Biology - Cell Organelles
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Cells
Basic unit of all living things, STRUCTURE AND SUPPORT growth, development, reproduction, waste removal
Cell theory
Fundamental biological principle, all living organisms are composed of cells, all cells arise from pre-existing cells. Provides framework for modern biology
Cell membrane
Thin flexible barrier, separates interior from the exterior environment, regulate the passage of substances
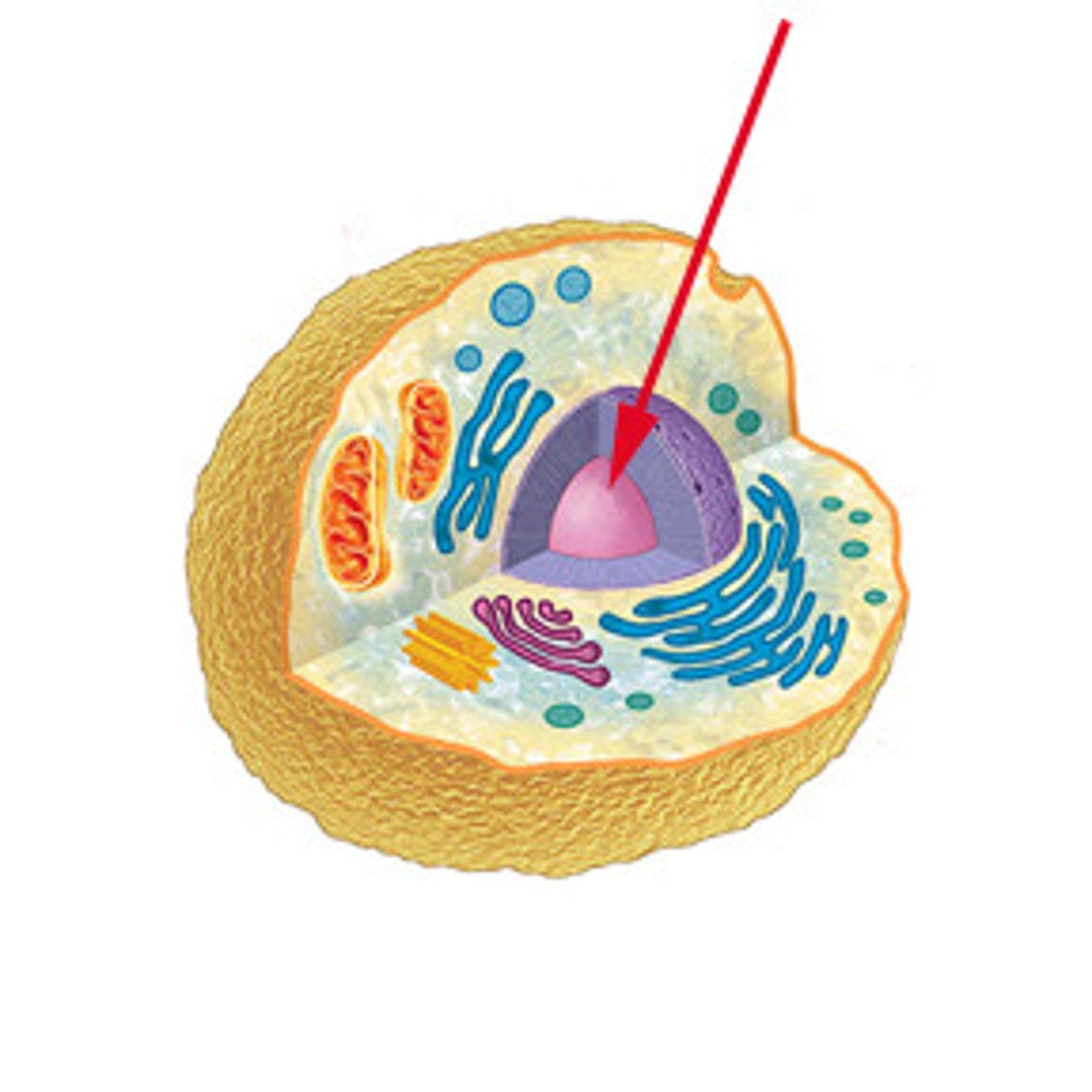
Nucleus
Large membrane, enclosed structure that contains genetic material in the form of DNA, (CONTROLS CENTER OF CELL) control center of eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotes
Enclose DNA in nuclei, housing genetic material in nucleus, generating energy through cellular respiration in mitochondria, synthesizing proteins. (Compartmentalization)
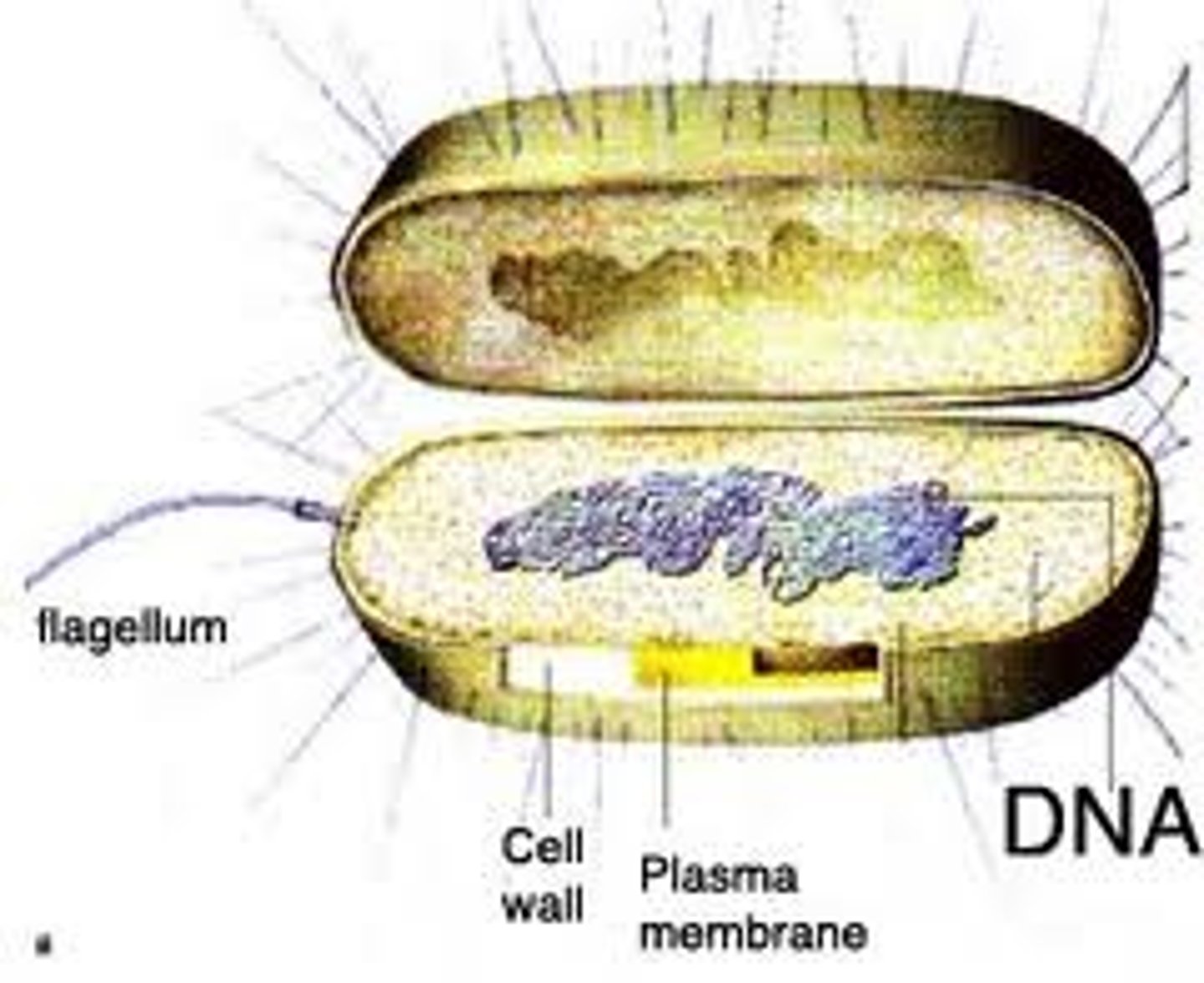
Prokaryotes
Do not enclose DNA in nuclei, nutrient cycling, decomposition, food digestion, immune system training. (BACTERIA)(EVERYTHING NEEDED FOR LIFE)
Cytoplasm
