
- total revenue
total variable costs =
variable cost per unit x quantity
total costs =
fixed costs + total variable costs
contribution per unit
equals the price less the variable cost per unit
competition
- the fourth C
- focus on its affect
-four levels of this
what are the four levels of competition?
- monopoly
- oligopolistic competition - monopolistic competition
- pure competition
monopoly
- one firm controls the market
- less price competition
- fewer firms
oligopolistic competition
- a handful of firms control the market
- more price competition
- fewer firms
price war
two or more firms compete primarily by lowering their prices
predatory pricing
the practice of charging a very low price for a product with the intent of driving competitors out of business or out of a market (illegal in U.S.)
monopolistic competition
- many firms sell differentiated products at different prices
- less price competition
- many firms
- most common
pure competition
- many firms sell commodities for the same prices
- more price competition
- many firms
channel members
- the fifth C
- manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers
- must carefully communicate their pricing goals and select channel partners that agree with them
Retailers cooperative (channel members)
- helps its members achieve economies of scale by buying as a group
- similar to wholesaler, except retailers have some control over the operation
pricing strategy
a long-term approach to setting prices broadly in an integrative effort (across all the firms product) based on the 5 C's of pricing
everyday low pricing (EDLP)
- strategy companies use to emphasize the continuity of their retail prices at a level somewhere between the regular, non-sale price and the deep-discount sale prices their competitors may offer
- reduces customer search cost
high/low pricing
- a pricing strategy that relies on the promotion of sales, during which prices are temporarily reduced to encourage purchases
- creates a "get them while they last" atmosphere
what two distinct markets does a high/low pricing strategy attract?
- non-price sensitive
- price sensitive
reference price
- the price against which buyers compare the actual selling price of the product and that facilitates their evaluation process
- regular price vs. sale price
- consumer perception of value of deal increase
what is one of the most challenging tasks for managers?
new product pricing strategies
what are the two distinct new product pricing strategies?
- penetration pricing
- price skimming
penetration pricing
- setting a low initial price on a new product to appeal immediately to the mass market
- incentive: build sales, market share, and profits quickly and deter competition from entering the market because the profit margin is low
experience curve effect
as sales continue to grow, the costs continue to drop
penetration pricing disadvantages
- must have the capacity to satisfy a rapid rise in demand
- low prices does not signal high quality
- avoid this strat if some segment of market are willing to pay more for the product (waste)
price skimming
- selling a new product at a high price
- appeals to innovators and early adopters willing to pay the big bucks
- common in tech. markets (ex. video games)
why use a price skimming strategy?
- signal high quality
- limit demand -> earn back $ investments made for new product development
- test consumers price sensitivity
price skimming disadvantages
- relatively high unit costs associated with producing small volumes of products
- having to eventually lower the price as demand wanes
price ads should ____ deceive consumers to the point of causing harm
NEVER
if a reference price is bona fide, that means that the ad is...
informative
loss-leader pricing
- takes the tactic of leader pricing one step further by lowering the price below the store's cost
- ex. buy on get one free
bait and switch
occurs when sellers advertise items for a very low price without the intent of really selling any
predatory pricing
selling a product below cost to drive competitors out of the market
predatory pricing is illegal under both...
the Sherman Antitrust Act and the Federal Trade Commission Act
price discrimination
- when firms sell the same product to different resellers at different prices ( usually larger firms receive lower prices)
- quantity discounts must be available to all customers and not favor one over others
price fixing
the practice of colluding with other firms to control prices
horizontal price fixing
occurs when competitors that produce and sell competing products collude, or work together, to control prices, effectively taking price out of the decision process for consumers
vertical price fixing
occurs when parties at different levels of the same marketing channel (e.g., manufacturers and retailers) collude to control the prices passed on to consumers
manufacturer's suggest retail price (MSRP)
set to reduce retail price competition among retailers, stimulate retailers to provide complementary service, and support the manufacturer's merchandise
gray market pricing
employs irregular but not necessarily illegal methods; generally, it legally circumvents authorized channels of distribution to sell goods at prices lower than those intended by the manufacturer