Wound management
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Recap: what are the functions of the skin an layers of the skin?
• Epidermis - the top layer
• Dermis - the middle area
• Hypodermis (Subcutaneous layer) - the bottom or fatty layer
Functions:
• Control of body temperature • Keeping out infection • Monitors pain • A waterproof barrier • Communication • Production of Vitamin D • Protects delicate organs • Mends itself when damaged
What is a wound?
A breakdown in the protective function of the skin; the loss of continuity of epithelium, with or without loss of underlying connective tissue (i.e. muscle, bone, nerves) following injury to the skin or underlying tissues/ organs
What are the 2 classes of wounds
-Acute - traumatic or surgical
•Chronic - fail to proceed normally through the repair process. 4 weeks or 8-12 weeks
Types of wound healing
• Primary intention
• Secondary intention
• Tertiary intention
What are the 4 phases of wound healing ?
There are four (4) phases of wound healing:
• Hemostasis: immediate
-Initial vasoconstriction
-Release of clotting
-Fibrin clot formation
• Inflammation: day 1-4
-Vasodilation
-Delivery of macrophages
-Phagocytosis blood clot formation loosely unites wound edges
• Proliferation: Day 4-21
-Epithelial cells migrate bridging the wound
-Angiogenesis - growth of new capillaries
-Fibroplasts migrate along fibrin strands synthesising scar tissue
• Maturation/remodelling: Day 21 - Year 2
-Develop tensile
-Collagen remodelling
-Vascular maturation and regression
What factors effect wound healing: Give 3
