Cofactors and Coenzymes
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is an intracellular ?
catalyst reaction within cells
Eg : respiration
What is extracellular
Enzyme catalyses reactions outdoes of cells
Eg : saprotrophoc digestion by bacteria / fungi OR amylose sliced by salivary glands/ intestinal epithelial cells
What is a catalase + usage ?
Intracellular enzyme found in all organisms, it’s exposed to O2.
It protect cells digesting hydrogen peroxide into hydrogen + water.
faster reacting enzyme , with a turnover of 6 million / sec , cuz of the toxicity of H2O2.
WBC uses to kill microbes when they ingest them
Where is catalase found ?
It’s found inside cells in vesicles called ‘ peroxisomes ‘
What is H2 O2 ?
H2O2 is a harmful by product of many metabolic reactions.
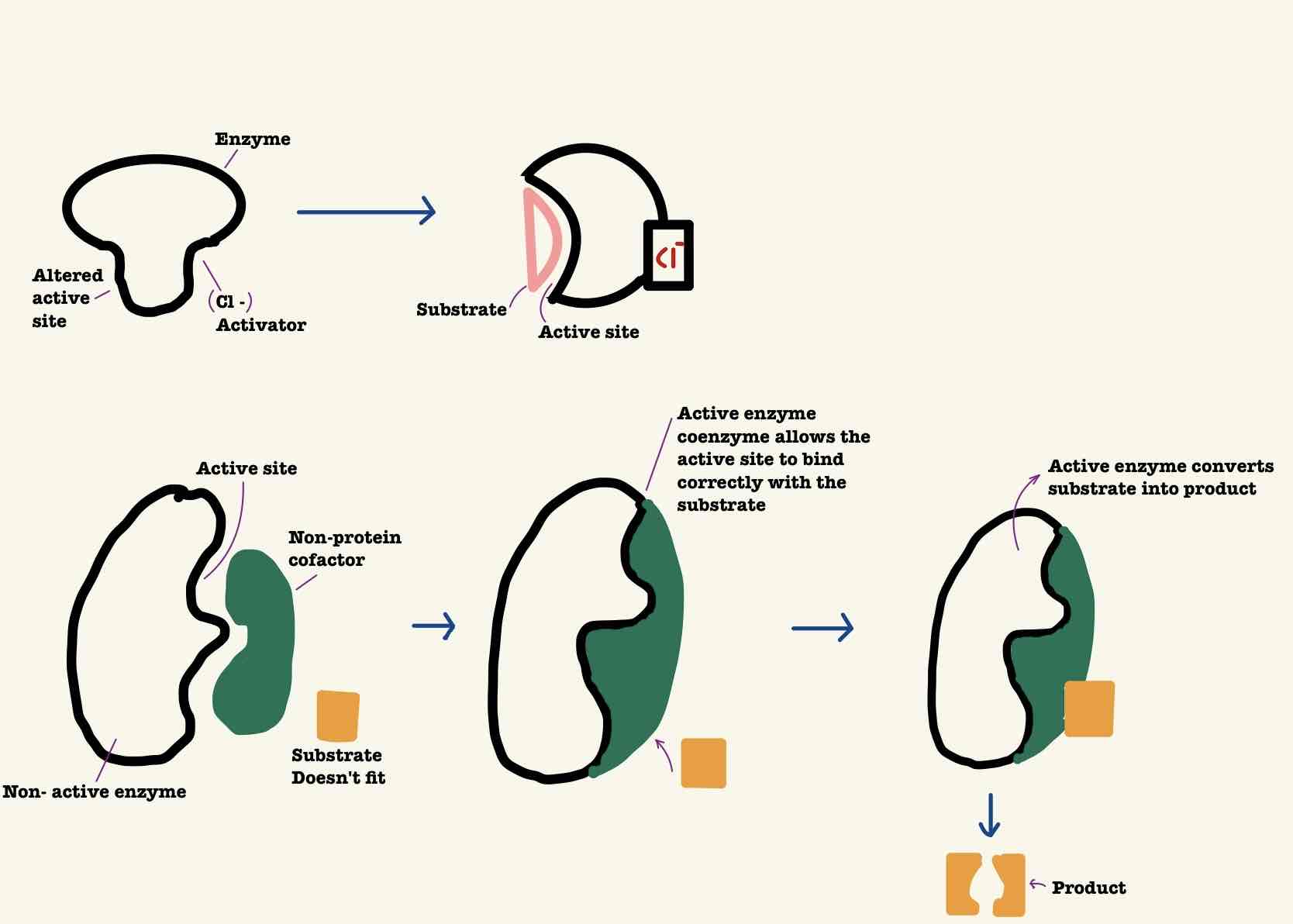
What is a cofactors + usage ?
A small , non protein molecule which bind to enzyme’s active site or the allosteric site to enable them to work.
Acts as co - substance, to bind to the substrate to form/ change the complementary shape for active site.
Some cofactors change the distribution of charge on the active site at substrate , making enzyme substrate bonds easier to form.
Extra info about cofactors
Prosthetic Groups
These are cofactors permanently- bond to enzyme ( bound by covent bond )
Eg : Hemoglobin has an iron ion permanently bound to each of its 4 polypeptide chains, to bind to O2
What is a coenzyme ?
A small, non protein mole- protein molecule that bind temporary to the active site.
This happens either at the same time , or just before the substrate binds.
Coenzymes are changed during the reaction and have to be replaced before they can be used again.
Allosteric Activation
a mechanism of enzyme regulation where an activator molecule binds to a specific site on the enzyme other than the active site called the allosteric site causing a conformational change in the enzyme's structure that increases the affinity of the active site for its substrate, thereby increasing the enzyme's activity.