Unit 6: Cities & Urban Land-Use Patterns & Processes
1/168
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
city
an agglomeration of people & buildings clustered together to serve as a center of politics, culture, & economics
At the global scale, where do most people live in?
cities
The large concentration of people in cities gives…
people access to goods, services, & opportunities not available in rural areas
Cities are centers of:
political & economic power
higher education & technology innovation
artistic achievement
historical records
research & medical advances
What are the hearths of urbanization?
Mesopotamia
The Nile River Valley
Indus River Valley
The Huanan & Wei River Valleys
Mesoamerica
Peru
How did urbanization began?
when hunters & gathers fist clustered in permanent settlements to defend themselves & their leaders, grow crops, develop new arts & industries, cluster around sacred sites, & build places that aligned with their understanding of the universe
What were the first permanent settlements?
small agricultural villages
The First Urban Revolutions occurred…
independently in six different hearths
Fertile Crescent Urban Revolution
archaeologists find evidence of cities
Nile River Valley Urban Revolution
3200 BCE
Irrigation
Use of social classes
lack of walls which was an environmental decision
Indus River Valley Urban Revolution
no signs of social classes
houses were equal in size and had access to the same infrastructure
thick walls
Huang He & Wei Valleys Urban Revolution
1500 BCE
cities planned to coincide with the cardinal directions
vertical structure in the middle of the city
Mesoamerica Urban Revolution
1100 BCE
religious centers
stone monuments
What do cities reflect?
the power & economic structures of the time they were built
urban morphology
the layout of a city including sizes/shapes of buildings & infrastructures
functional zonation
division of a city into regions by use or purpose
the site of a city is its…
absolute location
How is site chosen?
for its advantages in trade or defense or as a center for religious practice
the situation of a city is its…
relative location
Before European Exploration, most cities in the world were…
sites on trade routes in the interiors of continents
What does the rank-size rule state?
the population of a city will be inversely proportional to its rank in the hierarchy
Rank-size rule
the 2nd largest city in an area is ½ the population of the largest city & the 3rd largest city will have 1/3 of the largest city’s population
What is an example of the rank-size rule theory?
Belgium
Why does the rank-size rule theory work?
the relationship between rank & size is inherently negative
primate city definition
a country’s leading city, always disproportionally large & exceptionally expressive of the national capacity & feeling
primate city simplified definition
the largest & most economically & politically influential city
Walter Christaller’s Central Place Theory
the size & locations of cities, towns, & villages, are logically, & regularly distributed
hinterland
an area of economic production that is located inland & is connected to the world by a port
Assumptions of Walter Christaller’s Central Place Theory
the surface of the ideal region would be flat & have no physical barriers
soil fertility would be the same everywhere
population & purchasing power would be evenly distributed
the region would have an uniform transportation network to permit direct travel from each settlement to the other
from any given city, a good or service could be sold in all direction as far from the city as might be profitable
What shape did christaller choose as the shape of trade areas?
hexagons
What do city models reveal?
the structure of the city & disservice where functions take place
What do city models show?
the combination of historic, spatial, economic, cultural, & political processes that have shaped cities in each world region
Each model of the city is a study in….
functional zonation
central business district CBD
the zone of a city where buisness cluster & around which a city
central city
urban area that is not suburban usually the older/orginal city that is surrounded by suburbs
suburb
an outlying, primarily residential area on the outskirts of a city
How does suburbanization?
lands once outside the urban area are transferred into urban areas
Characteristics of cities built during the Roman Empire:
sited on prime trade locations like rivers or ports
streets in the central city are narrow & winding
Characteristics of cities built during the Middle Ages
have town centers with elaborate church on one end, a town hall on the other end, and shops around the square
Suburbs of European cities may be centers of….