Portion of cell outside the nucleus, host the cellular processes essential for cell survival.
Organelles
Specialized organs, “little organs”, energy production, protein synthesis, waste disposal. (All crucial for survival of cell)
Ribosomes
Small particles of RNA + protein found in large numbers in the cytoplasm of living cells (both eukaryotes and prokaryotes), translate genetic code, create enzymes and hormones from RNA and DNA.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Network of membranes within eukaryotic cells that functions in protein and lipid synthesis and transport ,rough ER=processes and folds proteins, smooth ER=synthesizes lipids, stores calcium, detoxifies
Golgi apparatus
Stack of flattened membranes, “post office” receiving proteins and lipids processing them and sending to proper locations.
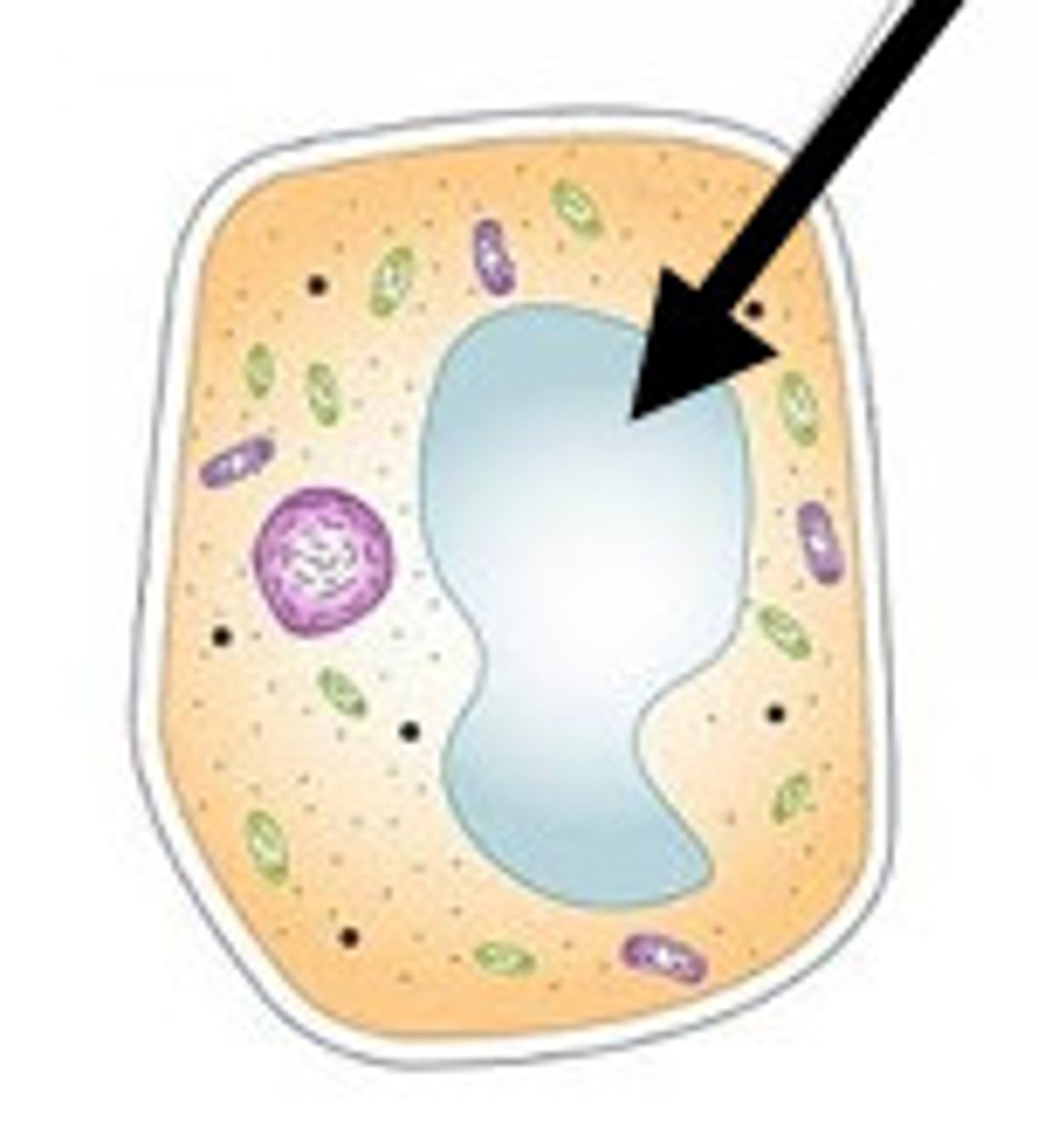
Vacuoles
Large saclike enclosed structures (membrane), STORE MATERIALS *WATER,SALT,PROTEIN,CARBS
Cystoskeleton
Certain parts help transport materials to different parts of the cell, maintain cells shape, hold organelles in place, enable various forms of transport and movement.
