2.2 Antibody structure
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
another name for an abbrev for antibody
Ab = Immunoglobulin (Ig)
it is soluble
describe components of an antibody
2 heavy chains (in the middle, attached by disulfide bonds at bottom; identical)
2 light chains (attached to heavy by disulfide bonds; identical)
antigen binding pocket (each duo forms one)
constant region (same for every antibody)
variable regions (heavy and light chains; differ btwn ab)
hinge
Fc (can be swapped to change effector functions; the 5 isotypes/classes)
papain significance
taught about ab structure what is structurally similar and different between different antibodies
cleaves at certain aa recognition points at hinge junction
Fab: fragment antigen-binding, a heavy and light duo that contains one antigen-binding site; differs btwn Abs, above the hinge joint
what determines Ab isotype/class?
constant region of heavy chain
how many subclasses does IgG have?
4
how many subclasses does IgA have?
2
how many subclasses do IgM, IgD, and IgE have?
1
how many different heavy chain isotypes are there?
9 total; 4 of IgG + 2 of IgA + 1 IgM +1 IgD +1 IgE = 9
how many isotypes does he light chain have?
lambda or kappa
which Ig classes can form polymeric Ig
pentameric IgM and dimeric IgA
what chain do polymeric Abs have bound to them
J-chain
T or F: IgM producing plasma cells always make pentameric IgM
T (10 antigen binding sites 2/Fab)
T or F: IgA producing plasma cells always make dimeric IgA
F; can make monomeric too
where do you find dimeric IgA?
secretion; mother’s milk, saliva, mucosal site
What is the only antibody that can be transferred through placenta?
IgG
what is the half-life of IgG?
about 4 weeks, need vax in this early period to continue protection
in third trimester mother’s get Tdap vax to pass to baby
describe composition of B cell receptors:
on each B cell there are antigen-specific receptors consisting of a monomeric Ig molecule (2 H and 2 L chains) and an additional heterodimer of Ig⍺ and Igβ
Ig⍺ and Igβ function to deliver signals to the cell
what classes of BCRs do naive B cells express?
IgM and IgD
what classes of BCRs do memory B cells express?
IgG or IgA or IgE
what is the first antibody to appear in a primary response to antigen?
IgM (then IgG and at higher quantity)
what response produces rapid and greatly increased IgG levels in blood?
memory response
which of these is involved in adherence?
A. pili
B. capsules
C. lectins
all of them!
how does the effector function of antibodies work?
by binding and disrupting pathogen function
enhancing immune response
the three ways antibodies can bind and disrupt pathogen function:
neutralization of virus/toxin
ex: SARS-CoV-2 its spike protein helps it enter the cell via ACE2 receptor of host cell
ab block SARS from binding to receptor
inhibition of bacterial adhesion
ex: ab bind to adhesins (of pili, etc.)
agglutination (clump antigen together)
ex: using IgM, cross-link diff entities of the same antigen, clumps are more readily removed by phagocytes
the four ways antibodies can enhance immune response:
opsonization via IgG and Fc𝛾R (recognize IgG only-gamma)
bacteria bind to variable/antigen binding region of an antibody. an immune cell with a specific Fc receptor will bind the Fc region H-chain of the antibody and pull in pathogen in to be phagocytosed
ADCC (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity)
Fc receptors of NK cells recognize and bind antibody with attached pathogen. cell dies by apoptosis
ADCP (antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis)
macrophages and neutrophils express FcgR. Abs bind antigens on virus-infected or tumor cells (not the actual pathogen but an infected cell) leading to phagocytosis
Mast cell activation via IgE cross-linking FceR (parasites, allergies)
FceR of mast cell binds IgE Ab and multi cross-link causes mast cell to release granule contents (histamine)
inflam response resulting from mast cell degranulation functions in immunity to worms
what is opsonization?
pathogens or damaged cells are coated with molecules (opsonins) to enhance their recognition and ingestion by immune cells (e.g., macrophages and neutrophils) targeted for destruction
Opsonins bind to the pathogen or target surface.
Phagocytes recognize opsonins via specific receptors (e.g., Fc receptors, complement receptors).
The target is engulfed and destroyed by the immune cell
what are the types of opsonins?
