The market mechanism and market failure
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
What is the price mechanism?
the interaction of supply and demand and how the market allocates resources
What are the functions of the price mechanism?
signalling
incentivising
rationing
How does price signal information?
it sends messages to buyers and sellers about changes in conditions. It shows where resources are wanted (increasing price) or not (decreasing prices)
What does a rising price signal?
scarcity
How do prices create incentives?
prices motivate producers and consumers. Higher prices encourage more production (reallocate resources from a less profitable market to maximise profits) vice versa. Falling prices discourage production but incentivises consumers to buy
What is the rationing function of prices?
prices allocate scarce resources when demand > supply. Higher prices reduce demand so resources go to those who value them most. It leads to a contraction in demand
What are the advantages of the price mechanism?
Efficiency: Resources move to where they’re most valued (allocative efficiency).
Incentives: Profit motive encourages innovation and cost reduction (productive efficiency).
Freedom of choice: Consumers and producers make their own decisions — decentralised control.
Automatic adjustment: Prices respond flexibly to changing conditions.
What are the disadvantages of the price mechanism?
Inequality: Those with low income may be priced out (e.g. healthcare, housing).
Market failure: Prices ignore externalities (pollution, public goods).
Information failure: Prices may not reflect true costs/benefits.
Short-termism: Firms may prioritise profit over social/environmental goals.
Moral concerns: Some goods/services may change in nature when sold for money (e.g. blood, organs, education).
What are some evaluative points for the price mechanism?
The price mechanism is impersonal — it ignores need, focusing on purchasing power.
Governments often intervene where markets misallocate (e.g. taxes, subsidies, public goods).
In some areas (healthcare, education), equity and ethics may outweigh efficiency.
What is market failure?
when the price mechanism leads to a misallocation of resources and fails to achieve social efficiency
What is complete market failure?
when there is a missing market - no market exists at all for a good of service due to the functions of price breaking down. This is because they aren’t profitable for firms to make (public goods)
What is partial market failure?
when the market exists but resources are misallocated, outcome is not socially optimal
What are the major causes of market failure?
externalities
public goods
information gaps
merit and demerit goods
monopoly power
factor immobility - geographical and occupational
inequitable distribution
What is a public good?
a good that is non-rivalrous and non-excludable
Define non-excludable
when you can’t stop somebody from consuming the good or service)
Define non-rivalrous
when your consumption of the good or service doesn’t prevent anyone else from consuming it
What are some examples of public goods?
streetlights, flood defences,
What do the provision of public goods lead to?
market failure
Why are public goods underprovided in a free market?
Because of the free-rider problem - individuals can benefit without paying
What is the free-rider problem?
When people consume a good without contributing to its cost, leading to under-provision
How are public goods eventually provided?
via state provision through tax
What is a quasi-public good?
A good that has some but not all characteristics of a public good. They are sometimes non-excludable and non rivalrous
Give an example of a quasi-public good
Roads, parks, beaches. A lot of these a non-rivalrous when they are very busy
How has technological change affected the classification of goods?
It can make goods excludable e.g TV broadcasting was once non-excludable but it is now excludable due to subscriptions
What is the tragedy of the commons?
When common resources are overused because individuals act in self-interest
How do firms contribute to the tragedy of the commons?
they see that they can make profit from some of these goods and make it rival
Give two examples of the tragedy of the commons in real life.
Overfishing and air pollution.
How is the tragedy of the commons linked to environmental market failure?
Shared environmental resources are overused without ownership or regulation
What is a private good?
goods that are rivalrous and excludable
What are some examples of private goods?
foods, cars, clothes
How are private goods characterised?
the owners can exercise private property rights, preventing other people from using the good or consuming its benefits - excludability
when one person consumes a private good, the quantity available to others decreases - rivalry
How do private goods generate profit for firms?
customers can compete for these goods, which are limited in supply
Define externality
when the production or consumption of a good or service imposes a cost or benefit on third parties not involved in the transaction
Define private cost (MPC).
The cost to the individual producer or consumer.
Define external cost.
The cost to a third party.
Define social cost (MSC).
Total cost to society = private cost + external cost.
