Integumentary System
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is the epidermis
outer layer of skin
what 4 cells are found in the epidermis
keratinocytes
maleanocytes
markel cells
langerhans cells
what are keratinocytes (2)
makes keratin that gives skin strength
creates waterprrof layer of skin
what is melanocytes
pigment
what is markel cells
thought to be touch sensation
what are langerhans cells
defends from invading cells on the skin
what are the 4 layers of the epidermis
stratum corneum (pointy layer)
stratum lucidum (clear layer)
granular layer
stratum spinosum/spiny layer
what is the dermis
structural strength
what are the 2 layers of the dermis
papillary layer
reticular layer
what is the papillary layer (2)
made of loose connective tissue, fibres, and ground substance
nerve endings/meissners copuscles
what is the reticular layer in the dermis
made of irregular connective tissue
what is the hypodermis/subcutaneous layer? (3)
used as a thermoinsulator
mechanical shock absorber
mostly made of adipose
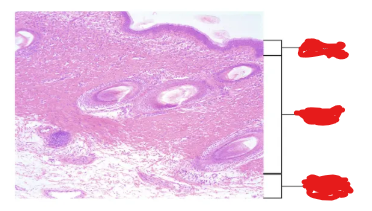
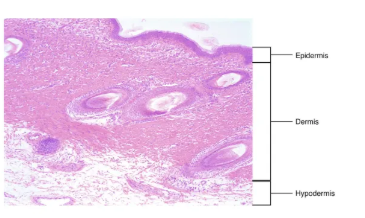
fill in the blanks
top - epidermis
mid - dermis
bot - hypodermis
— — is where the fur is
thick skin or thin skin
what do melanocytes do when they are stimulated by UV light
deposit melanin to protect from the uv rays
define macrophage
immune cell
what movement type does langerhans cells have
diapedesis
define diapedesis
white blood cells squeeze through the walls of tiny blood vessels
what is the 6 functions of the epidermis
protection - chemical, physical, biological barrier
Body temp regulation - sweating and dermo flow
Cutaneous sensation - touch, pressue, pain, temp receptors
Metabolic function - synthesis of vitamin d precursor
Blood resevoir - dermal vascular supply
Excretion - eliminates nitrogenous wastes and salt in sweat
what is feeding the epidermis
dermis