Paul Virology
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Define Influenza A (Avian Influenza Virus) in terms of
1. Host
2. Reservoir
1. Wild Waterbirds
2. Wild Waterbirds, Domestic Poultry

Describe the Clinical Signs of Influenza A in terms of Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza
Usually Asymptomatic
- Coughing/sneezing,
- Decreased egg production
- Resp. tract lesions
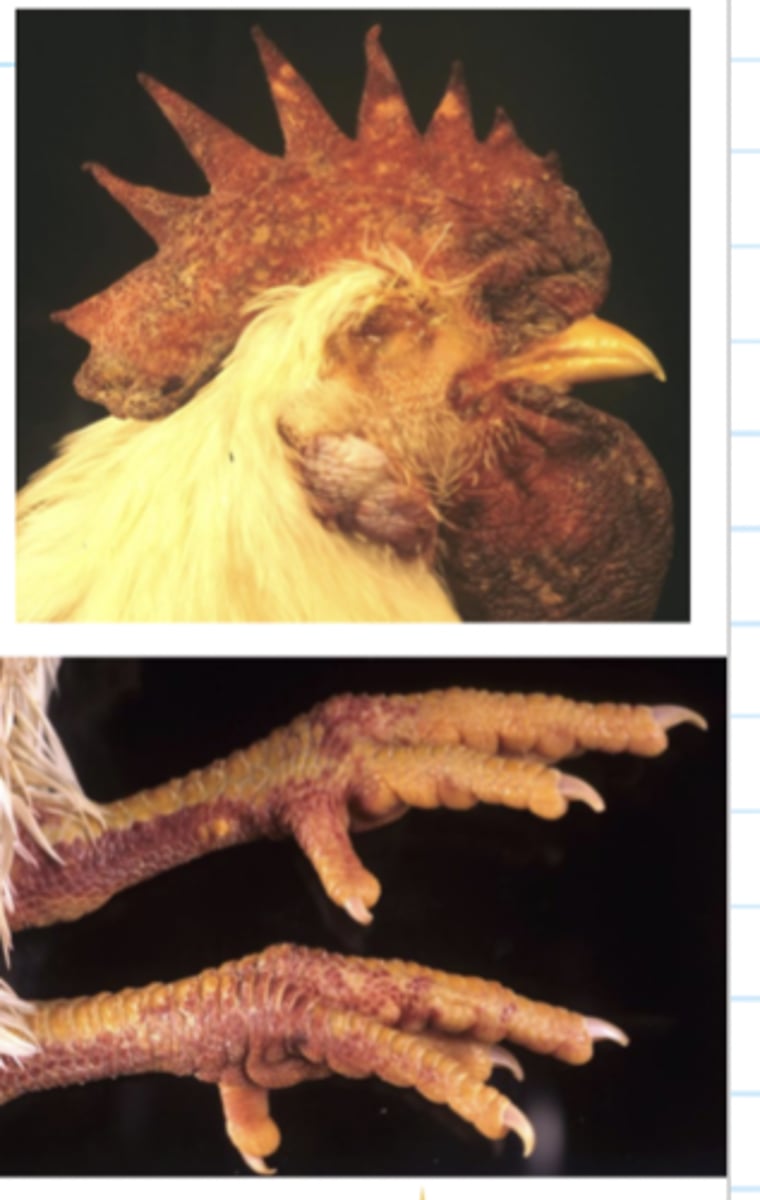
Describe the Clinical Signs of Influenza A in terms of High Pathogenic avian Influenza
Severe Systemic Disease
- High Mortality
- Cyanosis/ oedemaof head, comb, wattle
- Oedema/Red Feet
- Blood tinged oral/nasal discharge

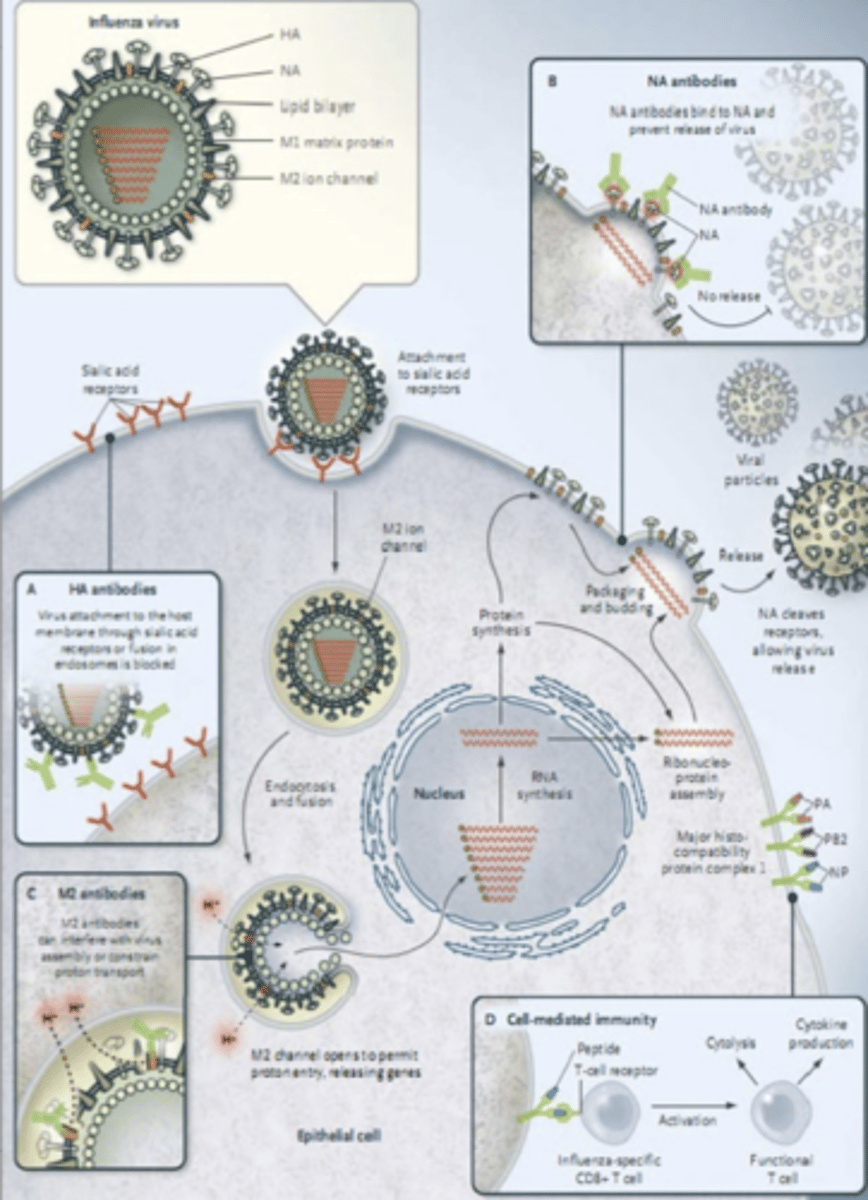
Describe the Replication of Influenza A (Avian Influenza Virus)
1. Enters Host
2. Haemogglutinin attaches to sialic acid receptors on cell (Usually GIT)
3. Enters cell
4. RNA synthesis in nucleus, protein synthesis in cytoplasm
5. Virus Frees itself