Define private benefit (MPB).
The benefit to the individual consumer or producer.
Define external benefit.
The benefit to a third party.
Define social benefit (MSB).
Total benefit to society = private benefit + external benefit.
What are negative externalities?
when the production or consumption of a good or service causes harm to third parties outside of the price mechanism
What are negative externalities also known as?
external costs
What are positive externalities?
when production or consumption creates benefits to others, third parties outside of the price mechanism
What are positive externalities also known as?
external benefits
What are negative externalities of production?
externalities caused by producer supply that result in a negative external impact on a third party
What is an example of negative externalities of production?
Pollution from factories
How do goods with negative externalities lead to market failure?
the overproduction of them
What is the supply curve equal to?
marginal cost (MC) as it tells us the lowest price producers are willing to sell a good for.
What is the demand curve equal to?
marginal benefit (MB) as it tells us the highest price consumers are willing to pay for a good
Why in the negative externality of production diagram does MSB=MPB?
usually, MSB= PB+EB. In negative externalities, there is no external benefit, it is 0 and so MSB=BPB.
Draw the negative production externalities graph
MSC > MPC → overproduction
The market equilibrium (MPB = MPC) produces too much
Socially optimal output is lower where MSB = MSC
The shaded area between MSC and MPC shows the welfare loss
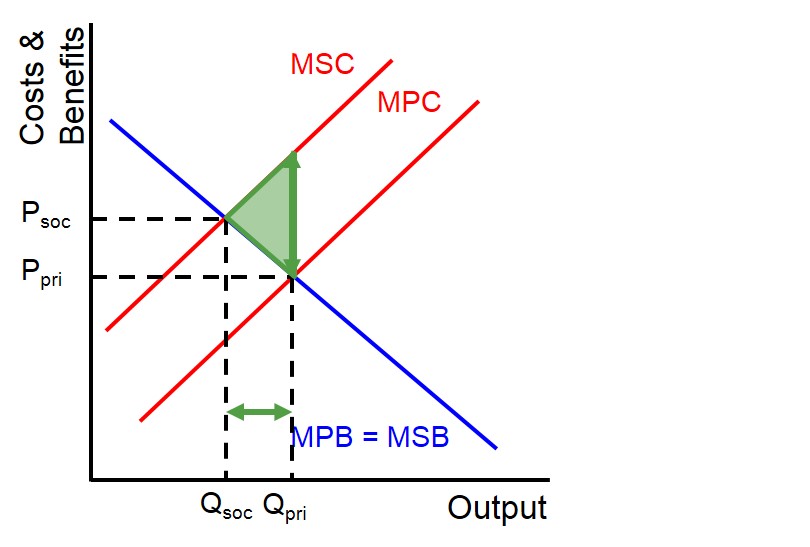
Is the socially efficient optimum efficient and if so which one?
it is allocatively efficient. There is no market failure at this equilibrium
What is welfare?
net benefit - net cost. MSB-MSC.
How is welfare shown?
as the gap between the market equilibrium and the socially efficient equilibrium
What are positive externalities of production?
externalities caused by producer supply and result in a positive external impact on a third party
What is an example of positive externalities of production?
Beekeeping benefits nearby crops
How do positive externalities of production lead to market failure?
the market is failing due to under-provision, as only private benefits are considered by producers, not external benefits
In production externalities, why is MSB assumed to be equal to MPB?
because we focus on the supply side of the market
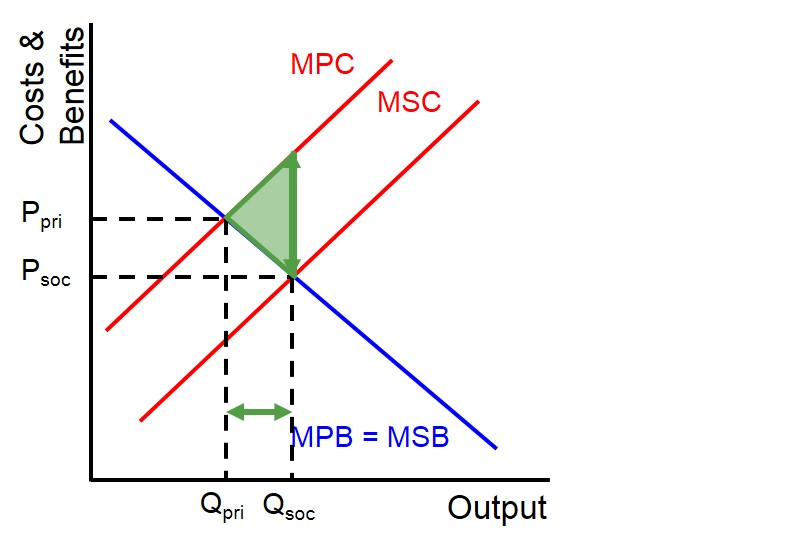
Draw the positive production externality diagram.
