Respiratory A&P
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
external nares
aka the nostril; the outer opening of the nose that allows air to enter the nasal cavity; starting point of the respiratory tract, where inhaled air is filtered, warmed and moistened before moving deeper into the body
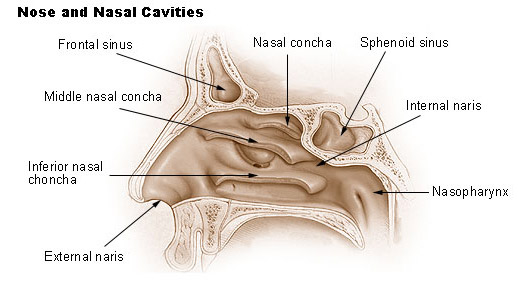
nasal vestibule
the most anterior part of the nasal cavity, located just inside each nostril; lined with skin nd contains coarse hairs that act as a filter to trap dust, dirt and other particles from inhaled air, preventing them from entering the lungs
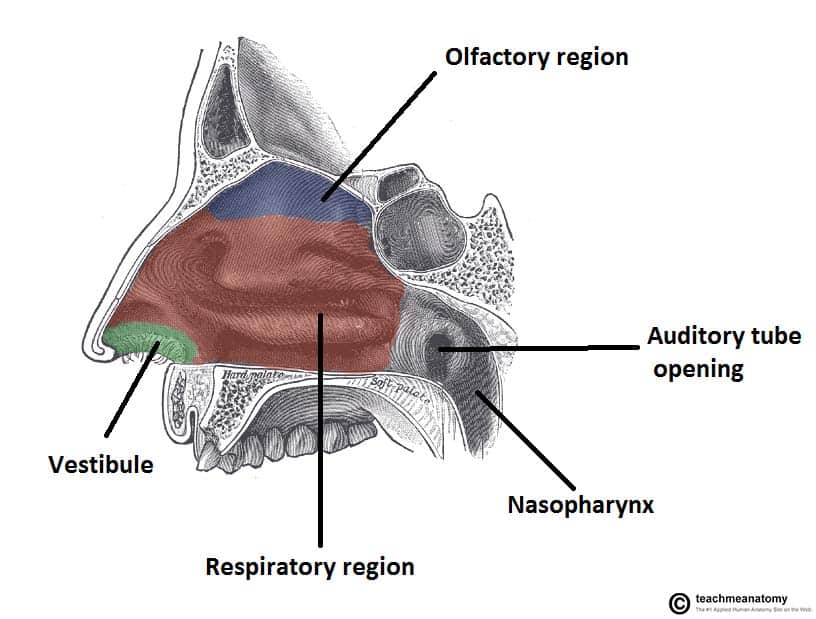
nasal cavity
the interior space of the nose that extends from the nostrils to the nasopharynx (upper part of the throat)
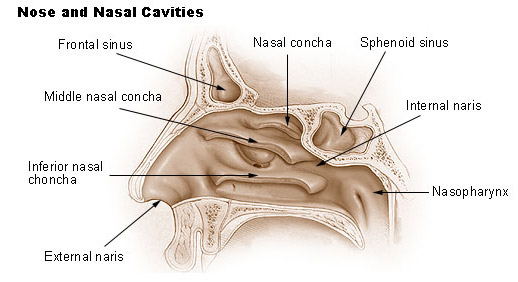
nasal conchae
