Coenzymes and Vitamins- Cole
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
What is a coenzyme?
a nonprotein organic molecule that binds to an enzyme to aid in the transfer of specific functional groups
Are coenzymes bound tightly or loosely?
usually bound loosely and can be easily separated from its enzyme
When the coenzyme is bound tightly to it's enzyme it is considered to be a ______________ __________ of the enzyme.
prosthetic group
How do cofactors differ from coenzymes?
Cofactors are metallic enzymes while coenzymes are organic molecules
What is the a holoenzyme and apoenzyme?
holoenzyme: an enzyme bound to its cofactor/coenzyme
apoenzyme: enzyme without its cofactor or coenzyme
Can vitamins be synthesized by humans?
no
How are most vitamins obtained?
through supplements or the diet
Which two types of vitamins serve as water-soluble vitamins and as coenzymes or co-enzyme precursors?
all B vitamins
Vitamin C
What is the most common cause of vitamin deficiency?
no obtaining enough vitamins because of poor diets
What is TPP?
Thiamine Pyrophosphate
What is TPP a ester of?
thiamine or vitamin B1
What will be generated as a product of TPP
CO₂
TPP is required for any reaction that goes from a _______ number of carbons to a ___________ lower number of carbons.
higher; lower
What is a common reaction that TPP is a coenzyme for?
Pyruvate (3C) to Acetyl- CoA (2C)
(decarboxylation of a α-keto acid)
take note on how CO₂ is a generated as a product
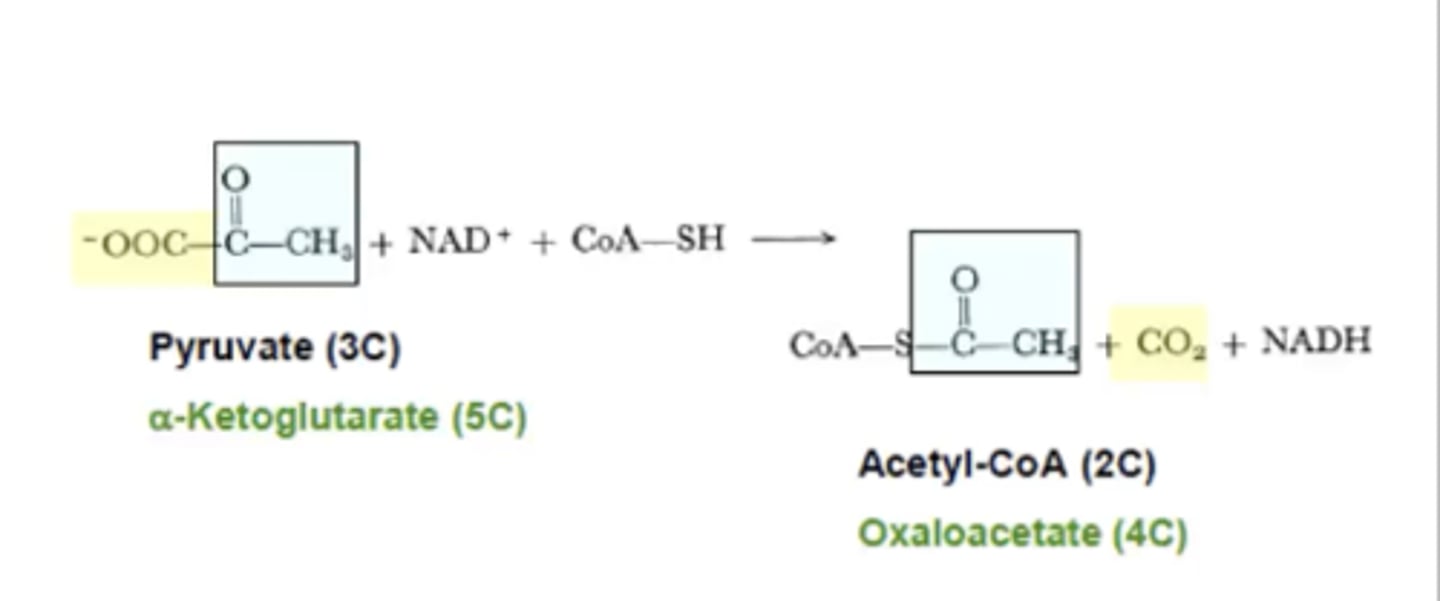
In addition to the decarboxylation of a α-keto acids TPP is also used in what other reactions?
transketolase reaction
What can the lack of Vitamin B1 in the diet lead too?
beriberi, characterized through the accumulation of body fluids, pain, paralysis, and can lead to death
What kinds of reactions to FMN and FAD participate in?
Redox reactions, they both transfer hydrogen atoms
how many times are FAD be reduced?
2
What is generated by the phosphorylation of Riboflavin or vitamin B₂?
FMN
What does FMN react with and what doe sit yield?
FMN reacts with ATP and yields FAD
1 FADH2=________ATP
2
Why is the fully reduced form of riboflavin preferred?
the reduced form will produce energy (atp)
1 NADH=-____ ATP
3
What are some sources for FMN and FAD?
dairy products, eggs, and organ meat
NAD+/ NADP⁺ are known as
Niacin or nicotinamide
What type of reactions are niacins involved in?
Redox reactions, they transfer a hydride ion 2e-, 1H+
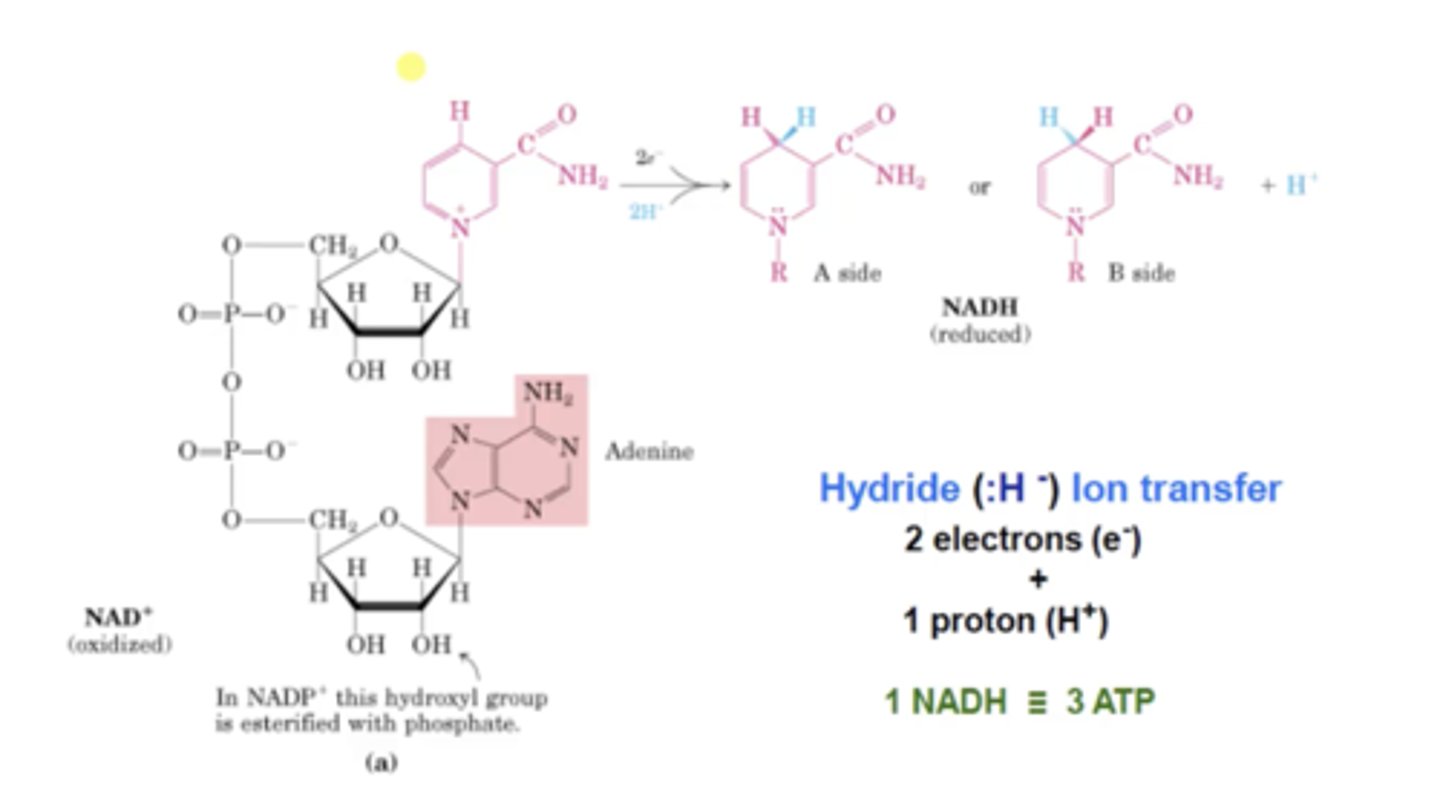
What are some sources of niacins?
