Human Osteology - Trail #1
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bone structure and vocab
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
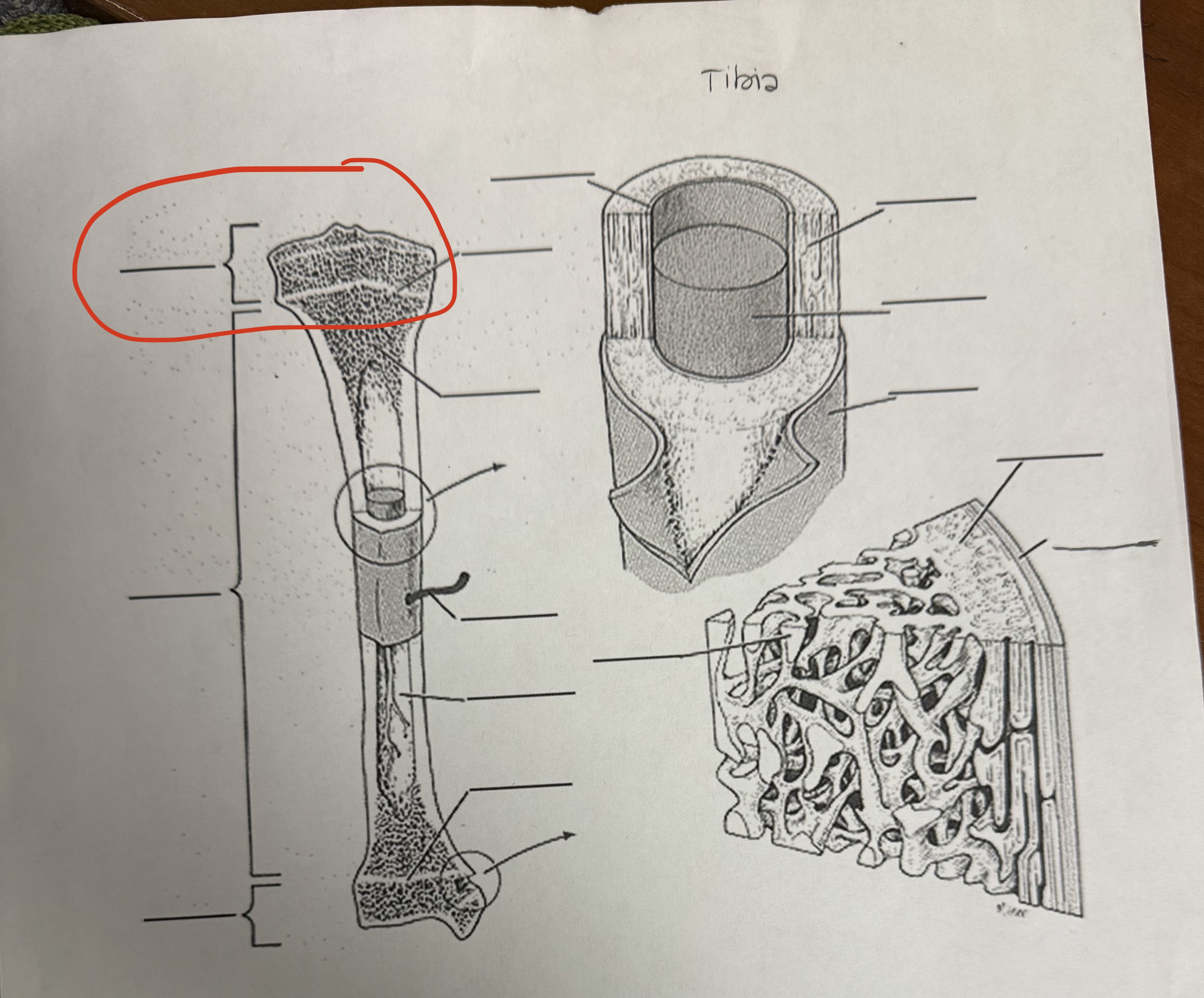
Proximal Epiphysis
The end part of a long bone that is closest to the body’s center.
