Lecture 8: Slit Lamp Exam Intro and Illumination Techniques
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
patient observation occurs throughout ___ parts of the exam
all
slit beam of light allows for ___________ imaging of layered tissues
cross section
purpose of slit lamp
routine ocular health assessment
contact lens evals
problem oriented, emergency care
used in combo w ophthalmic lenses for more advanced procedures
gonio
foreign body removal
epilation
fundoscopic exam
goldmann tonometry
whats different between Haag Style and Zeiss Style
haag - newer
lighthouse positioned above oculars
zeiss - older
lighthouse positioned belowt he microscope
microscope =
oculars
what are the haag style slit lamps in cs lab
topcon
haag streit - no built in yellow retina filter
marco
teaching tube shares a view w
the ocular it is mounted on
handheld portable slit lamps
heine
haag streit
keeler
reichert
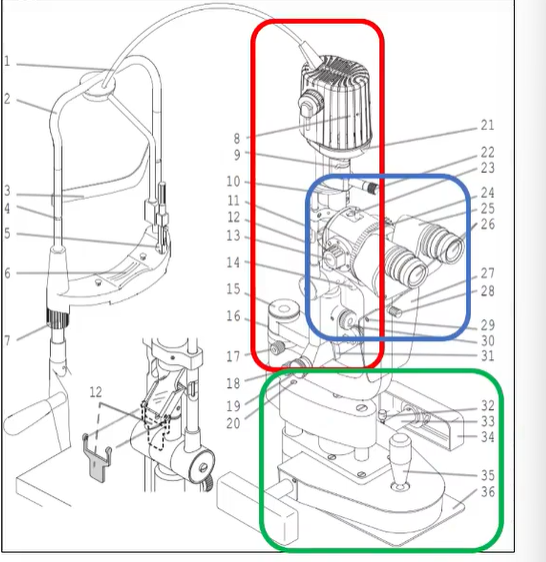
anatomy of a slit lamp
illumination system - lighthouse
where we make adjustment to light source
magnification - oculars
change mag
adjust to PD
adjust ocular focus
mechanical base/joystick
moves it
changes focus in to thigns deeper in eye or more external
illumination system schematic
light source
stenopaic slit
changes height or width and orientation angle
condensing lens
rotating mirror
illumination system lighthouse
variable apertures, change slit height
changes beam width (thickness)
can apply brightness diffuser and or filters
change orientation of slit beam from vertical to horizontal etc

parts
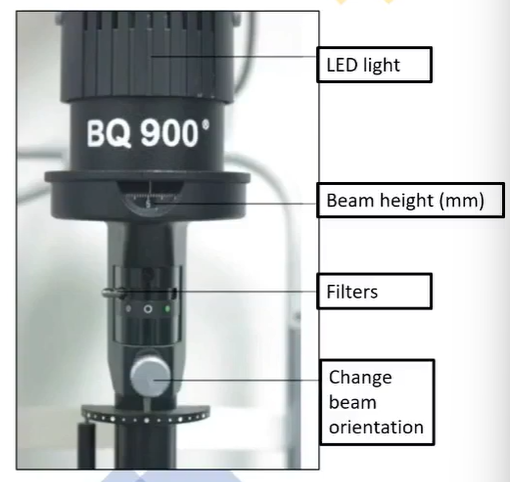
whats the first stop over after you get past max height
cobalt blue filter
what filters are there
open (full intensity)
neutral density (gray) filter
red free filter
optional yellow filter
