Psychology Unit 3 Personality & Development
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Creativity
The ability to generate, create, or discover new ideas, solutions, & possibilities
Alternate uses test
Assesses functional fixedness
Divergent Thinking
There are many possible solutions, more creative
Convergent Thinking
There is one correct answer, the typical
Intelligence
The capacity to understand the world, think rationally, and use resources effectively when faced with challenges.
G-Factor
Theory of Intelligence hypothesized by Spearmen that states there is a single general factor underlying intelligence.
Two-Typed Intelligence
Theory of Intelligence hypothesized by Catell that states there are two major types of intelligence: Fluid & Crystallized.
Fluid intelligence
Our ability to reason and analyze; this intelligence peaks.
Crystallized Intelligence
Intelligence that grows throughout your whole life because it is based on experience and culture.
Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
Theory of Intelligence proposed by Sternberg that states there are 3 major types of intelligence: Creativity, Analytical, and Practical.
Analytical (Conventional)
How to analyze; what we think of conventional intelligence.
Practical
Street smart; how to take advantage of a situation.
Theory of Multiple Intelligences
Theory proposed by Gardner that most people believe because it gives the ability for all people to be smart.
Francis Galton
Created an Intelligence test based off of head size stating that the bigger the head the more intelligent.
Alfred Binet
Created the intelligence quotient test, that compares two numbers; Your chronological age & your mental age.
IQ correlation
School Attendance
Birthday
Breast Feeding
Head Size
Income
Processing Speed
Diet
Assessing Intelligence Tests
Considers 3 Factors: Reliability, Validity, & Norms
Reliability
Consistently yields the same results
Validity
Measuring the correct construct (things).
Norms
What is normal or typical for that test.
Savants
An atypical intelligence where an individual has an incredible and often unusual intellectual ability; Can be acquired or congenital.
Congenital Savant
Born with those unique intellectual abilities; Ability can be talented or prodigious.
Acquired Savant
Somehow get ability; Not born with it
Talented
Savant who’s ability is only amazing because they are otherwise cognitively impaired.
Prodigious
Savant who’s ability is amazing even for a non-impaired person.
MENSA
An organization that can only be joined by the top 2% of people of intelligence.
Intellectual disabilities
mainstreaming vs. inclusion; included as much as possible vs. fully included in the classroom no matter the disability.
Twin studies
used to answer or help answer the debate of “nature vs. nurture.
studies similar genetics in different environments to see if they behave the same
Potential problem: confirmation bias
Cross-Sectional Research
A research design that studies different aged individuals at one point in time.
Longitudinal Research
A research design that studies the same individuals at multiple points in time
Sequential Research
A research design that studies different aged individuals at multiple points in time.
Psychosocial Development
Created by Erikson
Is a stage theory
Involves emotions, personality and emotional relationships.
Identity development
Each stage involves a conflict and resolution/virtue
1st Stage of Psychosocial Development
Age - 0-1
Trust vs. Mistrust
Trust that basic needs such as nourishment and affection will be met.
2nd Stage of Psychosocial Development
Age: 1-3
Autonomy vs Shame/Doubt
Develop a sense of independence in many tasks
3rd Stage of Psychosocial Development
Age: 3-6
Initiative vs. Guilt
Take initiative on some activities; may develop guilt when unsuccessful or boundaries overstepped
4th Stage of Psychosocial Development
Age: 7-11
Industry vs. Inferiority
Develop self confidence in abilities when competent or sense of inferiority when not
5th Stage of Psychosocial Development
Age: 12-18
Identity vs. Confusion
Experiment with and develop identity and roles
6th Stage of Psychosocial Development
Age: 19-29
Intimacy vs. Isolation
Establish Intimacy and Relationships with others
7th Stage of Psychosocial Development
Age: 30-64
Generativity vs. Stagnation
Contribute to society and be part of a family
8th Stage of Psychosocial Development
Age: 65—
Integrity vs. Despair
Assess and make sense of life and meaning of contributions
Cognitive Development Theory
Created by Piaget
Stage theory
Says individuals develop schemata to help understand the world
Adjust their schemata through Assimilation and Accommodation.
Schemata
Concepts (mental models) that are used to help us categorize and interpret information
Assimilation
When individuals take in information that is comparable to what they already know.
Accommodation
When individuals change their schemata based on new information
1st Stage of Cognitive Development Theory
Age: 2-6
Sensorimotor stage
object permanence
world experienced through sense and actions
2nd Stage of Cognitive Development Theory
Age: 2-6
Preoperational stage
Egocentric thinking
use words and images to represent things, but lack logical reasoning
3rd Stage of Cognitive Development
Age: 7-11
Concrete operational
Conservation (knowledge that quantity doesn’t change as form changes.