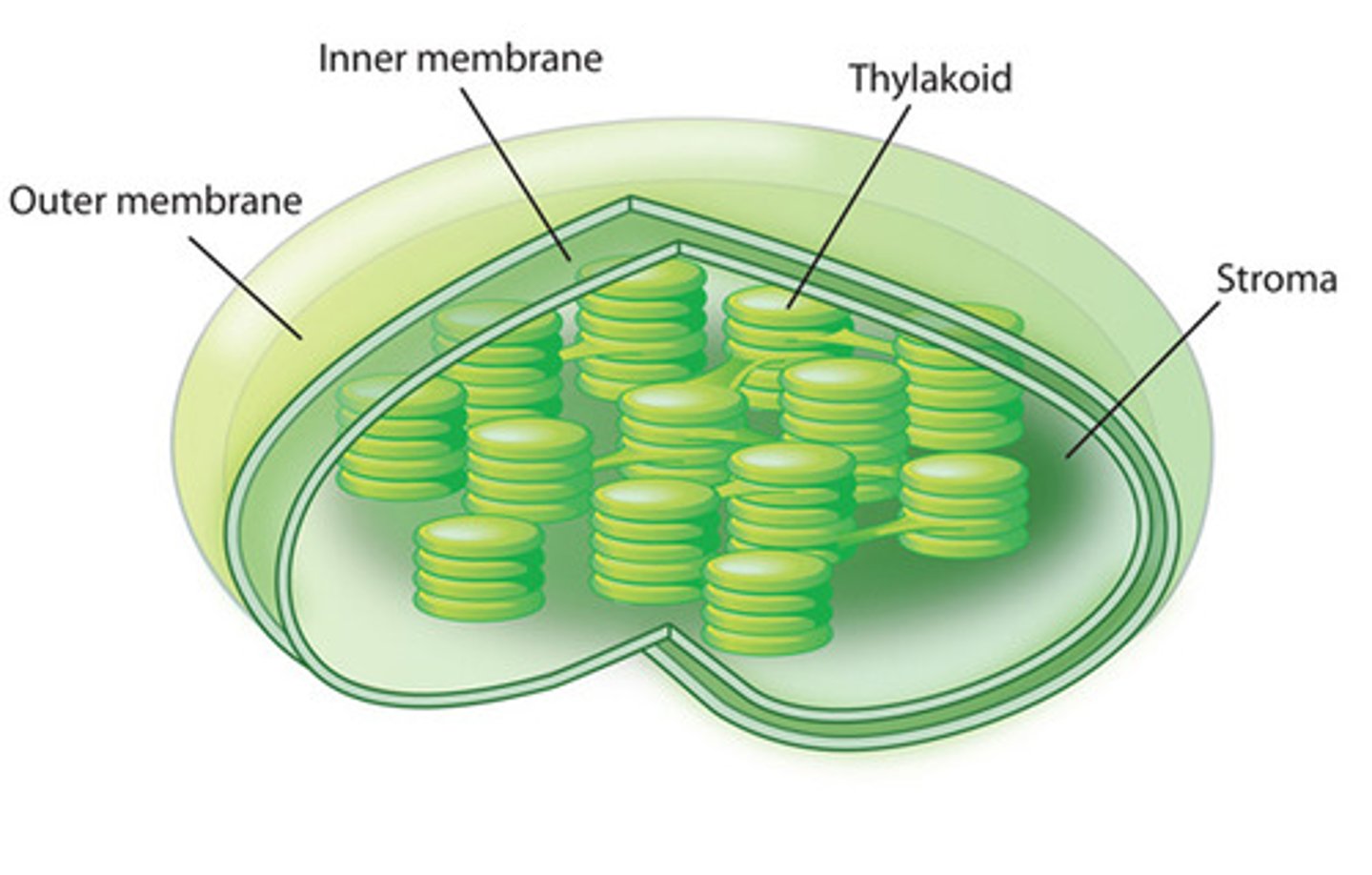
Chloroplast
Biological equivalent of solar power plants, energy production through photosynthesis
Mitochondria
Power plants of the cell (“power house”), generate energy, break down food (chemical energy) into compounds.
Cell wall
Most prokaryotes, produce strong layer around the cell membrane, preventing excessive water intake, maintain cells shape shape. (SUPPORT,SHAPE,PROTECT)
Lipid Bilayer
Gives cell membranes flexible structure that forms strong barrier between cell and surroundings, create a selectively permeable barrier that separates the inside of a cell from the outside environment
Lysosomes
Small organelles filled with enzymes, break down organelles that outlived their usefulness, break down worm out or excess cell parts, BREAK DOWN LIP,CARB,PRO INTO SMALL MOLECULES FOR CELL
Selectively permeable
Some substances can pass across them while others cannot, maintaining homeostasis.