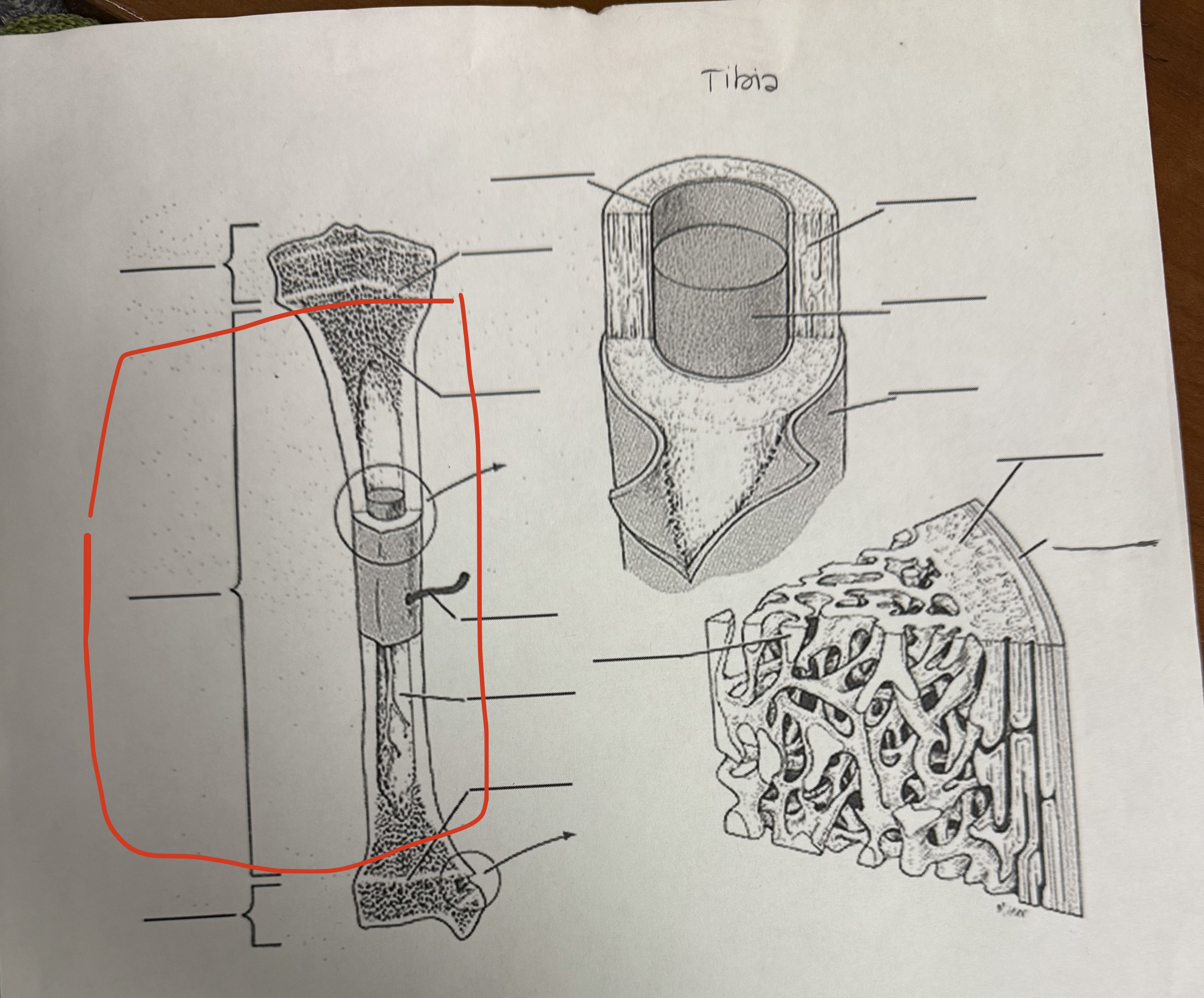
Diaphysis
The shaft or central part of a long bone
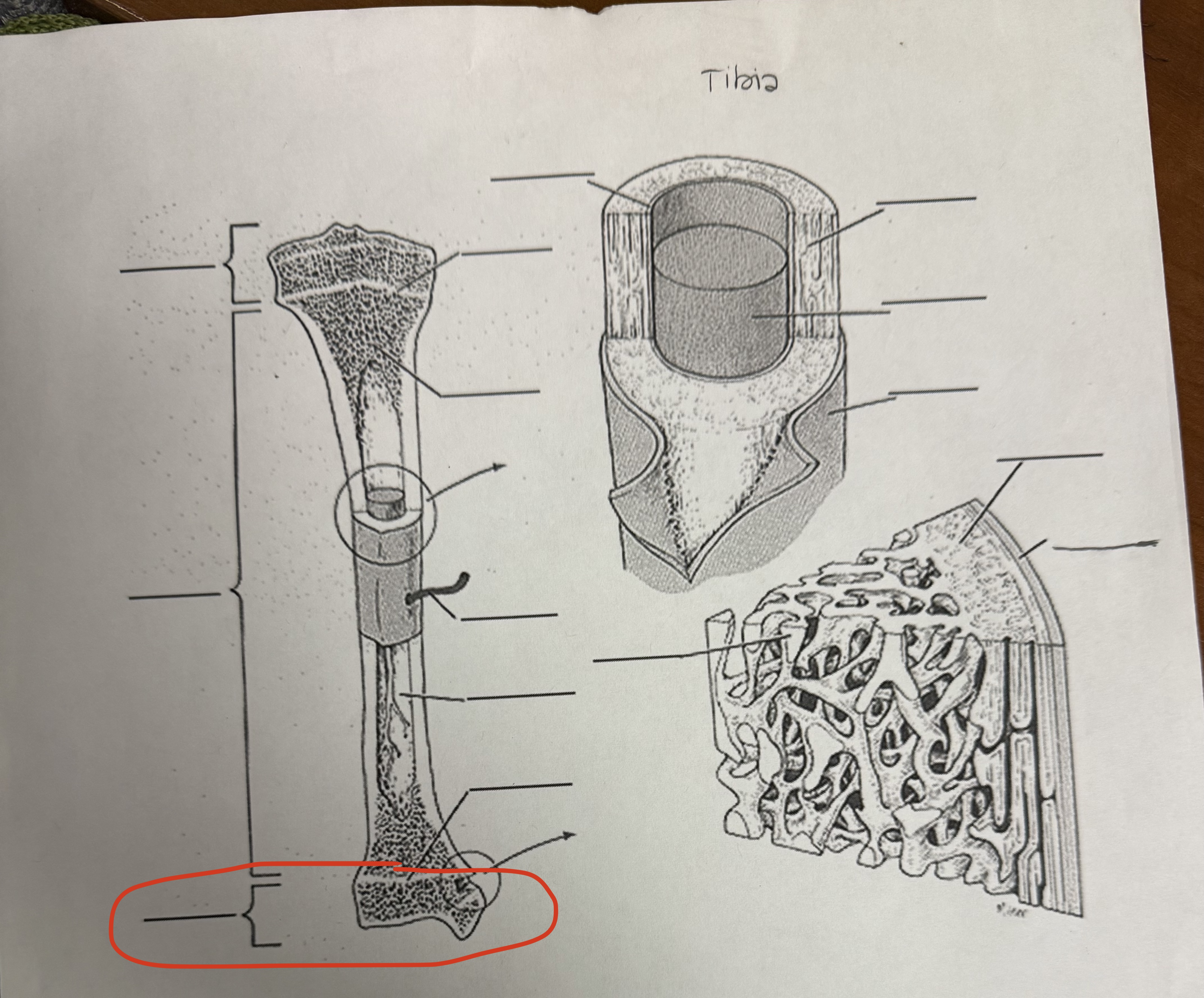
Distal Epiphysis
The end part of a long bone farthest away from the body’s center
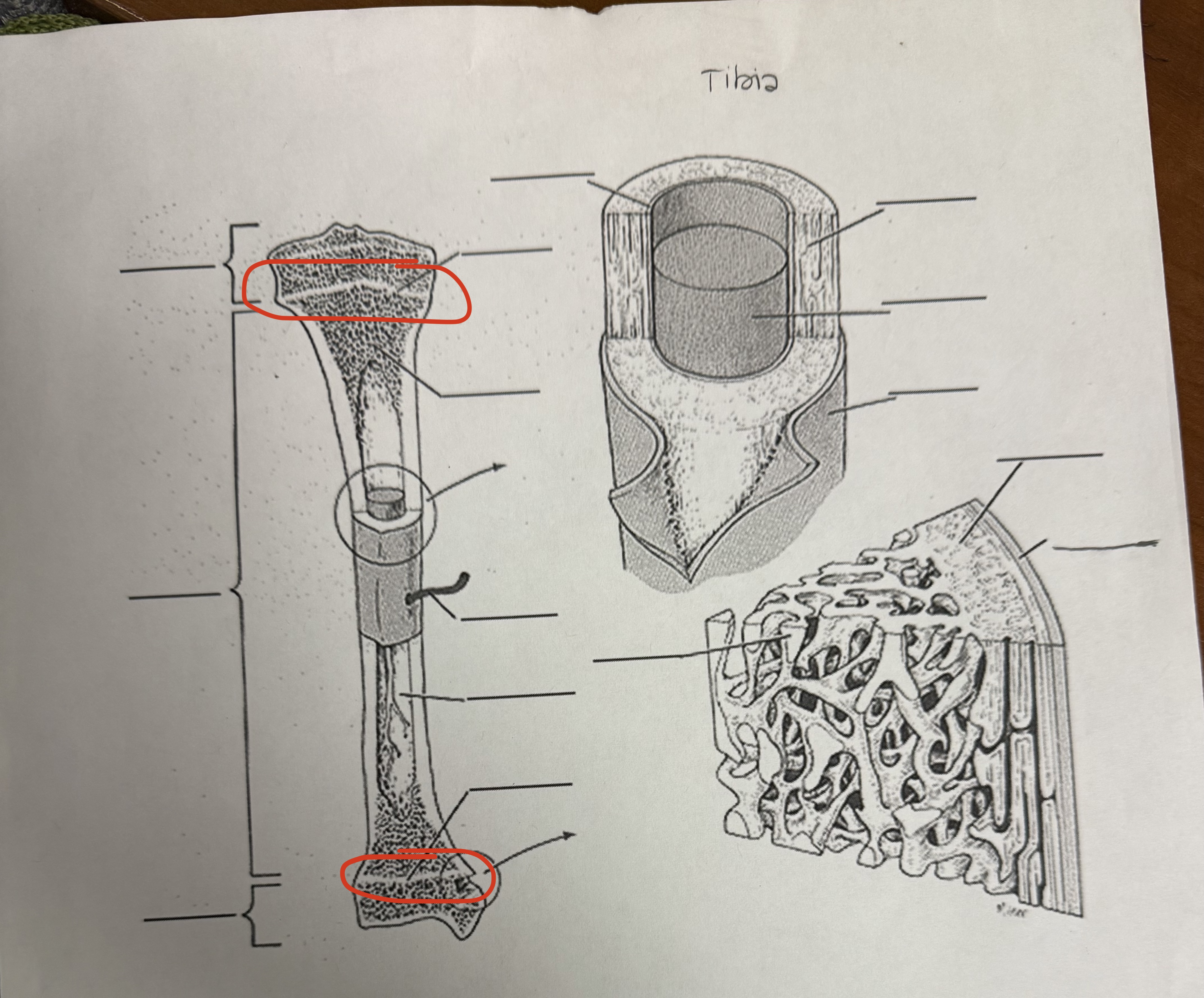
Epiphyseal Line