cobalt blue
cobalt blue filter
excites fluorescein
in the top scrolling mm ruler
what can enance the green flow you see w a cobalt blue filter
handheld yellow Wratten filter
good for contact lens evals
red free (green filter)
causes blood vessels to appear black
helps localize pigmented lesions in the fundus to either choroid or RPE
RPE lesions REMAIN in your view
choriodal nevus will leave us
improved contrast when looking at retina layers
retina nerve fiber dropout (loss) appears as a black wedge inserting into the optic disc
external diffusor attachment
good for taking low mag photos showing natural colors
all structures relatively clear and in focus

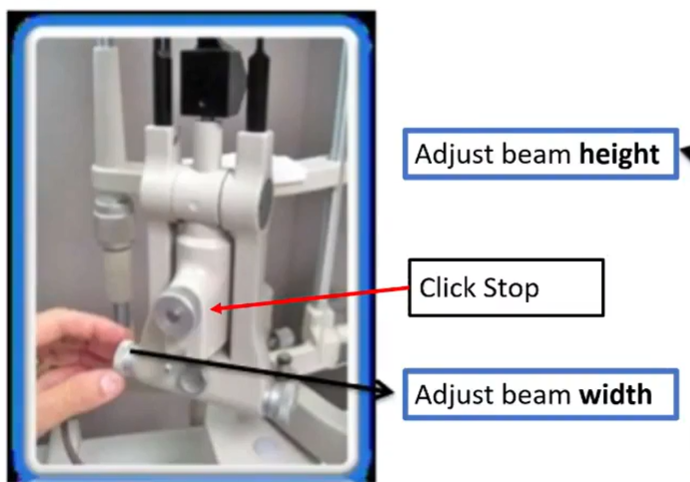
what do we ensure w the red arrow thing
click stop has to be in tight = in click vs out of click
keeps oculars focused at the same point the light is focusing
magnification system , microscope
focus one ocular at a time
dial in the max amount of plus then dial in minus until image is first clear
focusing oculars
insert focusing rods
adjust PD
put them apart then together until you see one single image
focus one image at a time
make sure focusing rod is perpendicular
SLOWLY REDUCE PLUS
UNTIL BAR IS FIRST CLEARif dr is fully corrected then each ocular should be close to 0
high mag =
less depth of focus
less field of view
more difficule to maintain sharp focus
mechanical base/joystick
scroll to move microscope up and down
move left to right to scan across
move forward and back to adjust plane of focus
base mounted rheostat for light intensity
leave at half
safety for slit amp
always lock the slit lamp
be careful w tonometry apparatus
never leave the tonometry tip in front of the pt
how do you position a heavy or large chested individual
sit further forward in exam chair