• Co-morbidities • Pressure Ulcer Risk • Nutritional status • Mobility status • Continence status • Vascular supply • Anaemia • Size • sleep • Poverty • Lack of knowledge • Depression • Advancing age • Cognitive impairment • Patient concordance Environment • Carer input/involvement • MDT involvement • Malignancy • Infection • Diabetes • Drugs • Dressing • Foreign bodies • Wound Temperature
What is holistic wound assessment?
-History
-Examination - whole body then wound
-Investigations - bloods, x-rays, scans
-Diagnosis
-Intervention - plan of care
What is TIMES and what is the aims of this framework ?
-a framework to guide wound care at all competency levels in all settings
-Tissue
-Infection
-Moisture imbalance
-Edge of wound, epidermal advancement
-Social and patient related factors
Aims:
-Remove actual/potential causes of delayed healing
-Create the optimum local healing environment
-Protect the individual from further tissue damage
-Relieve pain
What is necrotic tissue?
Dead tissue that is black/brown and may be eschar (hard) or soft
What is granulation tissue?
Red, moist, healthy tissue that indicates wound healing
What is slough tissue?
Non-viable tissue that appears yellow/white/green and needs debridement
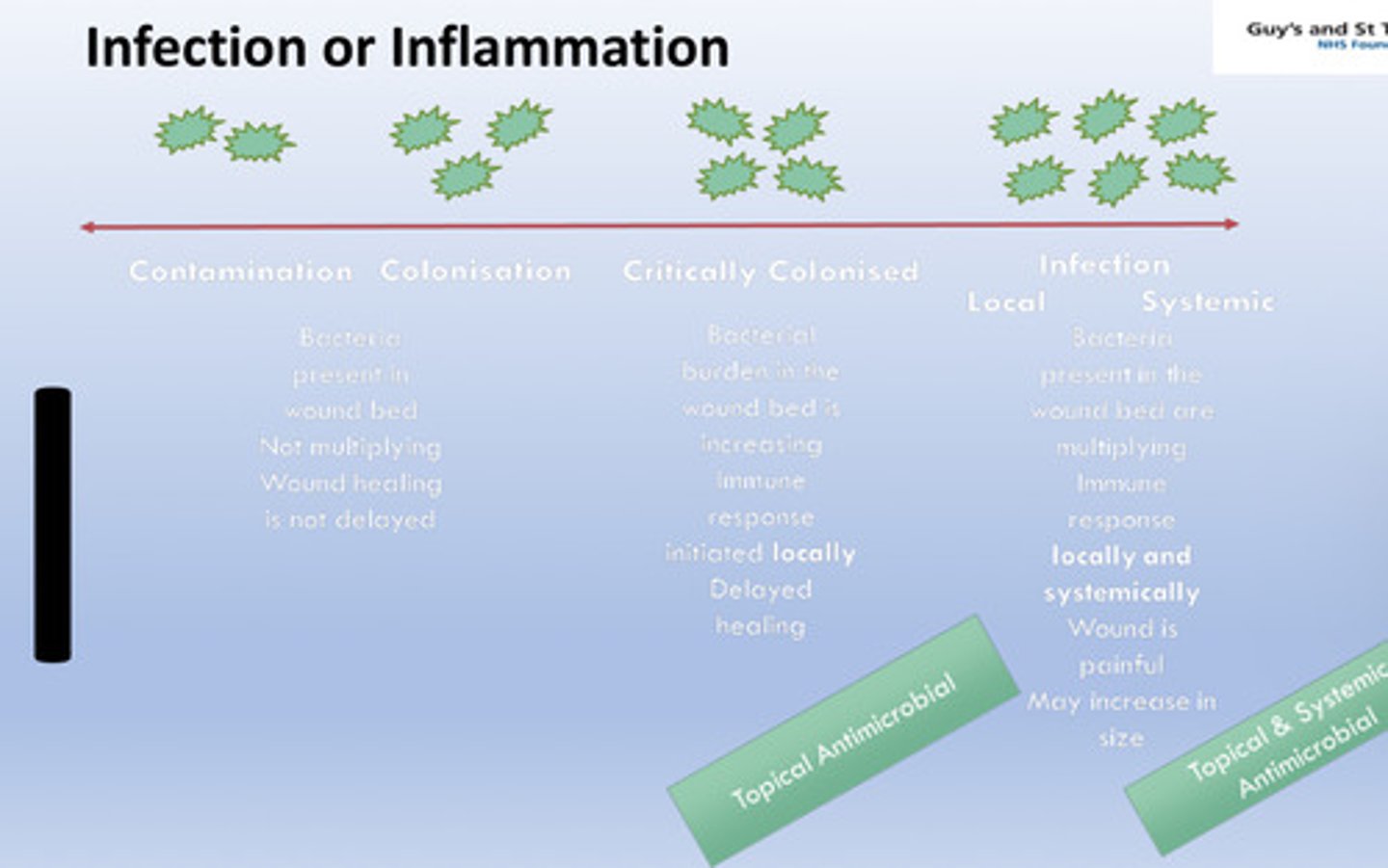
Name three signs of infection in a wound.
Redness, heat, pus, odour, increased pain, delayed healing, oedema, increased exudate, odour, pyrexia
Whats the difference between contamination and infection ?
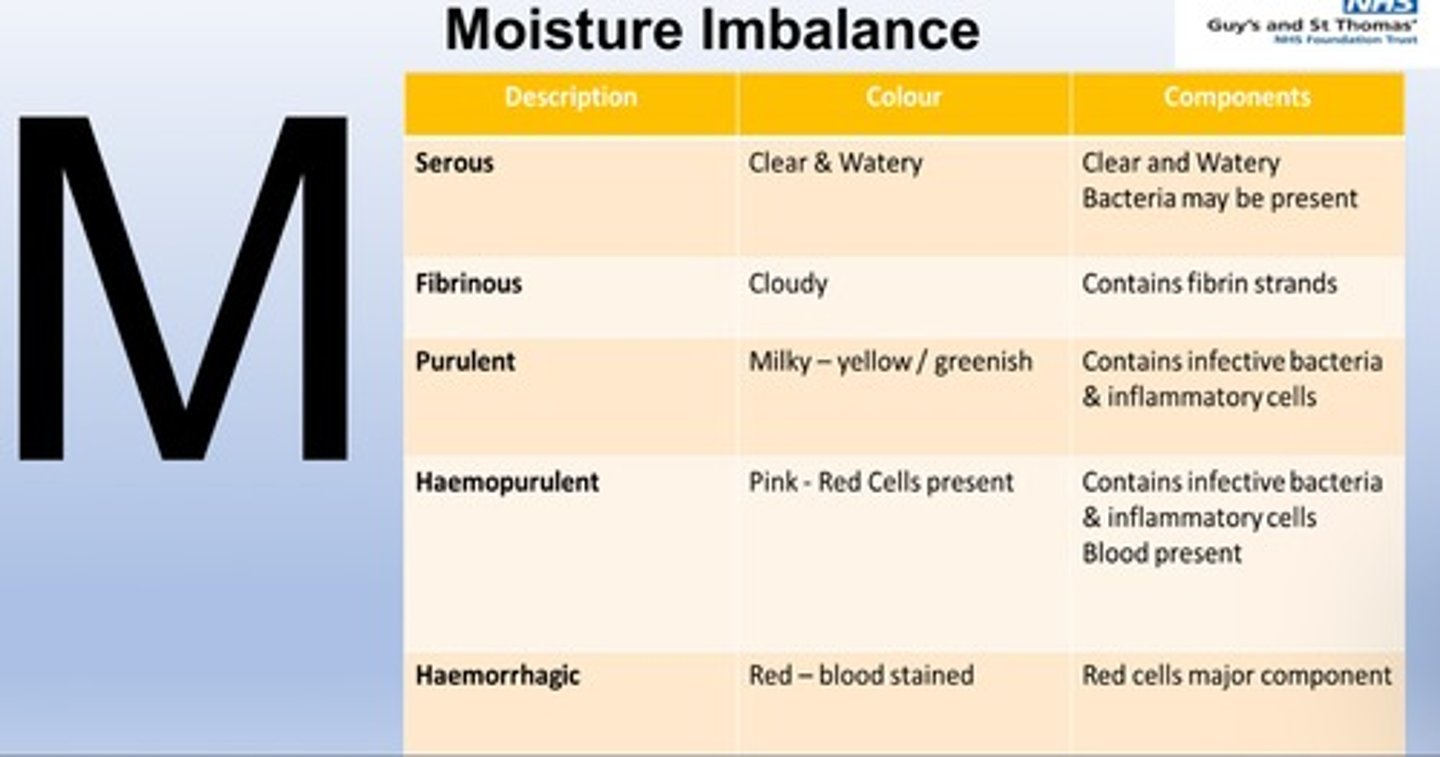
How does moisture imbalance affect wounds?
Too much exudate (fluid) causes maceration; too little delays healing
Types of moisture imbalance ?
