Cellular Differentiation: IB Bio HL
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IB Biology HL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Specialized Cells
Cells with specific functions or structures that are different to other cells and have specific roles and tasks
Examples: Blood Cells, Immune Cells, Nerve Cells
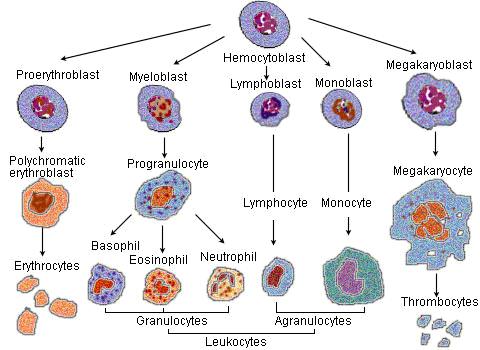
Differentiation
The process by which cells become specialized to carry out specific functions.
Example: A stem cell differentiating into a hemocytoblast,differentiating into a proerythoblast,which then develops into a red blood cell (erythocytes)
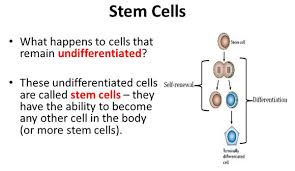
Undifferentiated
A cell that does not have the specific structural or functional characteristics of any mature cell type
Example: A stem cell which can then divide into other cells
Zygote
A fertilized egg
Examples: human egg cells

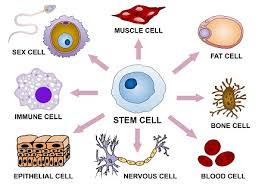
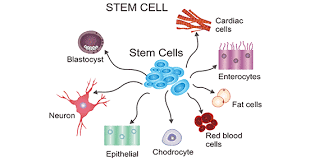
Stem Cell
A undifferentiated cell which can develop into many different types of cells in the body and are the body’s repair system
Ex: Embryonic stem cells, Adult stem cells
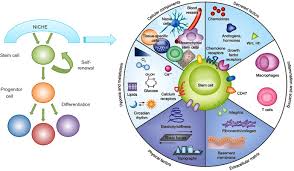
Stem Cell Niche
The microenvironment within the organism in which the stem cells exist and receive their instructions
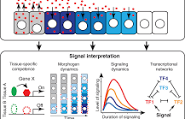
Morphogen
a chemical in the cell the concentration gradient of which determines the fate surrounding cells
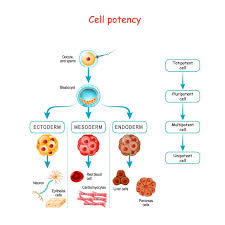
Totipotent stem cells
Cells have the ability to divide to generate the organism
Examples: embryo itself and extraembryonic tissues like the placenta
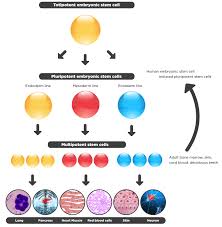
pluripotent stem cells
Cells that can generate multiple types of cells of an organism
Ex:In embryos and skin cells
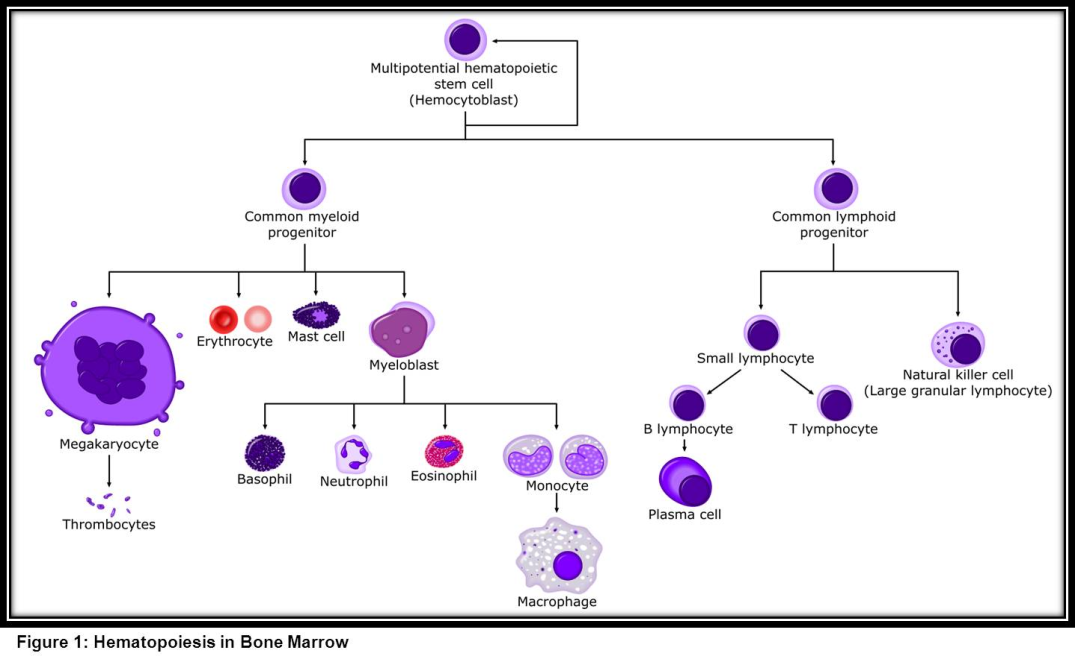
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Are derived from skin or blood cells that have been reprogrammed back into an embryonic-like pluripotent state that enables the development of an unlimited source of any type of human cell needed for therapeutic purposes.
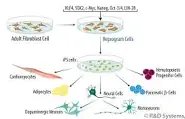
Multipotent stem cells
Cells that can generate many cells of an organism
Unipotent stem cells
cells that generate one cells type of an organism
Cell aggregation
the process by which cells come together to form a group or a cluster