Define the Following forms of Influenza A (Avian Influenza) Evolution:
1. Reassortment (Antigenic Shift)
2. Mutation (Antigenic Drift)
1. 2 viruses infect the same host, genetic material mixes during replication
2. Virus accumulates mutations for more efficient spread/infection
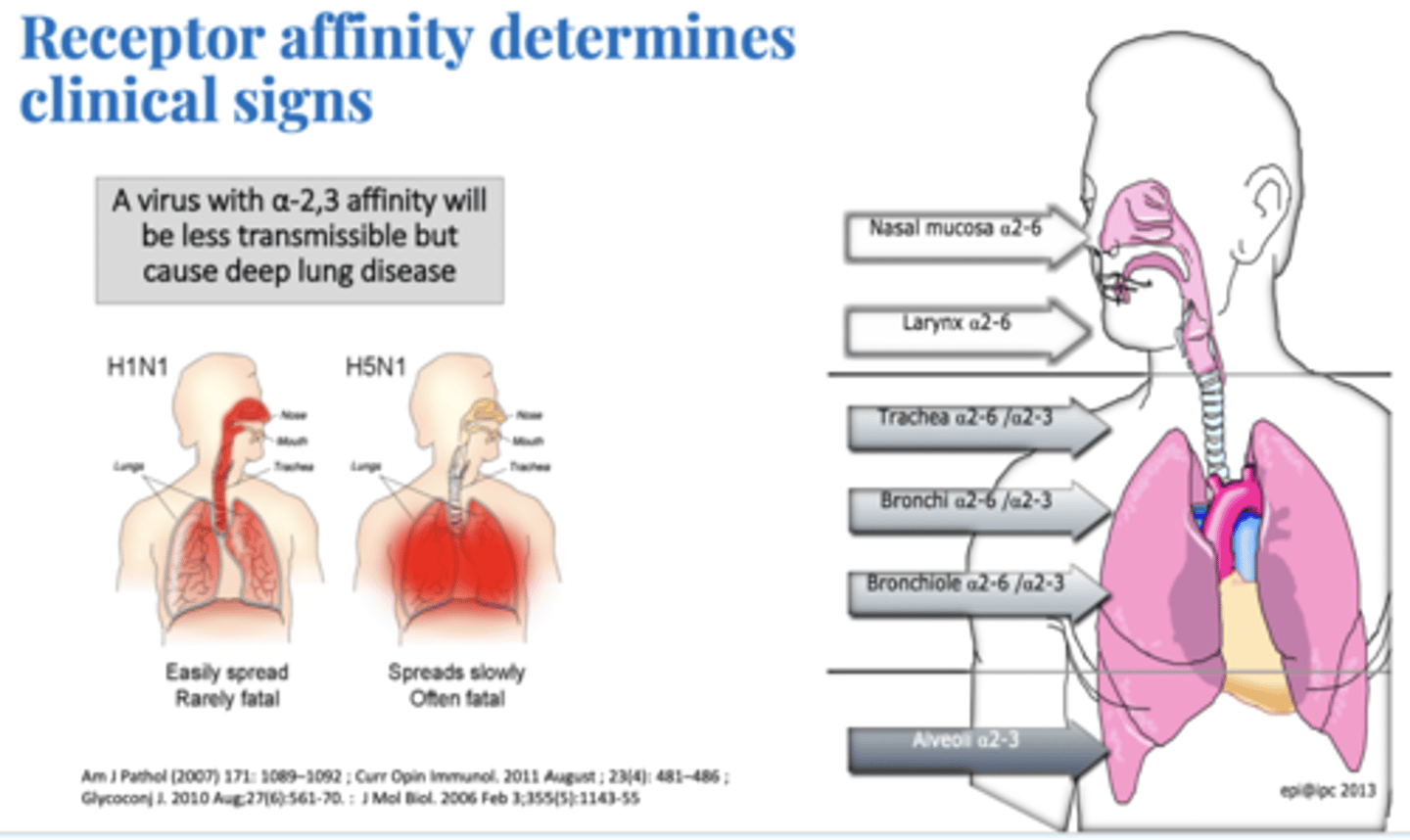
Discuss the Importance of Hemagglutinin and Receptors in terms of the Clinical Signs of Influenza A
Avian Influenza Binds to a2-3 sialic receptors causing severe pulmonary disease. LEss Transmissable but more severe
Describe the Control/Vaccination Strategies for Avian Influenza (Influenza A)
Culling, Depopulation
Vaccine:
- Costly
- Birds still spread Virus
Define Swine Influenza in terms of
1. Characterised by
Large number of pigs infected but low death rates

What are the Clinical Signs of Swine Influenza
- Going off Feed
- High Fever
- Discharge from eyes/nose
- Sneezing
- Cough
- Inactivity
Explain why pigs are seen as Mixing Vessels
Pigs Can be infected with both avian and mammalian viruses (have both receptors for viruses – a2,3 and a2,6 in trachea)
Avian Virus Replicates in pigs and gives rise to strains that recognise human receptors
Define Equine Influenza in terms of:
1. Horses Most Susceptible
2. Contageous?
1. Horses 1-5 Years Old
2. Very Contageous
What are the Clinical Signs of Equine Influenza
Rarely fatal
- Sudden Fever
- Deep, Dry, Hacking Cough
- Thick and Smelly Nasal Discharge
Describe Canine Influenza in terms of:
1. Contageous?
2. What it causes
3. Mortality
1. Highly Contageous
2. Mild Resp. Infection
3. Low Mortality
Define Bovine parainfluenza virus 3 in terms of:
1. Associated Syndromes
2. What it causes
1. Bovine Resp. Disease complex, Shipping fever complex
2. mild-subclinical infections
Define Canine Parainfluenza Virus (Kennel Cough) in terms of:
1. What it is a part of
2. What it causes
1. Canine Respiratory Disease Complex
2. Upper Respiratory Disease
Define the Epidemiology of Canine Parainfluenza Virus in terms of:
