Bio- Exam 1
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Anything that has mass and occupies space is considered to be
Matter
Where does all matter come from?
Stars
3 Forms of matter are?
Solids, Liquids, Gases
What is the smallest mass?
An electron
An atomic nucleus has protons and neutrons and is positively charged?
True
Corp-
Body
Gastro-
Stomach/Belly
Osteo-
Bone
Thorac-
Chest
Arthro-
Bone
Do all atoms have neutrons in their nuclei?
No
Describe an electron
They are in orbitals outside the nucleus and have a negative charge
An elements atomic number is determined by the number of
Protons
On periodic table, elements are organized by
Atomic number within rows
The number of neutrons in an atom can be determined by
Subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass
Are neutrons meaningless because they do not have a charge/mass, so its like they don’t exist
False
When diagramming an atom the intermost shell is filled with how many electrons?
Two
Atoms tend to have properties according to the fact that how many electrons is the optimal number in their outer (valence) shell. (Octet rule)
8
Two atoms that differ only in the number of neutrons they contain are known as
Isotopes
Do all isotopes of a given element have the same atomic mass?
No/False
Two chemicals that have the same chemical characteristics but different atomic masses are considered
Isotopes
Another name for the outer electron shell of an atom is the?
Valence shell
The number of electrons that would fill an atoms outer shell and make it nonreactive is
8
An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has
lost or gained an electron
An anion is an ion with a what charge?
Negative
A cation is an ion with a what charge?
Positive
Ionic bonds involve what?
Electrostatic interactions between anions and cations
Covalent bods are
Two nonmetal atom that share the same elements (they cooperate hence CO)
Do ionic compounds involve ionic bonds between their atoms that are usually between a metal and a nonmetal or a polyatomic ion and another element?
True
do covalent compounds involve atoms that are covalently bonded to each other ad are always between two or more nonmetals or a metalloid and a nonmetal?
False ( remember same element)
What are the four most common elements in the body?
CHON! (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen)
When two atoms with different electronegativity share electrons a polar covalent bond is formed?
Yes
In the human body do we find both ionic and covalent compounds?
Yes
Fatty acids consist mainly of carbon and hydrogen, so fatty acids are?
Nonpolar = Hydrophobic (they don’t dissolve in water)
Molecules that make up cells and tissues of living things are made up of the same elements as what they eat?
Yes
The four primary biomolecules that make up living organisms are
-Carbohydrates
-Nucleic acids (RNA/DNA)
-Protein
-Fatty acids
All of them polymers mind you
Ionic bonds are?
Metal atoms that donates electron to nonmetal atoms
Metallic bonds are?
Electrons move freely between metal atoms
What are polymers?
Biomolecule made up of repeating subunits linked together to form chains and sheets
If covalent bonds are nonpolar it means?
Shares electrons equally
If covalent bonds are polar that maeans?
They don’t share electrons equally
What is the primary structure of protein?
Individual amino acids linked together
Electronegativity means?
Ability of atomic/ion to attract electrons to itself (Attractiveness)
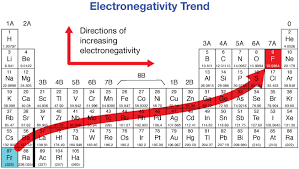
How to read electronegativity on the periodic table?
Further right on the table = greater electronegativity same with the further you go.
Left and down = less electronegativity
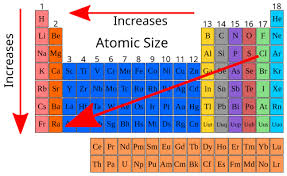
How to read atomic size on periodic table?
It is the opposite of electronegativity.
The size of the atom increases going towards the left and down
The size decreases moving right and up
How to read reactivity on periodic table?
If it is a metal down and left will increase reactivity
If its a non-metal the reactivity increases up to the right
What are the three types of chemical bonds?
Covalent, Metallic, and ionic
What is the force that will hold ionic bonds together?
Electrostatic attraction (this is the attraction between negative and positive like magnets)
What are characteristics of living things?
-Respiration/gas exchange
-React to external stimuli
-Reproduction
-Homeostasis (Can control its internal environment)
-Organization
The most important characteristic of living things is
Autopoiesis (The act of self making)
Why is life made of carbon?
Carbon is the easiest atom to bond with (Its a versatile Lego piece) Has four places to hook onto
What causes death of stars (explosion)
Iron
The four tissues in human body in order
Epilletal tissue (like lips, cheeks, nose outer layer)
Connective tissue (CT, this is the MOST diverse tissue in human body)
Muscular tissue (Can expand/contract/movement)
Nervous system (This is the MOST complex tissue)
(Every Cat Makes Noise ECMT)
What properties do metals have that non-metal dont?
They conduct heat and electricity.