commerce and residential zones that primarily house immigrants & guest workers
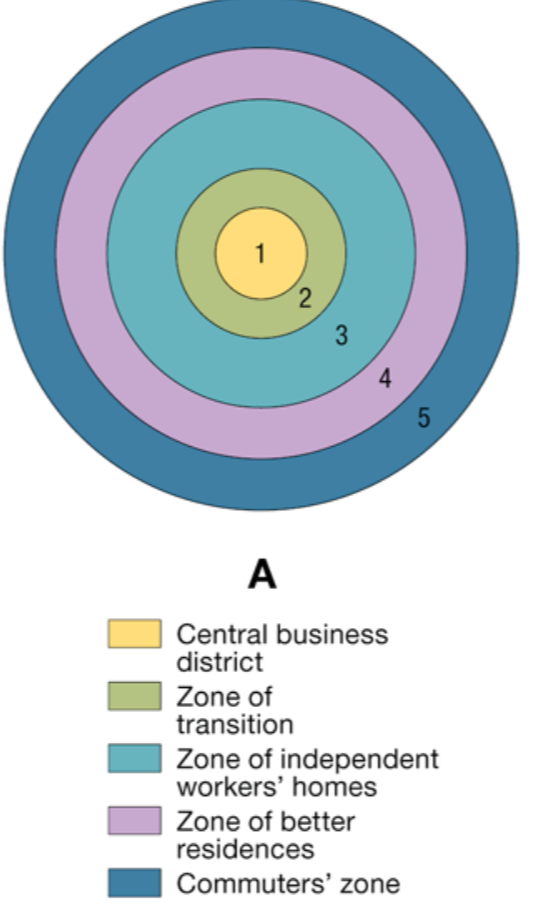
Whose model of cities is this?:
At the center is the CBD (1), which is itself subdivided into several subdistricts
The zone of transition (2) is characterized by residential deterioration and encroachment by business and light manufacturing.
Zone 3 is a ring of closely spaced, modest homes occupied by factory workers
Zone 4 is middle-class residences
Zone 5 is the suburban ring
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
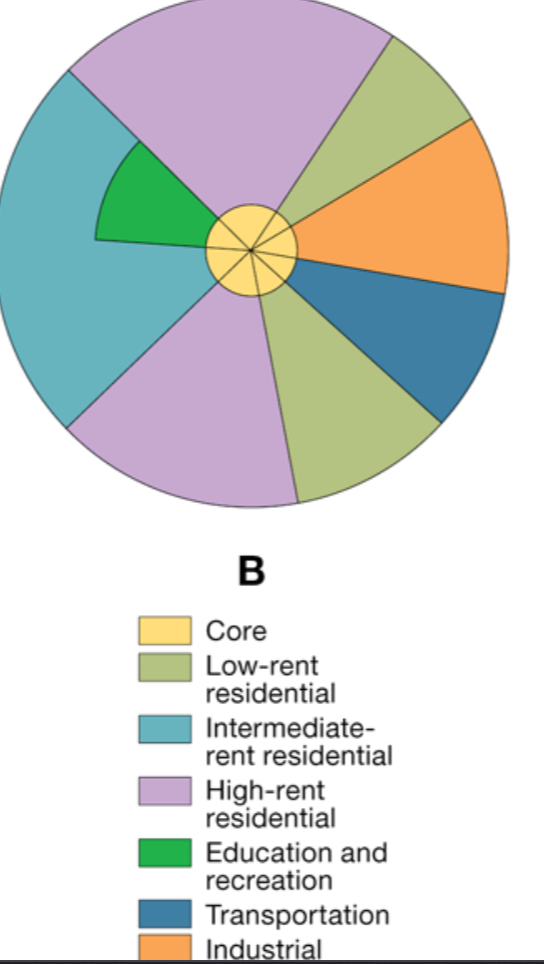
Whose model of cities is this?:
focused on residential patterns, explaining where the wealthy in a city chose to live.