red meats and nuts
When is coenzyme A/ pantothenic acid active?
When there is a reactive thiol group attached
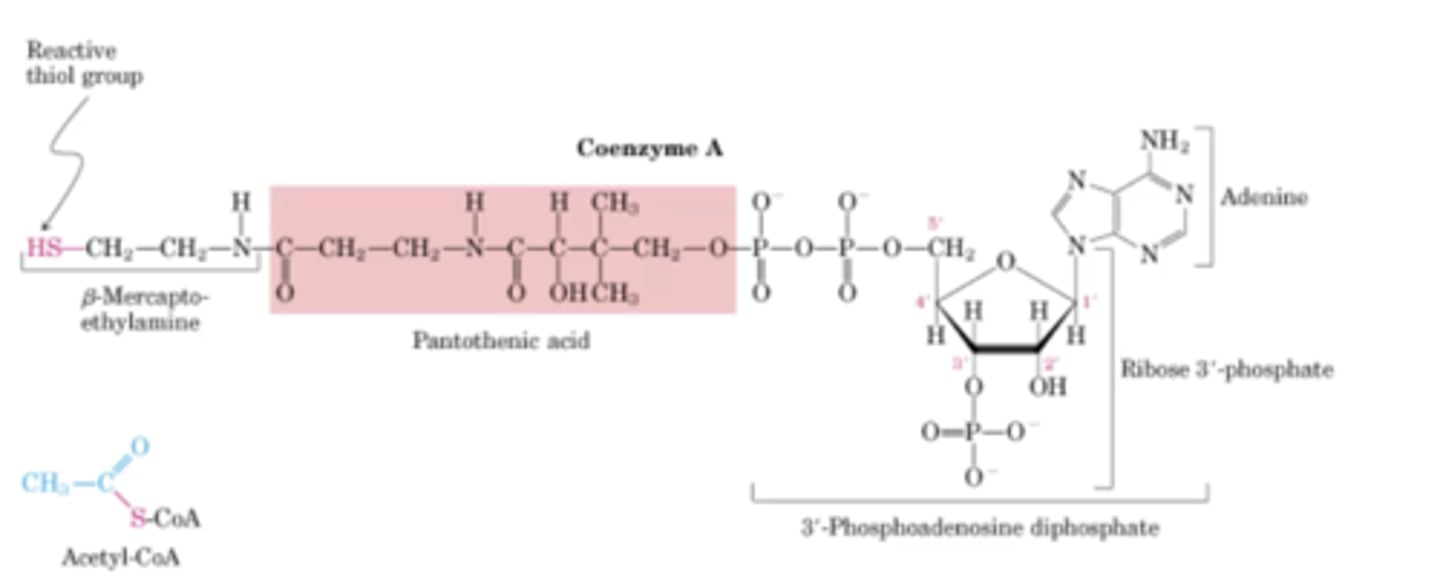
What is generated by pantothenic acid combined with ATP and cystine?
CoA- SH
what does CoA- SH transfer?
activated acyl groups
what are some sources of Coenzyme A?
many food, deficiency is rare
Why does the CoA-SH need to be attached to a fatty acid?
This will allow for the fatty acid to be converted from the storage form to the active form to be transported into the mitochondria to then be broken down for energy
What is PLP?
Pyridoxal phosphate
What is PLP required for the transfer of?
the transfer of amino groups in transamination reactions
In addition to transamination reactions what else is PLP required for?
glycogen phosphorylase
What are some sources of PLP?
required in a propiortion to the protein intake through a variety of foods
Biotin of vitamin B7 carries a activated ___________ ___________
carbon dioxide (N-carboxybiotin)
What is the purpose of Biotin or Vitamin B7?
allows for anabolic reactions (carboxylation) and the conversion of a lower numbered carbon to a higher numbered carbon
Biotin will convert pyruvate to ________.
oxaloacetate
Compare:
Biotin is required for any reaction that goes from a _______ number of carbons to a ___________ lower number of carbons.
TPP is is required for any reaction that goes from a _______ number of carbons to a ___________ lower number of carbons.
lower; higher
higher; lower
Where is biotin acquired from?
the diet and intestinal bacteria
What is the symptom when someone is B12 deficient?
tiredness
What population is more likely to experience a B12 deficiency?
vegetarians because there is not enough red meat in the diet
What is the best way to supplement vitamin b12?
through a injection
What is b12 also known as?
tetrahydrofolic and cyanocobalamin
What is the activated form of tetrahydrofolic acid?
methyl tetrahydrofolic acid
What are the activated one carbon groups that are carried on folic acid/ cyanocobalamin?
methyl(CH₃), methylene(CH₂), formyl (CHO)
What are some food rich in folic acid?
leafy greens, fresh fruits, liver
What will folate deficiency cause?
