Cellular Energetics
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1st law thermodynamics
All matter never disappears; matter moves through cycles
stays in one state for some time and then cycles into another state, but never disappears
2nd law thermodynamics
heat flows from hot to cold
Energy naturally spreads out, increasing towards entropy.
It takes extra energy to keep energy tightly stored in the bonds of matter instead of letting it disperse.
3rd law thermodynamics
As a substance gets closer to absolute zero, its particles lose energy and move less, so entropy goes down and approaches zero, reaching equilibrium state.
kilocalories
1000 calories
calorie
heat input needed to raise 1g of water 1 degree
a joule of energy = __ calories
0.239
potential energy
stored energy due to an object's state/position
kinetic energy
energy that comes from motion
metabolism
The sum of an organism's chemical reactions determines how cells use energy
catabolic pathways
breaks down complex molecules into simple compounds to release energy
(think: a cat breaks stuff; cat breaks down complex into simple)
anabolic pathways
builds complex molecules from simple compounds by consuming energy
free energy
energy that’s available to do work
exergonic reaction
free energy is released
endergonic reaction
absorbs free energy to proceed reaction
free energy equation
ΔG=ΔH−T(ΔS)
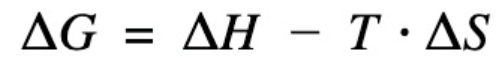
G in free energy equation
Gibbs free energy
H in free energy equation
energy in chemical bonds (enthalpy)
S in free energy equation
energy available because of disorder (entropy)
T in free energy equation
absolute temperature in K (Celcius+273)
when ΔG is positive
more free energy
not spontaneous
endergonic
when ΔG is negative
less free energy
spontaneous
exogenic
oxidation
loss of electrons, hydrogen atoms, or gain oxygen atom
eg: combustion, rusting, and cellular respiration
reduction/redux reaction
gains electrons
decreases its oxidation state
or loses oxygen.
redox reaction
chemical reaction where one substance is oxidized and another is reduced
energy coupling
exergonic process to drive endergonic process.
primary source is ATP
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
made up of: adenine (nitrogenous bases), ribose (5-carbon sugar), and a chain of 3 phosphate molecules.
Function: used by cells to do work; stores/transfers energy within a cell
activation energy
The amount of energy needed to start a reaction and also break the bonds of reactant molecules
catalyst
substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being used up or changed.
enzyme
macromolecules that act as catalyst (speed up reaction) by lowering activation energy of the reaction.
it doesn't change the overall energy released/absorbed in the reaction
substrate
The reactant that the enzyme acts on
activation sites
where enzyme binds to substrate
enzyme substrate complex
temporary structure formed by enzyme and substrate.
The substrate converted into products
the products are released from the enzyme
catalysis
activation energy is decreased due to enzymatic activity
cofactor
non-protein helper that some enzymes need to work properly
eg: metal ions like zinc and iron
NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
essential cofactor in all living cells
It helps enzymes carry out redox reactions (transferring electrons).
It cycles between NAD⁺ (oxidized form) and NADH (reduced form).
NAD is crucial for cellular respiration and energy production.
coenzyme
organic cofactor
Multi-enzyme complex
enzymes joined together that pass products directly to the next enzyme, making reactions faster and more efficient
cooperativity
Enzyme has multiple active sites.
Binding one substrate makes it easier for others to bind.
Multiple reactions can happen at once.
competitive inhibitors
reversible inhibitors that compete w/substrate for the active site on the enzyme.
Non-Competitive Inhibitors
doesn't compete with substrate
prevents enzyme activity by binding to diff part of the enzyme
penecillin
blocks the active site of DD-transpeptidase, stopping bacteria from building cell walls, which leads to bacterial death.
Methotrexate
similar to folic acid.
Competitively inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR).
Prevents nucleic acid synthesis, slowing cancer cell growth.
allosteric site
specific site on an enzyme (not the active site) where regulators bind
Feedback inhibition
process where a product of metabolic pathway slows down its own production by binding to and inhibiting an enzyme that acts earlier in the pathway
activators
bind to Allosteric sites on enzymes to to keep the enzymes in active form