grows outward from the center
Hoyt Sector Model
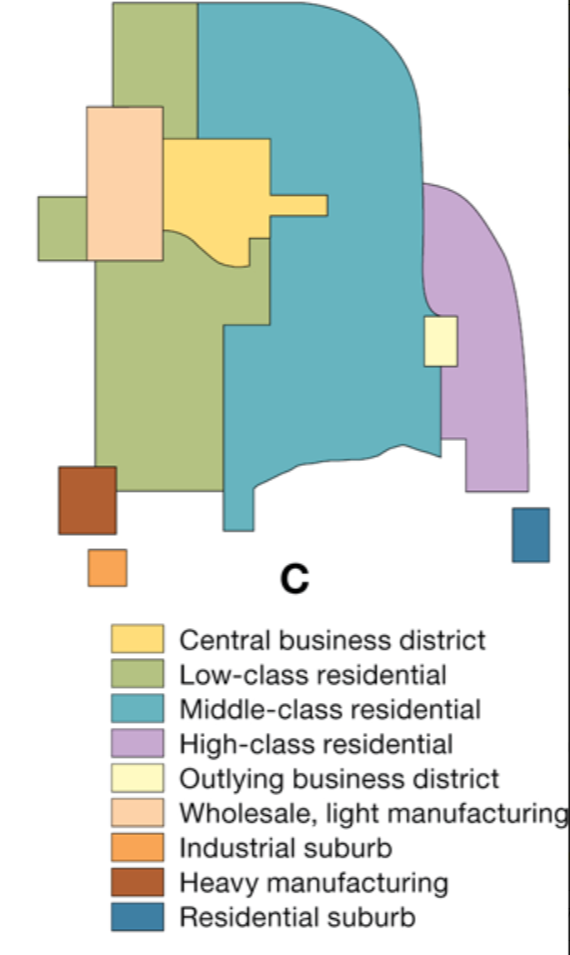
Whose model of cities is this?:
argued that neither the concentric rings nor the sector model adequately reflected city structure
recognizes that the CBD was losing its dominant position as the single nucleus of the urban area
Harris-Ullman Multiple Nuclei Model
edge cities
large urban areas with extensive space for offices & retail businesses on the outskirts of major cities
galactic city
a complex urban area where functions of the city are not centered in one place
Whose model of cities is this?:
combined radial sectors and concentric zones
two radial sectors of squatter settlements are the oldest low-income neighborhoods
zone of maturity is the closest to the CBD and has the oldest housing and the best transportation links to the CBD.
zone of in situ accretion is marked by constant building and rebuilding and is mainly a middle-class residential zone
ring around the outside of the city is the zone of peripheral squatter settlements where more recent migrants from rural areas live
