Paper 1 mistakes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is a monoclonal antibody? (1)
an antibody produced from identical B cells/cloned plasma cells
Describe the pathway taken by an oxygen molecule from the atmosphere to the respiring tissues of an insect (4)
oxygen enters through spiracles
down trachea
to tracheoles
diffuses into respiring tissues
down conc grad
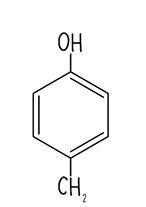
Figure 4 shows the R group for the amino acid tyrosine.
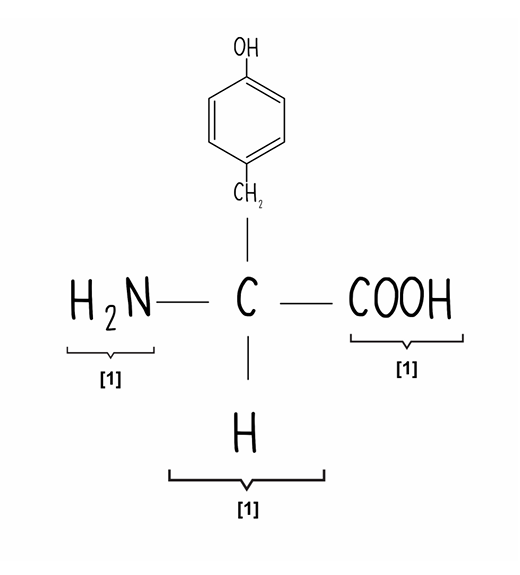
Draw the amino acid tyrosine (3)
Suggest why clonal cuttings of a plant would be used for an experiment (2)
control variable
reduce impact of genetic variation
Explain what is meant by herd immunity and explain the advantages of it (5)
herd immunity = majority of population vaccinated
prevents transmission of pathogen in community
reduces infection rate in population
can lead to eradication of disease
protects vulnerable populations
prevents future pandemics
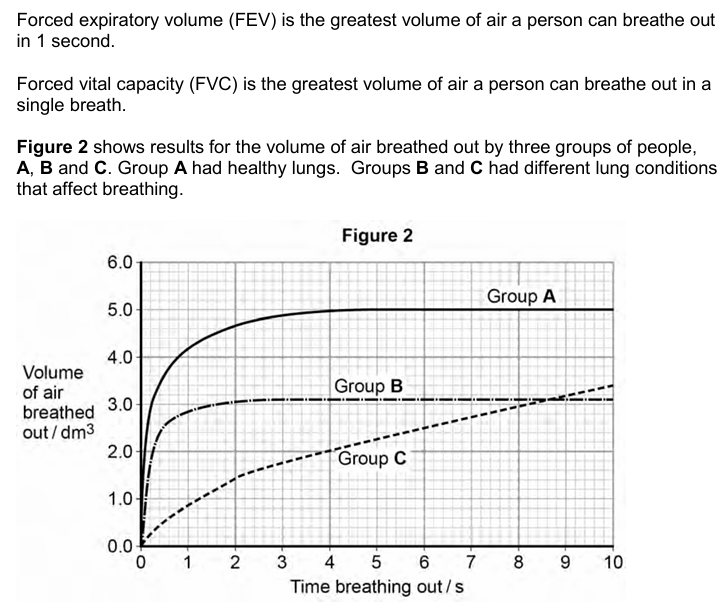
Asthma affects bronchioles and reduces flow of air in and out of the lungs. Fibrosis does not affect bronchioles.