lower the slit lamp table allowing for them to lean forward into chin rest
how do you position long leg pt (daddy long legs if you will)
remove footrest
allow them to put feet on floor
how do you position wheelchair person
entire chair can be pushed back so wheel chair can go where it was
how do you position kids
may need to stand on footrest
sit on knees in chair
sit on parents lap
use handheld slit lamp
operating the slit lamp
two hands
one on base or joystick
base = big movements
joystick = fine movements
other hand light houes - adjusting beam angle and beam width
when assessing temporal aspect of eye lighthouse is
temporal
beam angle
angle created between microscope arm and lighthoues
should be at least 30-50 degrees for most anterior structures
necessary for dept localization w layered tissue
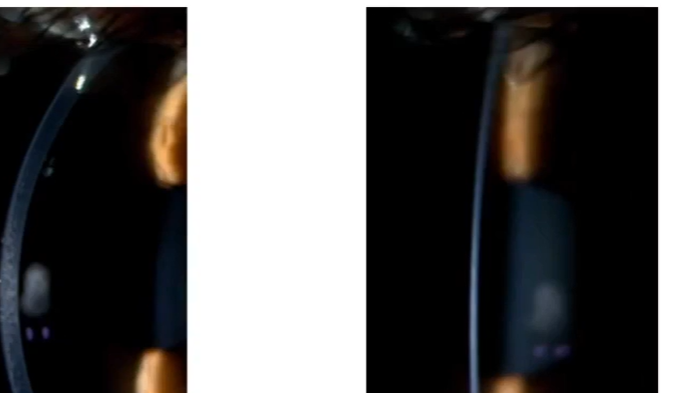
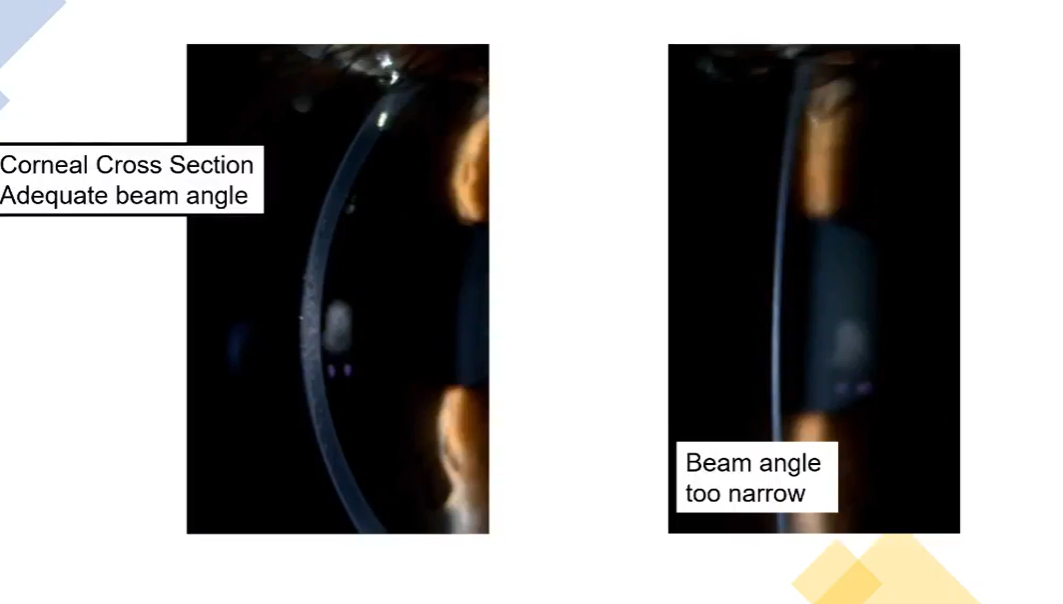
corneal cross section - which is good and which is bad
adequate = 30-50 degrees
direct illumination
light is directed at and focused on the tissue to be examined
techniques of direct
diffuse illumination - broad beam
focal illuminatino
optic section
parallelepiped
conical beam
specular reflection
indirect illuminatino
light is directed to a secondary surface then reflected onto the tissue to be examined
indirect illuminatino techniques
proximal
retroilluminatino
sclerotic scatter
diffuse - broad beam
see large amount of area at once
beam be 3-4 mm wide
max beam height
beam angle 30-5- deg
low mag (10x)
moderate brightness intensity
lids, lashes, meibomian glands, conj, sclera, iris
optic section
thinnest brightest beam
max height
beam angle 30-60 deg
low to moderade mag (10-16x)
max brightness
provides max structural detail
most acturate detail
more layers tan parallelpiped
cornea