Ernst Griffin and Larry Ford model of South American cities
What is a common structural element common to many south american cities?
the dissymmetry sector
dissymmetry sector
the poorest areas that may not be close to regular city services or may be controlled by gangs or drug lords who run the formal economy
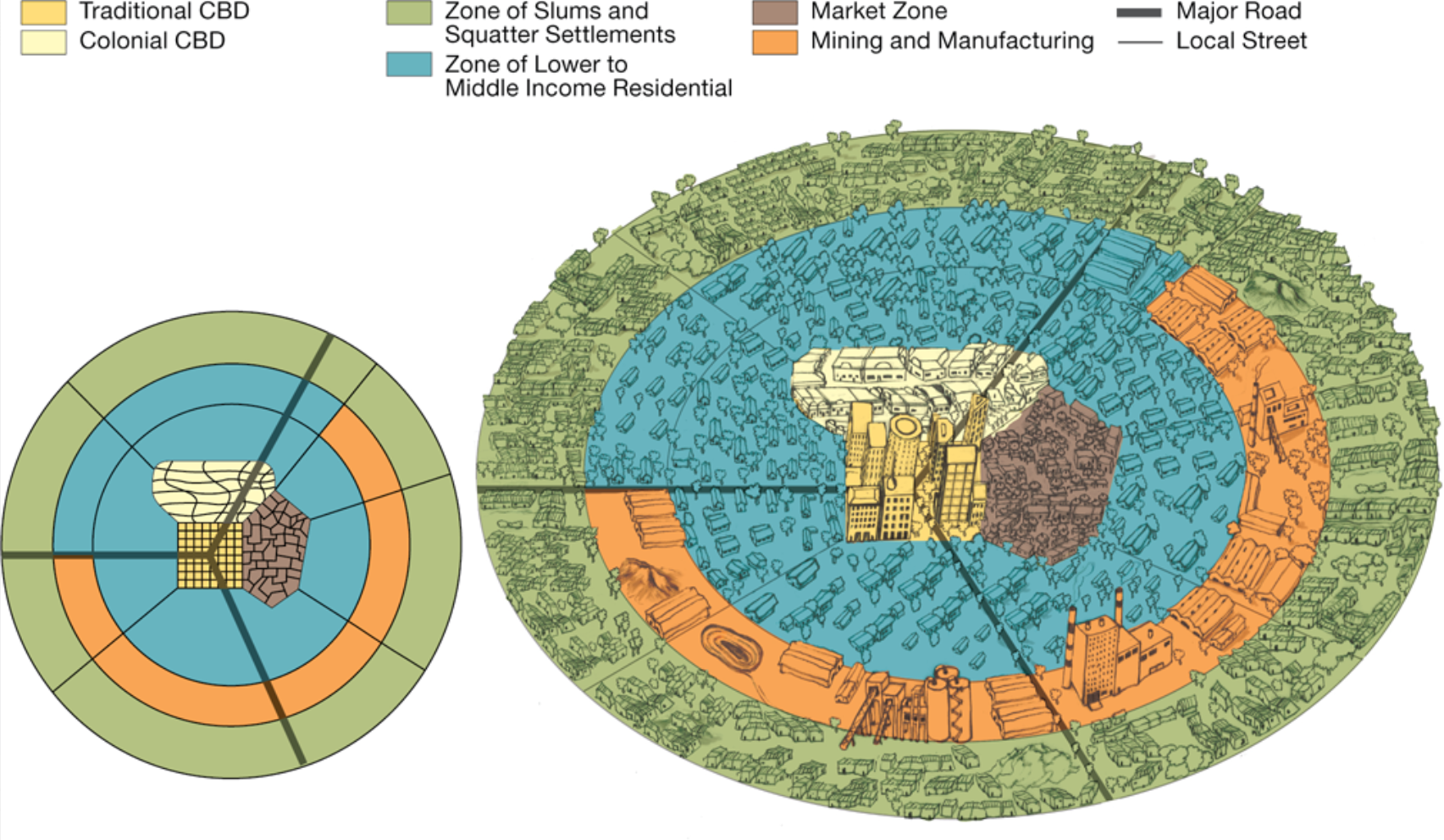
Whose model of cities is this?:
show how colonial cities were often built
a traditional CBD where commerce is conducted on streets, in stalls, and behind storefronts
an informal and sometimes periodic market zone
a colonial CBD
de Blij model of african cities
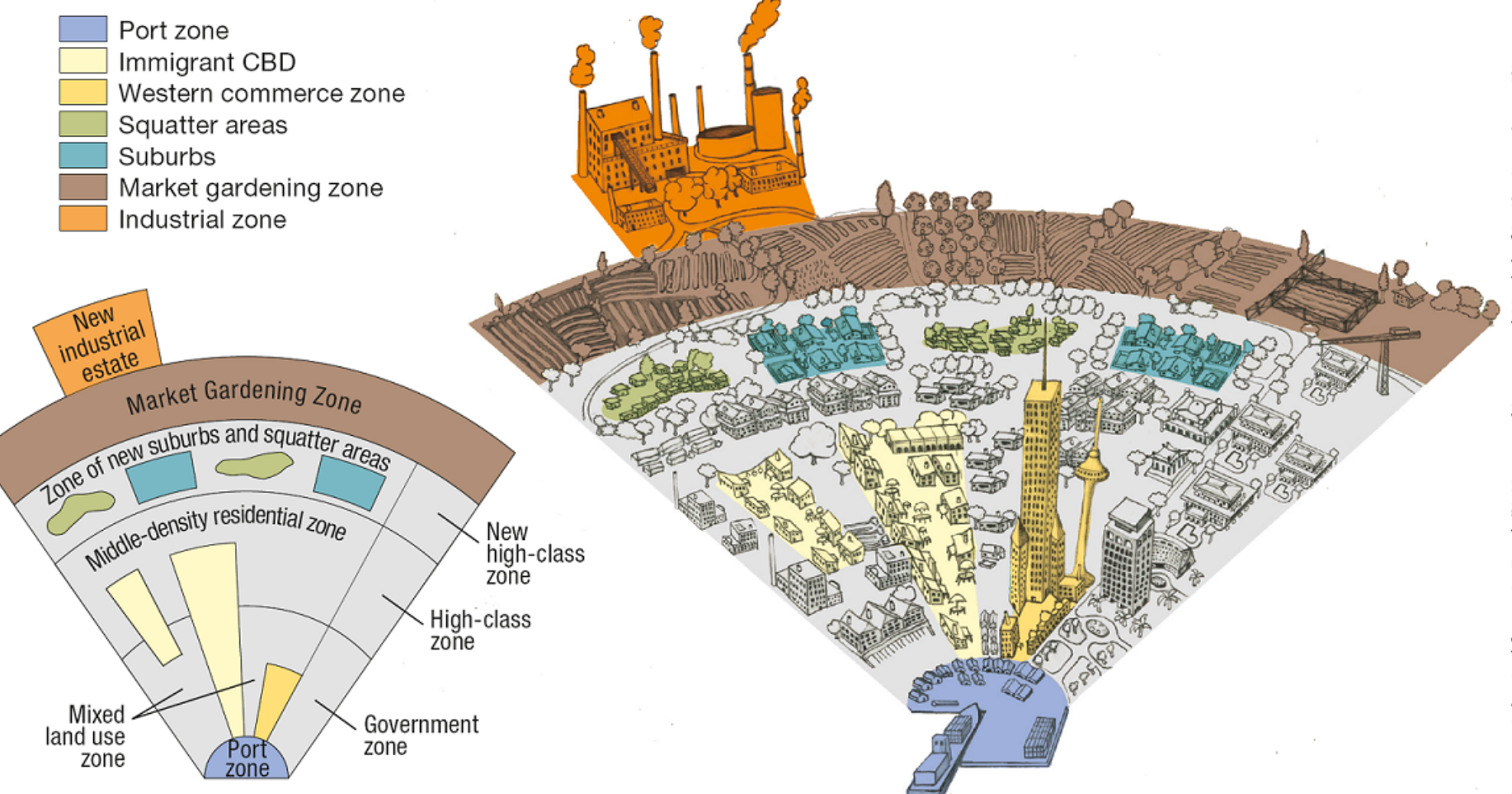
Whose model of cities is this?:
focal point of the city is the old colonial port zone, which is combined with the largely commercial district that surrounds it
no formal CBD
the elements of the CBD are present as separate clusters surrounding the old colonial port zone: the government zone; the Western commercial zone (WC on the model); and the immigrant CBD
McGee model of Southeast Asian CitiesWHo
Who shapes the layout of cities?
individuals, governments, corporations, developers, financial leaders, and realtors
How can government planning agencies directly affect the layout of cities?
by restricting the kinds of development allowed in certain regions/zones
zoning laws
divided up the city & designate the kinds of development allowed in each zone
Cities in the global economic periphery lack…
enforceable zoning laws
Without zoning laws…
people live anywhere there is space in cities
redlining
discriminatory real estate practice that prevents minorities from getting loans to purchase homes or property in predominately white neighborhoods
How did redlining earn its name?
because governments & banks would draw “hazardous” areas in red lines
What was the effect of redlining?
grew the page gap between white people and people of color
block busting
practiced used by relators that purposely sold a house in a white neighborhoods at a low price to a black buyer. relators would then solcit white residents of the neighborhood to sell their homes under the guise that the neighborhood was going ‘down hill’ because a black person/family moved in
What did block busting produce?