bony structures located within the nasal cavity; play crucial roles in regulating airflow, warming and humidifying air, and filtering particles
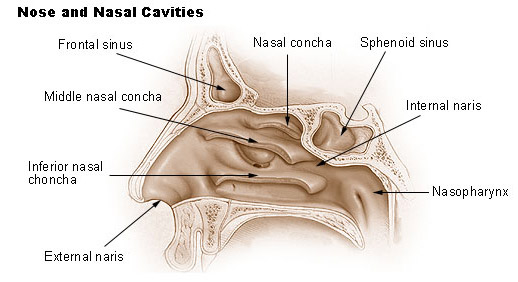
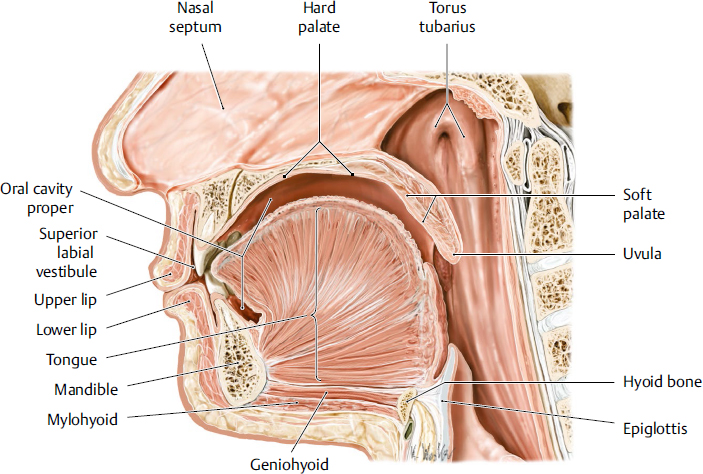
oral cavity
the mouth; the initial part of the digestive system a complex structure that plays essential roles in digestion, speech, and oral health
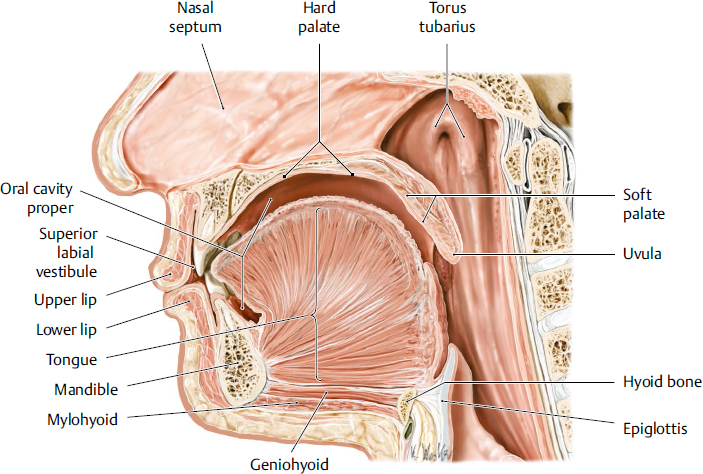
tongue
a muscular organ located in the oral cavity that plays crucial roles in taste, speech and swallowing; innervated by hypoglossal nerve
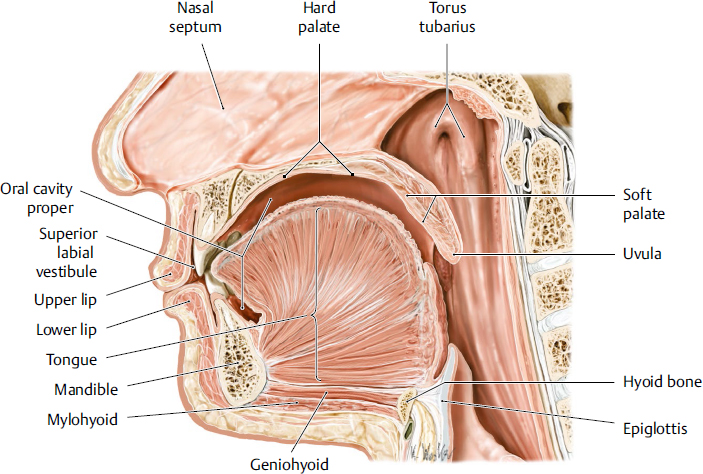
hard palate
the bony roof of the mouth, forming the anterior portion of the palate; located between the upper teeth and the soft palate; composed of part of the maxilla and palatine bones; separates oral cavity from nasal cavity