should see a glistening of regular collagen lamellae of stroma
lens
good for localizing depth of things
foreign body
scars
ulcers
edema
parallelepiped
beam 1-2 mm wide
max beam height
beam angle 30-50 deg
low, moderate, or high mag (depends on tissue)
moderate brightness - bc beam is thicker
fewer layers than optic section
starting point for sclerotic scatter and specular reflection
cornea and lens
parallelelpiped benefit
enhanced surface detail than optic section
front half is epithelium second part is stroma and third part is endo
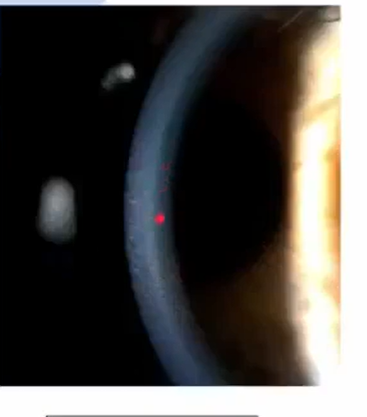
whats thsi
focus parallelepiped
look at center of beam
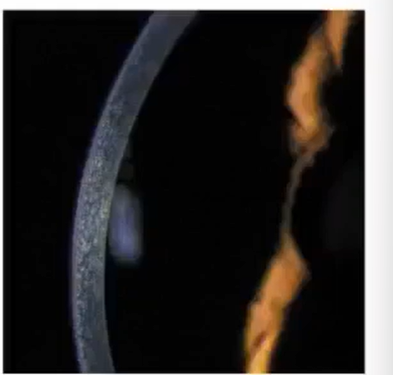
whats this
in focus optic section
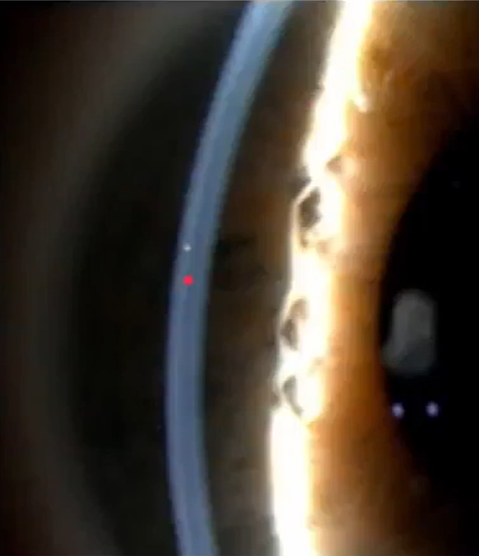

whats this
neither
increase veam thickness until theres a white line
optic sectino for lens
optic section focused on cornea first
then push into pupil along the angle of the beam of light - not straight in or out
may need to dec beam angle to fit the posterior capsule into pupil margin
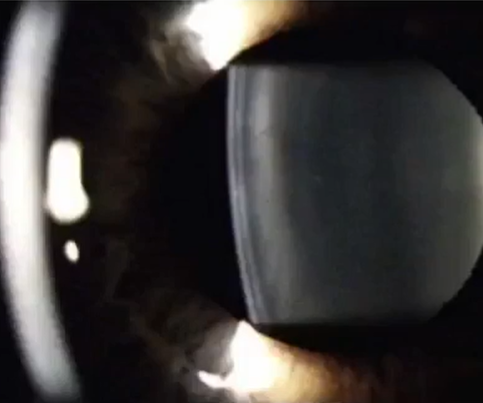
name
anterior lens
white black white
ant lens capsule
subcapsular space
beginning of cortex

name
posterior inverted Y suture
theres also a really hard to see anterior y suture
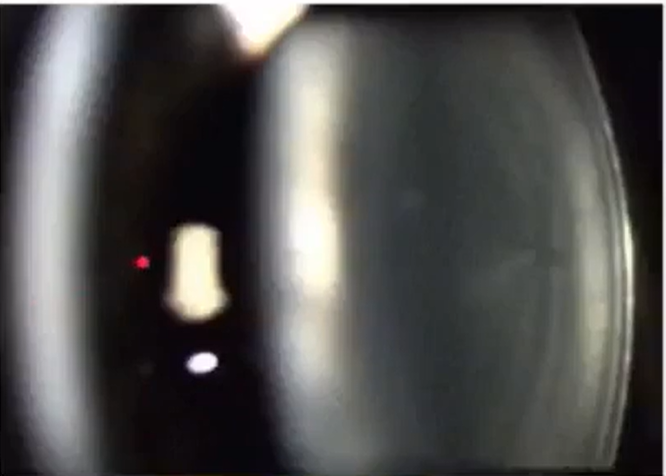

name
posterior lens capsule part that is furthest right
parallelepiped - ascension phenomenon of the anterior vitreous
visualize movement of the anterior vitreous
dilated pupil
parallelpiped depper than posterior lens capsule
instruct pt to look up and then straight ahead
observe vitreous fibers floating down
conical beam
height small as possible = 0.2 or 1 mm circle
beam angle 40-69
moderate or high mag (16 25 40)
max brightness
anterior chamber cells and flare
specular reflection