Thin, bony structure that marks the boundary between epiphysis and diaphysis
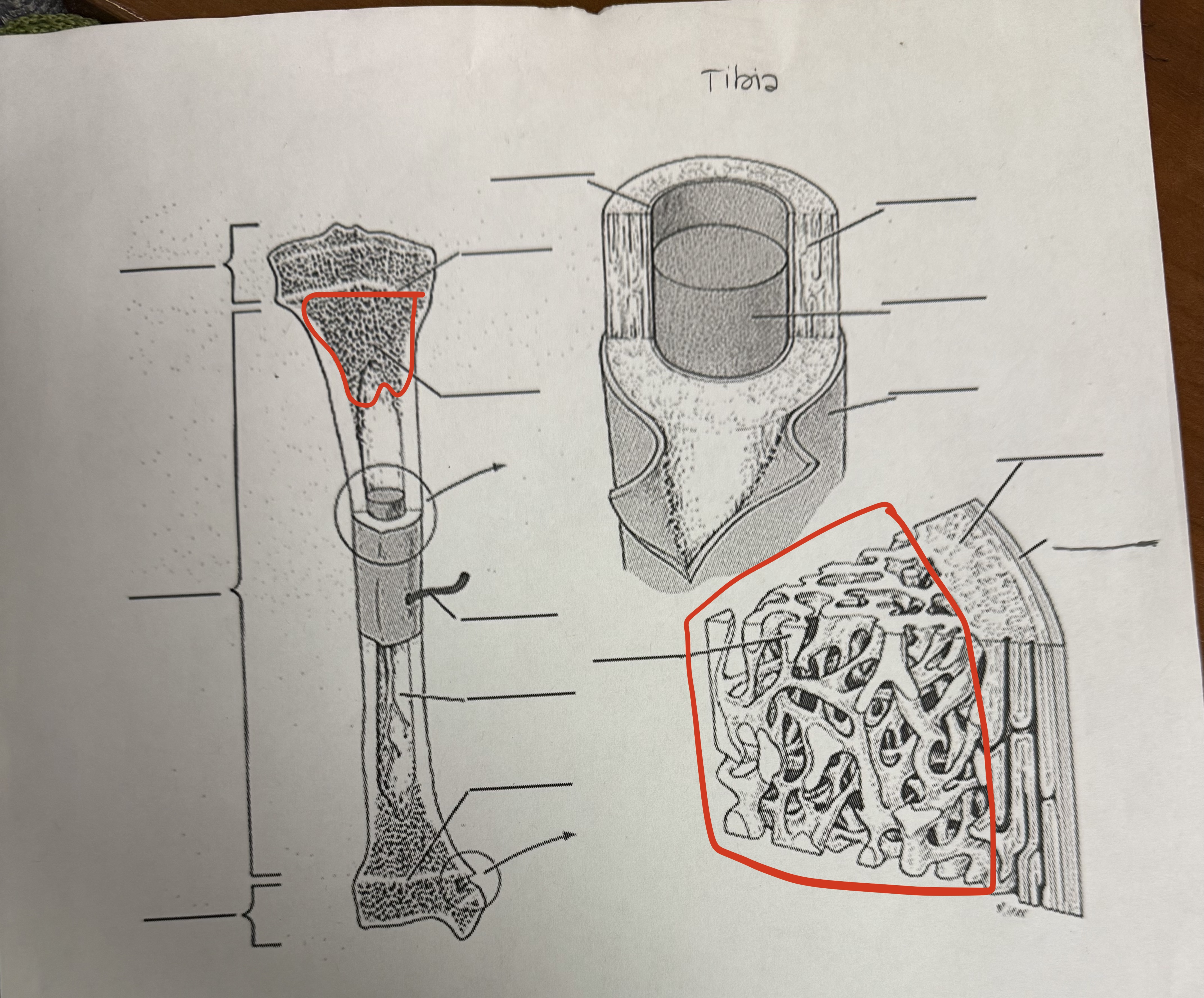
Spongy Bone
Type of bone tissue, mesh-like network of trabeculae, helps to make bones lighter
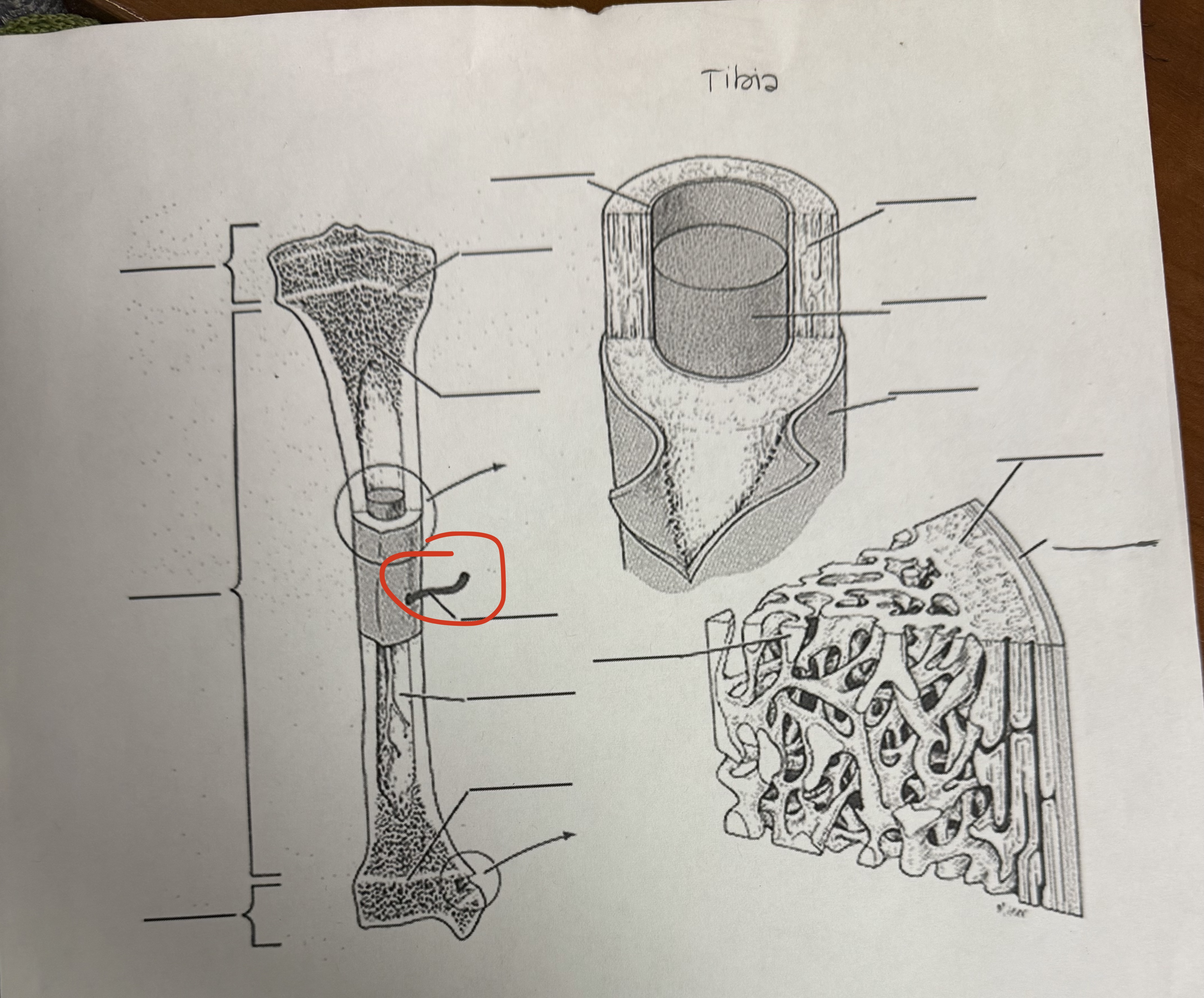
Nutrient Artery
Hole in the bone, brings red blood cells in and out of bones (also called foramen)