1. Incubation
2. Where it is commonly seen
1. 5-9 Days
2. Kennels/Animal Shelters/daycares ect.
What are the Clinical Signs of Canine Parainfluenza Virus
1. Dry, Harsh, Hacking Cough
2. Fever
3. Nasal Discharge
4. Pharyngitis
5. Tonsilitis

Describe the methods of Treatment and Prevention of Canine Parainfluenza Virus in terms of:
1. Diagnosis
2. Vaccination
1. RT-PCR
2. Often in combination with other vaccines, don't prevent infection however reduce severity
Describe Manangle Virus in terms of:
1. Hosts
2. Reservoir
1. Pigs
2. Native Australian fruit bats (Flying Foxes)
Describe the Clinical Signs of Menangle
1. Reduced Farrowing Rate + Litter Size
2. Mummified/stillborn foetuses

Describe what Post Mortem Findings are found in cases of Menangle in terms of:
1. Births
2. Degenerations
1. Mummified, autolysed, stillborn, and normal Piglets
2. Degredation of CNS, Joints, Jaw
Define the Transmission of Menangle in terms of:
1. Bat → Pig
2. Pig → Pig
3. Human
1. Faecal-Oral
2. Faecal Oral
3. Close Contact with Pigs
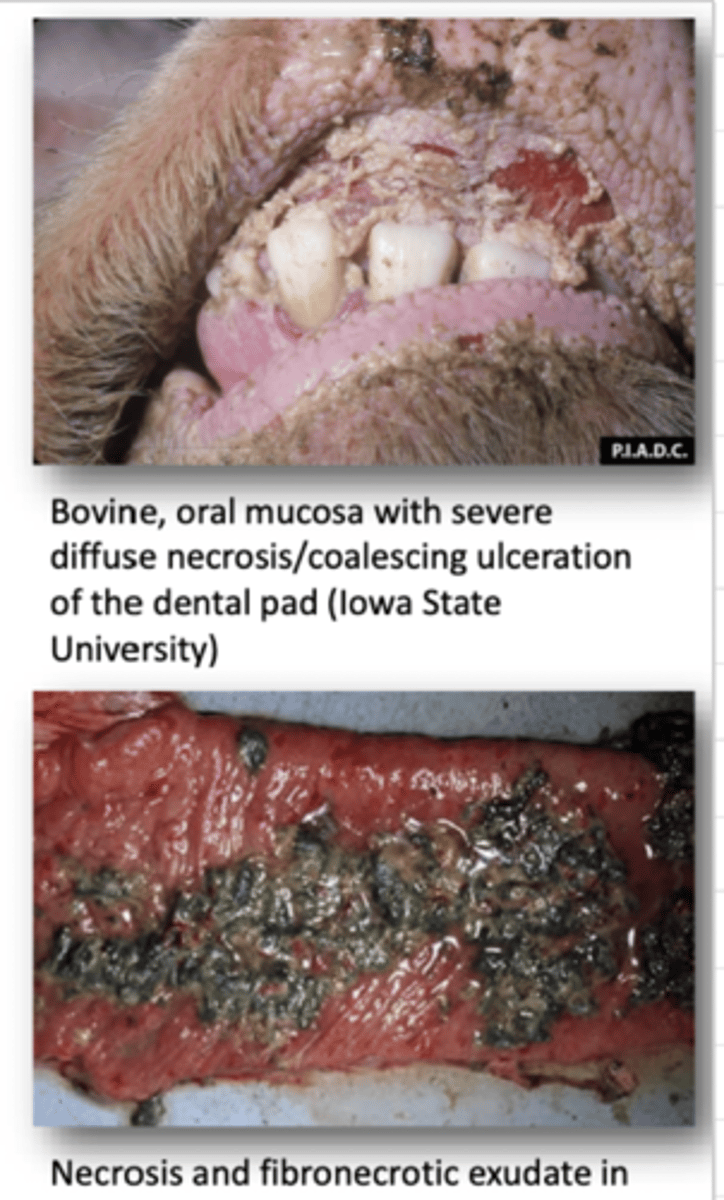
Define Rinderpest in terms of:
1. Hosts
2. Eradication
3. What it causes