monocular phenomenom
parallel piped beam to start
full height
wide beam angle
mod or high mag
moderate brightness
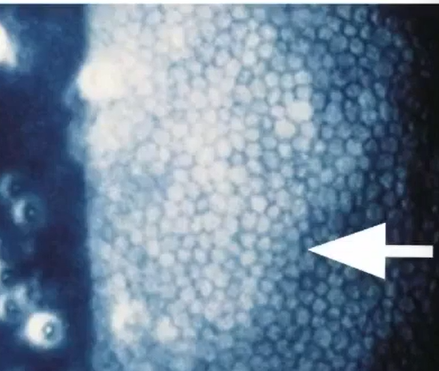
corneal endothelium , anterior and posterior lens capsules
specular reflection of corneal endo
monocular
PPD
bring ep of parallelpiped over to purkinje reflection/light box and look to see orange peel texture, structural detail of endothelium
provides textural surface detail under high mag
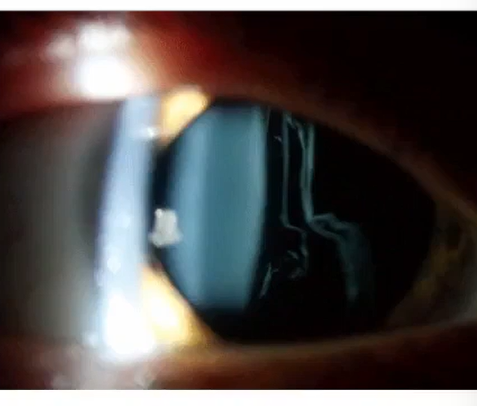
specular reflection of anterior and posterior lens capsule
monocular
PPD
full beam height
reduced beam angle
moderate mag
mod brightness
provides textual surface detail

proximal indirect illumination
light from illumination system is focused immediately adjacent tot he structure to be examined
good for corneal nerves, corneal neovascularization
PPD to start
full beam height
wide beam angle
mod bright
moderate mag
focus light at limbus and can see corneal nerves stretching into cornea
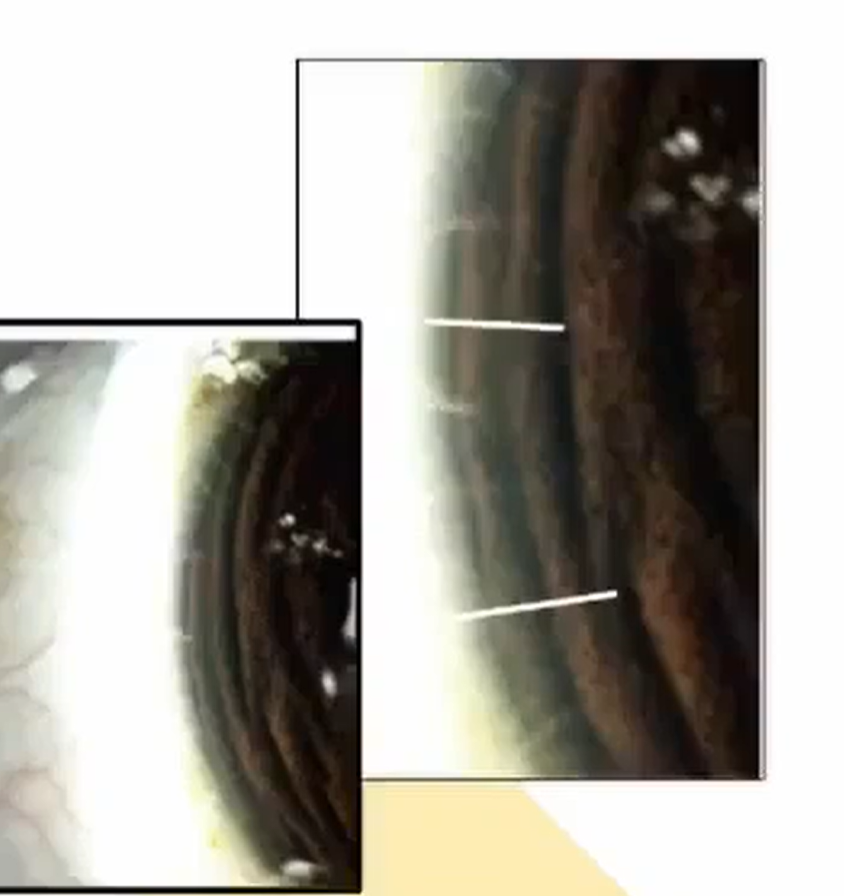
retroilluminatino from iris
PPD
full height
wide angle
mod bright
mod mag
light focused on cornes and lands on iris directly psoterior to it
light reflecting off the iris illuminates subtle corneal abnormalities
used when direct illuminatino would cause bleaching of image details
good for corneal neovascularization and keratic precipitates
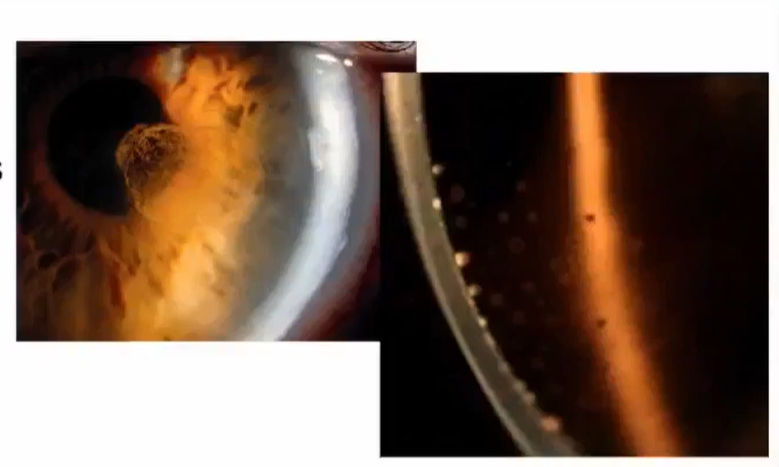

retroilluminatino from fundus
monocular
PPD
focus on tissue to be examined - know where you are focused first
reduce beam angle to see red glow
cornea, lens, iris
sclerotic scatter
ppd
viewed from outside the slit lamp
wide angle - at least 60 deg
light will undergo total internal reflection
any corneal opactity will scatter light
shows cornea (abrasions, scars, FB, keratic precipitates)