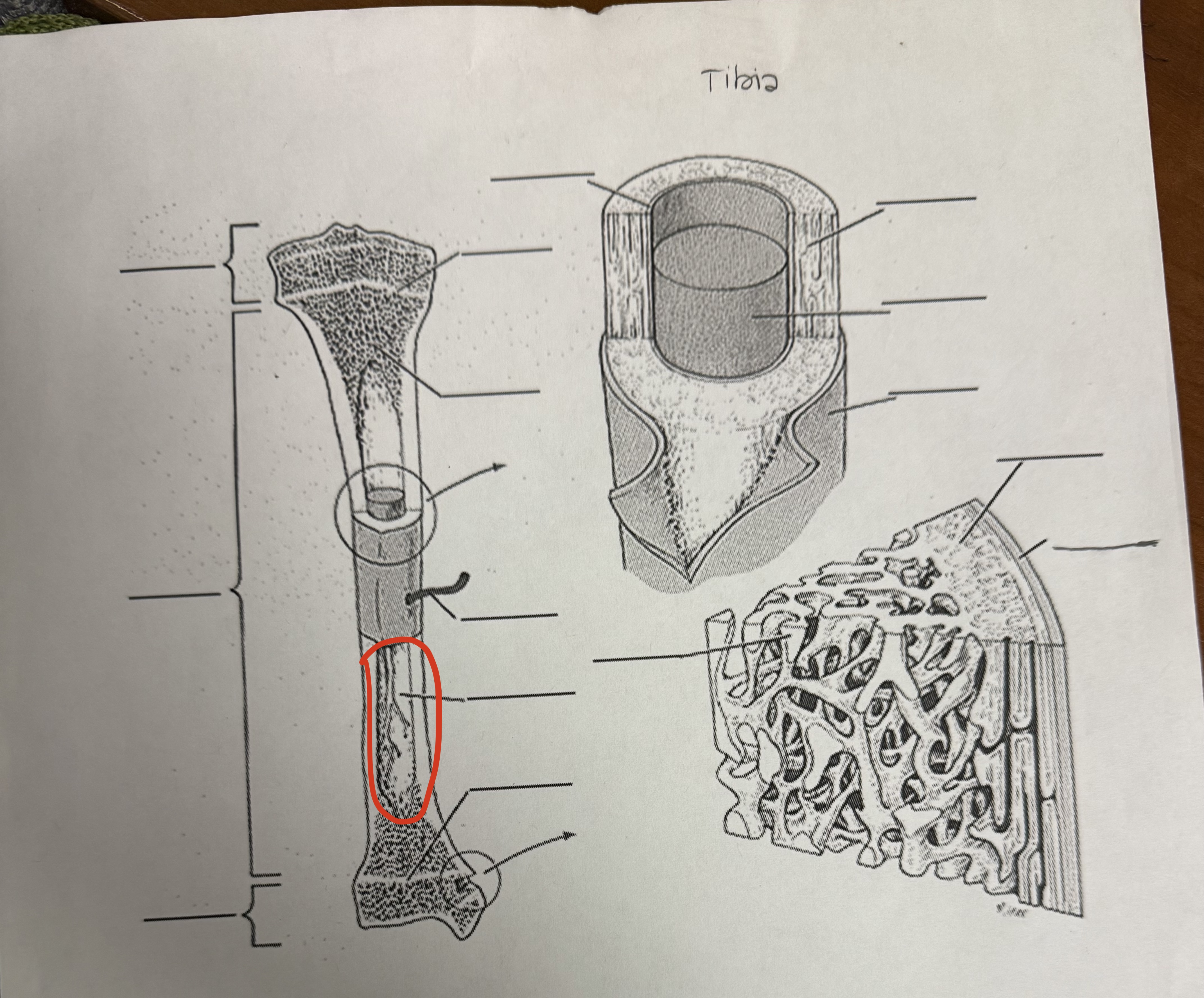
Medullary Cavity
Hollow central space in shaft of long bone, Rigid tube with a hollow chamber, stores bone marrow, lined with endosteum
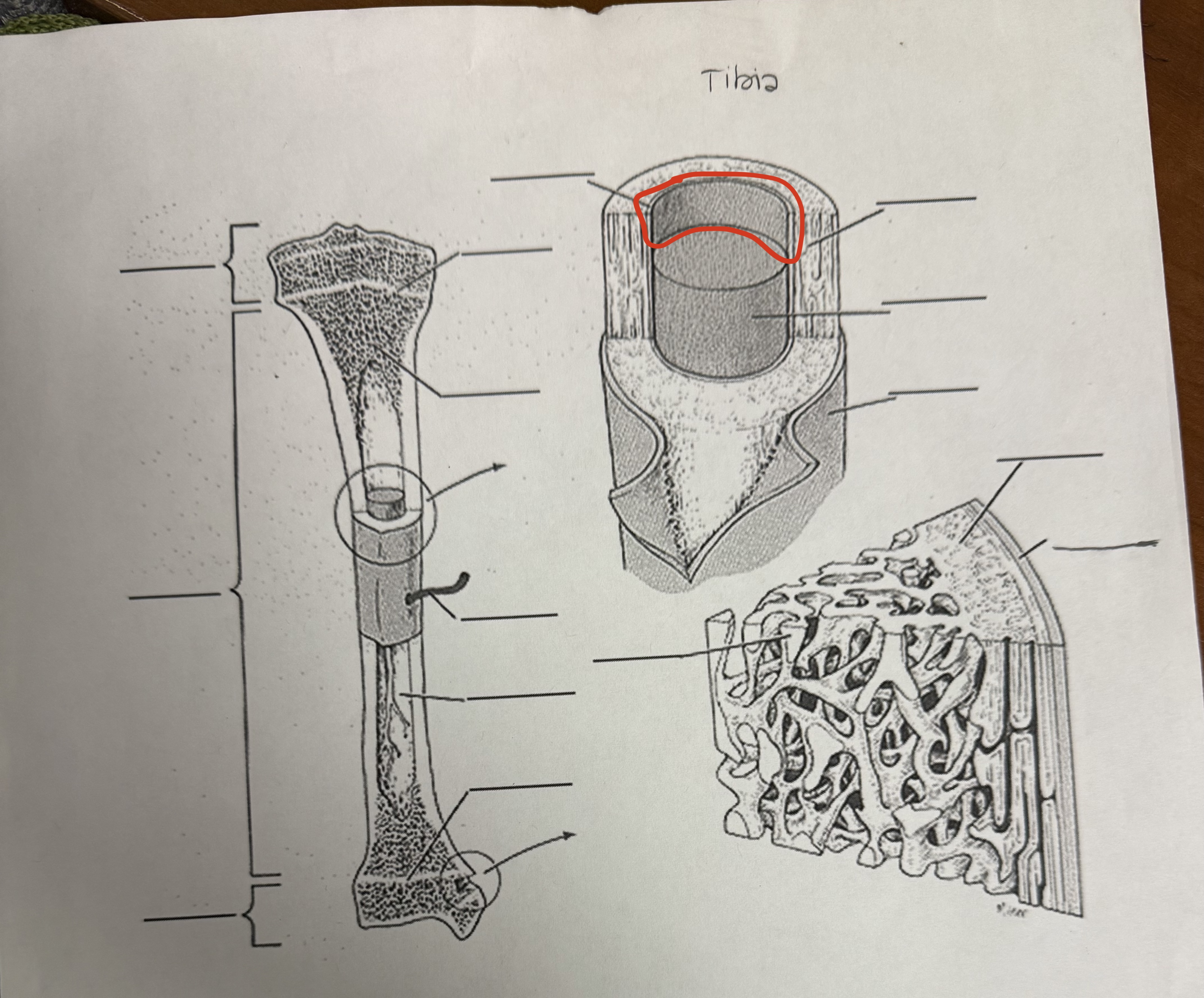
Endosteum
Delicate membrane lining internal surfaces of bones (medullary cavity)
