Unit 6 Biology: Meiosis and Genetic Variation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the two types of cells in our bodies?
Sex cells (gametes) and somatic cells (body cells).
What are the two types of chromosomes in our cells?
Autosomes, which control inheritance of traits, and sex chromosomes, which control sex and sex-related traits.
What is meiosis?
The process by which gametes are formed, reducing the chromosome number by half and producing haploid cells.
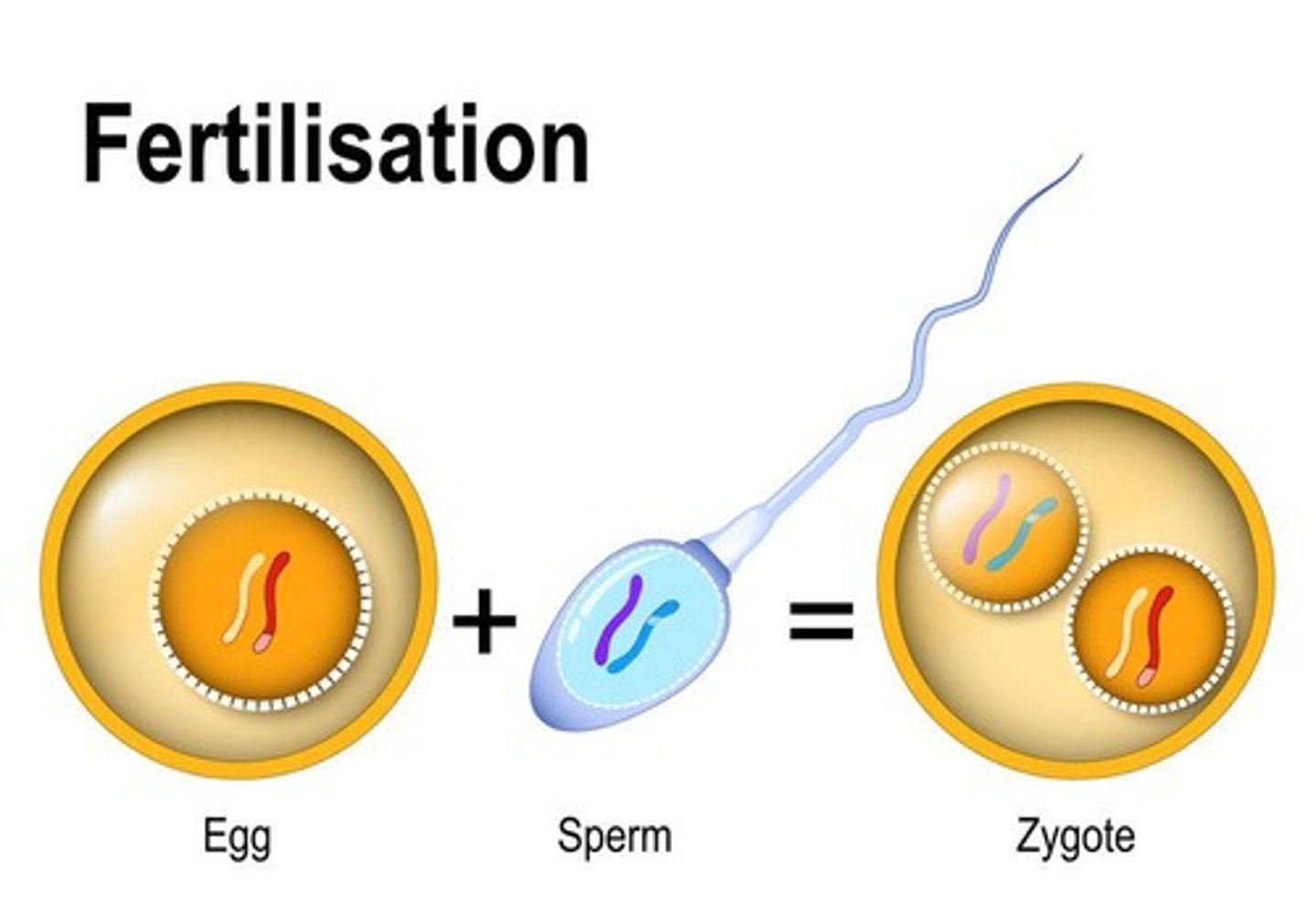
What happens when gametes combine to form a zygote?
The original chromosome number is restored.
What are the two phases of meiosis?
Meiosis I, which separates homologous chromosomes, and Meiosis II, which separates sister chromatids.
What occurs during Interphase before meiosis?
G1: Cells grow and perform functions; S: DNA is copied; G2: Proteins are made and cells grow.
What happens during Prophase I of meiosis?
The nuclear membrane breaks down, centrosomes move to opposite sides, spindle fibers assemble, and homologous chromosomes pair up.
