7. Climate change: Science and policy
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is global warming?
Certain gases in the earth’s atmoshphere have the effect of blocking emmissions of heat from the earths surface
Heat from the sun allowed to pass through these gases to reach the earth but when it rebounds from the earths surface it is prevented from escaping back into space
In effect these gases form a glass screen above the earth → green house effect → GDG gases
What is the science behind GHG?
GHG all occur naturally, they regulate earths temperature
without them the average tenoerature of earths surface would be -19oC rather than +15oC
There is a natural greenhouse effect
there is increasing evidence that there is an enhanced greenhouse effect caused by increasing emissions of these gases as a result of human activity (anthropogenic GHG emissions)
Scientific consensus is that human activity is influencing the climate
What are the 5 main green house gases?
carbon dioxide (CO2) : burning fossil fuels, solid waste, trees and other biological materials
Methane (CH4): agriculture, foaail fuels, and decomposition of landfill waste
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC-11 and CFC-12) : refrigerators, air conditioners, different types of sprays, fire extinguishers and paints
Nitrous oxide (N2O): agriculture, particularly fertilised soila nd animal waste
What is Global Warming Potential (GWP)
the relative strength of one unit of each gas in contributing to global warming
What is the lifespan of GHG?
some have a very long atmoshpheric life
even if emissions start to fall, atmoshpheric concentrations will continue to increase for many years
Which GHGs are especially higher than pre-industrial concentrations?
CFCs which are a man made gas
How are the gases released?
Gases are all released by industrial and agricultural activity
Carbon dioxide is released when fossil fuels are burnt. others come from a variety of sources

What are the 2 main discussions for GHG emissions?
Who emits the most?
Asia is by far the largest emitter → 53% of global emissions
However, Asia is home to 60% of the worlds population
Who has contribute dthe most to global CO2 Emissions?
The US has emmitted more CO2 than any other country to date
Since 1751, US is responsible for 25% of historical CO2 emissions
Who emits the most vs who is impacted the most
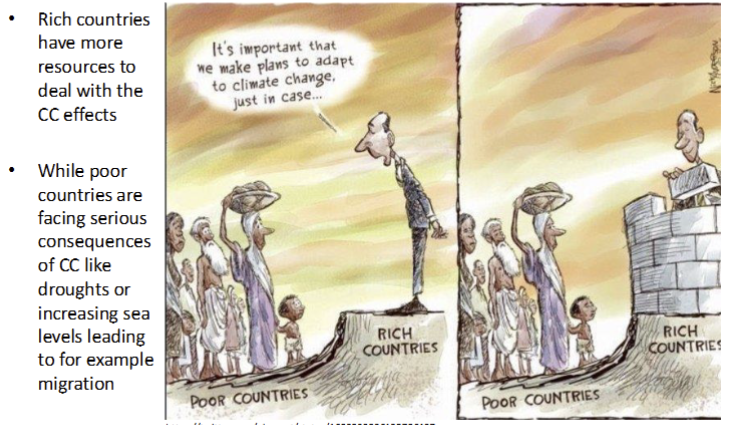

What are the states for Global CO2 emiisions and cumulative global CO2 emissions?

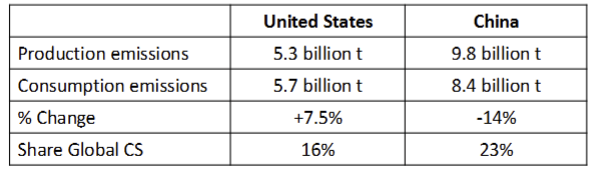
What is production based emissions?
Considers emissions that take place within national territroy and offshore areas over which the country has jurisdiction → aka territorial based emmisions
What are consumption based emissions?
emissions from domestic final consumption and those caused by the production of imports → take into account the effects of trade
Who emits the most?
Is there uncertainty with climate change?
great deal of uncertainty surrounding the exact effect that these gases have on global climate patterns
scenarious below e.g. based on changes in human life, governmental policy response, atmoshpheric changes etc.
What are the different sources of uncertainty?
change in technology
change in weather conditions and feedbacks in the atmosphere once warming starts
change in scientific thresholds
change in our adaption policie
What are the impacts of climate change?
IPCC 5th Assessment Report 2014:
anthropogenic GHG emissions are extremely likely to have been the dominant cause of the observed warming since the mid 20th C
“Surface temperature is projected to risk over the 21st century under all assessed emission scenarious. it is very likely that heat waves will occur more often and last longer, and that extreme precipitation events will become more intense and frequent in many regions. the ocean will continue to warm and acidify, and global mean sea level to rise
What are the consequences of climate change?
Likely to be complex and far reaching
sea level increase will cause major problems for low lying areas and will necessitate the construction of large scale sea defences
rising temperatures will have serious implications for ecology and agriculture
occurence of storms and hurricanes will uncrease and new areas will start to experience tropical storm
What are the several points to bear in mind when it comes to formulating policy responses:
There is a long time lag btw our current actions and the effect of them on the climate. Climate change is an intergenerational issue: do we act now or save money for the future
For the main GHG there is no end of pipe technology, i.e. we cannot use new technology to reduce emissions , in the same way that we can for other air pollutants
since the effect of emissions is felt globally, it is not good if one or two countries reduce emissions, if other do not → any action has to be implemented globally
What are potential policy responses?
Mitigation: actions to limit the magnitude or rate of long-term climate change, i.e. actions that reduce the amount of GHG released into the atmosphere
Adaptation: Actions to reduce the vulnerability of social and biological systems to climate change, i.e. actions that lower the risks caused by climate change
How would a policy of mitigation work?
policies that concentrate on the reduction of energy use and encouraging the switch to cleaner fuels since this provides the greatest scope for emissions reduction
CO2 mitigation policies
use energy more efficiently and switch to less carbon intensive fuel (gas and renewables ), i.e. to prevent emissions
Increase the amount of carbon that is absorbed by trees by increasing forested areas and preventing deforestation
How would the policy of adaptation work?
Policies that concentrate on teh reduction of local or regional vulnerabilities
What is deforestation?
the purposeful clearing of forested land, especially for the purpose of making space for agriculture and animal grazing, and to obatin wood for fuel, manufacturing and construction
What are the challenges for the design of climate policies
policy makers will select policies that yield the greatest net benefits (benefits minus costs)
Costs of climate policies (e.g. building a flood defence
uncertainty of cost → low
time scale of benefit → short term
Benefits of climate policies:
Mitigation: reduction of future CC damages due to the decrease in GHG
Adaptation: reduction of future CC damages due to the implementation of policies to reduce the vulnerability of social and biological systems
Benefits depend on future climate
uncertainty of cost → high
time scale of benefit → short term
Uncertainty may lead to regret in design of climate policies
What are the time-scale challenges for the design of climate policies?
different time scale costs and benefits of climate policies means that projects to tackle climate change are not likely to be favoured
Costs of climate policy: time scale → sjort term
Benefits of climate policy: time scale → long term
Cost benefit analysis
Cost-benefit rule: politicians will focus on Net Present Value (NPV)
NPV calculate the difference btw PV benefits and PV costs of the project
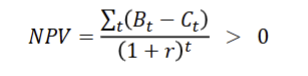
In summary, what are the 3 main challenges for the design of climate policies?
Global phenomenon (local actions are not enough)
Long term phenomenon (intergenerational nature)
Uncertainty (benefits are long-term, mostly)