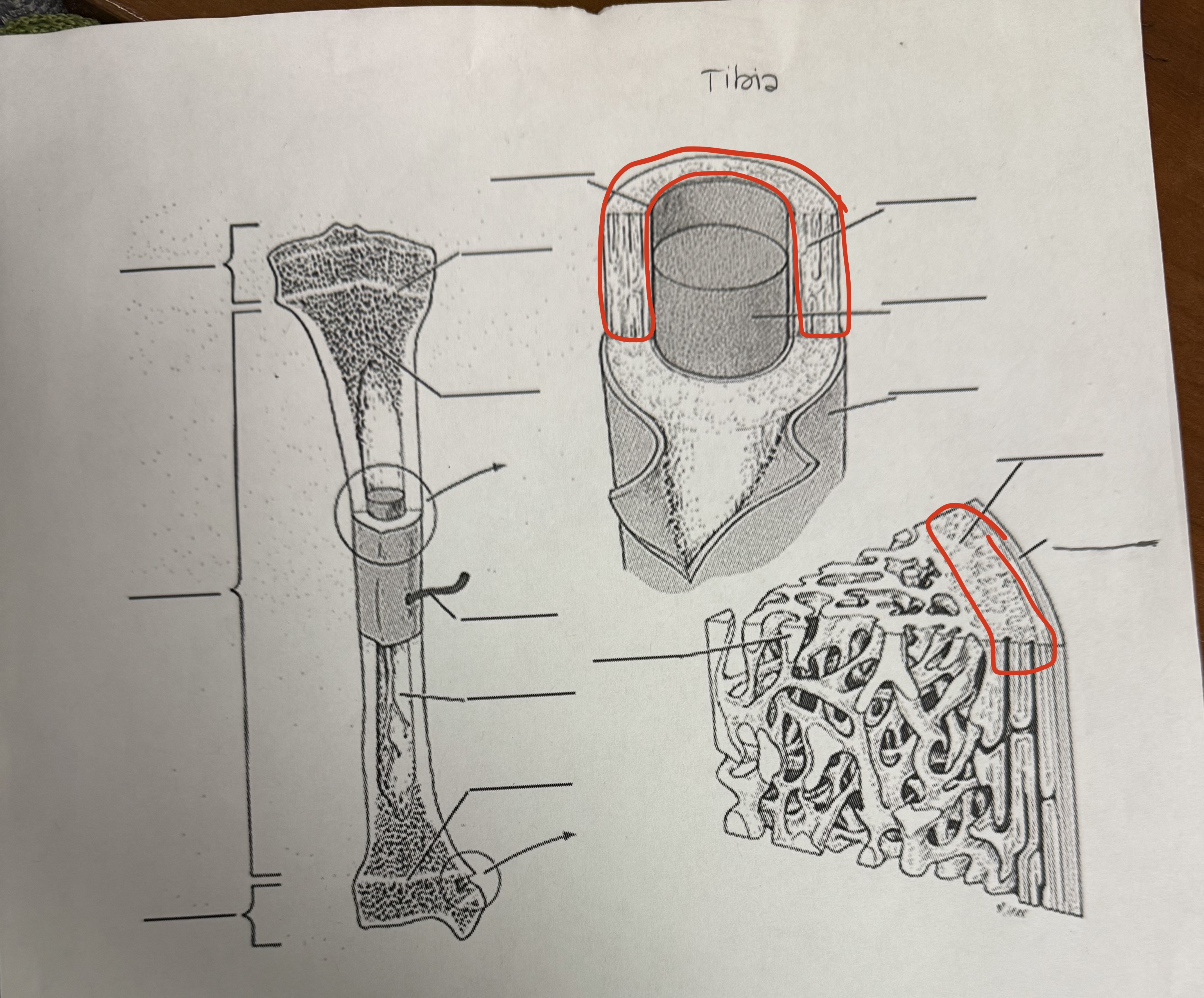
Compact Bone (Cortical Bone)
Wall of Diaphysis, solid, strong, adds weight, mostly on outside of bone
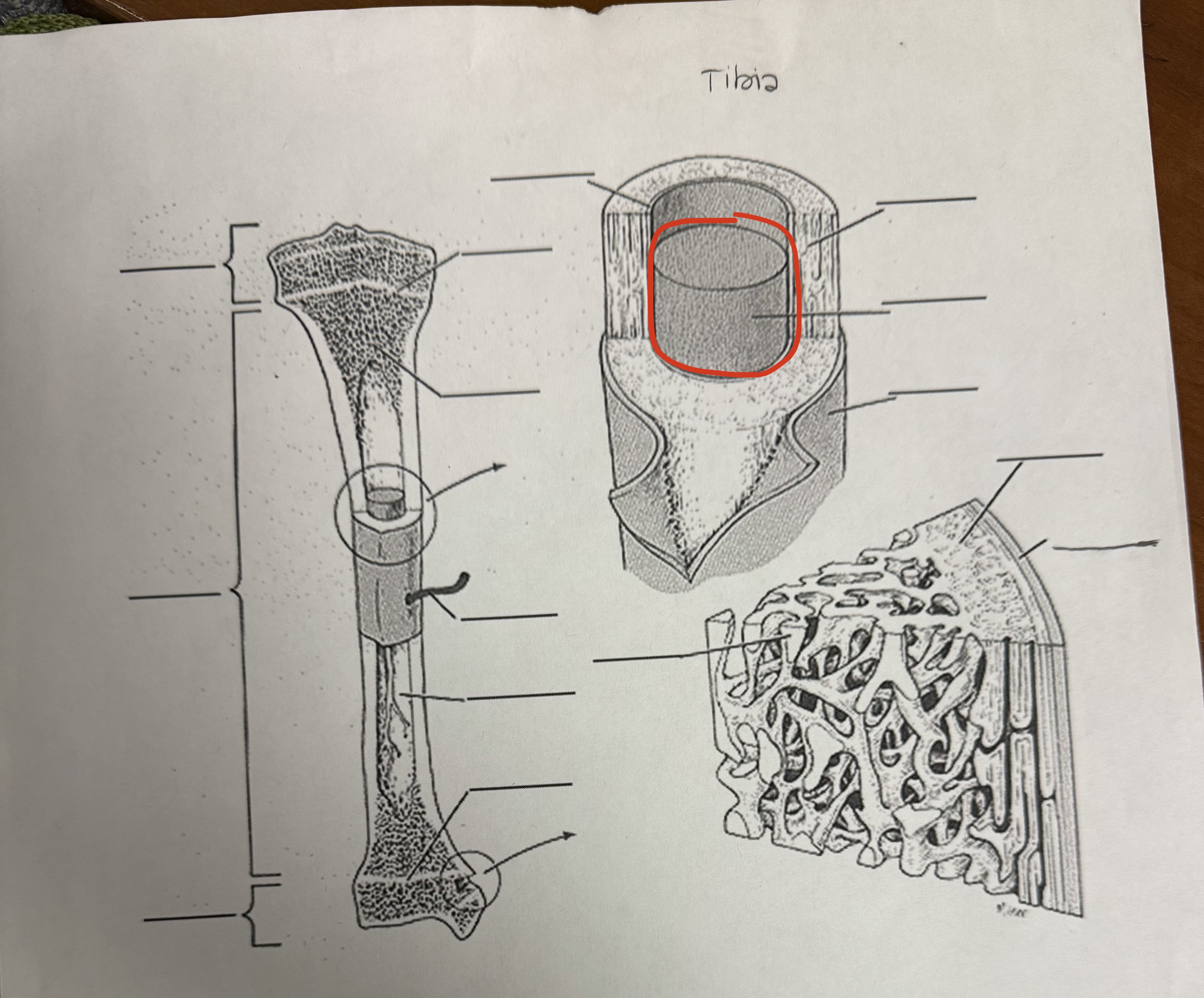
Yellow Marrow
Replaces red as person ages; fat storage tissue; inactive in blood cell production