Centrioles
protein structures involved in cell division and the formation of cilia and flagella
Vesicle
membrane-bound sacs that transport materials within the cell
Nucleus
the control center of the cell
Vacuole
Central Vacuole (Plants)
storage (larger in plants to store water)
Smooth ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
transports proteins, makes phospholipids & detoxifies poisons
Golgi
(AKA Golgi Apparatus, Golgi Bodies, Golgi Complex)
packages and transports proteins, like UPS, adds carbohydrates and lipids to proteins
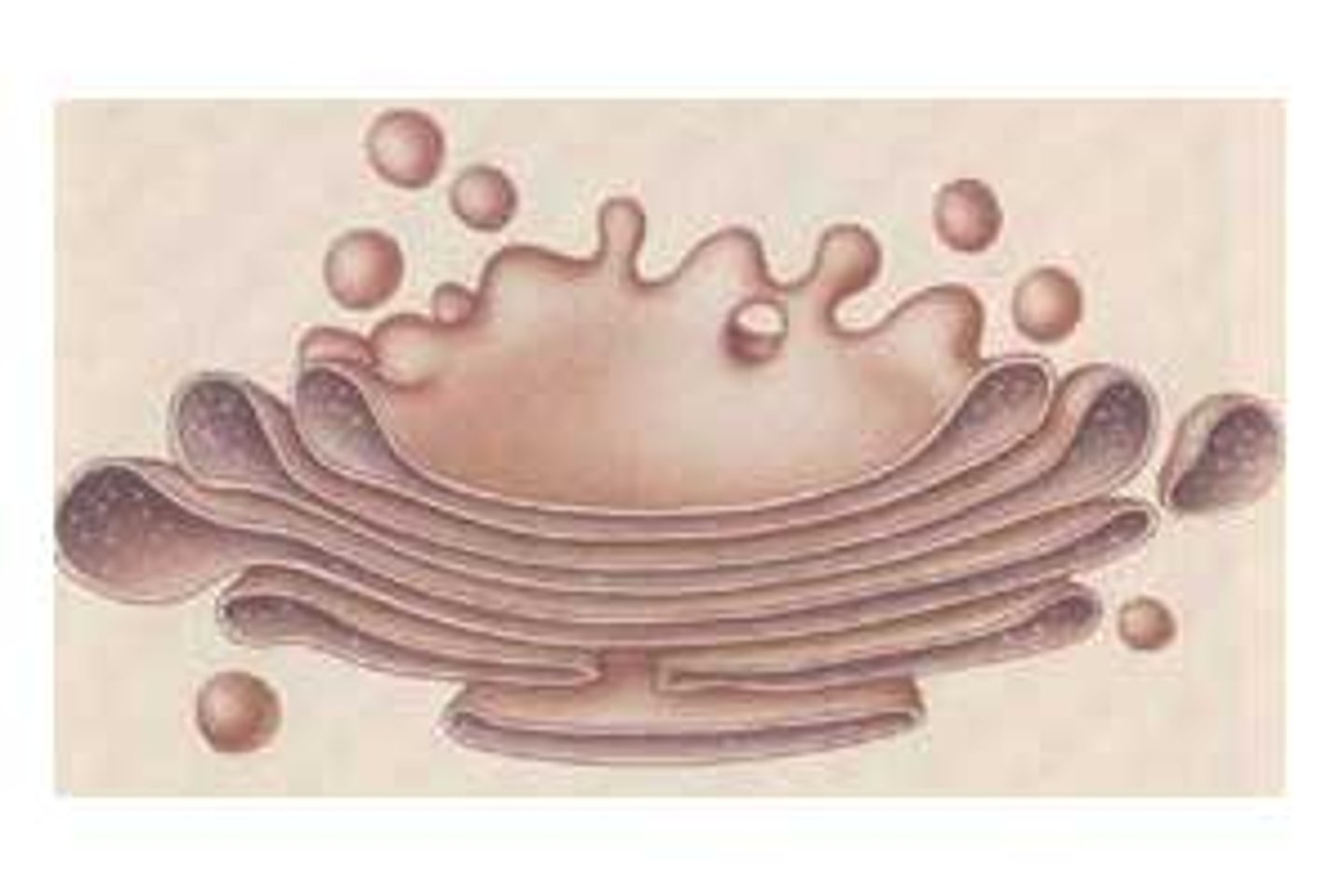
Free Ribosome
makes protein in cytoplasm
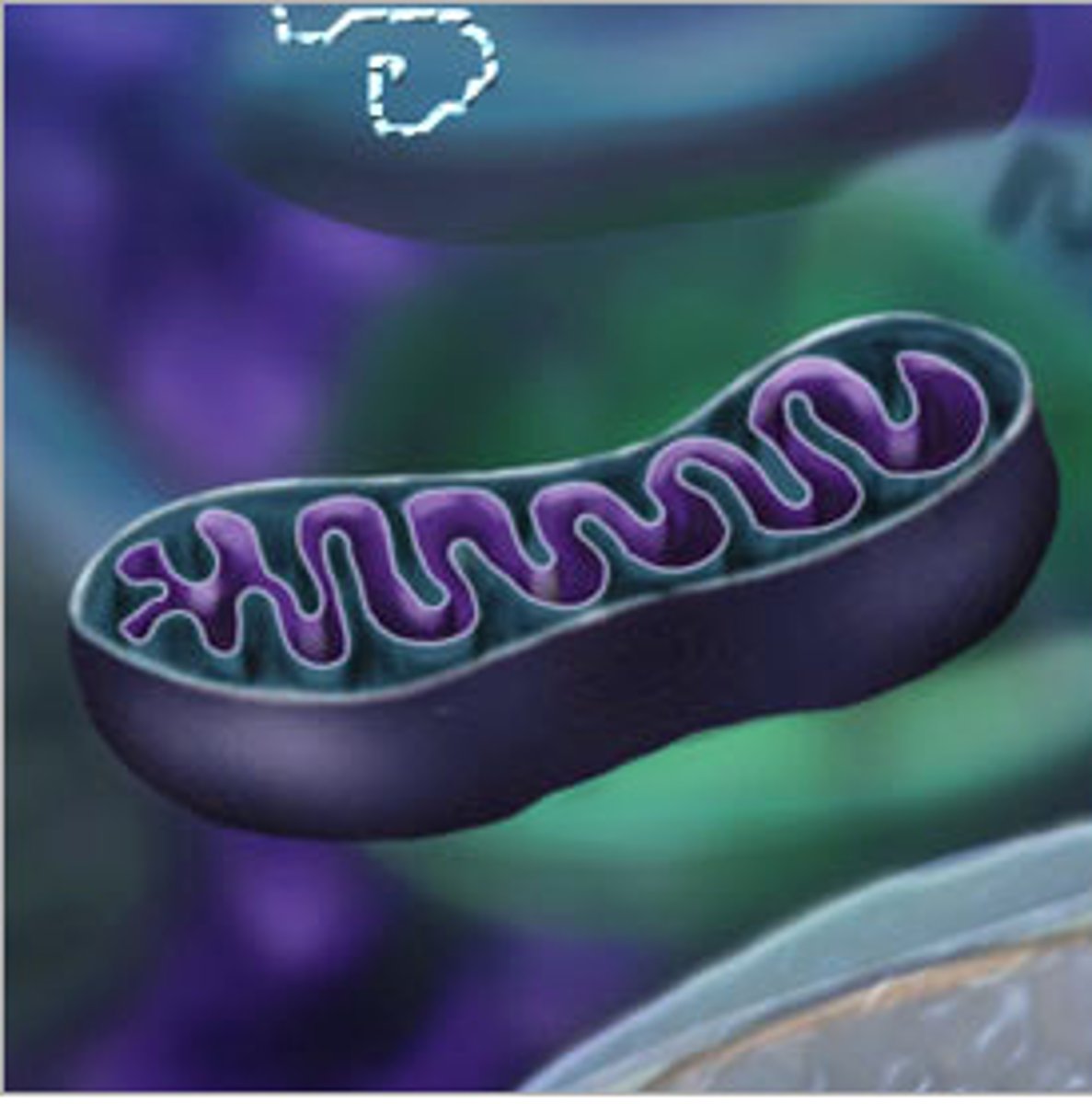
Mitochondria
Makes ATP energy
Cell Wall
structure and support, found in plant, fungus, and bacteria cells, the rigid outer layer
