Convergence and Divergence Tests for Series
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards summarizing key convergence and divergence tests for series.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
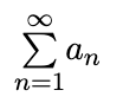
Test for Divergence
Diverges if limn→∞ an ≠ 0 or limn→∞ an does not exist; inconclusive if limn→∞ an = 0.
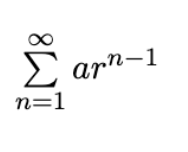
Geometric Series
Converges if |r| < 1; diverges if |r| ≥ 1; sum is Σ∞ n=1 arn−1 = a / (1 - r).
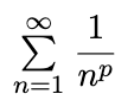
p-series
Converges if p > 1; diverges if p ≤ 1.
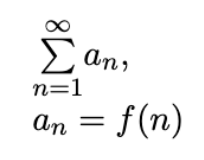
Integral Test
Converges if ∫∞1 f(x)dx converges; diverges if ∫∞1 f(x)dx diverges, where f derived from an is continuous, positive, and decreasing.
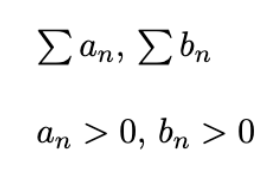
Comparison Test
If Σbn converges and an ≤ bn for all n ≥ 1, then Σan converges; if Σbn diverges and an ≥ bn for all n ≥ 1, then Σan diverges.
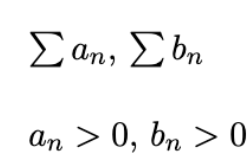
Limit Comparison Test
If limn→∞ an/bn = c > 0, then either both series converge or both diverge.
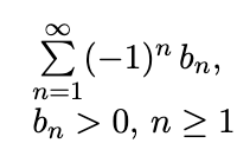
Alternating Series
Converges if bn+1 ≤ bn for all n ≥ 1 and limn→∞ bn = 0.
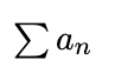
Absolutely Convergence
If Σ|an| converges, then Σan converges.
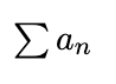
Conditionally Convergence
If Σan converges but Σ|an| diverges.
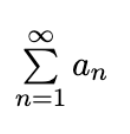
Ratio Test
If limn→∞ |an+1/an| = L, then the series is absolutely convergent if L < 1, divergent if L > 1 or ∞, inconclusive if L = 1.
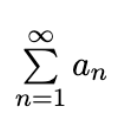
Root Test
If limn→∞ n√|an| = L, then the series is absolutely convergent if L < 1, divergent if L > 1 or ∞, inconclusive if L = 1.