MSB > MPB → underproduction
free market equilibrium is where MPB = MPC
socially efficient equilibrium is where MSB=MSC
potential welfare gain (welfare loss) between Qpri and Qsoc
What is a negative externality of consumption?
externalities that are caused by consumer demand and result in a negative impact in a third party
How do negative consumption externalities cause market failure?
as only private costs are considered by consumers and not external costs and so goods are over-consumed
What are some examples of negative externalities of consumption?
Smoking, loud music
In this graph, why is MSC assumed to be equal to MPC?
as it focuses on the consumer (demand) side.
Draw the negative consumption externalities graph
MSB < MPB → overconsumption
government intervention forces the market to be more socially efficient and reduce the overall welfare loss to society
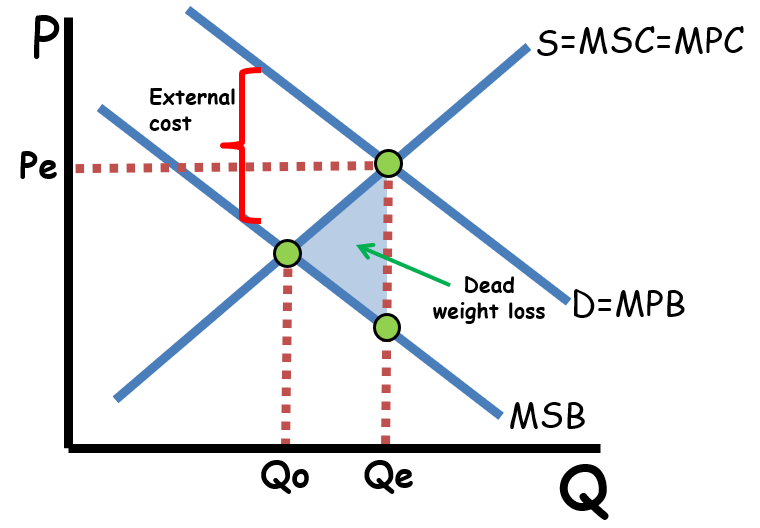
What are positive externalities of consumption?
externalities that are caused by consumer demand and result in a positive external impact on a third-party
How do positive consumption externalities result in market failure?
as only private costs are considered and not external costs, individuals will under-consume
What are some examples of positive consumption externalities?
Vaccinations, education, healthcare
Draw the positive consumption externality diagram
MSB > MPB → underconsumption
dead weightloss to society
there is an opportunity for government intervention to force the market to be socially efficient
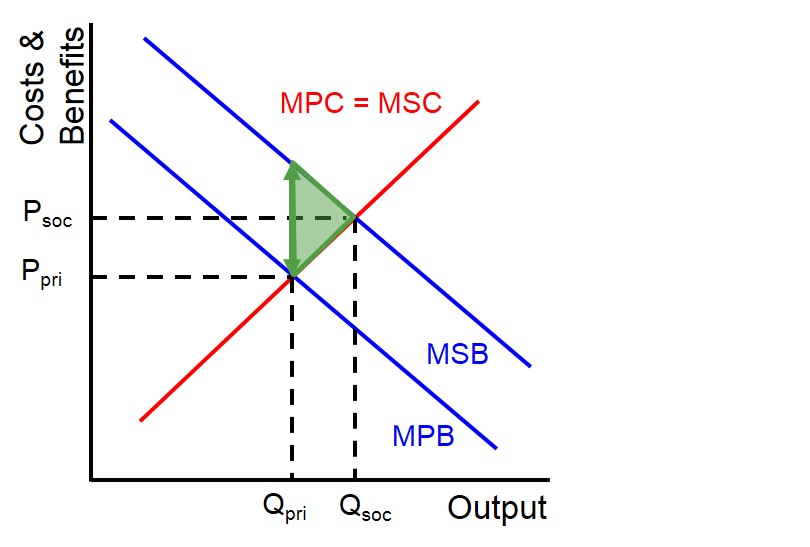
What is a merit good?
