PSCI 3500 Midterm
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Science and Falsification
provisionally understanding the world
quest for knowledge that relies on criticism
might be wrong, might be potentially testable
Scientific Method
Research Question
Theory
Hypothesis: X (IV) → Y (DV)
Test Hypothesis
Evaluation
Albert Hirschman (1970)
Exit: Your behavior to achieve the best outcome possible given your new environment
Voice: “Voice” (complain, protests, lobby, take direct action) to try change the environment
Loyalty: Accept the fact and make no changes
Game Theory
is a tool, not theory
Choices, strategies, equilibrium
Contractarian view of the state
State of Nature: “war of every man against every man” (Hobbes)
Predatory view of the state
Extortion (Charles Tilly)
Concert for security leads states to use their power to extract resources from others
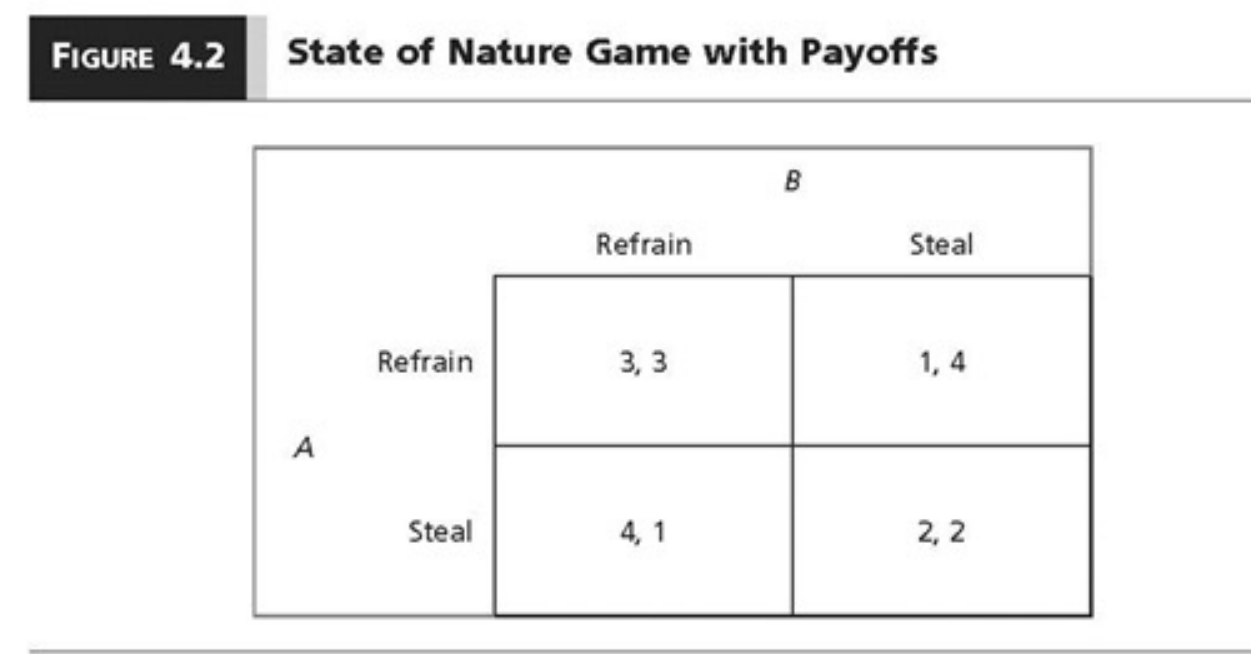
State of Nature Game with Payoffs
Democracy
Demokratia, dangerous and unstable by the middle of the 19th century
Many philosophers preferred Monarchy to Democracy
View of Democracy
Substantive View: outcomes
Procedural view: minimalist, institutions or procedures, Dahl’s view
Polyarchies: inclusion, contestation
Nominal measure
discrete categories
a democracy or a dictatorship
Ordinal measure
rank order cases
ex. income: low income, middle income, high income
Interval measure
Difference between variables can be evaluated
Polity IV and Freedom House
How do you evaluate measures?