Understand concrete events and analogies logically; Perform arithmetical operations
4th Stage of Cognitive Development
Age: 12—
Formal operational
Abstract thought
Formal operations; utilize abstract reasoning
Sociocultural Development
Created by Vygotsky
Zone of proximal development
NOT a stage theory
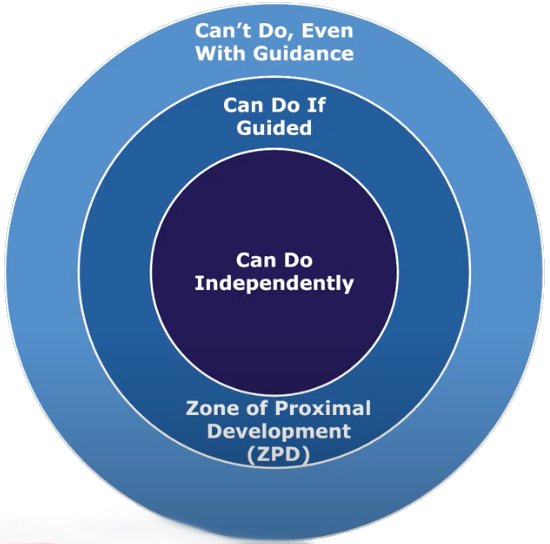
Zone proximal development
The area of nearby development
Basic Principles of Sociocultural Development
Children construct or play an active role in their knowledge
Development cannot be separated from its social context
Learning (can) leads Development
Language plays a central role in development
Moral Development Theory
Created by Kohlberg
How people decide what is right and wrong
Consists of 3 levels with 2 stages within each level
Level 1 (Pre-Conventional Morality) Stage 1 of Moral Development Theory
Obedience and punishment
Behavior driven by avoiding punishment
Level 1 (Pre-Conventional Morality) Stage 2 of Moral Development Theory
Individual interest
Behavior driven by self-interest and rewards
Level 2 (Conventional Morality) Stage 3 of Moral Development Theory
Interpersonal
Behavior driven by social approval
Level 2 (Conventional Morality) Stage 4 of Moral Development Theory
Authority
Behavior driven by obeying authority and conforming to social order
Level 3 (Post-Conventional Morality) Stage 5 of Moral Development Theory
Social Contract
behavior driven by balance of social order and individual rights
Level 3 (Post-Conventional Morality) Stage 6 of Moral Development Theory
Universal ethics
Behavior driven by internal moral principles
Stages of Lifespan
Levels of aging and development from conception to death
Prenatal Development
Conception occurs; the moment the sperm penetrates the egg
Infancy through childhood
Reflexes developed where some are grown out of and where attachment occurs.
Attachment
A long standing connection or bond with others.
Harry Harlow
Psychologist that asked the question what drives attachment?
What drives attachment
Safety & Security
Mary Ainsworth
Psychologist who asked the question what are the types of attachment; Derived a test to determine the types of attachment and what they are.
The Strange Situation Classification
Measures security of an attachment in 1 & 2 year olds
Consists of 8 stages
Baby & Mother
Baby Stranger & Mother
Stranger & Baby
Stranger Baby & Mother
Baby
Baby & Stranger
Baby Stranger & Mother
Caregiver Sensitivity Hypothesis
Difference in infants attachments styles are dependent on the caregivers behavior during a critical period of development
Secure Attachment
The result of the caregivers consistently meeting the needs of the child
How daycare affects attachment
Can still have secure attachment with caregivers
Daycare can cause advancements in developments
Most daycare’s aren’t high quality
Parenting styles
4 types of styles that caregivers treat their children
Authoritarian
No support and high expectations; low responsiveness and high demandingness
Uninvolved
No support and no expectation; Low responsiveness and low demandingness
Authoritative
support and high expectations; high demanding and high responsiveness.
Permissive
support and no expectations; low demandingness and low responsiveness.
Adolescence
Puberty occurs in this stage of lifespan
Adulthood
Starting to become an adult up until midlife.
Failure to launch
Failure to get out of your parents house when emerging adulthood
Helicopter Parenting
Hover over child; don’t let child learn to be independent.
Boomerang Children
Launches out of the family and then comes back to live
Middle Adulthood & Midlife Crisis
Stage where midlife crisis occurs; It isn’t normal to have a midlife crisis but occurs around the age of 40.
Old age
Stage of lifespan where Alzheimer's most commonly occurs.
Alzheimer’s
Plaques and tangles accumulate in the hippocampus and destroys the brain cells and hippocampus; slow gradual process
Disengagement theory of aging
Individuals slowly withdrawal from society (not supported by research).
Activity theory of aging
Staying with relationships withing the community
Stages of Grief Theory
Proposed by Cooper Ross
Denial
Anger
Bargaining
Depression
Acceptance
Personality
The pattern of enduring characteristics that produce consistency & individuality in a given person.
Psychoanalytic Theory
Proposed by Freud stating that there are layers of consciousness
Conscious Level
Conscious Awareness, Thoughts and Perceptions
Preconscious level
Where we keep memory and stored knowledge; Easy to bring into consciousness
Unconscious level
Store our memories unacceptable or unpleasant.
How to study the consciousness
Look for clues like a detective
Freudian Slips
Slip of the tongue; accidentally say or word that makes you uncomfortable that is pulled from your unconscious
Dream Analysis
Analyze Dreams
Id
inborn personality trait that operates on pleasure
Ego
Personality trait that operates on reality principle
Superego
Personality trait of the conscience that we learn from society.
Repression
A defense mechanism where you bury something into your unconscious
Regression
Going back to a previous developmental stage
Rationalization
Justifying your thoughts or behavior
Reaction Formation
Expressing the opposite