anemia and nueral-tube defects during pregnancy
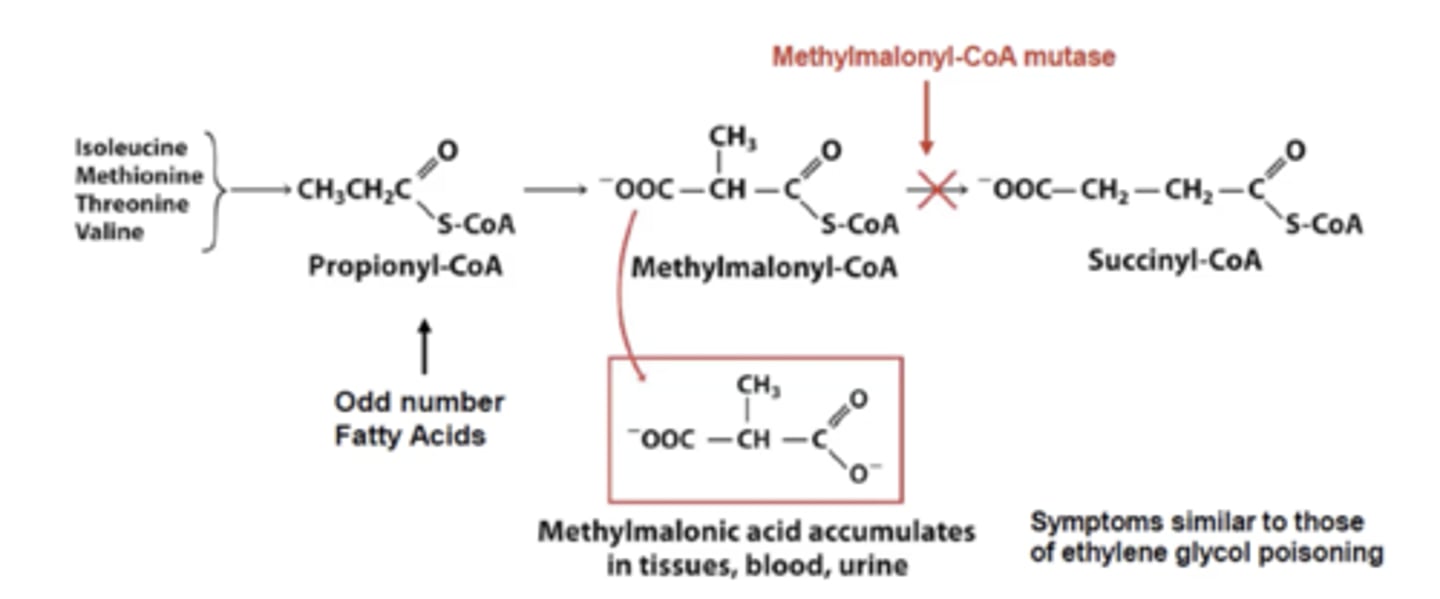
What is the coenzyme for methylmalonyl-CoA mutase?
cyanocobalamin
What can synthesize vitamin b12?
microorganisms
When a enzyme is lacking its coenzyme there will be a build-up of the substrate. If cyanocobalamin is absent it will cause what to build up and what is the result?
methylmalonyl- CoA will be built up and it will accumulate in the tissues, blood and urine.
What can Ascorbic Acid/ vitamin C function as?
antioxidant and a coenzyme used in a oxygenation reactions
Can humans synthesize ascorbic acid?
no, while most species can synthesize their own, humans lack the necessary enzymes and are dependent on fresh fruits and vegetables for this vitamin
What is a syndrome of vitamin C deficiency?
Scurvy: defective collagen synthesis leading to muscle weakness and loose teeth
What are the coenzymes that can be synthesized?
Lipoic acid and coenzyme Q
Why are lipoic acid and coenzyme Q not considered vitamins?
because they CAN be synthesized
Both lipoic acid and coenzyme Q transfer __ ________
H atoms
Is coenzyme Q considered a antioxidant?
yes
By definition carbohydrates are
polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketone derivatives
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Energy storage, fuels, structural supports, lubricants, metabolic intermediates, structural frameworks of DNA and RNA, protein and lipid modifications.