Lysosome
digests and recycles; found only in animal cells
Cell Membrane
Plasma Membrane
controls what goes in and out of the cell
Cytoplasm
the jelly-like part of the cell
Chloroplast
does photosynthesis, makes sugar from carbon dioxide and the sun; found only in plant cells
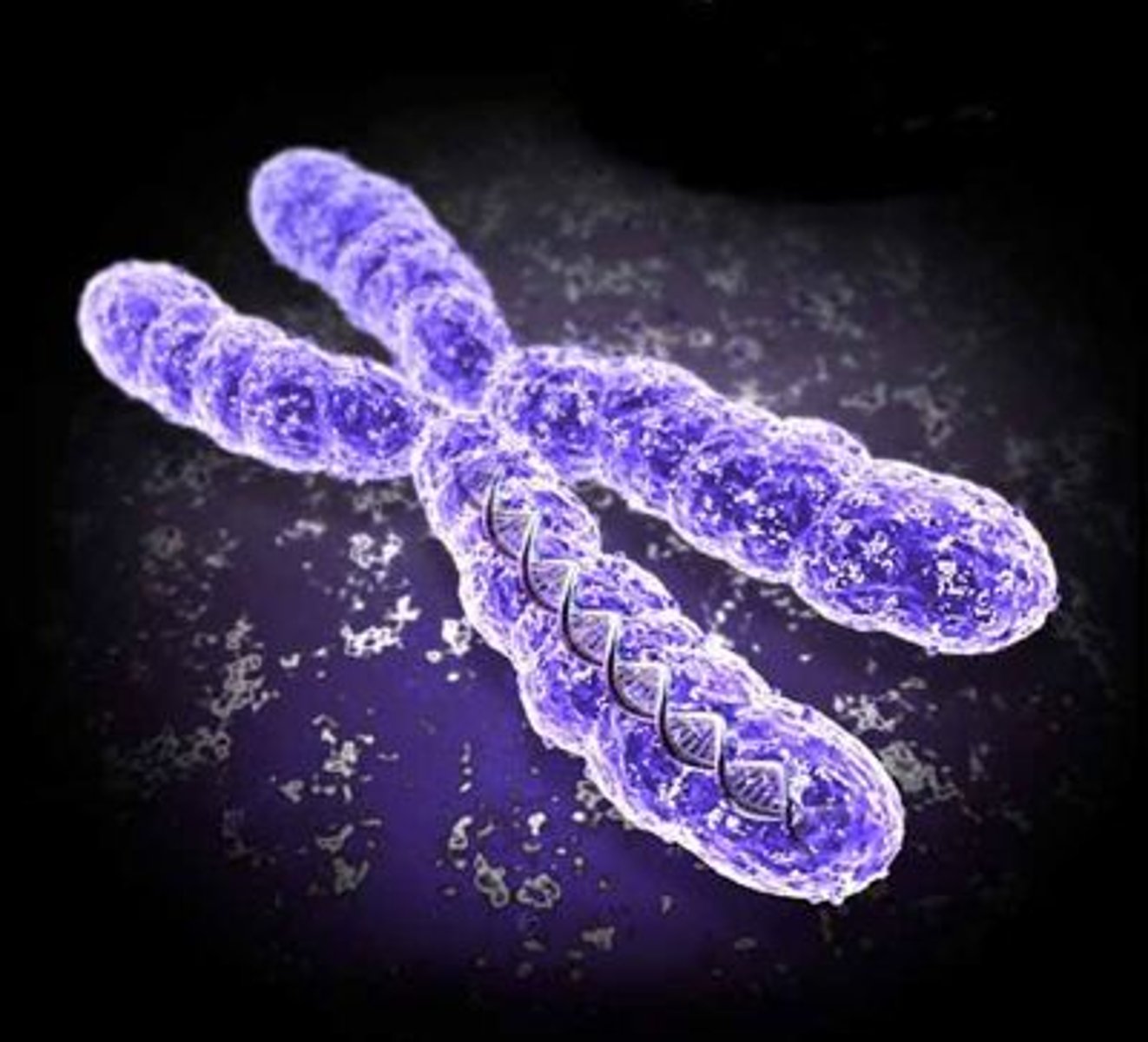
Chromosomes
made of hereditary material
Centrioles