4. What Virus is it Similar to
1. Cloven-Hooved Animals
2. Eradicated Worldwide
3. Fever, Oral Necrosis, High Mortlaity
4. Similar to Peste Des Petits Ruminant Virus
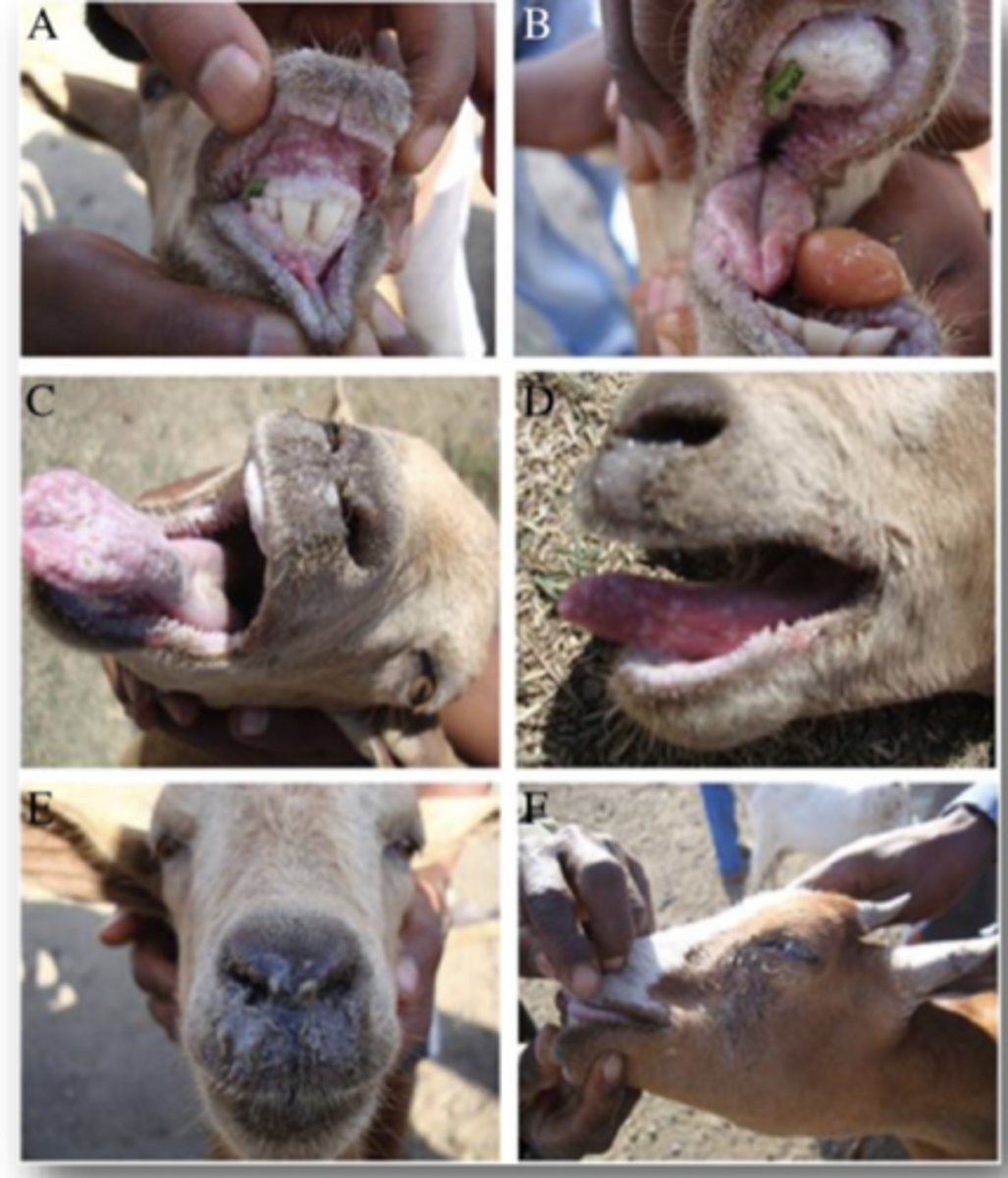
Define Peste Des Petits Ruminant Virus (PPRV) in terms of:
1. Hosts
2. What Virus is it similar to and why
3. Mortality in Naive Herds
1. Goats and Sheep
2. Similar to Rinderpest (antigenically similar, cross-protective antibodies,)
3. Up to 100%
Describe the Transmission of Peste Des Petits Ruminant Virus (PPRV)
Transmitted by close contact (Inhalation, ocular/nasal/urine/faeces secretion)
Describe the Clinical Signs of Peste Des Petits Ruminant Virus (PPRV)
Young animals most effected
- High Fever
- lack of apetite
- Depression
- Nasal/Occular Discharge
- Oral LEsions
- Diarrhoea
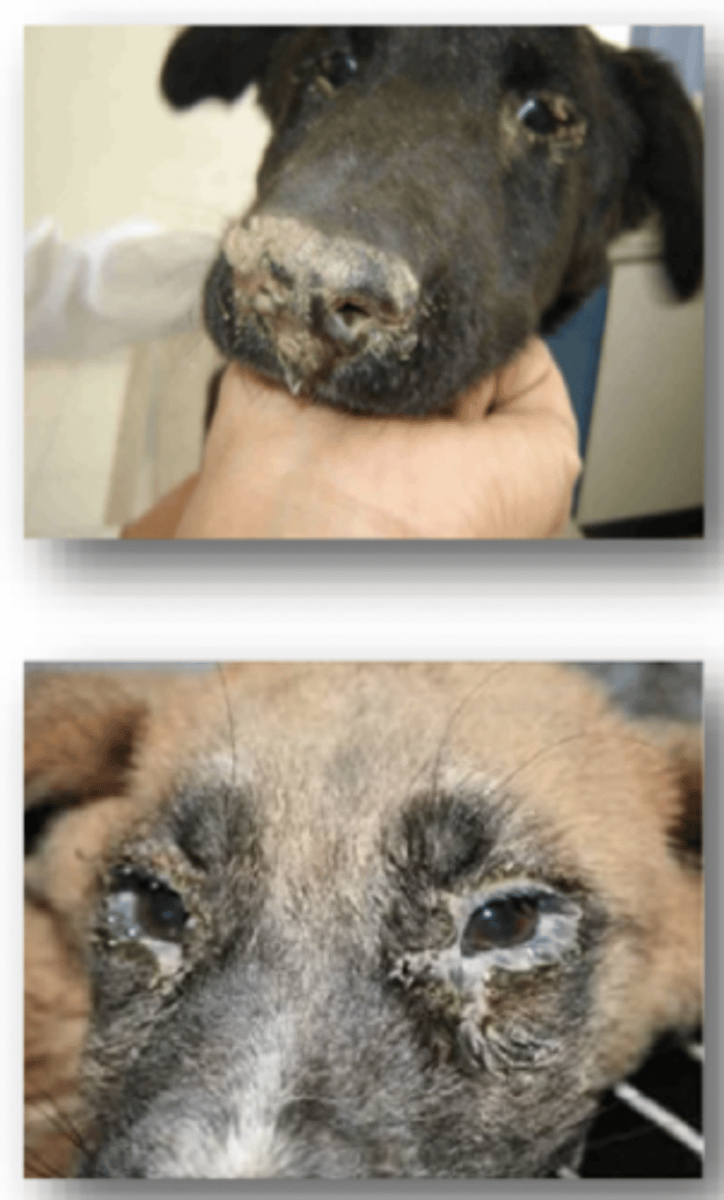
Define Canine Distemper in terms of:
1. Reservoir
2. Type of disease
1. Domestic and wild dogs
2. Highly contagious, systemic viral disease
Describe the Clinical Signs of canine Distemper in terms of:
1. First Fever
2. Second Fever
3. What Follows second Fever
1. Transient fever for 3-6 days. Subsides for several days