Goods that the government thinks people should consume more of, because they create positive externalities or consumers underestimate their benefits
What is a demerit good?
Goods that the government thinks people should consume less of, because they create negative externalities or consumers underestimate their harm.
What are some examples of merit goods?
education and healthcare
What are some examples of demerit goods?
cigarettes, junk food, alcohol
Why is classifying a good as merit or demerit a value judgement?
It depends on societal views about what people “should” or “shouldn’t” consume
What type of externality is associated with merit goods?
Positive externalities in consumption → society gains more than the individual realises
What type of externality is associated with demerit goods?
Negative externalities in consumption → society loses more than the individual considers
Why do merit goods tend to be underprovided in a free market?
Consumers lack information and don’t recognise their full benefits - misallocation of resources - too few merit goods and too many demerit goods
Why do demerit goods tend to be overprovided in a free market?
Consumers lack information and underestimate the harm they cause
How does imperfect information cause market failure in merit/demerit goods?
It leads to consumption decisions that don’t reflect true costs or benefits to society
What does the welfare area on a merit good diagram represent?
The potential welfare gain from increasing consumption to the socially optimal level
What does the welfare area on a demerit good diagram represent?
The extra cost to society
Are all goods with externalities merit or demerit goods?
No — externalities are objective, while merit/demerit status involves value judgements
Define imperfect information.
when consumers or producers lack the information needed to make an informed decision
What does more information do?
it closes the information gap
What are the two types of imperfect information?
incomplete information and asymmetric information
What is incomplete information?
when someone doesn’t have full information (some is missing) about the benefits or costs of their decisions
Explain how incomplete information about education leads to market failure.
children are not fully informed about the benefits of education causing them to be under-consumed even as a merit good. This is a misallocation of resources leading to market failure
How has the government intervened to improve the consumption of education?
regulations - education is compulsory till the age of 18
provide information - e.g science fairs and museums
subsidies - they subsidise university degrees decreasing the cost and increasing the quantity
How has the government intervened to reduce the consumption of demerit goods like cigarettes?
regulations - like you can’t smoke indoors
advertising and information - says on cigarette packs
specific tax - reduces quantity and increases price
What is asymmetric information?
when one party has more information than the other
Give an example of asymmetric information
Used car sales — sellers know more about quality than buyers -’lemons’
What is monopoly power?
power of firms to be price makers rather than take the price as it is given - barriers to entry limit competition
Why does monopoly power cause market failure?
It leads to higher prices, restricted output, and allocative inefficiency. Consumers face higher prices, less choice and lower welfare
How can monopoly power not lead to market failure in the long-run?
if the firms invest the profit they got from exploiting consumers into research and development. This will lead to innovations that consumers will benefit from. As long as the benefits from innovations outweigh the higher prices consumers pay in the short-run
What is the welfare impact of monopoly compared to perfect competition?
Price is higher, output lower, and there’s deadweight welfare loss
What is factor immobility?
when it is difficult for resources to move to where they are most needed, leading to inefficiency and market failure
What are two types of factor immobility?
Occupational immobility and geographical immobility
What is occupational immobility?
when workers can’t easily switch jobs because they lack the required skills e.g coal miners
How does occupational immobility cause market failure?
Workers can’t switch to new industries, leading to structural unemployment
How can the government reduce occupational immobility?
investing in education
training
apprenticeships
What is geographical immobility?
when workers or resources can’t move to where jobs are
How does geographical immobility cause market failure?
People can’t move to where jobs are, reducing labour market efficiency