Which group, B or C, was the one containing people with fibrosis of their lungs? Use the information provided and evidence form Figure 2 to explain your answer (3)
Group B because they breathe out as quickly as healthy
so bronchioles are not affected
FVC reduced/total volume breathed out reduced
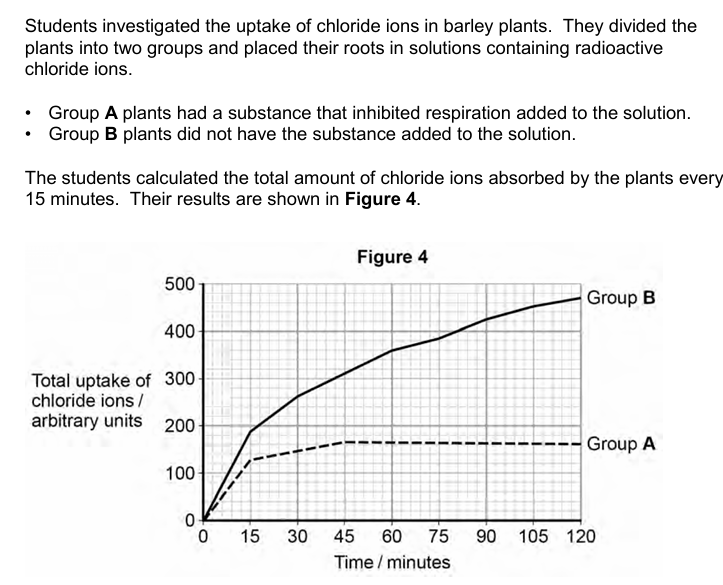
Explain the results shown in Figure 4
Group A - initial uptake slower because by diffusion only
Group A - levels off because same concentrations inside cells and outside cells/reached equilibrium
Group B - uptake faster because by diffusion and active transport
Group B fails to level off because uptake against gradient/no equilibrium to reach
Group B - rate slower because few/fewer chloride ions in external solution
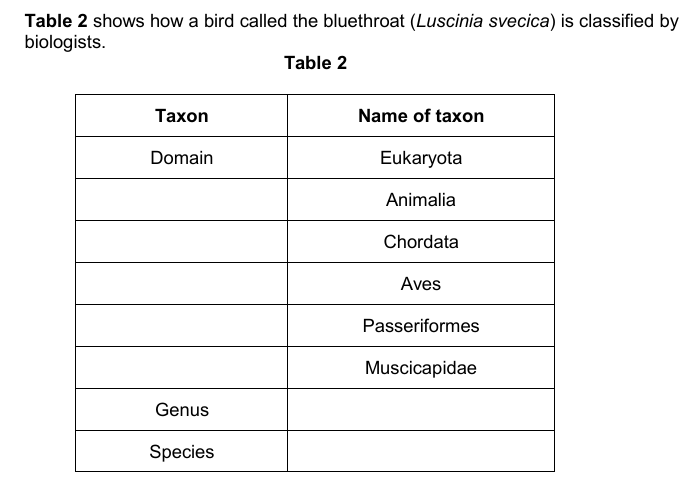
Luscinia must be capitalised!!
This test only detects the presence of HIV antibodies. Give two reasons why it cannot be used to find out if a person has AIDS (2)
(to diagnose AIDS, need to look for)
AIDS related symptoms
number of helper T cells
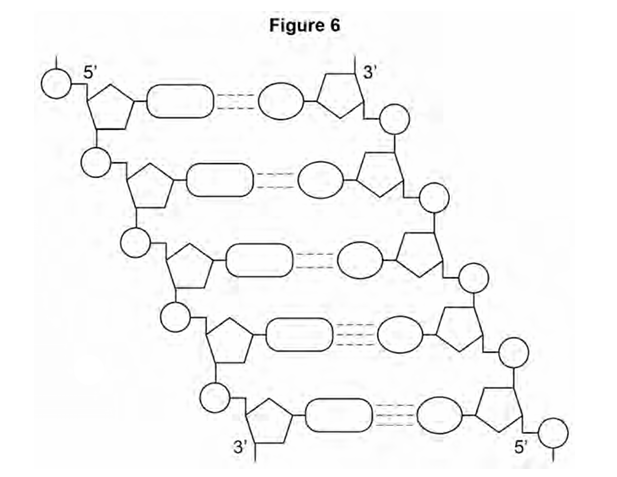
During replication, the two DNA strands separate and each acts as a template for the production of a new strand. As new DNA strands are produced, nucleotides can only be added in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
Use Figure 6 and your knowledge of enzyme action and DNA replication to explain why new nucleotides can only be added in a 5’ to 3’ direction. (4)
reference to DNA polymerase
which is specific
only complementory with 5’ end
shapes of 5’ end and 3’ end are different

Describe the mass flow hypothesis for the mechanism of translocation in plants (4)
in leaf/source sugars actively transported into phloem
by companion cells
lowers water potential of sieve cell/tube and water enters by osmosis
increase in pressure causes mass movement towards sink/root
sugars used in root for respiration for storage
Describe the role of micelles in the absorption of fats into the cells lining the ileum (3)
Micelles include bile salts and fatty acids; Ignore other correct components of micelles.
Make the fatty acids (more) soluble in water;
For 'fatty acids' accept fats / lipids.
Bring/release/carry fatty acids to cell/lining (of the ileum);
For ‘fatty acids’ accept fats/lipids.
Maintain high(er) concentration of fatty acids to cell/lining (of the ileum);
Fatty acids (absorbed) by diffusion; Reject if absorbed by facilitated diffusion Ignore if micelles themselves are being absorbed. Ignore references to monoglycerides.