2. Second Fever occurs with nasal/occular discharge, annorexia, lethargy
3. Followed by GIT and resp. signs
Describe the Neurological Signs of canine Distemper
Long Illness is associated with neuro signs
- Chewing of the jaw
- Increased salivation
- Muscle Twitching
- Convolutions
Define the Treatment and Prevention of Canine Distemper in terms of:
1. Diagnosis
2. Treatments
3. Vaccine
1. RT-PCR
2. Supportive, limit secondary bacterial infection
3. Core AVA vaccination
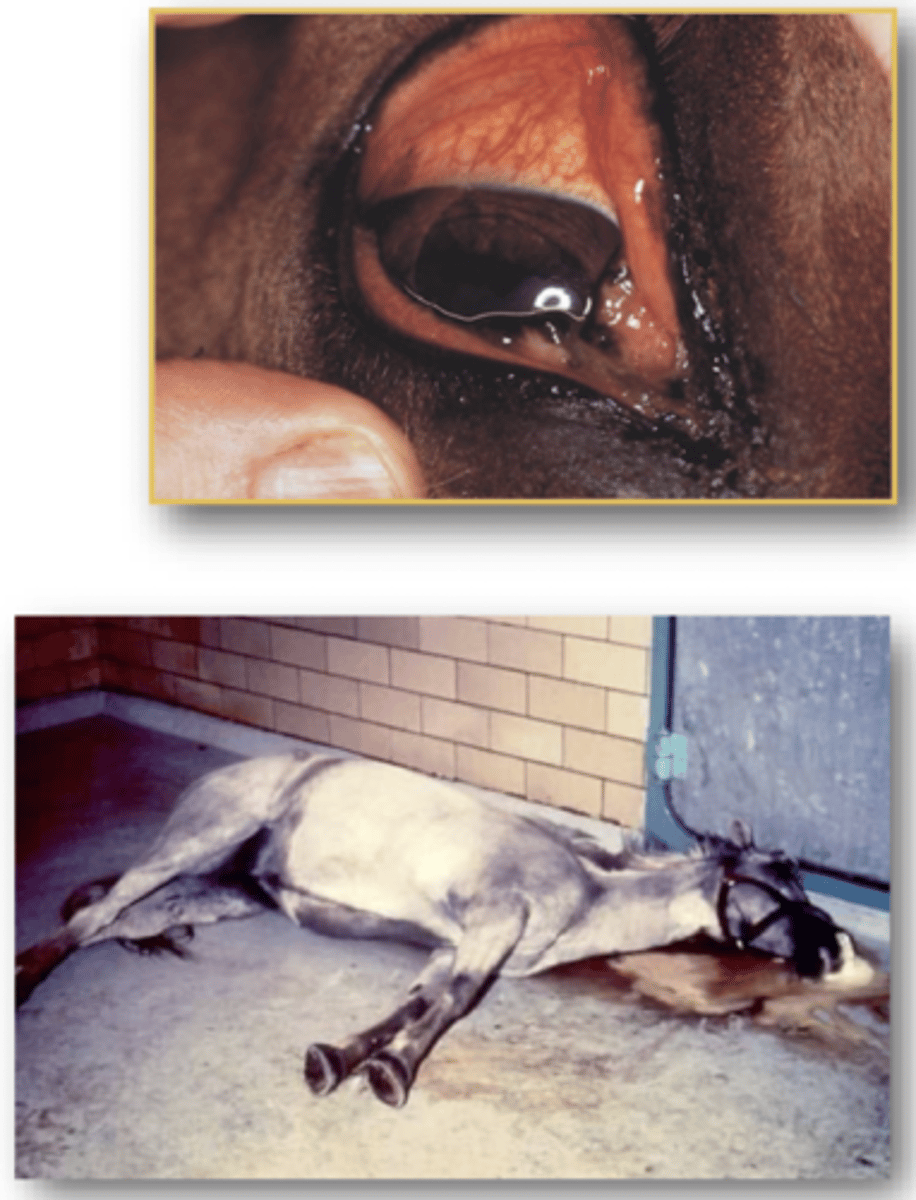
Define Hendra Virus in terms of:
1. Incubation
2. Reservoir
1. 8-16 Days, Shed during this time
2. Fruit Bats
Describe some Clinical Signs of Hendravirus
1. Depression
2. Fever
3. Short breath,
4. Nasal discharge
5. Dependant Oedema
6. Head Pressing/Ataxia
Explain the Prevention and Control of Hendra Virus
1. VACCINATE
2. Avoid bat-horse transmission (stable, secure water/feed containers
Define Nipah Virus in terms of:
1. Host
2. Clinical signs
1. Pigs
2. Severe resp. disease, Harsh "barking", Neurological Signs

Define Newcastle Disease Virus in terms of:
1. Hosts
2. Transmission
3. Virulence
1. Poultry
2. Resp. / GI Tract