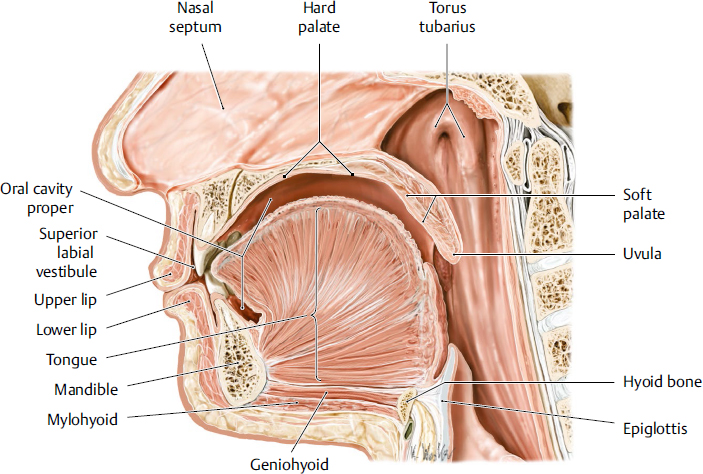
soft palate
the muscular, flexible back part of the roof of the mouth that separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity; primarily functions to aid speech, prevent food from entering the nasal cavity and aiding breathing
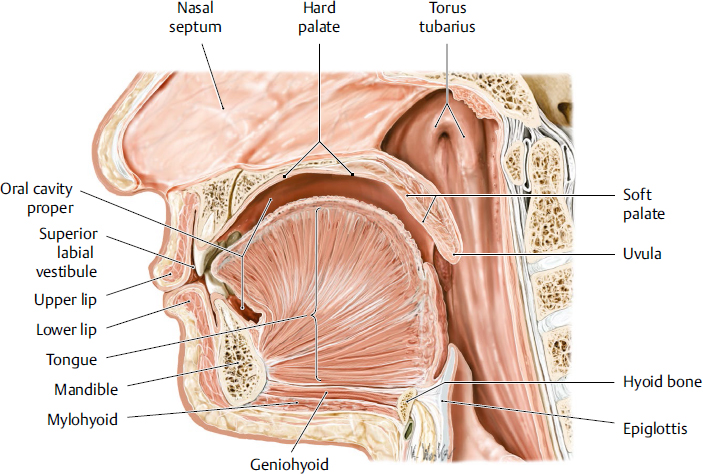
uvula
a fleshy extension at the back of the soft palate which hangs above the throat
pharynx
the membrane-lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the esophagus; a muscular tube in the middle of the neck that helps you breathe and directs food and liquid into the digestive system
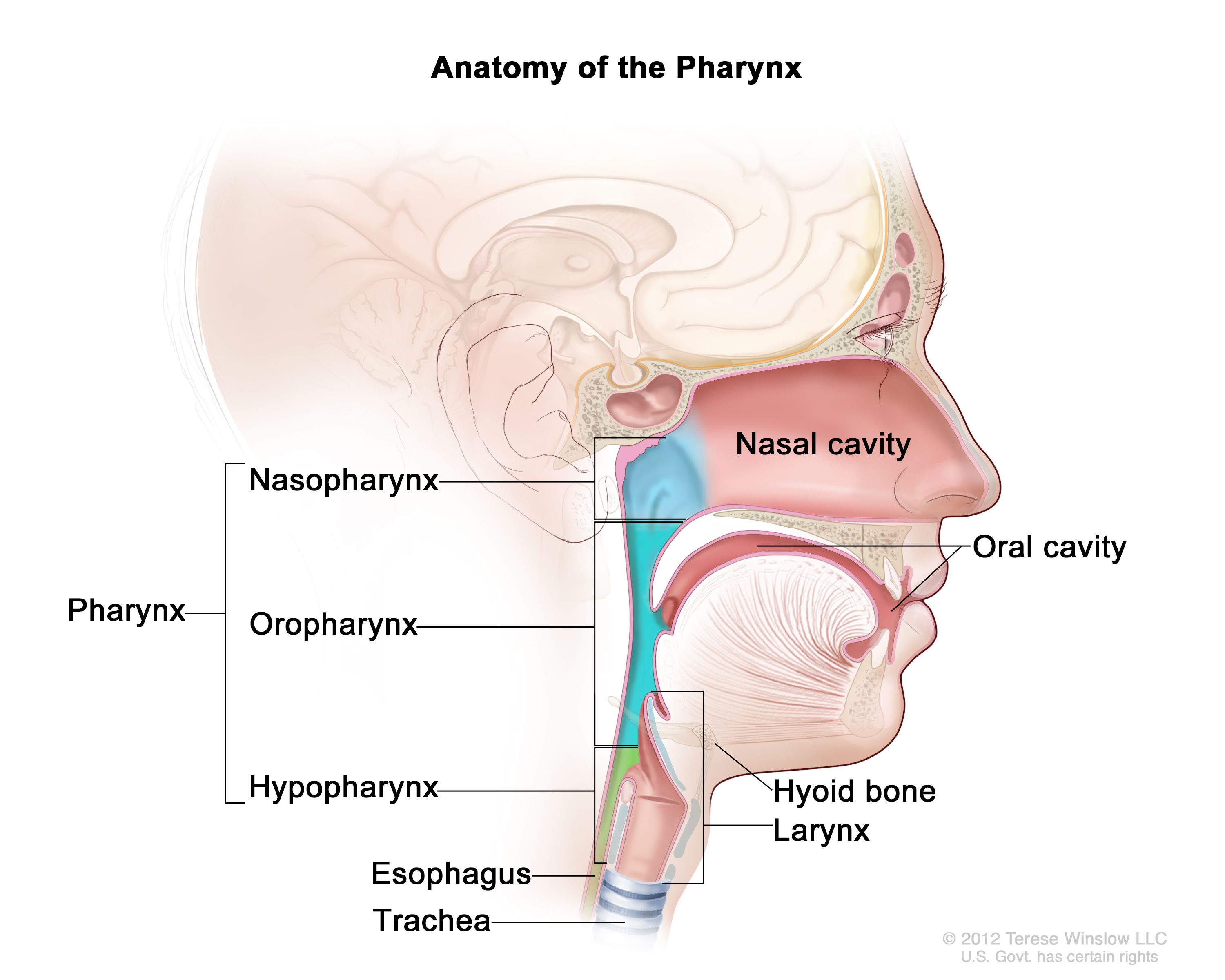
nasopharynx
the upper part of the pharynx; the passageway at the back of the nose and throat that connects the nasal cavity to the mouth and windpipe
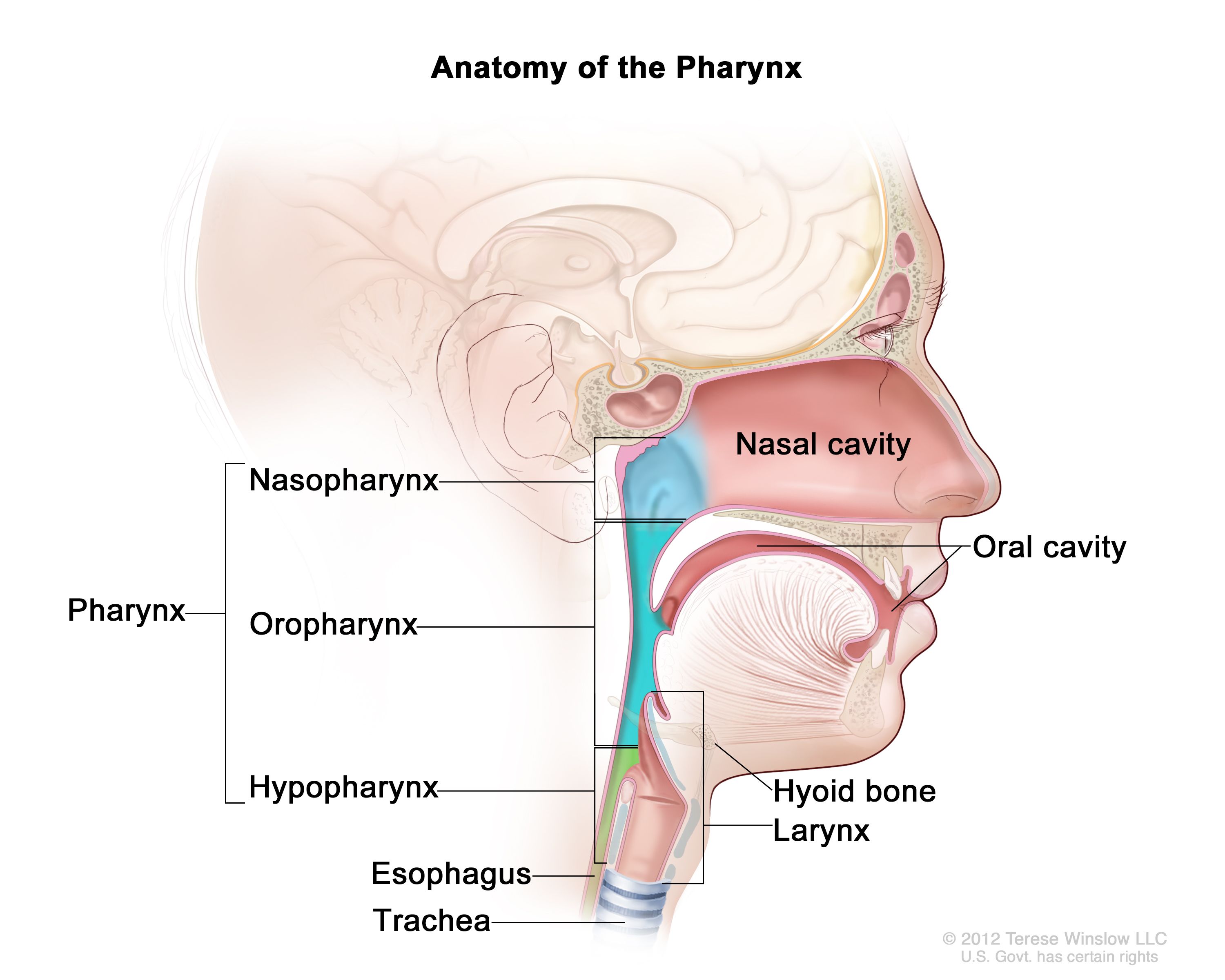