What are considered simple carbohydrates?
monosaccharides and disaccharides
Define a monosaccharide
simplest carbohydrates, composed of an aldehyde or ketone with two or more hydroxyl groups.
Up to how many carbons can a monosaccharide contain?
7
What is the smallest monosaccharide?
triose
What is a common ketose?
fructose
Aldehydes/ aldoses have carbonyl group at carbon ___
Ketones/ ketoses have carbonyl groups at carbon __
1;2
Al monosaccharides with the exception of ____________ _________ have one or more asymmetric (chiral) carbon atom and exist as stereoisomers.
dihydroxy acetone (no chiral carbon)
If 2ⁿ= the number of stereoisomers and n= the number of chiral centers how many chiral centers and stereoisomers does a 2⁴ molecule have?
4 chiral centers and 16 stereoisomers
What is a epimer?
are any two diastereomers that differ only in the configuration at a single carbon atom.
how are l-sugars and d-sugars related?
they are enantiomers of each other
Monosaccharides exist as
diastereomers
Compare:
Enantiomers are:
Diastereomers are:
Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images
Diastereomers isomers that are not mirror images of each other
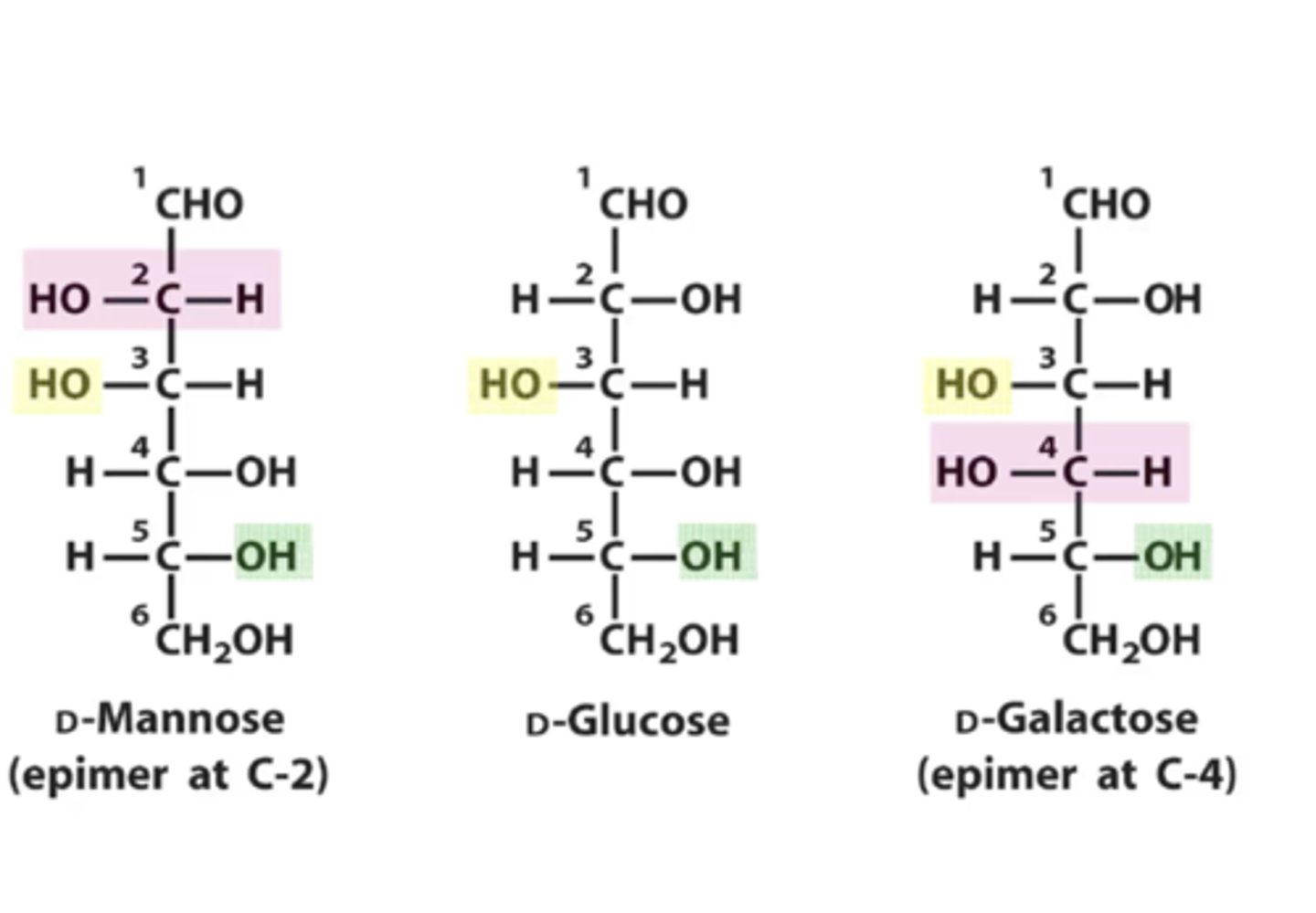
D-Mannose is a _____ of D-glucose at position ___
D- Galactose is a _______ of D-glucose at position ___
epimer; C-2
epimer; C-4
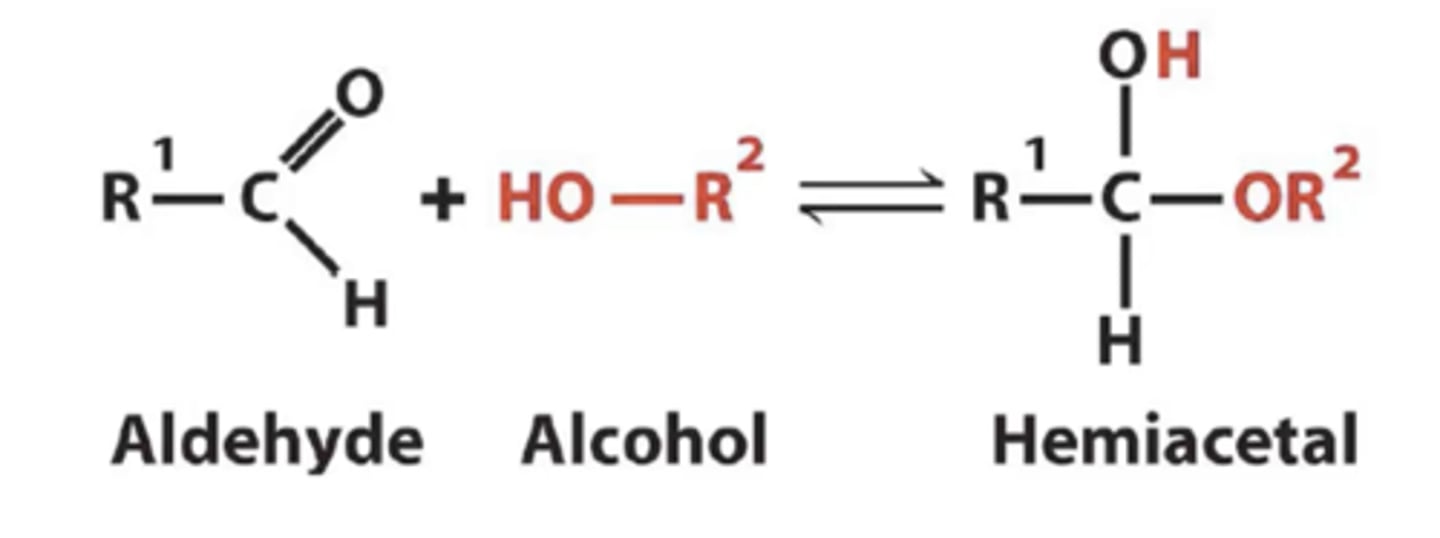
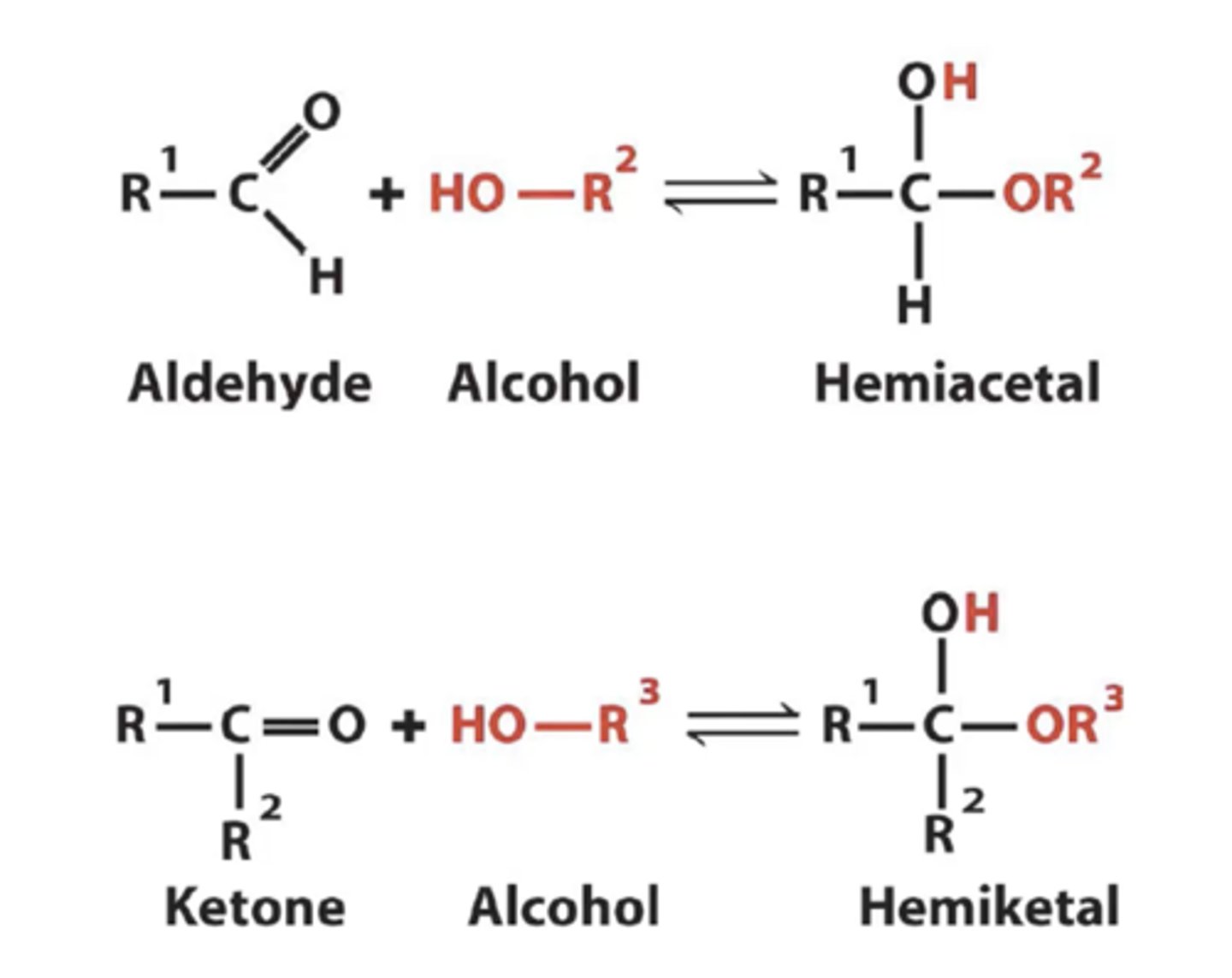
Pertaining to the ring structure what will glucose form?