3. Virus precursor fusion must be cleaved by host enzymes
Describe the following 4 Clinical Manifestations of Newcastle disease Virus:
1. Viscerotropic Velogenic
2. Neurotropic Velogenic
3. Mesogenic
4. Lentogenic
1. Acute lethal infections, haemoragic lesions in intestines
2. High mortality following neuro/resp disease, no gut lesions
3. Neuro/resp disease, low mortality
4. mild resp. infections / asymptomatic (usually vaccine viruses)
Describe the Clinical Signs of Newcastle Disease Virus
1.↓ Egg Production, accompanied by abnormal eggs
2.↓ appetite, fever, weakness
3. Swelling/cyanosis of comb and wattles
4. resp. / neuro signs

Explain Laborotory Detection fo newcastle disease virus in terms of:
1. Live Birds
2. Dead Birds
1. Serum, cloacal + tracheal swabs
2. Alimentary Tract Tissues
Define Bovine Respiratory syncytial Virus in terms of:
1. Hosts
2. What Infection causes
3. What is it a component of
4. Importance
1. Young dairy/beef Cattle
2. Respiratory Disease
3. Bovine respiratory disease Complex
4. Predisposes lower resp. tract to secondary bacterial infection
Define Rhaboviridae in terms of:
1. Virus Shape
2. mRNA
3. Specificity
1. Bullet/Cone