oropharynx
the part of the pharynx that lies between the soft palate and the hyoid bone; middle part of the throat, behind the mouth
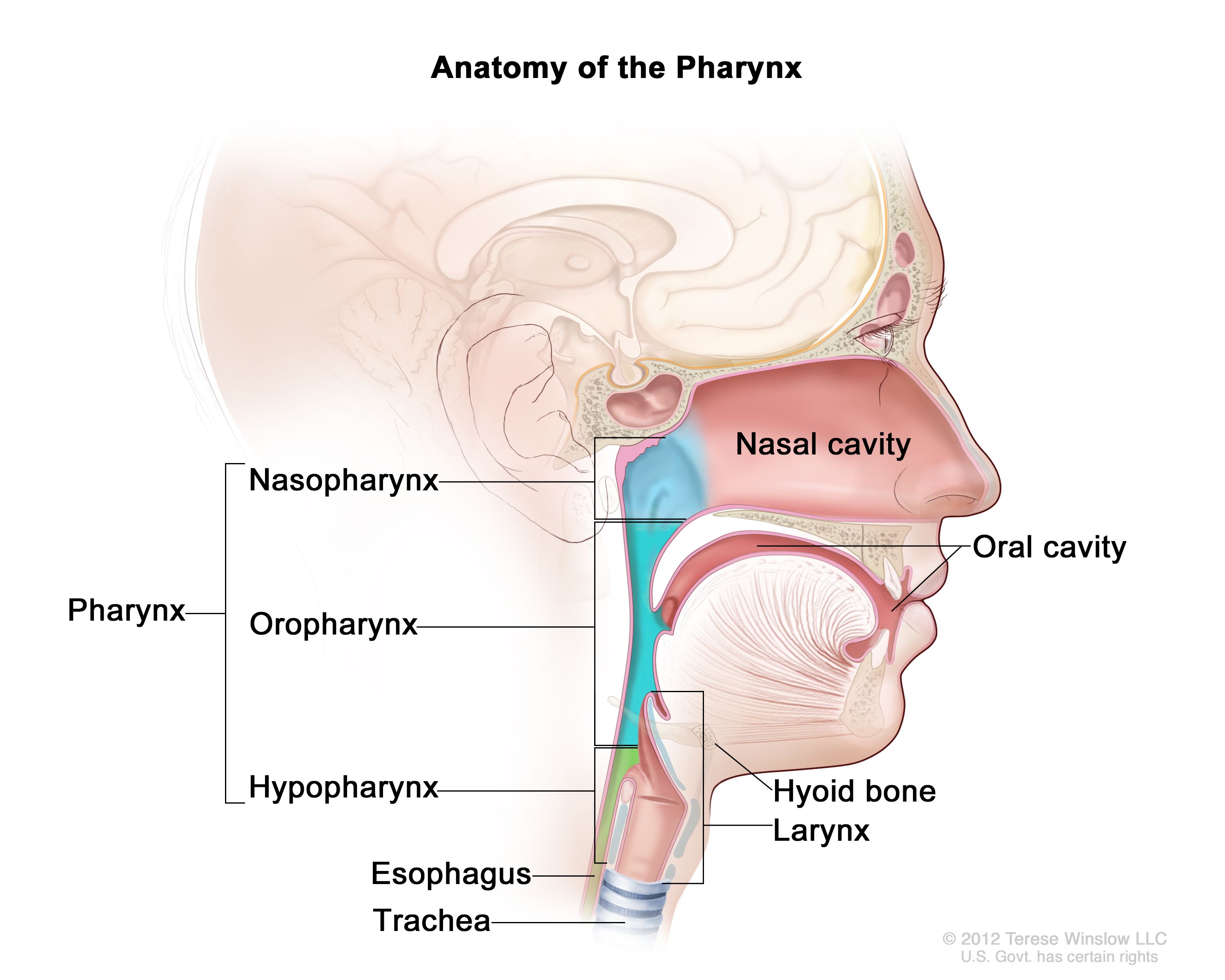
laryngopharynx
the most caudal portion of the pharynx; crucial connection point where food, water and air pass; refers to the point at which the pharynx divides anteriorly into the larynx and posteriorly into the esophagus; also referred to as the hypo pharynx
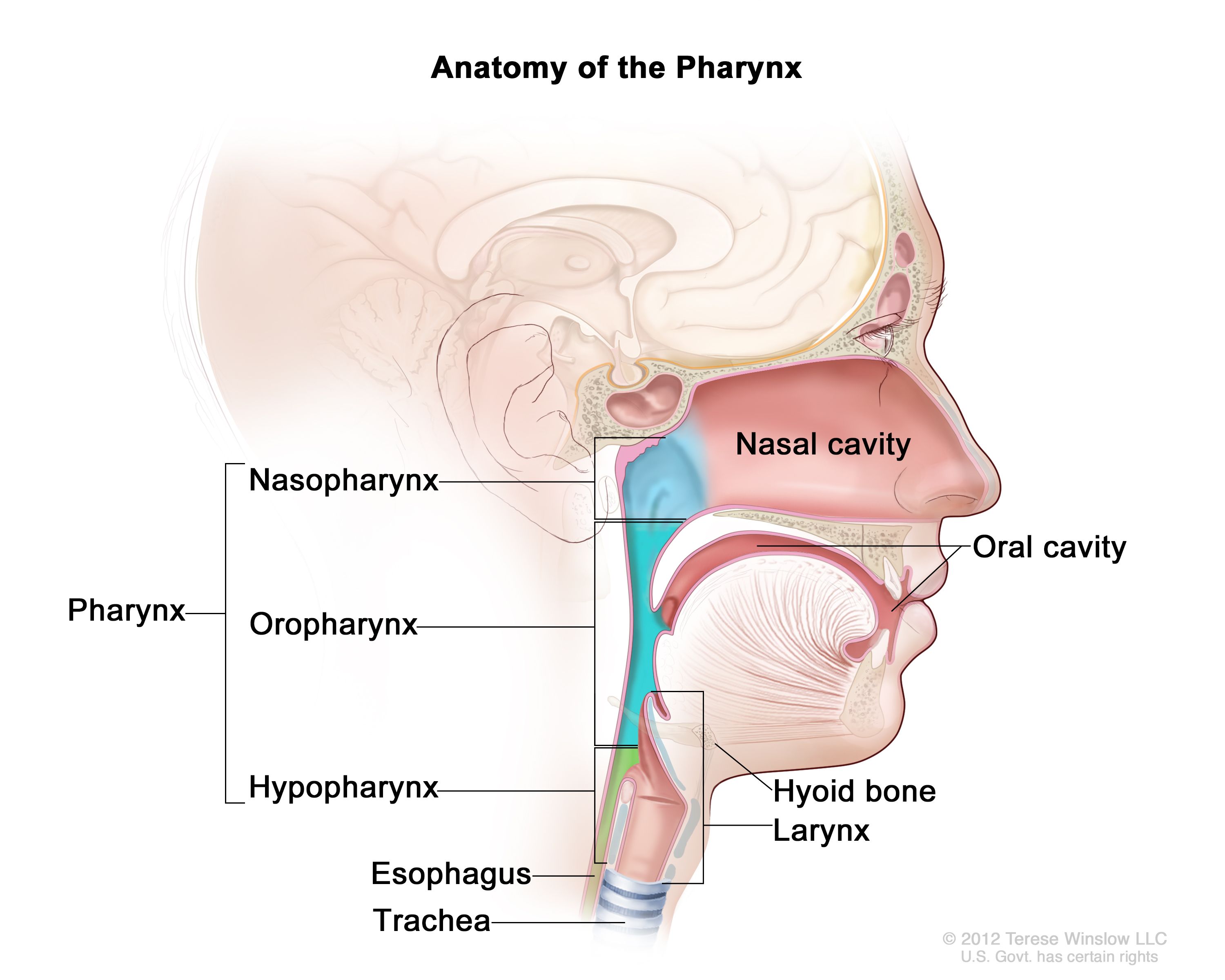
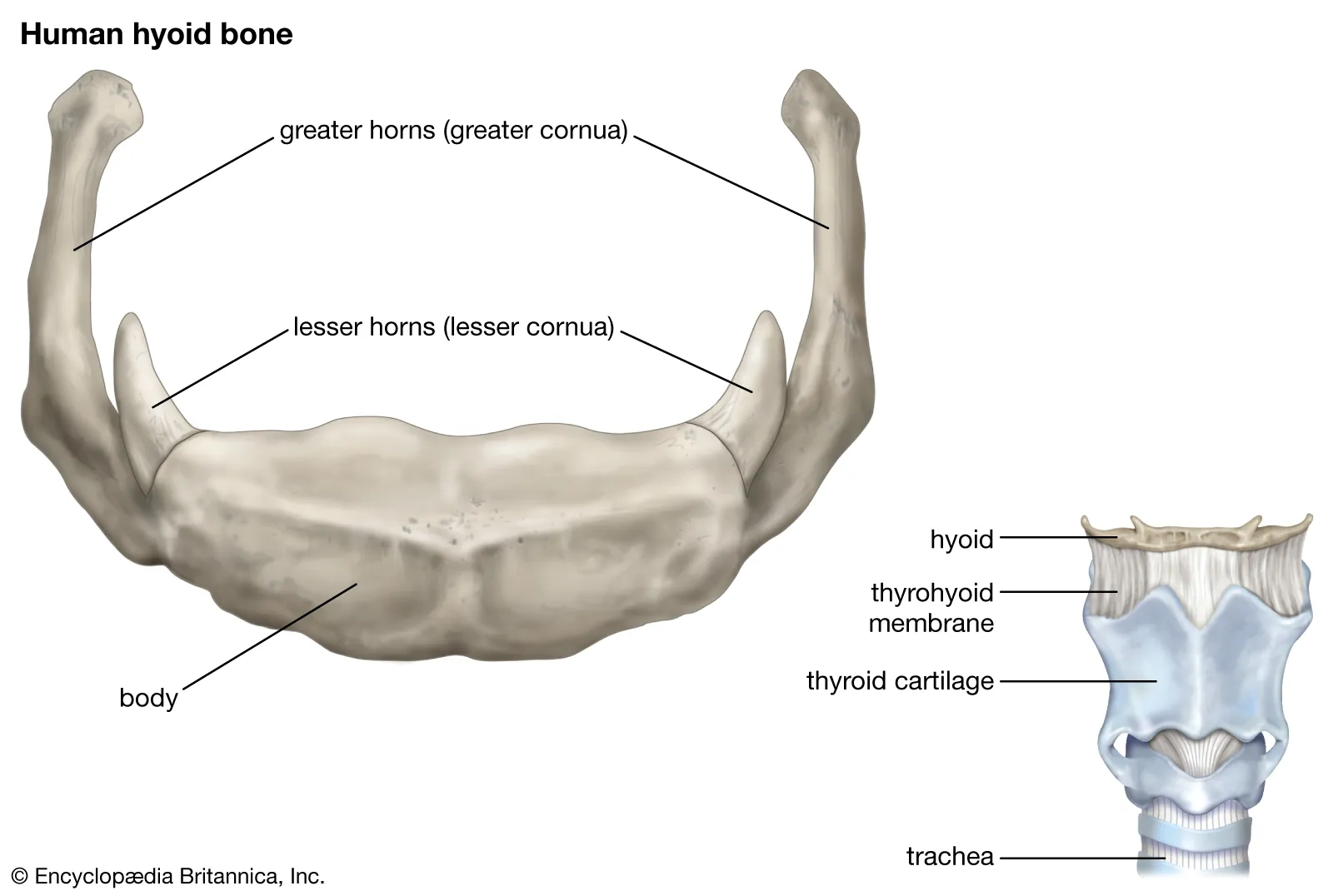
hyoid
a u-shaped bone in the neck located at the base of the mandible and above the larynx; not connected to any other bones — suspended by muscles and ligament and serves as a crucial anchor for muscles involved in speaking, swallowing, breathing and keeping the airway open.
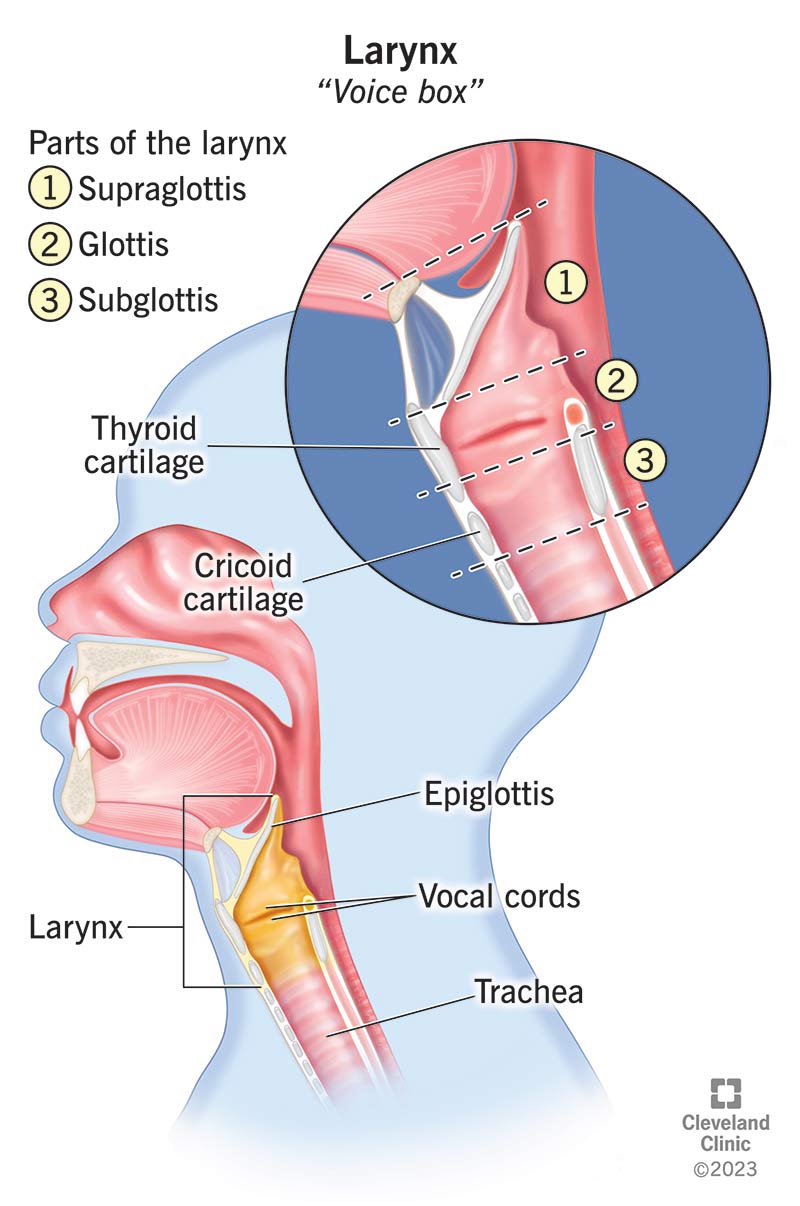