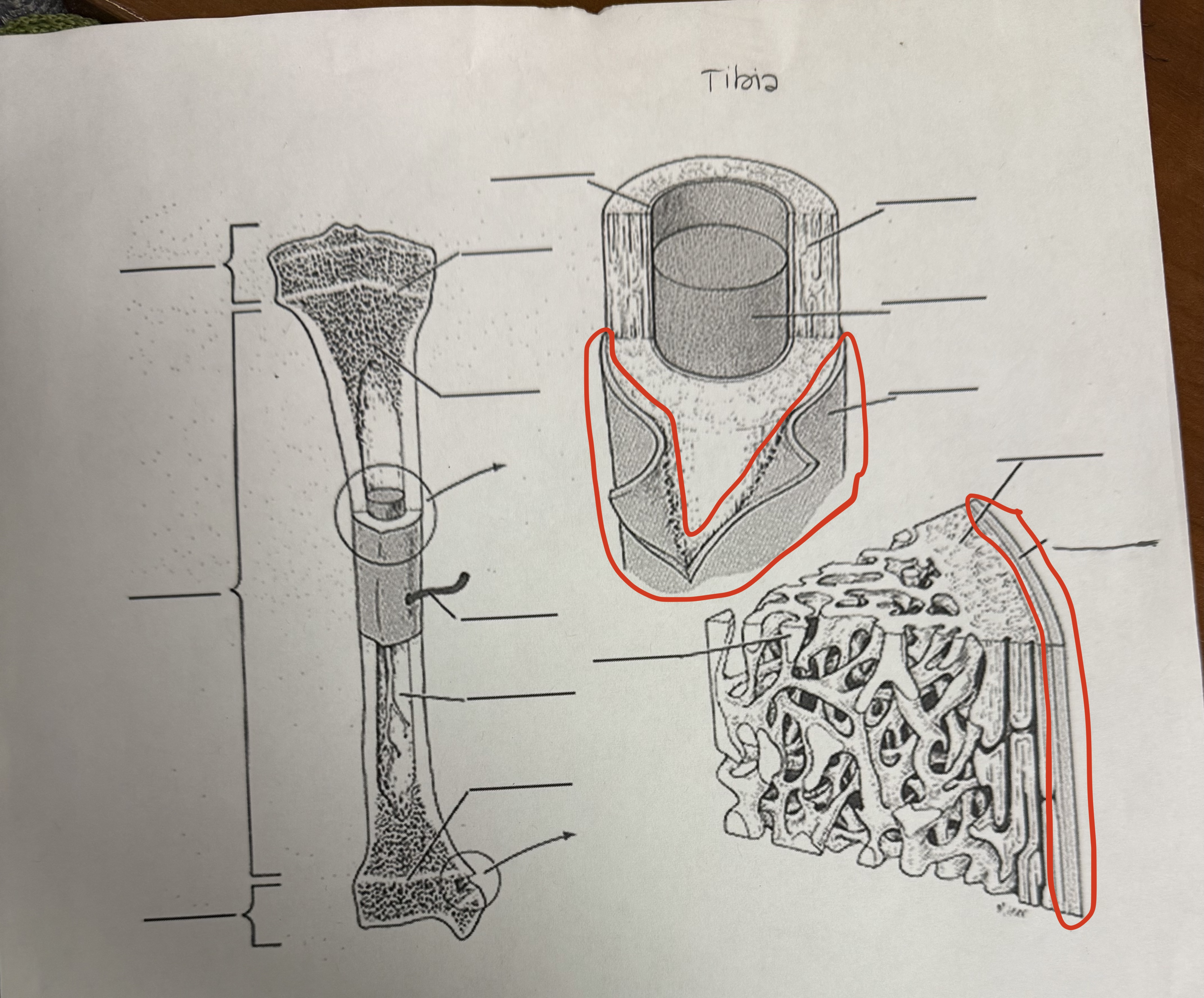
Periosteum
What bones are covered in (it is alive!), protects, aids in repair, 1st line of defense
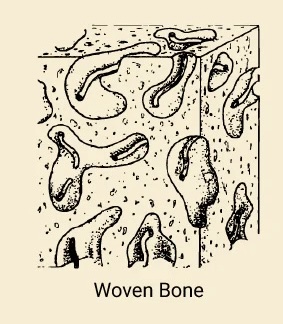
Woven Bone
Immature, mechanically weak bone tissue found during fetal development, fracture repair, and in some bone diseases and tumors
