Chemistry - Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Displacement Reaction
A reaction in which the more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its compound in solution or in molten forn
Iron and Copper Sulphate Reaction
Fe + CuSO4 —— FeSO4 + Cu
CuSO4 - blue
FeSO4 - green
Zinc and Copper Sulphate Reaction
Zn + CuSO4 —— ZnSO4 + Cu
ZnSO4 - colourless
Lead and Copper Chloride Reaction
Pb + CuCl2 —— PbCl2 + Cu
PbCl2 - colourless
Double Displacement Reaction
Reactions in which there is an exchange of ions between the reactants are called double displacement reaction.
Precipitation Reaction
Any reaction that produces a precipitate
Sodium Sulphate and Barium Chloride Reaction
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 —— BaSO4 + 2NaCl
All colourless except BaSO4 (white precipitate)
Lead Nitrate and Potassium Iodide Reaction
Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI —— 2KNO3 + PBI2
Pb(NO3)2, KI - white
KNO3 - white/grey
PbI2 - yellow precipitate
Oxidation
If a substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen during a reaction, it is said to be oxidised
Reduction
If a substance loses oxygen or gains hydrogen during a reaction, it is said to be reduced.
Redox Reaction
During a reaction, if one reactant gets oxidised while the other gets reduced it is called a redox reaction.
Oxidisation of Copper to Copper Oxide
2Cu + O2 —— 2CuO
Cu - brown
Copper Oxide and Hydrogen Reaction (Redox Reaction)
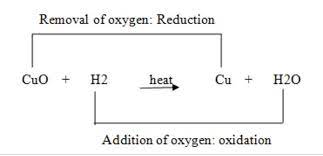
Zinc Oxide and Carbon Reaction
ZnO + C —— Zn + CO
Oxidising agent - ZnO
Reducing agent - C
Manganese Oxide and Hydrochloric Acid Reaction
MnO2 + 4HCl —— MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Oxidising agent - MnO2
Reducing agent - HCl
Corrosion
When a metal is attacked by substances around it such as moisture, acid, etc. it is said to corrode and this process is known as corrosion.
Eg - black coating on silver
- green coating on copper
- brown coating on iron
Rancidity
Oxidation of fats and oil in food materials resulting in a bad smell or taste
Rusting of Iron
Iron, in the presence of moisture, reacts with oxygen to form hydrated iron oxide (brown coating). This is known as the rusting of iron.
Preventing Rancidity
Keep food in air-tight containers
Refrigeration
Add antioxidants to foods containing fats and oil
Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen
Antioxidant
Substance that prevents oxidisation
Chemical Reaction
Whenever a chemical change occurs, we can say that a chemical change occurs
Magnesium and Oxygen Reaction
2Mg + O2 —— 2MgO
Observations in a Chemical Reaction
Change in state
Change in colour
Evolution of gas
Change in temperature
Reactants and Products
The substances that undergo chemical change in a reaction are the reactants.
The new substance formed during the reaction is the product.
Unbalanced Equation
The equation is unbalanced when the mass is not the same on both sides of the equation. It is also known as a skeletal chemical equation.
Law of Conservation of Mass
The total mass of the elements present in the products of a chemical reaction has to be equal to the total mass of the elements present in the reactants.
Zinc and Sulphuric Acid Reaction
Zn + H2SO4 —— ZnSO4 + H2
Balanced Chemical Equation
If the number of atoms is the same on both sides of the arrow, it is a balanced chemical equation.
Iron and Water Vapour Reaction
3Fe + 4H2O(g) —— Fe3O4 + 4H2(g)
Carbon Monoxide and Hydrogen Reaction
CO + 2H2 —— CH3OH
CH3OH - Methanol
Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 12H2O —— C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O