larynx
the hollow muscular organ forming an air passage to the lungs and holding the vocal cords in humans and other mammals; the voice box
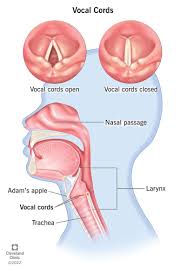
vocal folds
two bands of tissue located in the larynx that are essential for producing sound; vibrate as air from the lungs passes between them, creating sound waves that are then modulated by the throat, nose and moth; pitch and tone of a person’s voice are determined by the tension, length and vibration of the vocal folds
epiglottis
a flap of cartilage located at the top of the trachea; plays a crucial role in protecting the airways during swallowing
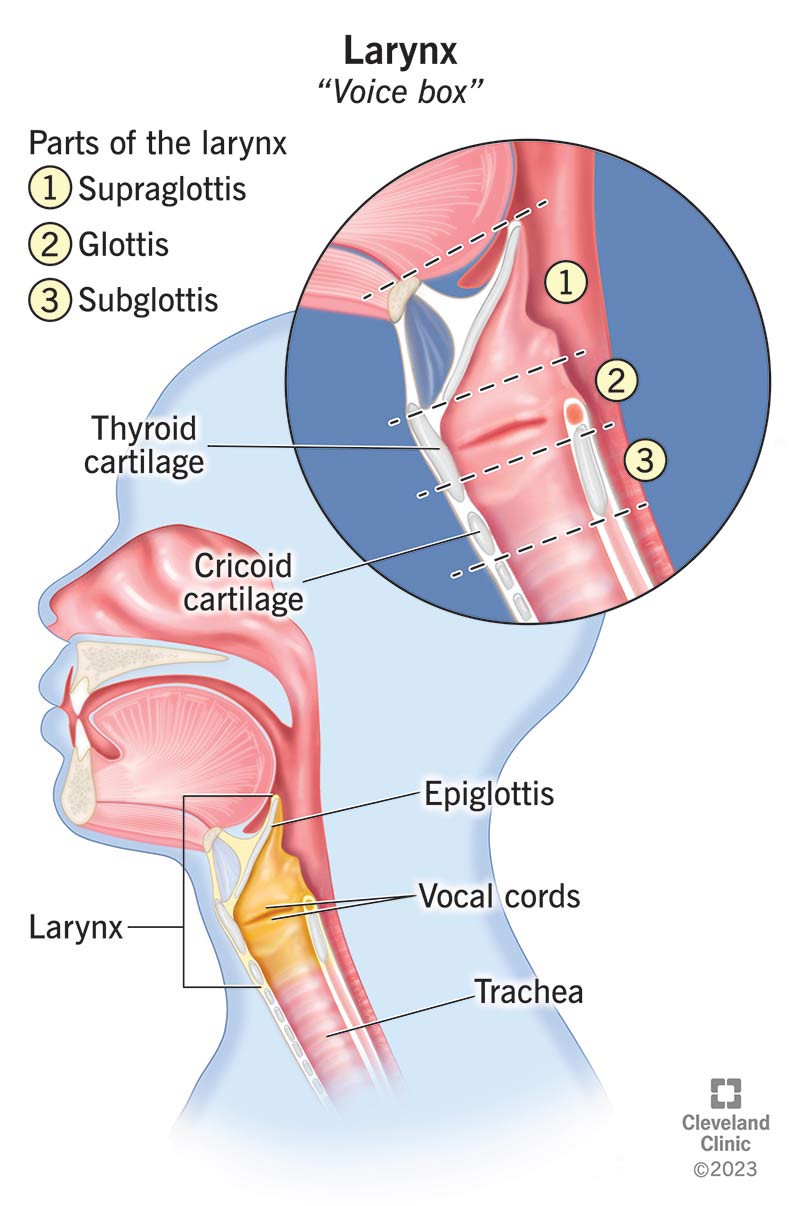
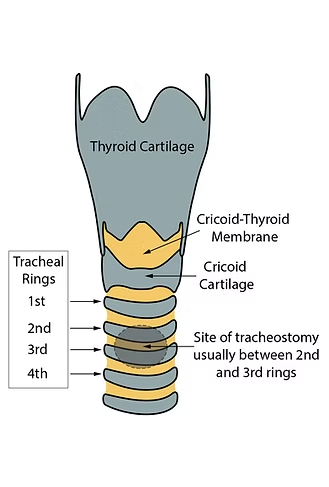
cricoid cartilage
ring-shaped cartilage of the larynx
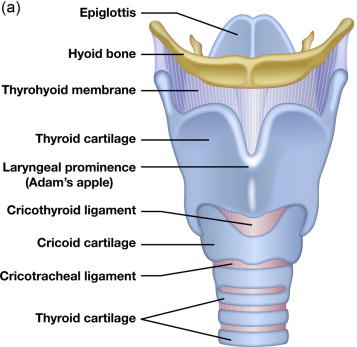