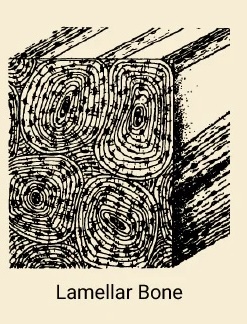
Lamellar Bone
Mature, most abundant type of bone in the adult human skeleton, layered + parallel collagen fibers, provides strength/stiffness
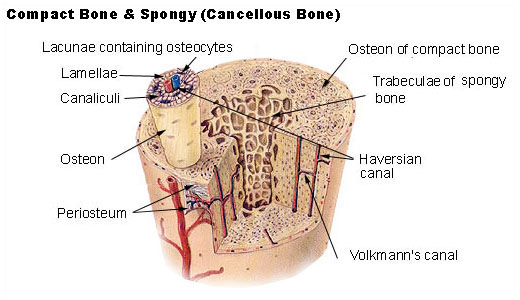
Haversian Canal (Secondary Osteons)
Freely anatomizing canals in compact bone, contain blood + lymph vessels, nerves, + marrow
Collagen
Fibrous structural protein constituting ~90% of bone’s organic content
Fossa
A shallow depression or hollow
Ectocranial
Relating to the exterior or outer surface of the skull
Endocranial
The inner surface of the skull, or the cranial cavity