hemiacetal
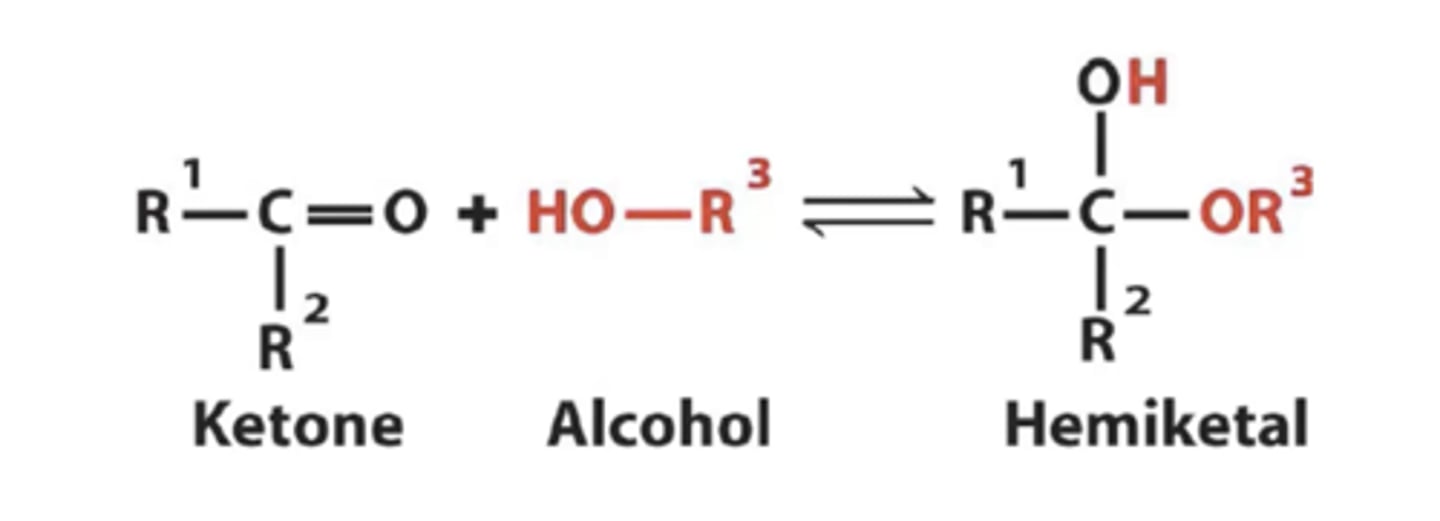
When fructose is forming a ring structure what will it form?
hemiketal
The open chain will form a cyclic structure of glucose and fructose are made by interactions between what two molecules?
Glucose: aldehyde + alcohol
Fructose: Ketone + alcohol
Pentoses and hexoses will frome what kinds of rings and through what kinds of bonds?
furanose and pyranose rings through hemiacetal and hemiketal bonds
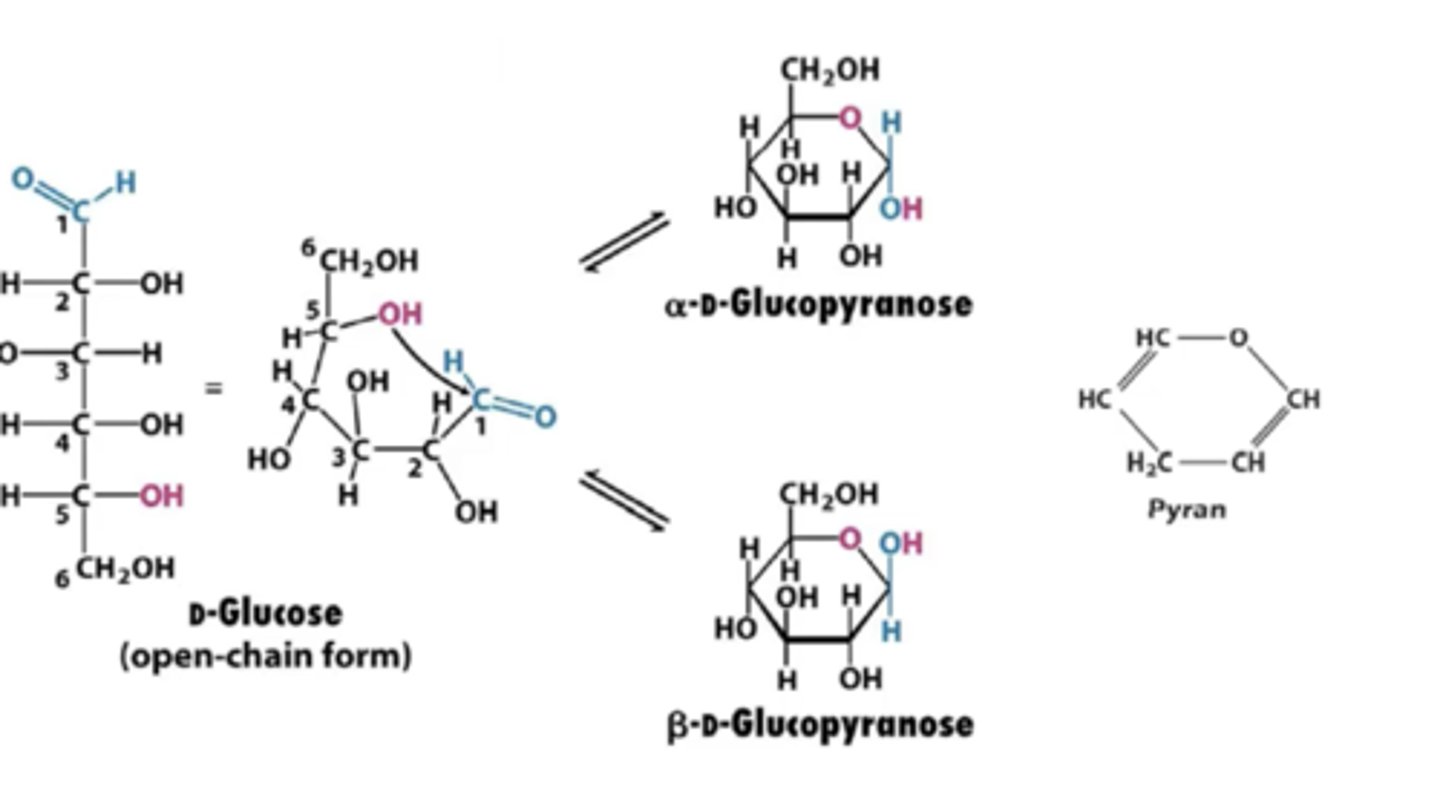
What is the anomeric carbon?