Antibodies (e.g., IgG)
Complement proteins (e.g., C3b)
C-reactive protein (CRP)
how does localization of IgE differ from IgG?
IgE under skin bc you encounter parasitic infection and allergies
IgG in circulation just like bacteria and viruses
where is monomeric IgA found in body?
Mucosal surfaces, secretions, blood
Mucosal immunity
where is IgG found in the body?
Blood, extracellular fluid, placenta
Systemic immunity, opsonization, neutralization, memory
where is IgM found in the body?
Blood, lymphatic fluid
Primary response, complement activation
where is dimeric IgA found in the body?
Secretion: mother to baby breast milk
Mucosal immunity
where is IgE found in the body?
Skin, tissues (mast cells, basophils), blood
Allergy, parasite defense
where is IgD found in the body?
Surface of immature B cells: Functions as a receptor for antigen recognition.
Bloodstream: Found in trace amounts in serum.
Function: Involved in the activation of B cells and their transition to antibody-secreting plasma cells.
best Ab for Ag specific receptor (BCR)?
all isotypes
best Ab for neutralization:
IgG and IgA
best Ab for agglutination:
IgM
best Ab for FcR-dependent effector functions:
IgG for opsonization, ADCC, and ADCP
IgE for mast cell activation
(all enhance immune responses)
what are the four FcR dependent Ab functions?
opsonization
ADCC
ADCP
cell mast cell activation
best Ab for complement activation:
IgM and IgG
what is the prominent g in secretions?
Secretory IgA (SIgA)
in saliva, milk, mucosal sited and protects by neutralization (prevents them from entering host cell) and inhibition of bacterial adherence (pili, etc.)
where does the secretory component (SC) come from?
all dimeric IgA form through J chain and has a SC
comes from the polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR) on epithelial cells. It is cleaved from the pIgR after transporting IgA (and sometimes IgM) across the epithelial layer into secretions like saliva, tears, and mucus
how does IgA cross the epithelium?
transcytosis
Ab attaches to polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR) on epithelial cells
Ab enters epithelial cell through endocytosis and can go to lumen (other side of epithelium). majority of SC left on IgA (sign that this IgA was secreted across layer)
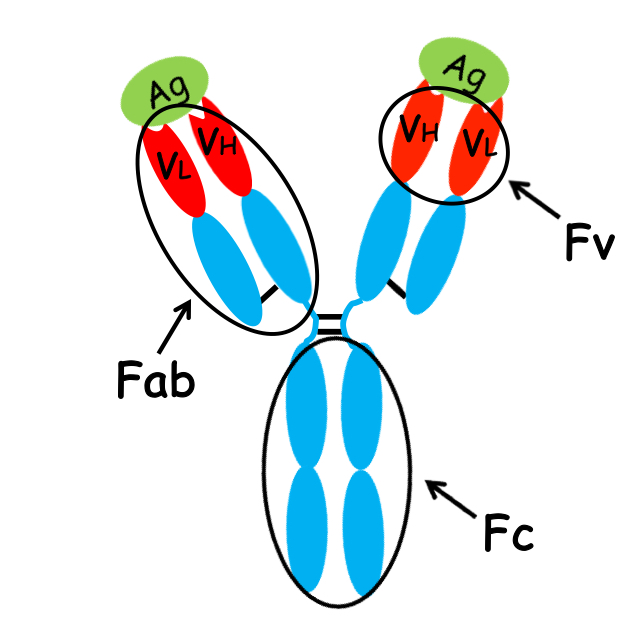
what do the red, blue, and green regions signify?
red: variable region
blue: constant region
green: antigen binding to antigen binding pocket
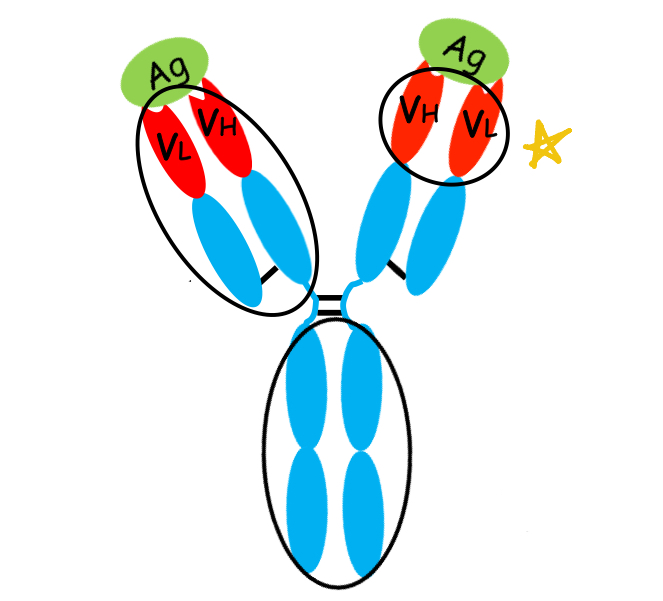
what is this region of the antibody?