What is undermining ?
-For chronic wounds
-Encourages cavity to fill with granulation tissue
What is tracking ?
Narrow opening or passage that can extend in any direction often making the wound larger beneath the skin than it appears on the surface
-Tracking indicates a chronic or deep wound that may need specialised care. - Helps guide treatment decisions, such as packing the tunnel to prevent abscess formation.
Why is measuring wound size important?
To track healing progress and adjust treatment accordingly.
Name two methods of wound measurement.
Ruler/tape measurement, tracing on a sterile transparency, photography.
What are the 3 Wound cleansing agents ?
-Tap water - used extensively in leg ulcer clinics
-Normal saline - used for clean, contaminated and colonised wounds
-Antimicrobial - used for critically colonised, infected wounds
Why do we clean wounds
-Remove contaminents
-Remove debris and foreign bodies bodie following trauma
- Remove dressings
-Remove excess exudate
-Remove crusting
-Remove superficial slough
What are pressure ulcers ?
localised damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue, usually over a bony prominence resulting from sustained pressure.
What is the difference between pressure vs shear?
Pressure: Force applied perpendicularly to the skin, compressing tissues and blood vessels. = Direct compression leads to ischemia and cell death, causing pressure ulcers.
Shear: Force applied parallel to the skin, causing tissues to stretch and distort. = Tissue layers separate, damaging blood vessels and leading to deep tissue injury.
4 categories of pressure ulcers?