the new chiral center formed in ring closure; it was the carbon containing the carbonyl in the straight-chain form
What will determine if a molecule is alpha or beta?
the anomeric carbon
This will always be numbered C1
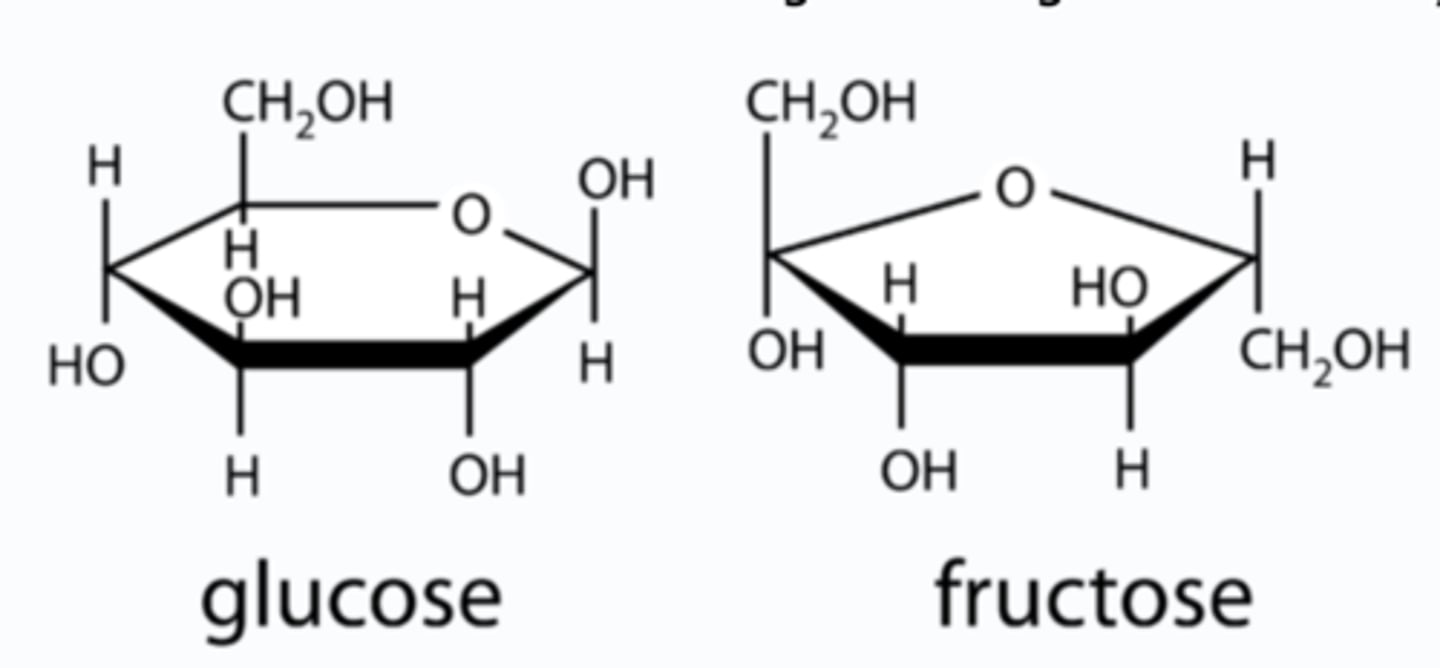
What is the difference in the ring structure between fructose and glucose?
Glucose forms a six ring structure
Fructose forms a five ring structure with six carbons
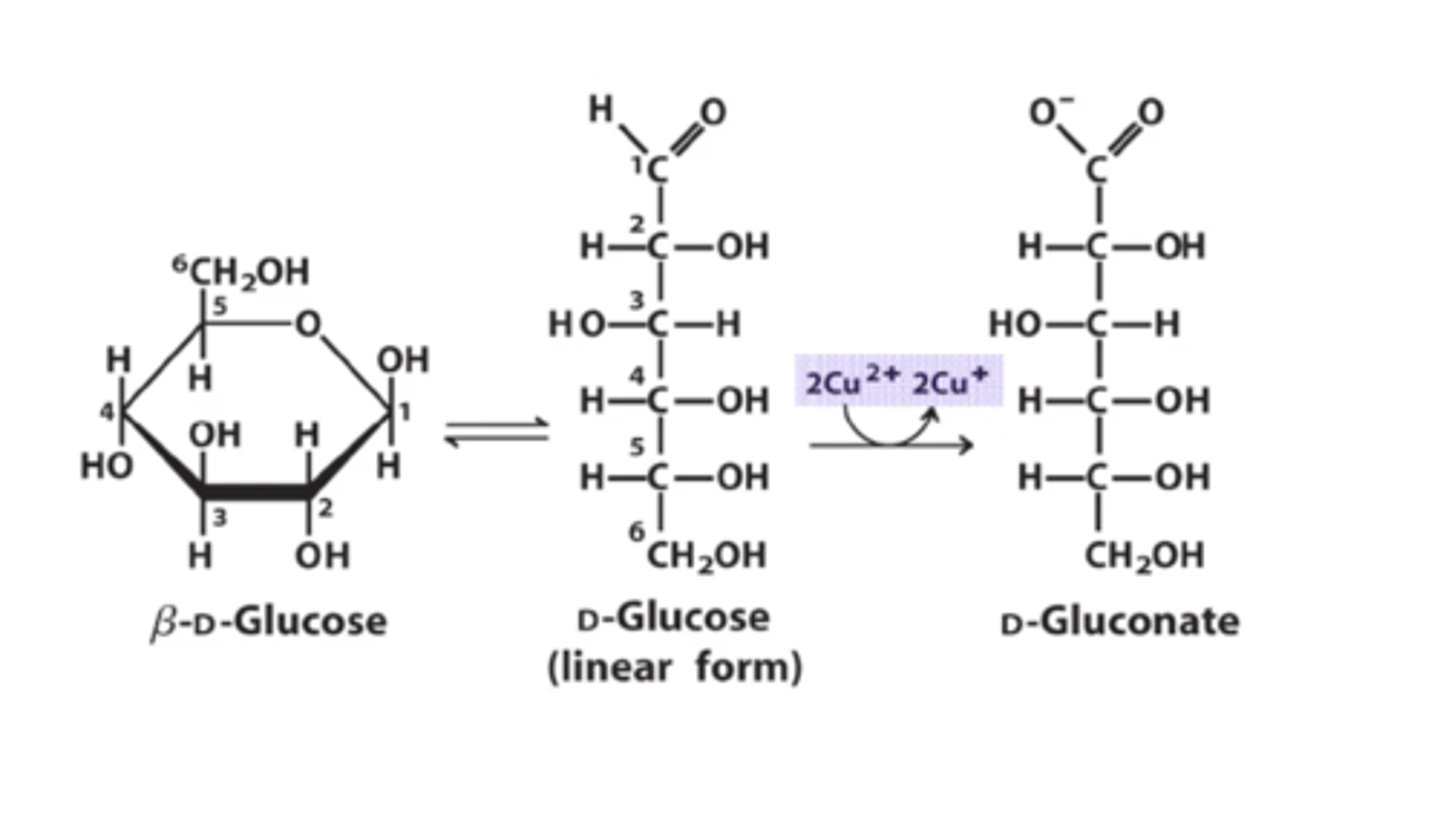
Carbohydrates with a free aldehyde or ketone group can reduce ____ to _____ and therefore called __________ __________.