Fv region: determines the antibody's specificity and binding affinity to its target antigen
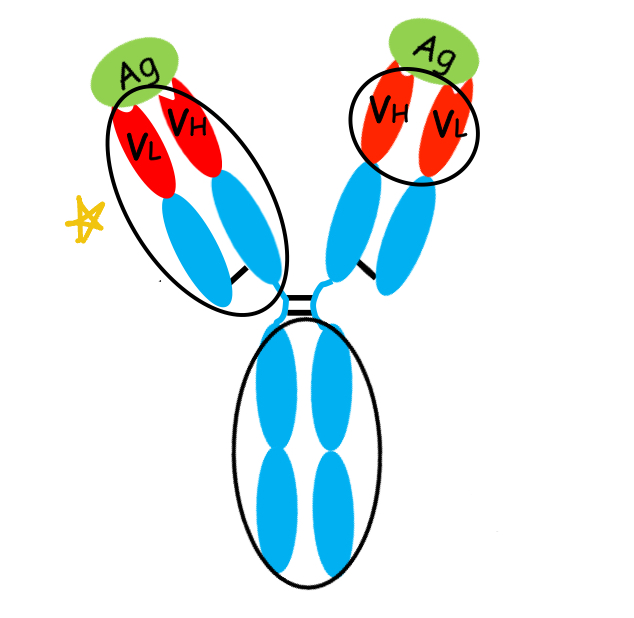
what is this region of the antibody?
Fab region: region of an antibody is the part responsible for binding to antigens. Each antibody has two Fab regions, one on each arm of the "Y" structure
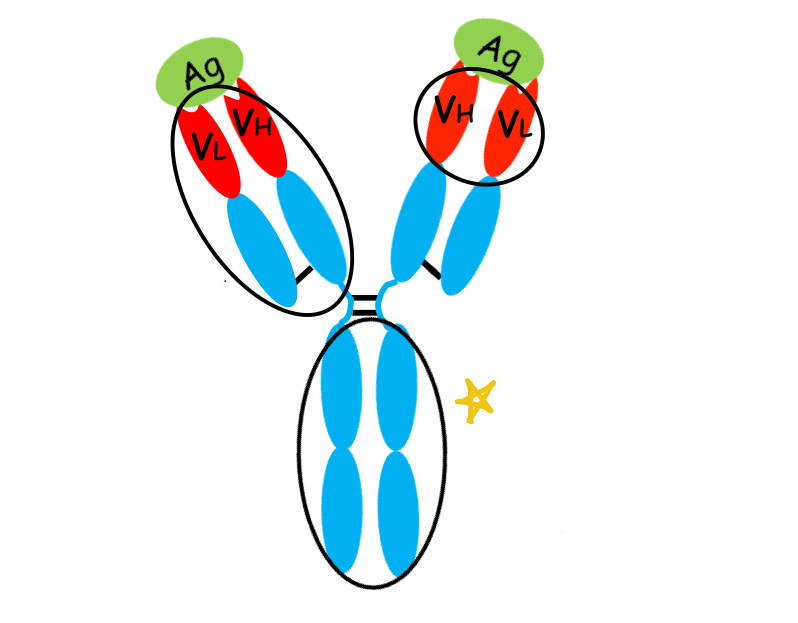
what is this region of the antibody?
Fc region: constant part of the antibody that doesn't bind to the antigen but is important for other functions, including interactions with immune cells and complement proteins., specific to isotype
which effector function is most likely to take place in saliva?
IgA so neutralization
if a bacterium is bound by IgM which effector functions can take place?
agglutination mainly and neutralization to an extent