thyroid cartilage
a large cartilage of the larynx; a projection which forms the Adam’s apple in humans
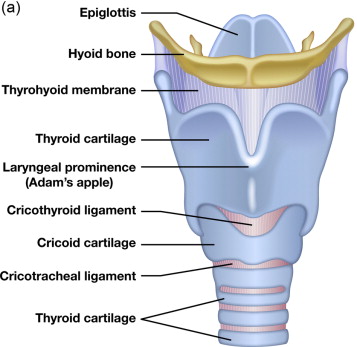
laryngeal prominence
the Adam’s apple; a visible bulge on the front of the neck; formed by the anterior portion of the thyroid cartilage
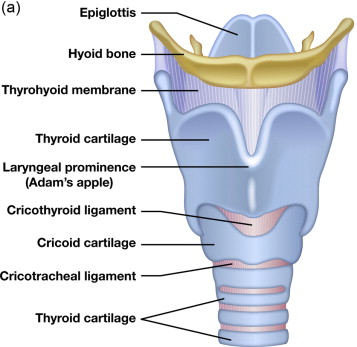
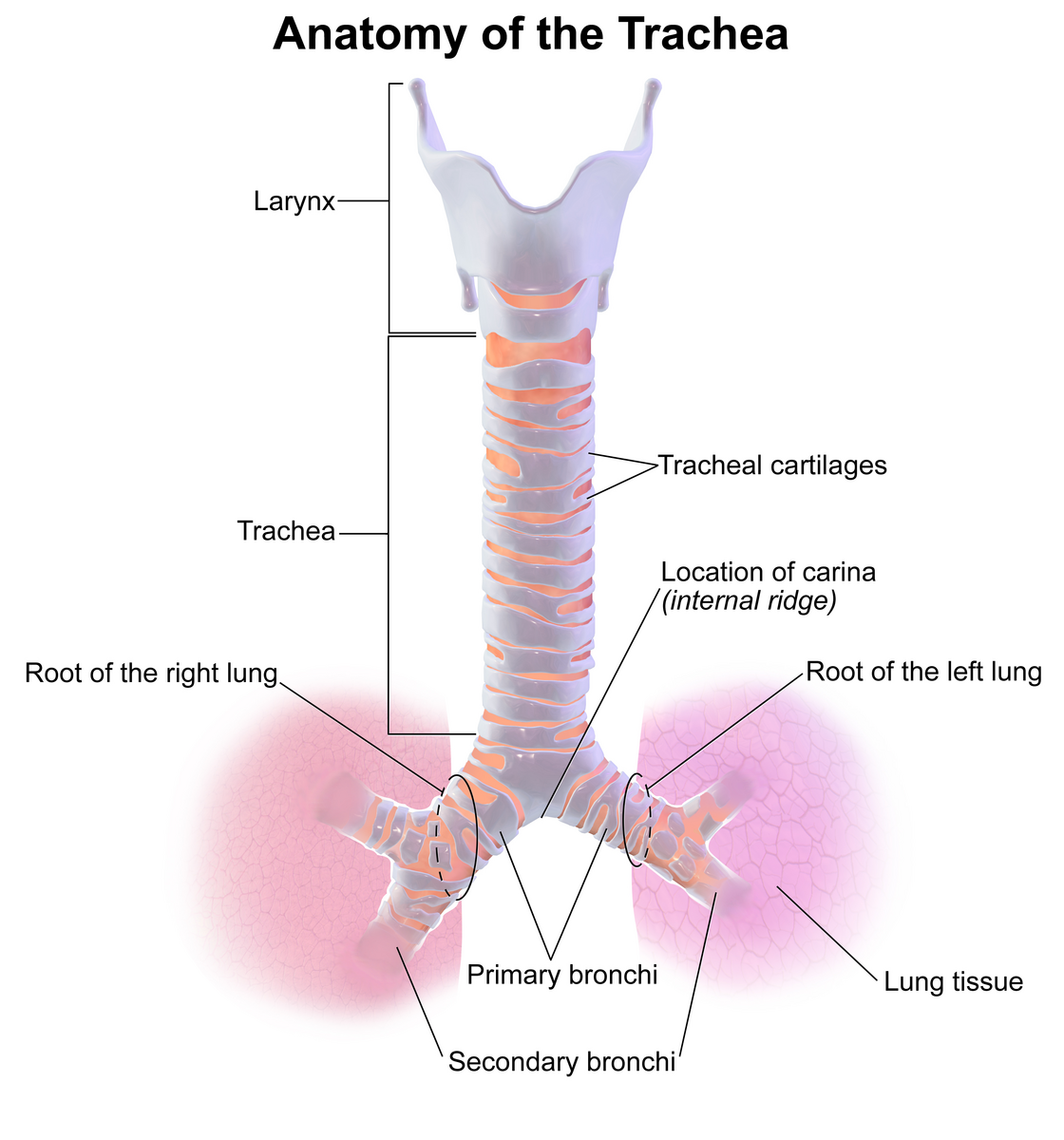
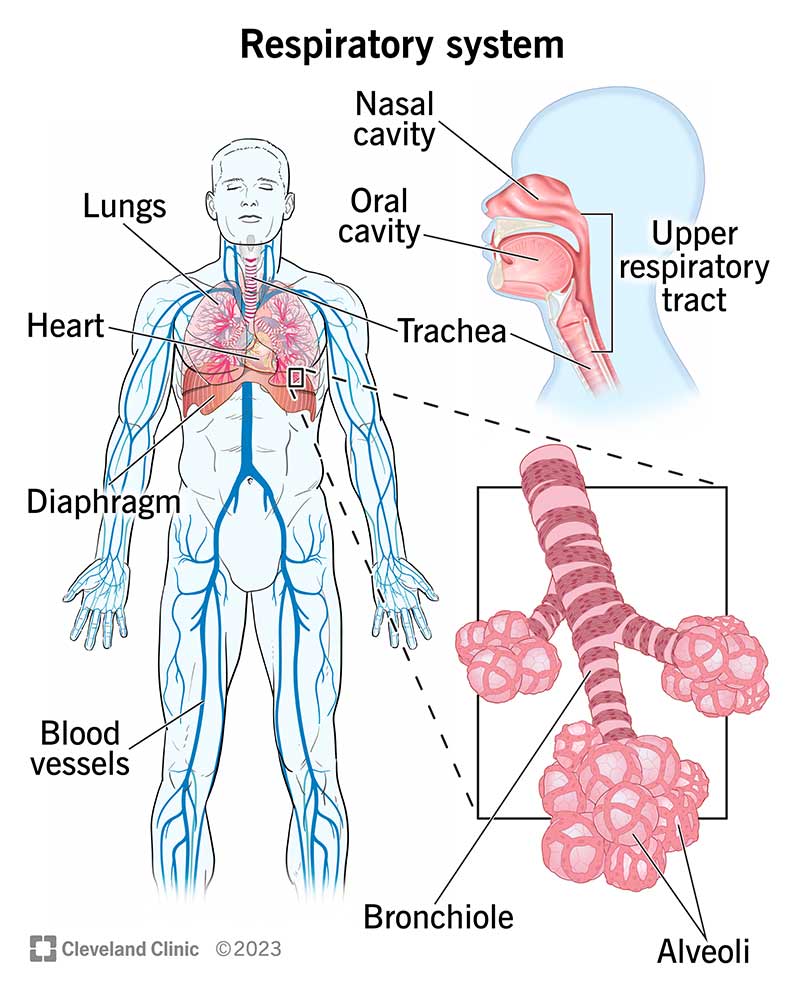
trachea
a large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage; extends from the larynx to the bronchial tubes; conveys air to and from the lungs; also referred to as the windpipe
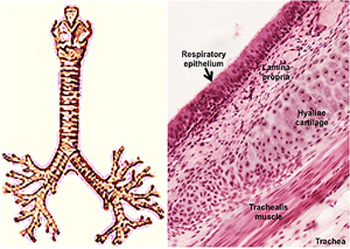
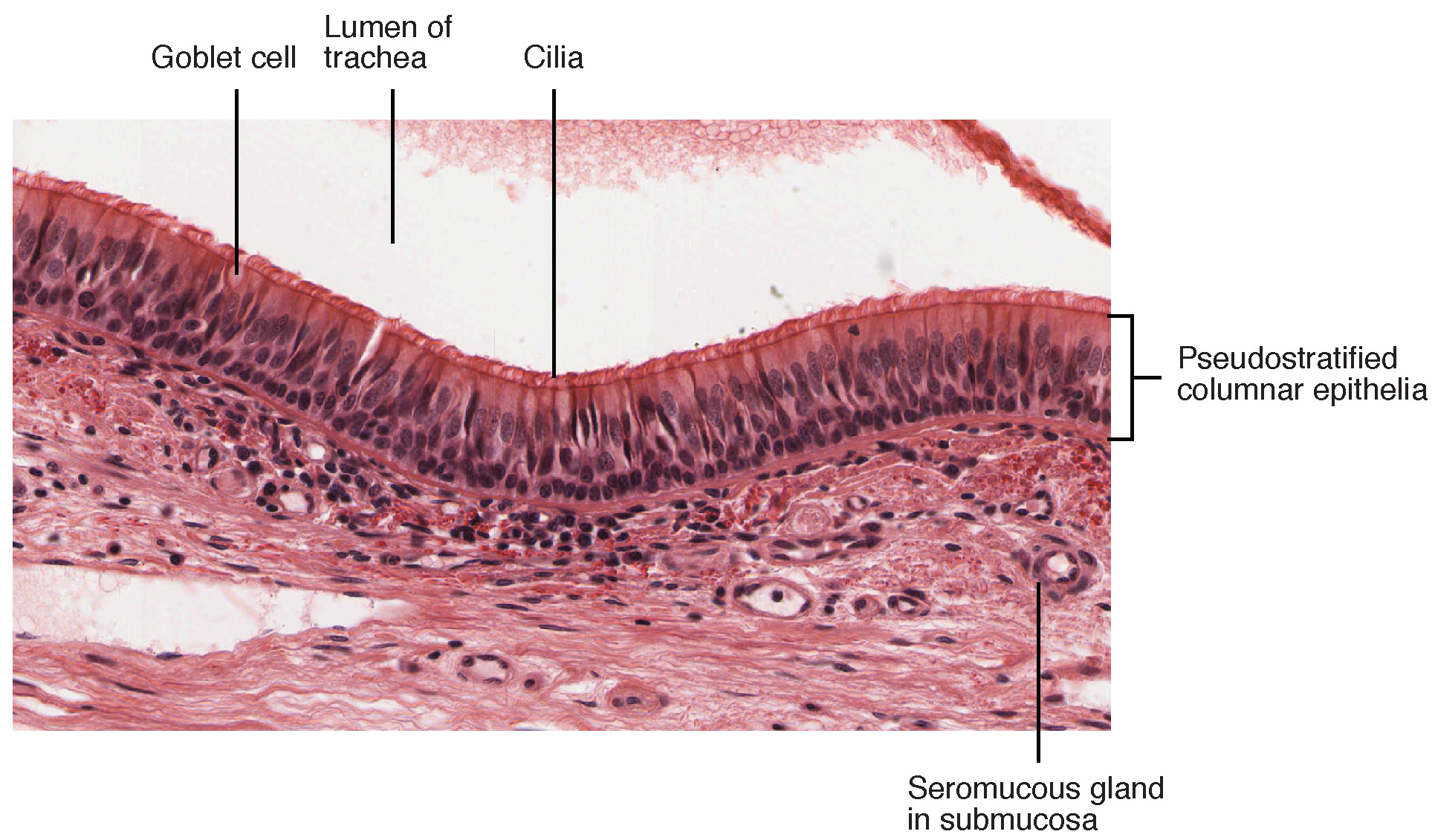
microscopic view of trachea
tracheal rings
cartilage; semicircular, cartilaginous structures that support and maintain the shape of the trachea (airway that connects the larynx to the lungs)