Cu²⁺; Cu⁺; reducing sugar
When glucose gets reduced what does it form?
gluconate
Why can't carbohydrate rings be planar?
The tetrahedral geometry of the carbons bonds has to much steric hindrance; carbohydrates prefer the chair form
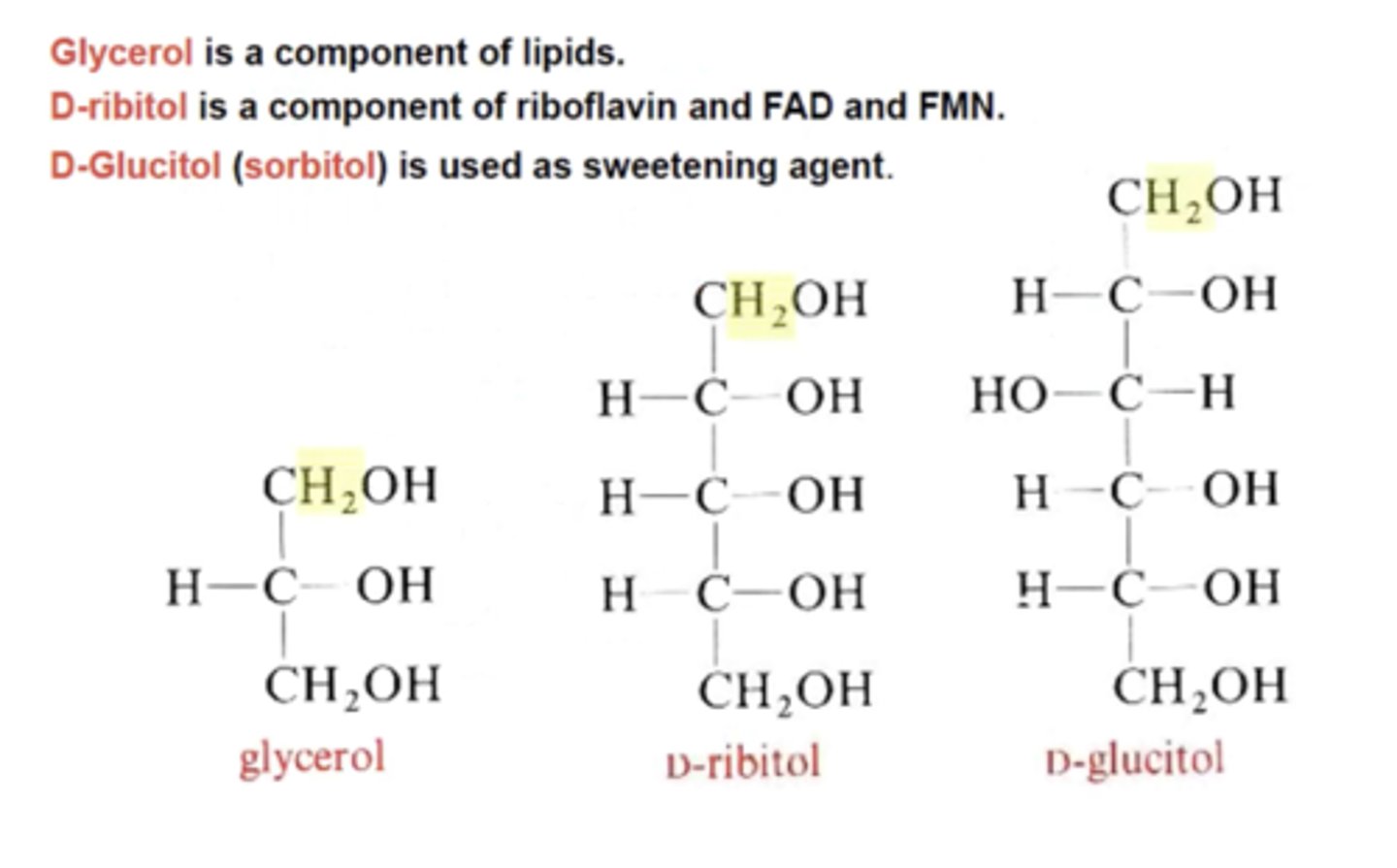
Which three compounds are considered the sugar alcohols and deoxy sugars?
Glycerol, D-ribitol, D- glucitol (sorbitol)
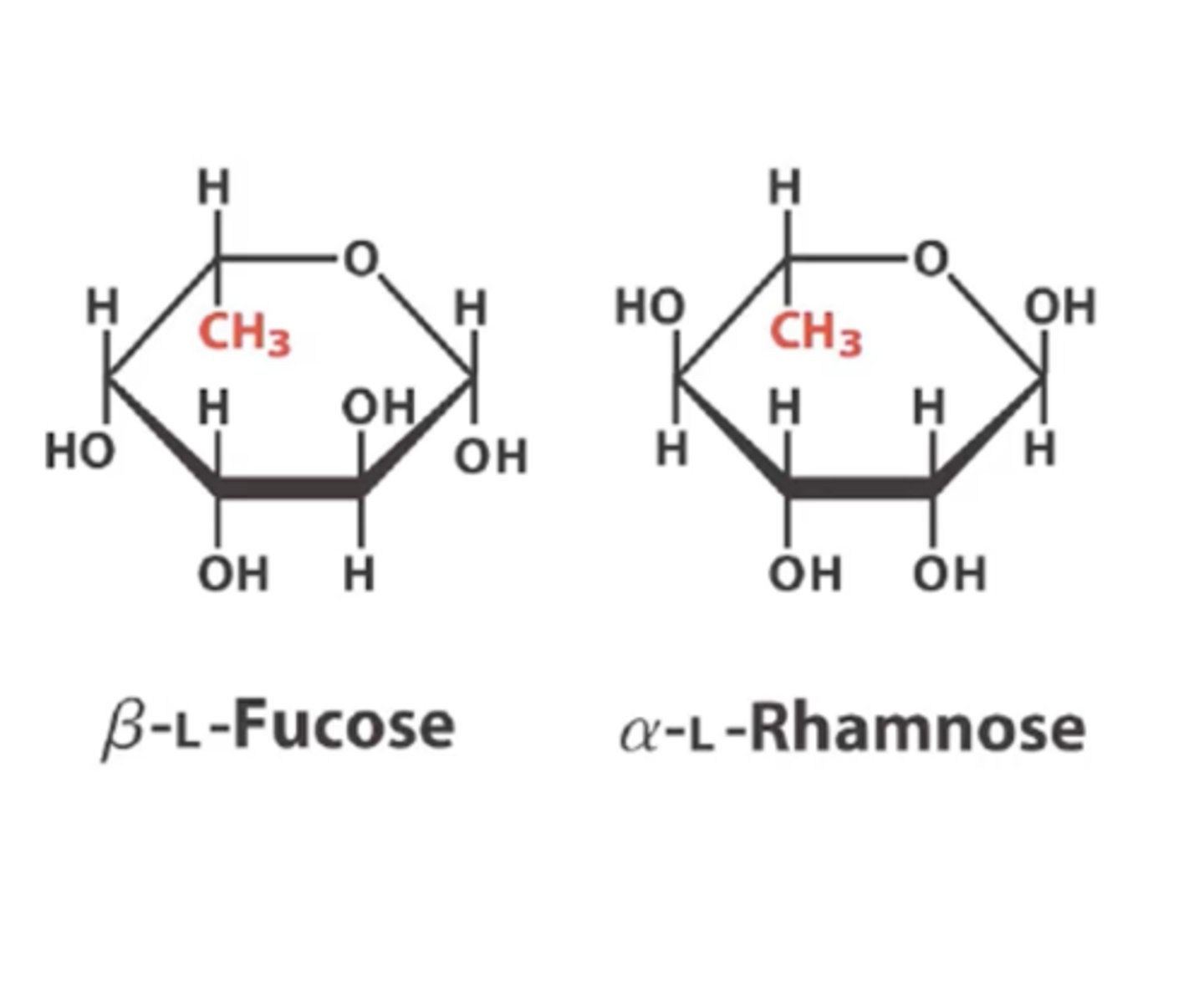
What position does the substitution of H of OH group happen for galactose and mannose?