helps in cell division, only found in animal cells near nucleus
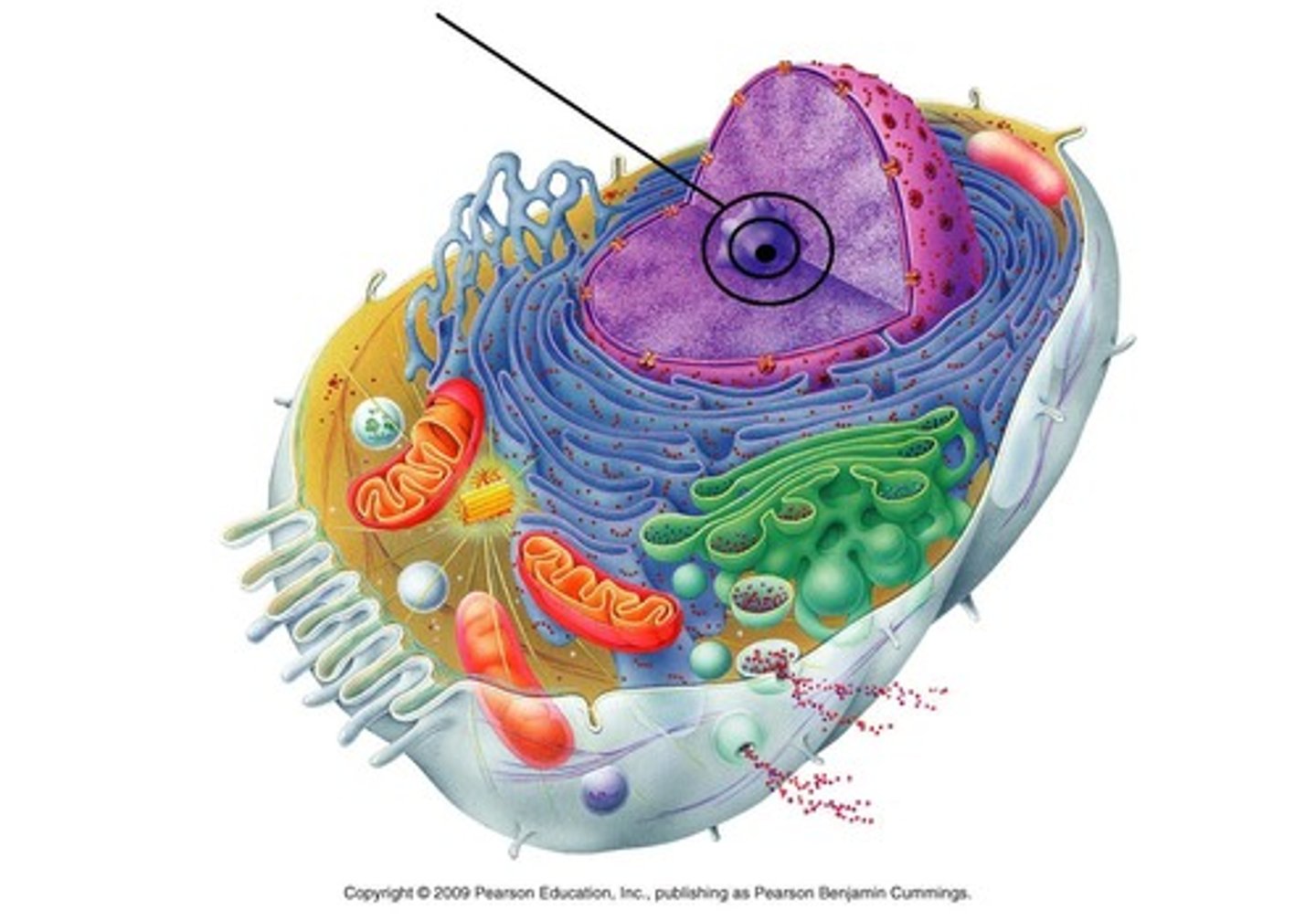
Nucleolus
makes ribosomes
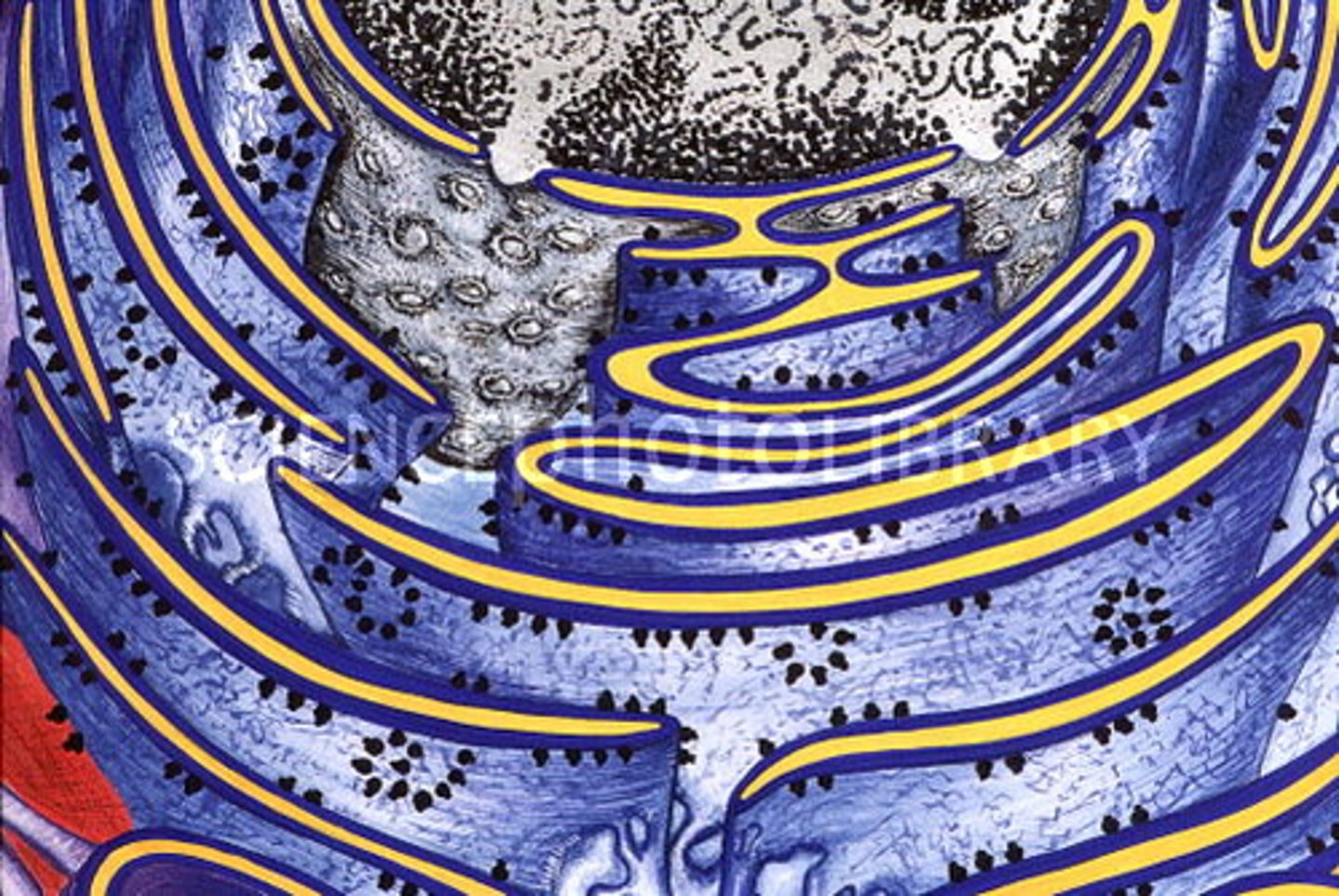
Rough ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
transports proteins

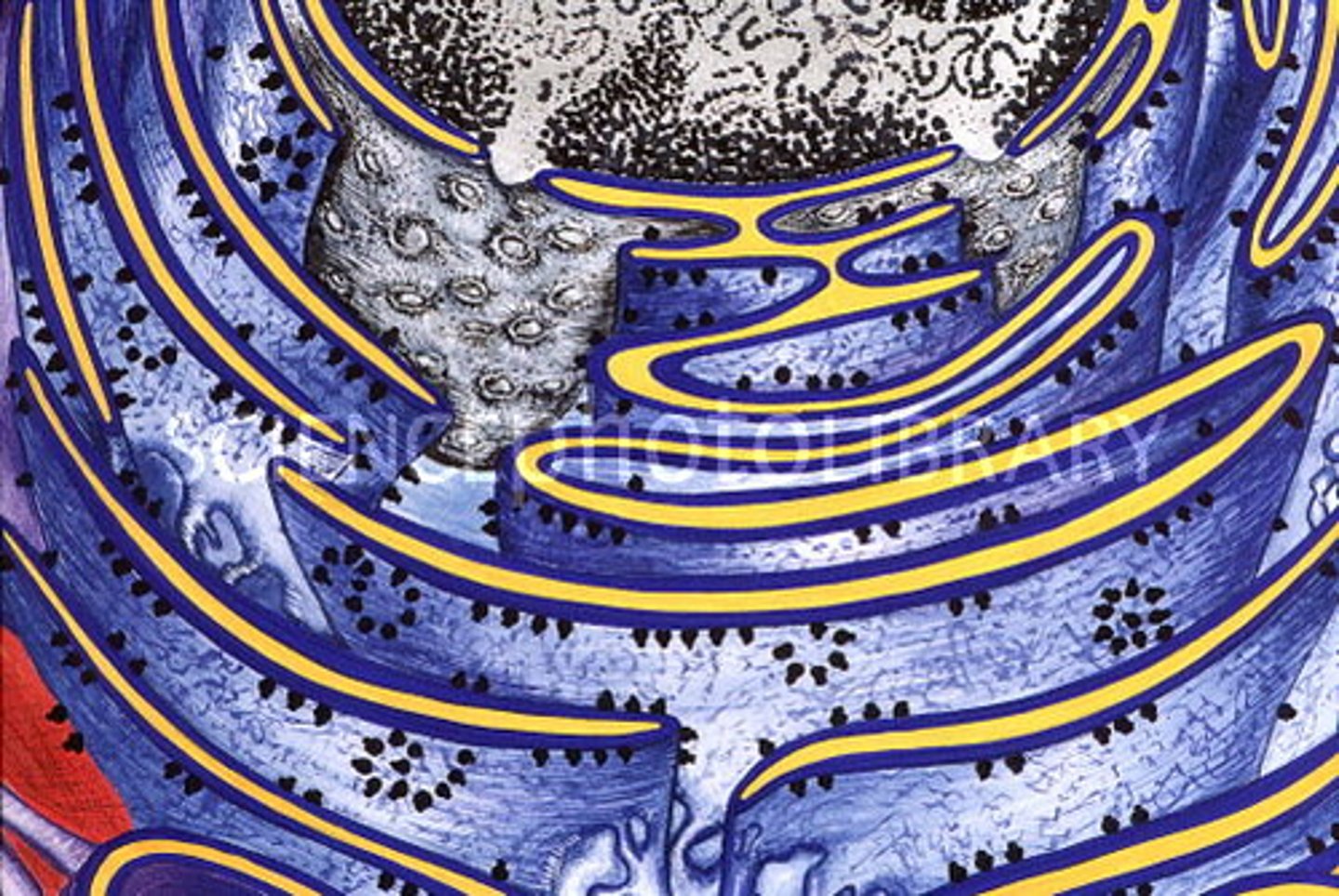
Attached Ribosome
makes protein on Rough ER

Cytoskeleton