1️⃣ Stage 1: Non-Blanchable Erythema
Intact skin with redness that does not fade when pressed.
May feel warm, firm, or painful.
2️⃣ Stage 2: Partial-Thickness Skin Loss
Loss of epidermis & partial dermis.
Appears as a shallow open ulcer or blister.
3️⃣ Stage 3: Full-Thickness Skin Loss
Damage through dermis into subcutaneous tissue.
May have fat exposure, but no bone, tendon, or muscle visible.
4️⃣ Stage 4: Full-Thickness Tissue Loss
Deep ulcer with exposed bone, tendon, or muscle.
High risk of infection, tunneling, and necrosis.
What is moisture associated skin damage (MASD)?
MASD is skin irritation and breakdown caused by prolonged exposure to moisture (e.g., sweat, urine, faeces, wound exudate).
-weakens the skin barrier, making it more vulnerable to infection and pressure ulcers.
What are the types of MASD ?
1️⃣ Incontinence-Associated Dermatitis (IAD) – Skin damage due to urine or faeces.
2️⃣ Intertrigo – Inflammation caused by skin-to-skin friction in moist areas (e.g., groin, under breasts).
3️⃣ Peri-Stomal MASD – Skin irritation due to stoma leakage.
4️⃣ Peri-Wound MASD – Skin damage from excess wound exudate, leading to maceration and breakdown
How can MASD be prevented?
✔️ Use barrier creams/films (e.g., Cavilon).✔️ Maintain skin hygiene (frequent cleansing and drying).✔️ Use absorbent dressings to manage exudate.✔️ Protect skin from friction (moisture-wicking fabrics, repositioning).✔️ Use appropriate incontinence care products.
How does MASD differ from pressure ulcers?
MASD is caused by moisture, while pressure ulcers result from prolonged pressure/shear forces.
Why do we dress wounds?
To protect, promote healing, absorb exudate, and reduce pain/infection risk.

Which dressing type is used for granulating wounds?
Hydrocolloid or foam dressings.
What is a key benefit of hydrocolloid dressings?
They promote autolytic debridement and provide a moist healing environment.
Which dressing is used for highly exudating wounds?
Hydrofibre (e.g., Aquacel) or alginate dressings
What dressing should NOT be used on diabetic foot ulcers?
Hydrocolloid dressings.
What type of wounds benefit from hydrogel dressings?
Dry, necrotic, or sloughy wounds requiring hydration.
What is the purpose of hydrofibre dressings?
To absorb and lock in high amounts of exudate, preventing leakage.
What is a unique property of alginate dressings?
They control bleeding and form a gel when in contact with wound fluid
What is the function of silver dressings?
Antimicrobial properties - used for infected or high-risk wounds.
What is a pressure ulcer?
Localised skin damage due to prolonged pressure or shear, often over bony areas.
Who is at risk of developing pressure ulcers?
Immobile patients, elderly, malnourished individuals, diabetics.
What is incontinence-associated dermatitis (IAD)?
Skin damage caused by prolonged exposure to urine or faeces
What is the best way to protect peri-wound skin?
Barrier films (e.g., Cavilon) to prevent maceration.
What are non-adherent dressings used for?
Granulating wounds, surgical wounds, and painful wounds to prevent sticking.
What type of wounds are film dressings used for?
Superficial wounds, minor burns, and wounds with low/no exudate.
What is negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT)?
A vacuum-assisted dressing that removes excess exudate, reduces infection, and promotes healing (granulation tissue formation)
What is larvae therapy used for?
Debridement of necrotic wounds by breaking down dead tissue with enzymes
What is the main function of honey dressings?
Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and promotes autolytic debridement.
What type of wounds are foam dressings best for?
Moderate-to-heavy exuding wounds, pressure ulcers.
Why are absorbent padding dressings used?
To manage heavy exudate and protect secondary dressings.
Which wounds may require odour-absorbing dressings?
Fungating or infected wounds.
Why are barrier films/creams used in wound care?
To protect surrounding skin from moisture damage (e.g., MASD, incontinence-associated dermatitis).