primary bronchi
the first parts of the bronchi; left and right bronchi in the center part of the lungs; widest part of the bronchi and attach to the trachea
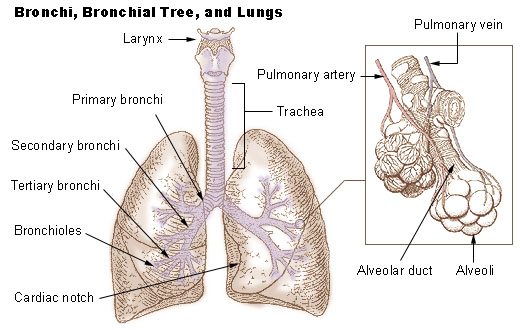
secondary bronchi
second part of the bronchi, near the middle of the lungs; parts of the bronchi that cross into the lobes of the lungs
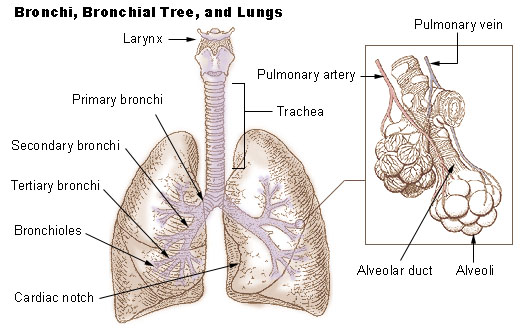
tertiary bronchi
the third order of branching on the bronchial tree; arise from the second bronchi and divide further into bronchioles
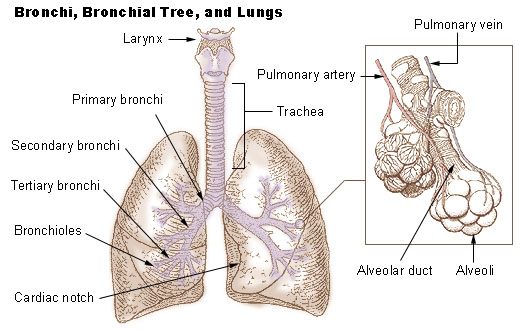
lungs
a pair of cone-shaped organs in the thoracic cavity that are responsible for respiration with the right lung being larger than the left due to the hearts position; receive air through the bronchial tubes
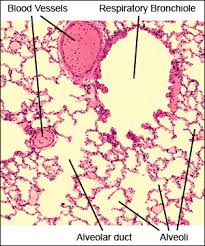