A network of long protein strands in the cytosol that helps support the cell
Cilia
Hair-like projections on the cell surface used for locomotion or the movement of fluid over a cell.
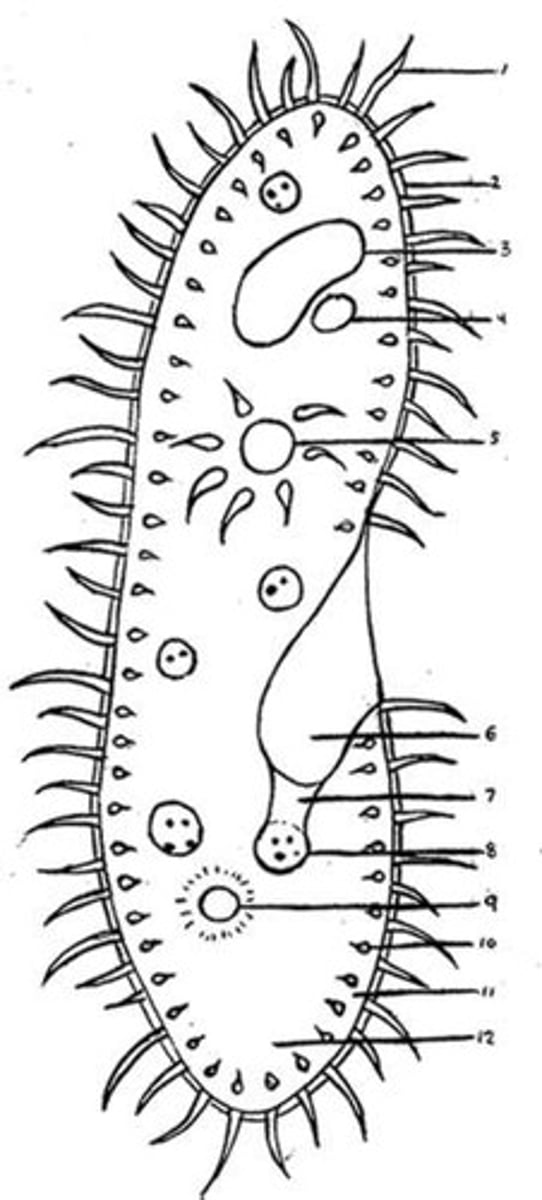
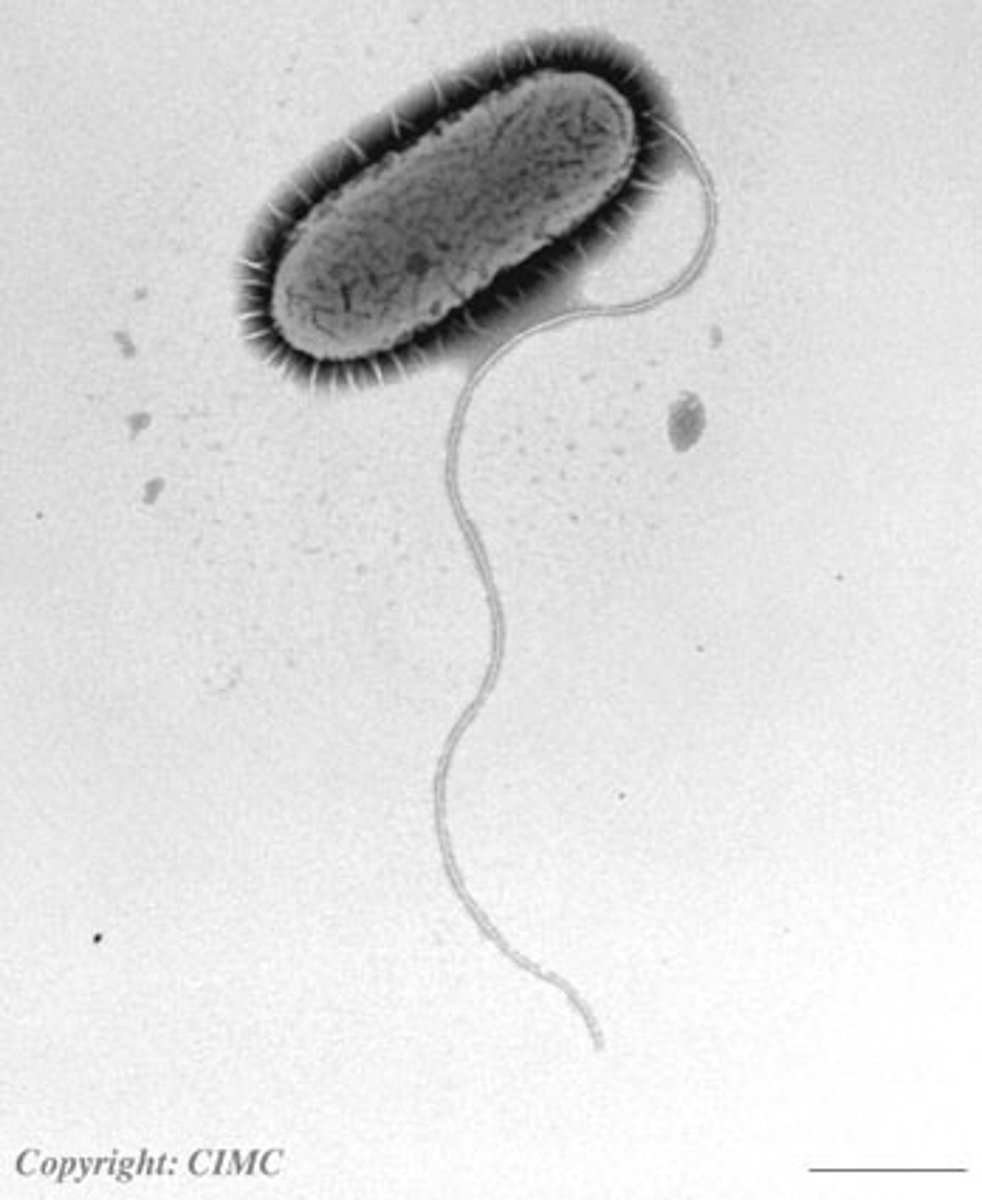
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
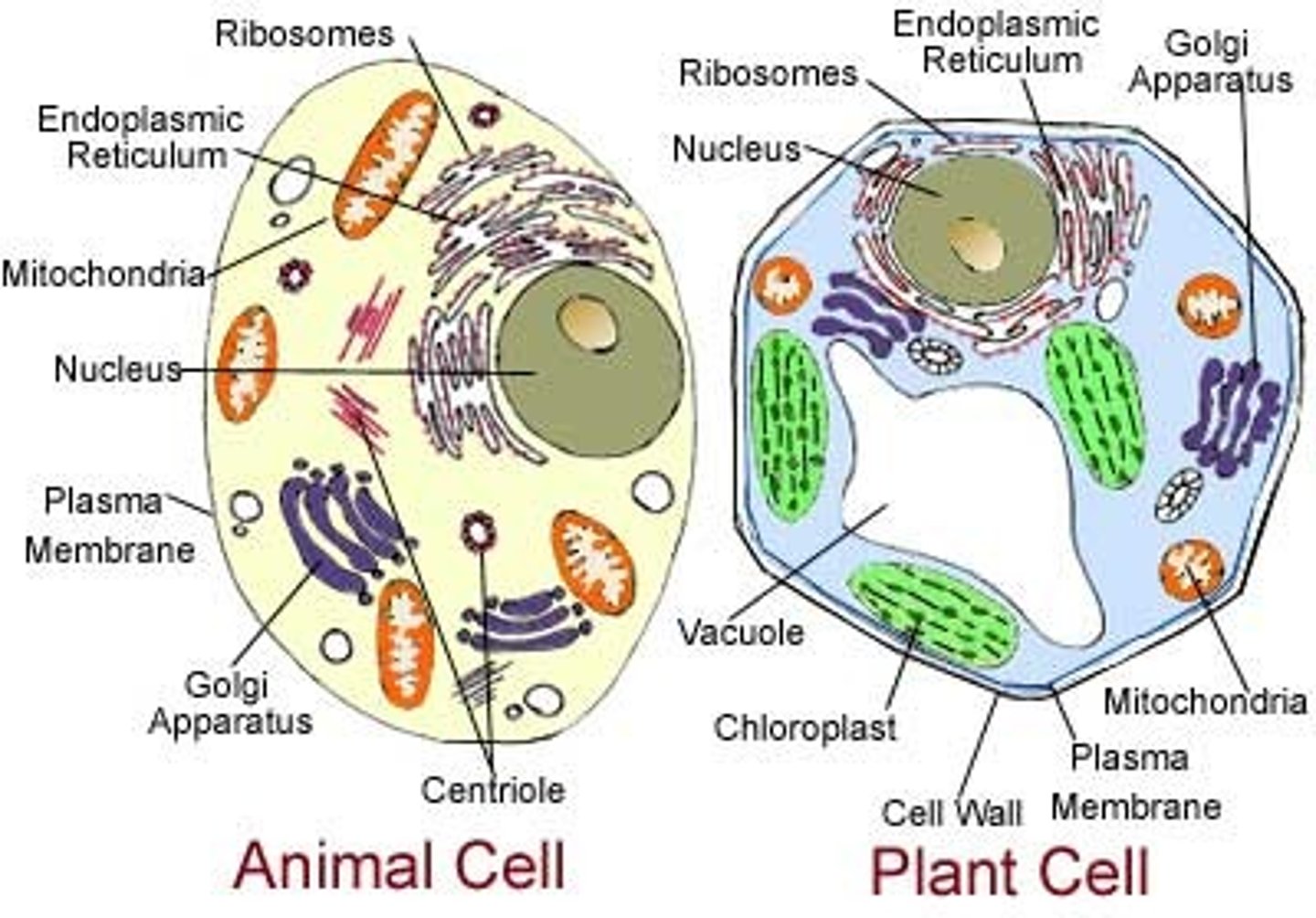
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles