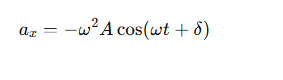L1- SHM
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 1 sem 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is the formula for the force exerted by a spring according to Hooke's Law?
F = the restoring force
k = the spring constant
x = the displacement from the equilibrium position.
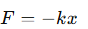
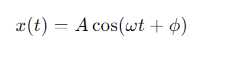
For this equation, when x(0)=0, what would the phase constant ϕ be?
If x(0)=0 and the object is moving toward positive x, then ϕ=−π/2
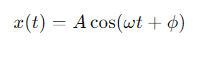
For this equation, when x(0)=A, what would the phase constant ϕ be?
If x(0)=A then ϕ=0
What does the minus sign in Hooke’s law indicate?
It indicates that the force exerted by the spring is a restoring force in the opposite direction to the displacement from equilibrium.
How does Newton’s second law relate to simple harmonic motion?
This shows that acceleration is proportional to displacement and in the opposite direction.
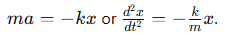
What is the defining characteristic of simple harmonic motion (SHM)?
The acceleration and net force are both:
proportional to the displacement from equilibrium
In the opposite direction to the displacement from equilibrium.
What is the period of simple harmonic motion?
Its the time it takes for an object to complete one full oscillation or cycle.
What is the frequency in simple harmonic motion?
The number of cycles per second
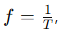
What is the equation for position in simple harmonic motion?
A = the amplitude
ω= the angular frequency
δ = the phase constant.
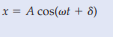
What is the amplitude in simple harmonic motion?
Its the maximum displacement of the object from its equilibrium position.
What is the formula for angular frequency?
When would you use the equation x(t)=Acos(ωt+δ)?
If the motion starts at a maximum or minimum use cosine
When would you use the equation x(t)=Asin(ωt+δ)?
If motion starts at equilibrium use sine
What is the phase of the motion in simple harmonic motion?
Its the argument of the cosine or sine function, ωt+δ
ω =the angular frequency
t = time
δ= the phase constant.
What is the phase constant in simple harmonic motion?
The phase constant δ is the phase at t=0
Its determines the starting point of the oscillation.
When are two oscillating systems said to be in phase?
When the phase difference between them is 0 or an integer multiple of 2π
When are two oscillating systems said to be out of phase?
When the phase difference is π or an odd multiple of π
What is the velocity equation for simple harmonic motion?
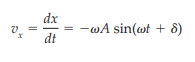
What is the acceleration equation for simple harmonic motion?
x=Acos(ωt+δ)
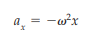
How can the amplitude and phase constant be determined?
From the initial position x0 and initial velocity v0:
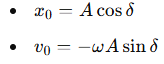
What is the relation between angular frequency ω\omegaω and the spring constant k and mass m?
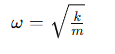
What condition defines the period T of the motion?
The period T is the shortest time interval satisfying the equation:
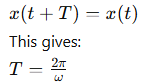
What is the relationship between a sine and cosine function in SHM?
The sine function can be expressed in terms of cosine with a phase shift:
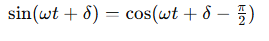
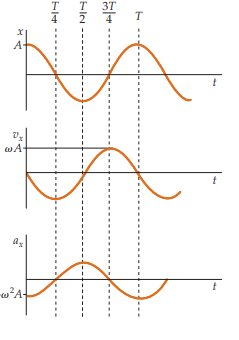
How do the position, velocity, and acceleration equations relate to each other?
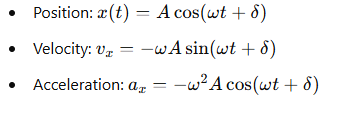
What happens to the motion if δ=0?
The motion starts at maximum displacement
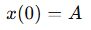
What is the formula for angular frequency?
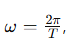
What is the relationship between angular frequency ω and frequency f?
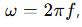
How does the phase of a cosine function relate to the period T?
The phase increases by 2π when t increases by T, completing one cycle of motion.
What is the frequency of an object on a spring in terms of the spring constant k and mass m?
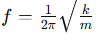
What is the relationship between the period T and the spring constant k and mass m?
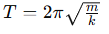
If two masses attached to identical springs are stretched by different amounts and released simultaneously, which mass reaches equilibrium first?
Both masses reach the equilibrium position at the same time
This is because the period of oscillation depends only on the spring constant k and mass m, not the amplitude.
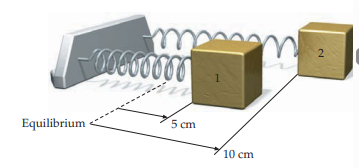
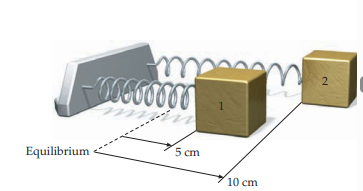
Why does the second mass (stretched further) have the same period as the first mass (stretched less)?
The second mass has twice the distance to travel, but it also has twice the speed at any given point
This results in the same period for both masses.
What is the equation showing the dependence of period on spring constant k and mass m?
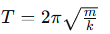
How does the amplitude affect the speed of the oscillating object in simple harmonic motion?
A larger amplitude results in greater maximum speed
This is because the object has more energy, but the period remains unchanged.
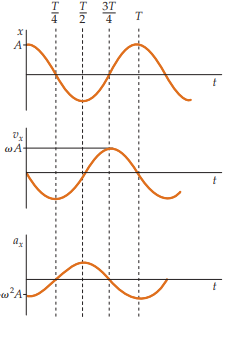
What is the position equation for simple harmonic motion when δ=0?
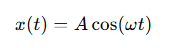
What is the velocity equation for simple harmonic motion when δ=0?
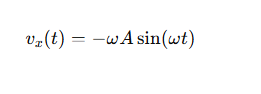
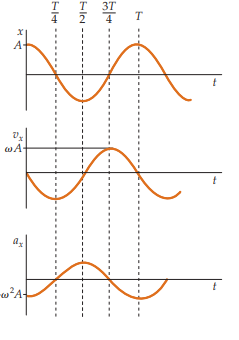
What is the acceleration equation for simple harmonic motion when δ=0?
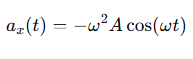
How is angular displacement in circular motion related to time?
ω =angular velocity
t = time
δ= the phase constant.

What is the relationship between the speed of circular motion and angular velocity?
R = the radius of the circular path.
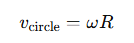
How is the velocity in SHM related to circular motion?
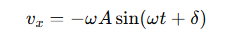
How is the acceleration in SHM related to circular motion?