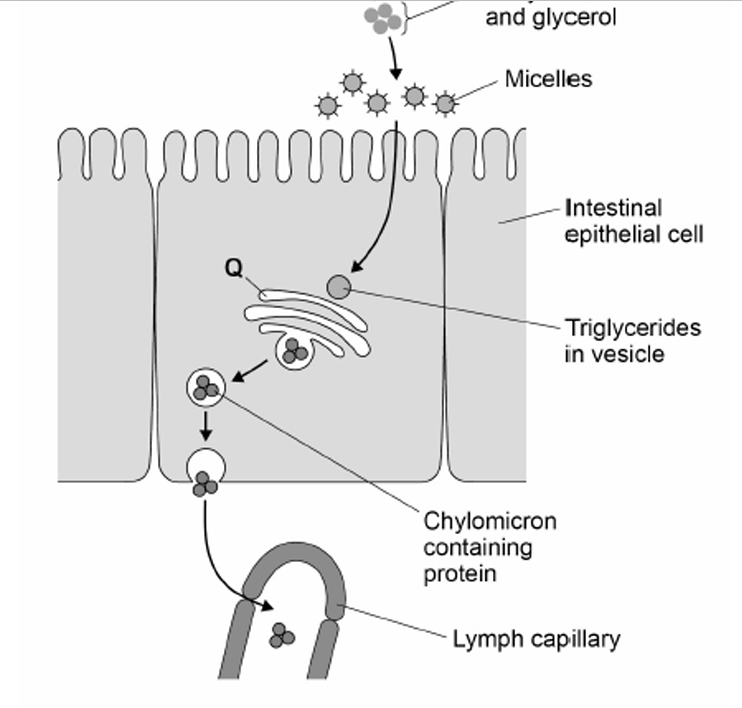
Name structure Q in the diagram above and suggest how it is involved in the absorption of lipids (4)
Golgi (apparatus);
Modifies / processes triglycerides
Combines triglycerides with proteins;
Packaged for release / exocytosis OR
Forms vesicles;
Ignore ‘processes and packages’ unqualified 2. Reject synthesises triglycerides 3. Accept ‘forms / are lipoproteins’
Describe the role of a ribosome in the production of a polypeptide. Do not include transcription in your answer (3)
mRNA binds to ribosome
idea of two codons/binding sites
allows tRNA with anticodons to bind/associate
catalyses formation of peptide bonds between amino acids
moves along mRNA to next codon
Describe the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem (5)
water lost from leaf in transpiration
lowers water potential of leaf cells
water pulled up xylem
continuous column - cohesive due to hydrogen bonds between water molecules
adhesion of water molecules to xylem
During vaccination, each animal is initially injected with a small volume of venom. Two weeks later, it is injected with a larger volume of venom.
Use your knowledge of the humoral immune response to explain this vaccination program (3)
B cells specific to the venom reproduce by mitosis
produce plasma cells and memory cells
the second dose produces antibodies in higher concentration and quickly
Describe the structure of HIV (4)
RNA as genetic material
reverse transcriptase
capsid
attachment proteins
phospholipid envelope
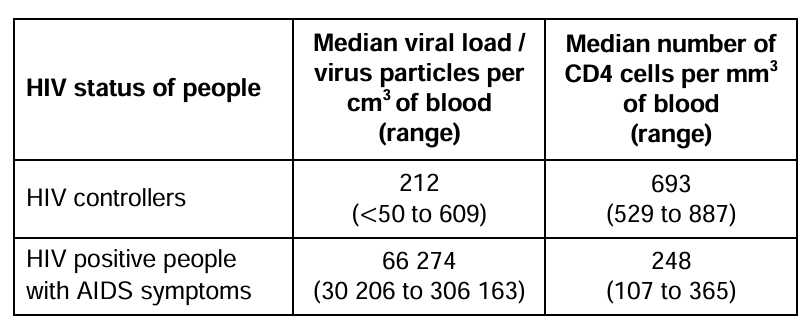
Use the data in Table 3 and your knowledge of the immune response to suggest why HIV controllers do not develop symptoms of AIDS (3)
all have more T helper cells
lower viral load to destroy helper T cells
activation of B cells/cytotoxic T cells/phagocytes
production of antibodies/ability to kill virus infected cells
more able to destroy other pathogens
Mammals such as a mouse and a horse are able to maintain a constant body temperature.
Use your knowledge of surface area to volume ratio to explain the higher metabolic rate of a mouse compared to a horse (3)
mouse smaller so larger surface area to volume ratio
faster heat loss
respiration releases heat
Describe the biochemical tests you would use to confirm the presence of lipid, non-reducing sugar and amylase in a sample (5)
Lipid
add ethanol then add water and shake
milky white emulsion
Non-reducing sugar
benedicts test and stays blue
boil with acid then neutralise with alkali
heat with benedicts and becomes red/orange
Amylase
add biuret and becomes purple
add starch, test for reducing sugar/absence of starch