(1) Trachea
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Trachea
The windpipe; a passage through which air moves in the respiratory system.
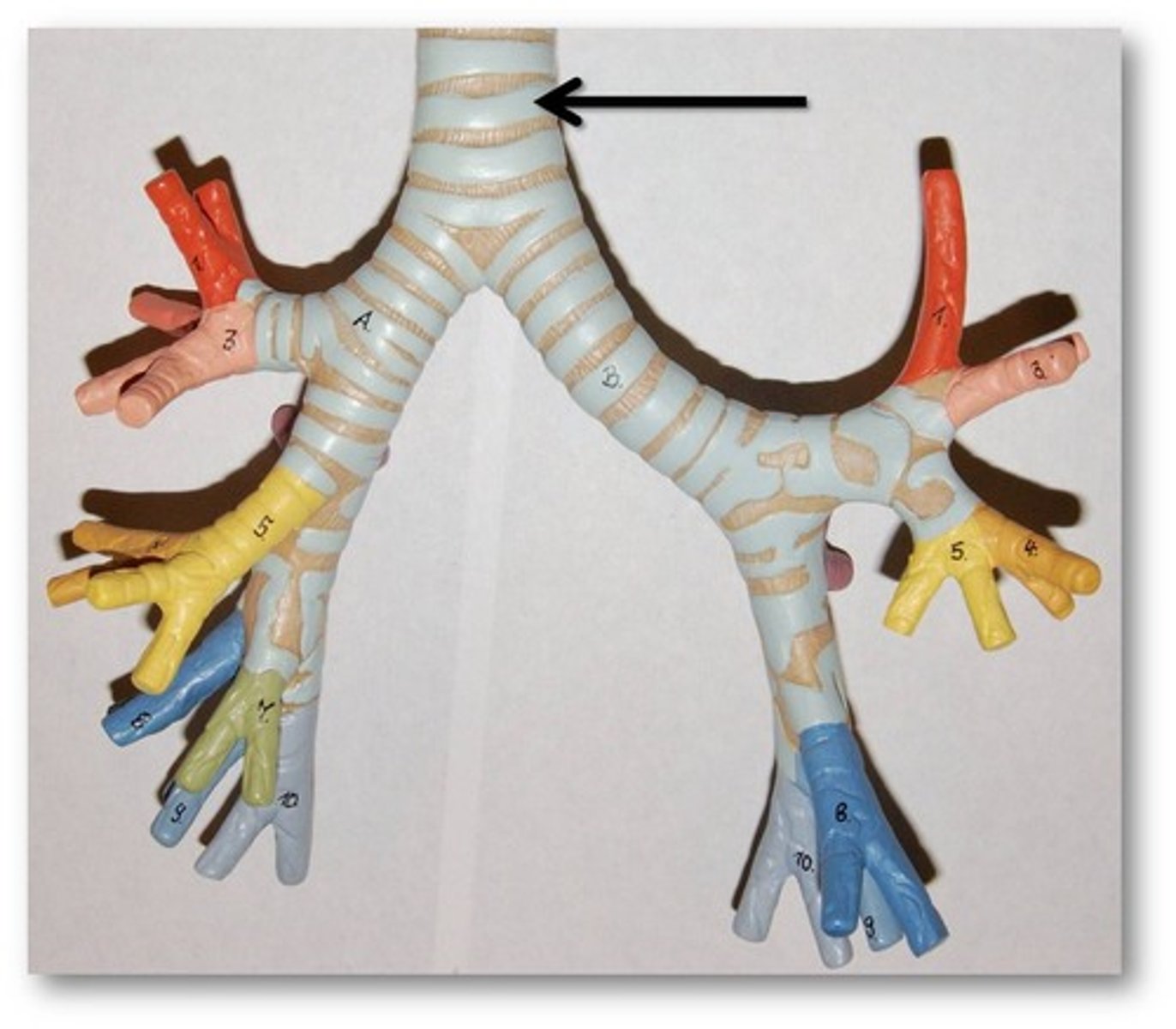
Features of Trachea
- C shaped rings of cartilage
- Elastic Fibres
- Smooth Muscle
- Ciliated epithelium
C-shaped rings of cartilage in Trachea
- Provides strength and support for the trachea and bronchi, keeping them open
- Prevents collapse during inhalation. As the chest volume increases, there will be a lower pressure in the trachea
- The rings are c-shaped so that food can move easily down the oesophagus behind the trachea
Elastic Fibres in Trachea
Elastic fibres recoil to their original shape, expel air, and prevent the lungs from bursting.
Smooth Muscle in Trachea
Contracts and relaxes airways
Goblet cells & ciliated epithelium in Trachea
- Goblet cells secrete mucus which traps dust/bacteria that enters the lungs
- The cilia then waft the mucus to the top of the trachea / back of the mouth, where it is swallowed or coughed up