white flight
white flight
movement of white people from the city & adjacent neighborhoods to the suburbs
What are governments encouraging to counter middle & upper class taxpayers from leaving the city?
commercialization of the CBD & gentrification of neighborhoods in/around the district
How are governments countering middle & upper class taxpayers from leaving the city?
cleaning streets, sidewalks, & buildings, tearing down old abandoned buildings, & building up commercial offerings & residences
What do the plans to counter middle & upper class taxpayers from the leaving the city do?
make the city look ‘attractive’ to residents and tourists
gentrification
the renewal or rebuilding of lower-income neighborhoods into middle & upper class neighborhoods
What are some cons about gentrification?
increases housing prices in the central city
displaces lower income residents because taxes and prices rise
teardowns
homes intended for suburban demolition
mcmansions
negative name for new supersized mansions
Where does the gentrification of suburbs happen?
where suburbs close to the city or connected & when homes that are smaller or older are bought with the intention of tearing the house down & building a larger house
What do people for teardowns argue?
the phenomenon solves urban sprawl by replacing existing homes with new homes, rather than converting farmland into residential lots
What do people against teardowns argue?
see the houses as too large for their lots, dwarfing the neighboring houses & destroying the character of the street by demolishing older homes on it
urban sprawl
unrestricted growth of housing, commercial developments, & roads over large expanses of land with little concern for urban planning
new urbanism
development urban revelation & suburban reforms that create walkable neighborhoods with a diversity of homes and jobs
New urbanists support what…
regional planning for open space, appreciate architecture, & planning, & the balanced development of jobs and housing
gated communities
fenced in neighborhoods with controlled access gates for people & cars
What do gated communities provide in global periphery cities?
another layer of comfort for the cities wealthy
urban geopolitics
how cities shape & are shaped by geopolitics processes at national, regional, & global scales
node
a place where action & interaction occur
The world city is a node in globalization, reflecting…
processes that have ‘redrawn the limits on spatial interaction’
hutment factories
centers of entrepreneurship where slum residents sow clothing, recycle plastic, & cardboard, build products & produce services
range
the maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service
threshold
the minimum number of people required to use a surface
market area
an area that pulls people in from surrounding areas, normally for the exchange of goods & service
why hexagons and not another shape in the Central City theory
circles cause gaps that would not let you have access to certain services and show that people are drawn to two market areas
squares do not show equidistance
What do companies use to determine if there is enough people in the threshold?
census data
What are site factors?
climate
availablity of water
soil quality
natural resources
What are situation factors?
the connections between one site and another site
river
port
megacity
cities with 10 or more million residents
meta city
sprawling urban areas with more than 20 million residents
Where did the term ‘developed’ originate from?
the industrial revolution & the idea that technology can improve the lives of people
Most measures of development focus on one of 3 factors:
economic well-being
technology
production
gross national product GNP
measure of the total value of the officially recorded goods & services produced by residents of a country in a given year in & out of country
gross domestic product GDP
a calculation of the monetary value of what is produced within a country, plus income received from investments outside the country, minus income payment to other countries around the world
How do economists compare GNI’s
must standardize the data
How do economists standardize GNI data
divide it by the population of the country
per capita GNI
the GNI divided by the population of the country
What does the GNI not tell us about?
the distribution of wealth or within a country
In 2015, the UN held the Agenda for Sustainable Development. What was their main goal?
to improve condition of people in the countries with lowest standard if human development
Sustainable development Goals
No poverty
Zero hunger
Good health and well-being
Quality education
Gender equality
Clean water and sanitation
Affordable and clean energy
Decent work and economic growth
Industry, innovation, and infrastructure
Reduced inequalities
Sustainable cities and communities
Responsible consumption and production
Climate action
Life below water
Life on land
Peace, justice, and strong institutions
Partnership for the goals
What does Walt Rostow’s Modernization Model assume?
that all countries follow a similar path to development or modernization, advancing through five stages of development