C6
When the H is replaced with OH at the C6 position for galactose and mannose what does it form?
fucose and rhamnose respectively
What is the most important deoxy sugar found in DNA?
D-2 deoxyribose
An amino sugar is when the OH group is replaced with ___
NH₃
What carbon do the amino sugars experience OH getting replaced with NH₃?
2
In bacterial cell wall when lactic acid is ether-linked to the at oxygen at C3 fpr N-acetylglucosamine what does it form?
N-acetylmuramic acid
In sugar acids what group gets oxidized?
terminal CH₂OH groups to COOH
Oxidation of terminal CH₂OH groups to COOH is most
prevalent of the monosaccharide acids. The resulting acids are termed ____________
uronic acids
What does the oxidation of C6 D-glucose yield?
D-glucuronic acid
What is produced when the carbonyl carbon of glucose is oxidized to a carboxylic acid?
gluconic acid
D-glucuronic acid and L-iduronic acid are both present in ________
glycosaminoglycans
If both terminal groups of D-glucose are oxidized what is produced?
glucaric acid
What forms sugar esters?
alcohols that readily form esteers when reacted with acids or anhydrides
What are the most important sugar ester that occur in living cells?
phosphate esters and nucleoside diphosphate esters
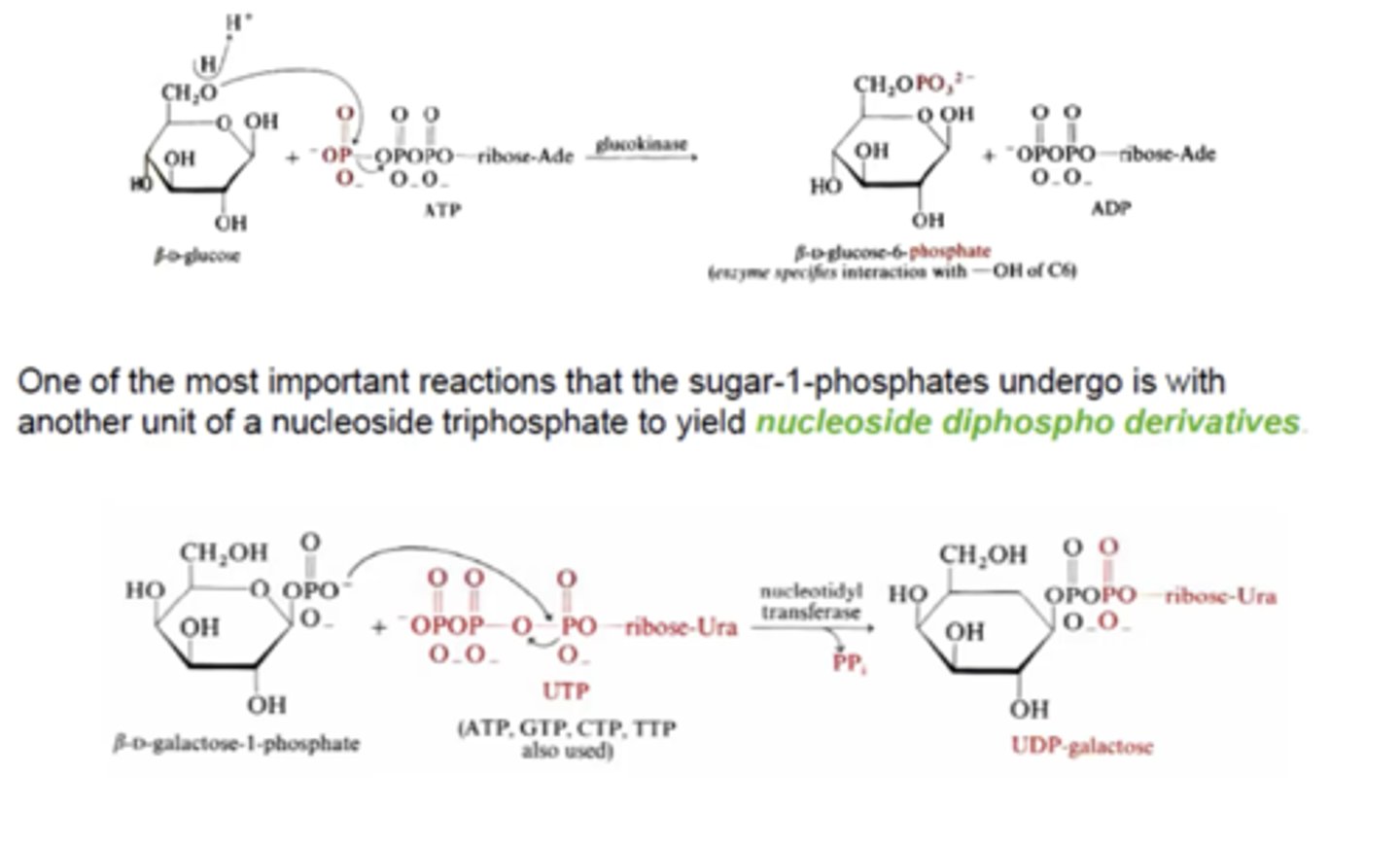
β-D- glucose-6-phosphate is consider what kind of sugar ester? What is UDP galactose considered?
β-D- glucose-6-phosphate: sugar 6 phosphate
UDP galactose: sugar 1 phosphate