(Mettaloids can conduct heat and electricity slowly)
The smallest, living component in all living things is a
Cell
Species is
Set of animal/plants, individuals that have similar characteristics to each other
Population is
Organisms of the same species in a particular area
Community area is
Interacting populations in a particular area
Ecosystem is
A community and the environment that contains it
Biosphere is
Regions of the earth crust inhabited
Which biological level of organization is described as similar cells performing similar (or the same) functions?
Tissue level
The various chemical reactions that organisms carry out are collectively called?
Metabolism
Is a molecule made up of a combination of two or more atoms
True
Describe organization of structures
Organs are made up of tissues, which are made up of cells, which are made up of organelles, and molecules.
All life on planet is dependent on photosynthesis for oxygen and fuel molecules
True
All life on this planet can be categorized into 6 different kingdoms, the 6 kingdoms can be grouped by 3 domains, which are?
Archaea
Bacteria
Eukaryotes
Which branch of microscopic anatomy is the study of tissue?
Histology
What are the three parts that make up phosolipids?
Phosphate, Glycerol, Fatty acid (lipid)
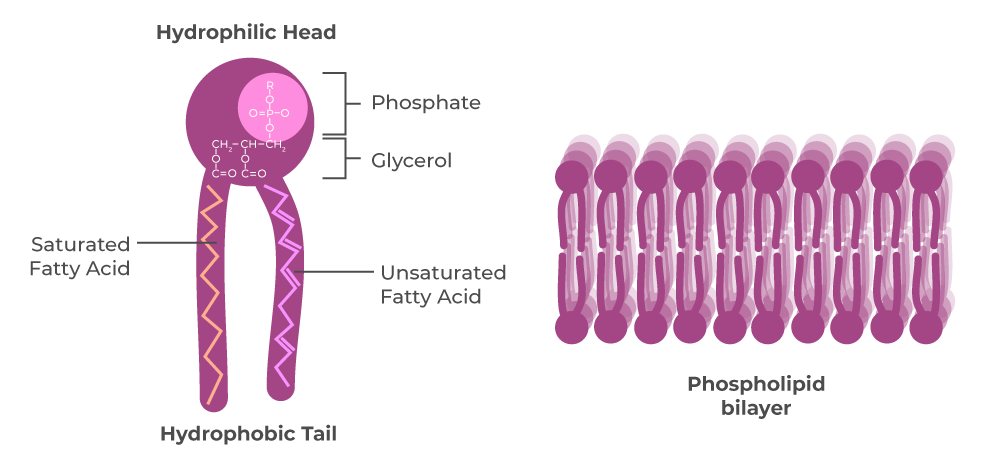
Which part on the phospholipid is polar and nonpolar?
They have polar heads (Hydrophilic- like water) and nonpolar tails (Hydrophobic)
What is plasma membrane made out of?
Phosolipids
What is the cell theory?
All life is made out of cells or is a cell, they can only come from existing cells
What organs do we have that cells don’t have?
Reproductive organs
What is the difference between Bacteria and Archae (Prokaryotes) VS Protoza, Fungi, Plants,, and animals (Eukaryotes)
Bacteria and Archae are tiny have no nucleus, no mitochondria, no endo
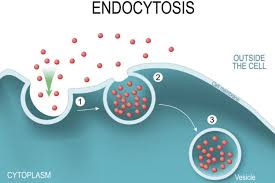
What is endocytosis?
where a cells membrane folds inwards, the plasma membrane covers and wraps around it. When eating.
What is the piece of evidence that supports the endosymbiosis theory (How the mitochondria came to be)
It is double membrane, the inner looks like bacteria while the outer looks like a humans outer membrane.
What kingdom of life does Mitochondria come from?
Bacteria
Why and how do Mitochondria generate power?
In the form of ATP (Biomolecule) they eat 2 or 3 carbon carbs then takes that energy and puts it in ATP (Which can be used in any cell)
What gets repeated three times on the ATP structure? (Know the structure for exam)
The three phosphate groups get repeated
(The structure of ATP is identical to Nucleotide, ATP has more P’s)

The main difference between a nucleotide and a RNA?
ATP has 3 phosphates
How do mitochondria generate energy for cells?
Cellular respiration (CR) - taking food molecules eaten and breaking it further down and putting it in ATP
what unit of measurement is often used to measure cell size
Micrometer
What is cytoplasma
all the cellular contents located between the plasma membrane and the nucleus
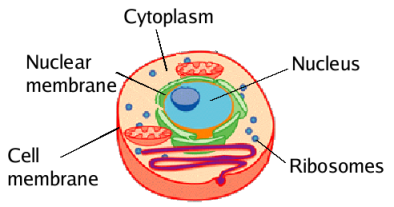
The fluid contained in the nucleus is called the
nucleoplasm
Another name for intracellular fluid is?
cystol/cystolplasmic matrix ( which is the fluid within the cell)
What is part of the cytoplasm
Cystol, organelles, Inclusions
Peroxisomes are membrane-bound organelles?
True, their enclosed by a single lipid bilayer membrane
What is responsible for forming the outer, limiting barrier of a cell
plasma membrane