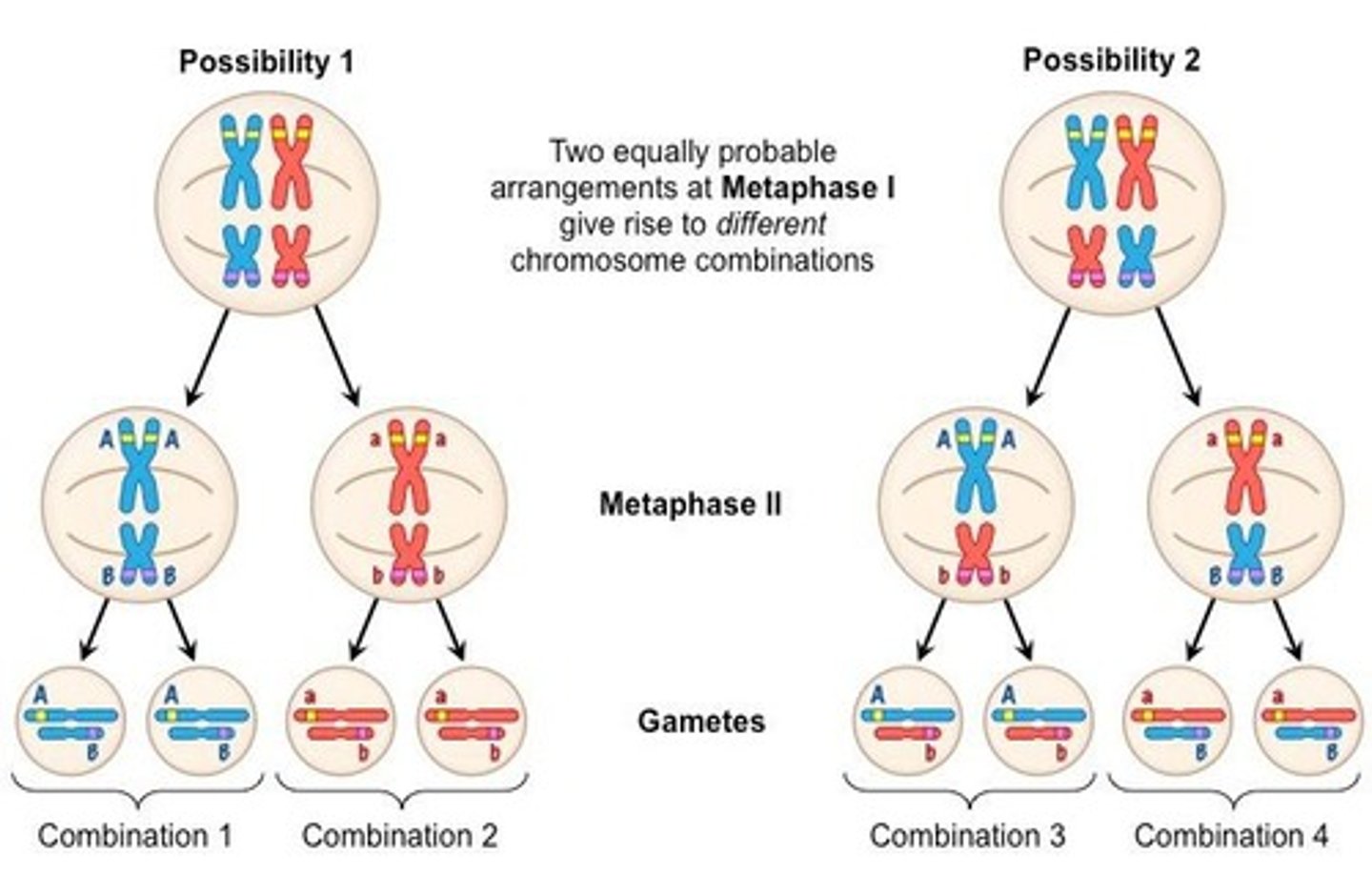
What occurs during Metaphase I of meiosis?
Homologous chromosome pairs are randomly lined up in the middle of the cell.
What happens during Anaphase I of meiosis?
Paired homologous chromosomes separate and move toward opposite sides, while sister chromatids remain together.
What is the result of Telophase I?
The nuclear membrane forms again, spindle fibers disassemble, and the cell undergoes cytokinesis, resulting in 2 cells with unique combinations of chromosomes.
What is crossing over in meiosis?
When homologous pairs line up at the equator, parts of chromatids twist around each other, resulting in new combinations of alleles.
What is independent assortment in meiosis?
The random alignment of homologous pairs at the equator, leading to a large number of possible combinations in daughter cells.
What happens during Prophase II of meiosis?
The nuclear membrane breaks down, centrosomes move to opposite sides, and spindle fibers assemble.
What occurs during Metaphase II of meiosis?
Spindle fibers align chromosomes at the cell equator, with each chromosome still having two sister chromatids.
What happens during Anaphase II of meiosis?
Sister chromatids are pulled apart and move to opposite sides of the cell.
What is the result of Telophase II?
Nuclear membranes form around chromosomes, spindle fibers break apart, and the cell undergoes cytokinesis, resulting in 4 haploid cells.
What is the starting and ending cell type in meiosis?
Starts with a single diploid cell (2n) and ends with 4 haploid cells (n).
What is the significance of genetic diversity in meiosis?
It is introduced through mechanisms like crossing over and independent assortment.
How does crossing over contribute to genetic variation?
It allows chromosomes to exchange genetic information, creating new allele combinations.
What is the end result of meiosis?
Four haploid cells with a combination of chromosomes from both mother and father.
What distinguishes meiosis from mitosis?
Meiosis results in gametes with half the chromosome number, while mitosis produces identical diploid cells.