microscopic view of lung tissue
superior right lung lobe
the uppermost lobe of the right lung; situated in the upper portion of the right thoracic cavity, above the horizontal fissure; plays crucial role in gas exchanges it receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary artery and releases CO2 into alveoli, oxygenated blood is then transported through pulmonary veins
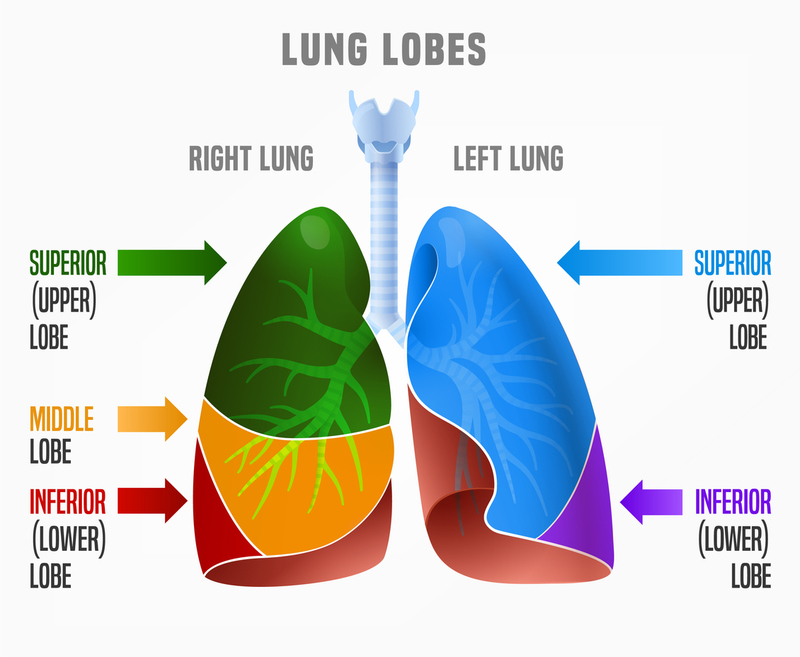
middle right lung lobe
one of three lobes in the right lung; se
inferior right lung lobe
superior right lung lobe
inferior left lung lobe
alveoli
diaphragm
obstructive pulmonary disease
restrictive pulmonary disease
lung parameters
tidal volume
inspiratory reserve volume
inspiratory capacity
expiratory reserve volume
residual volume
functional residual capacity
vital capacity
total lung capacity