validity
reliability
replicability
Validity
our measures correspond to the concepts
Reliability
repeatedly and consistently produces the same score
Replicability
the ability of third-party scholars to reproduce the process
Modernization theory
as countries develop economically, they are
more likely to become democratic
more likely to remain democratic
Survival Story
Przeworski (Przeworski and Limongi, 1997)
Democracy is more likely to survive as countries develop and become richer, but it is not more likely to emerge
Socioeconomic structure
a shift from agriculture to manufacturing and services
Peasants moved from rural to urban areas
Gentry became a rising class
Resource Curse
Democracy is less likely to emerge and survive in countries whose economies depend heavily on oil production or mineral extraction
Dependent variable (Y)
the thing we want to explain
Change in DV depends on IV
Independent variables (X)
the things we think explain or determine the value of the dependent variable
Doesn’t depend on anyone or anything
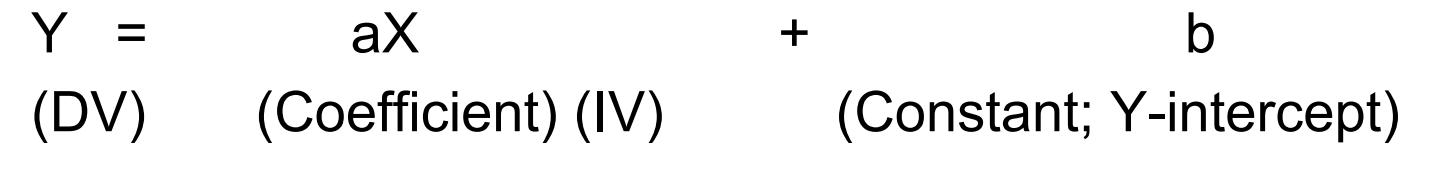
Empirical evidence model
Y against X

Economic Determinants of Transitions to Democracy
Primordialist arguments
fixed since “primordial” times
democracy is not for everyone
Constructivist arguments
constructed or invented rather than inherited
Parochial
traditional
What are subjects in political culture?
centralized authoritarian systems
What are civics (participants)?
Democratic
Compatible with democracy
Clash of civilization
cultural conflicts, certain cultures are incompatible with democracy
Is Protestantism compatible with democracy? Why or why not?
Yes bc of individual responsibility
types: lutherans, baptists
Why was catholicism considered incompatible with democracy?
Hierarchy
Conflicts with loyalty to church/pope
Why was confucianism considered incompatible with democracy?
Asian values
collectivist instead of individualists
Social harmony, yin and yang
Why was islam considered incompatible with democracy?
theocracy (government by religion)
violent
women as being unequal
Three waves of democracy–Huntington
Wave 1: 1828–1926. American and French revolutions, WWI
Wave 2: 1943–1962. Italy, West Germany, Japan, Austria, and so on
Wave 3: 1974– . Started with Greece, Spain, and Portugal. Then Latin America and Africa.
Transition to Democracy
external imposition
Bottom-up transition
Top-down transition
External Imposition
Intervention by democracies produces the trappings of democracy, but fails to increase the level of democracy
Preference Falsification
applaud dictators who they disliked (Kuran 1991)
Revolutionary threshold
type of tipping model
An individual has a protest size at which she/he is willing to participate
A = {0, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10}
won’t revolt
A’ = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10}
Change of of private preferences
Revolutionary cascade, east germany and arab spring
Sudden revolution
Predictability
Top-down transition
possible under incomplete information, under uncertainty, or by mistakes
Policy of liberalization on the part of the government
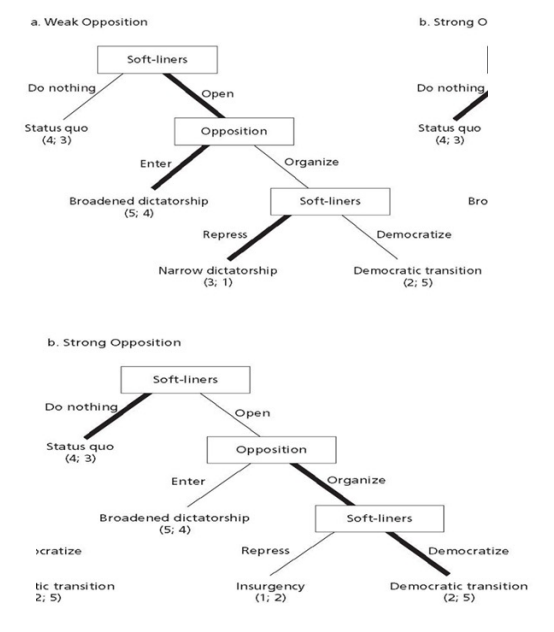
Best outcome for dictatorship group and opposition group
Dictatorship group: broaden dictatorship (5,4)
Opposition group: democratic transition (2,5)
How can democratic transitions be possible?
under incomplete information and under some uncertainty
How can top-down transitions occur?
when someone makes a mistake
What are the independent and dependent variables?
As Evangelical in district increases, support for trump increases
Independent variable: Evangelical in district increases
Dependent variable: support for trump increases
What are the independent and dependent variables?
As literacy increases, level of domestic violence against women decreases
Independent: Literacy increases
Dependent: level of domestic violence against women decreases
Who was the gentry?
New class that emerged when peasants moved to urban areas
Made a lot of money through businesses
Important for economic structure
Made representative gov
After industrial revolution, they got a lot of money, not nobles