2. Single Sense RNA
3. Host Specific
Define Rabies in terms of:
1. Most Important maintenance Hosts
2. Clinical Forms
1. Dogs
2. Furious rabies (20%) + Paralytic rabies (80%)
Define the Hosts of Rabies in terms of:
1. Maintenance Hosts
2. Spillover Hosts
1. Sustains life cycle = DOGS
2. Infected hosts that belong to a species that don't normally have virus

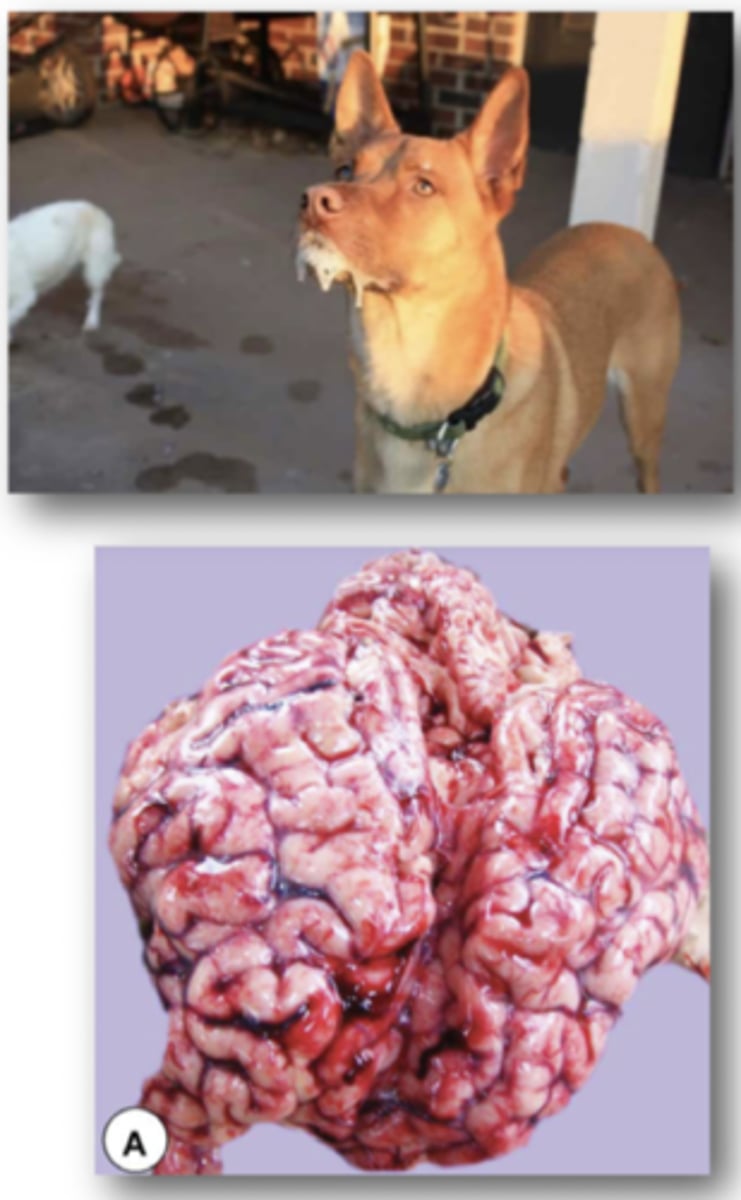
What are the Clinical Signs of Rabies:
Acute Encephalitis in all warm blooded Hosts
1. First symptoms are non-specific (lethargy, fever, vommiting)
2. Signs Progress to Cerebral Disfunction, nerve dysfunction, ataxia, weakness, paralysis, seizures, abnormal aggressive behaviour
3. Death 4 Days after onset of signs
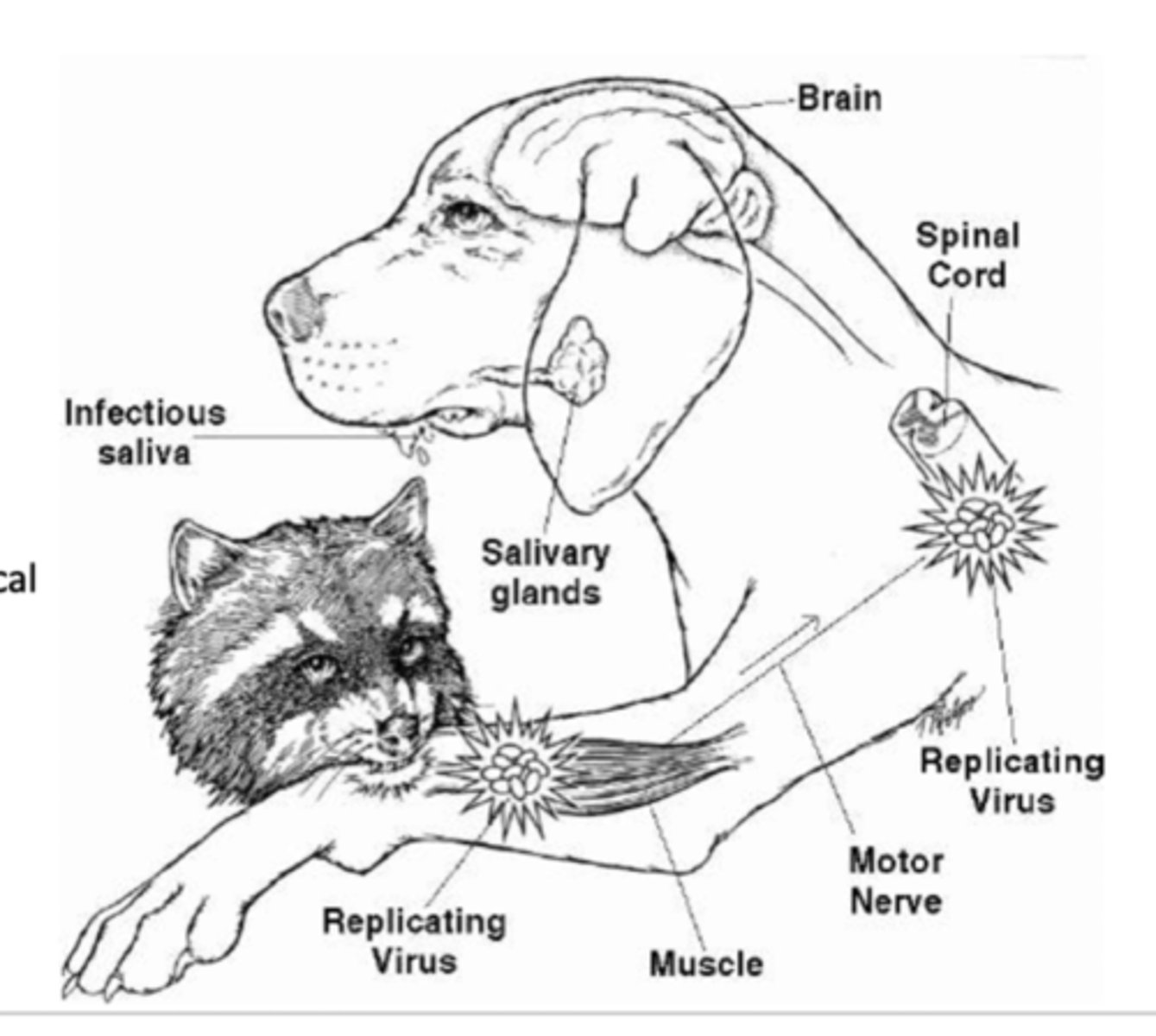
List the 6 Steps in the Pathogenesis of Rabies
1. Infects Myocytes at bite
2. Enters neurons at bite
3. propagates to CNS following neural connection
4. Replicates in CNS
5. Spreads through body nerves
6. Replicates in salivary glands and is released into saliva to complete transmission
Describe the Control Mechanisms of rabies
1. Vaccinating Dogs
2. Education of Dog Behaviour and Bites
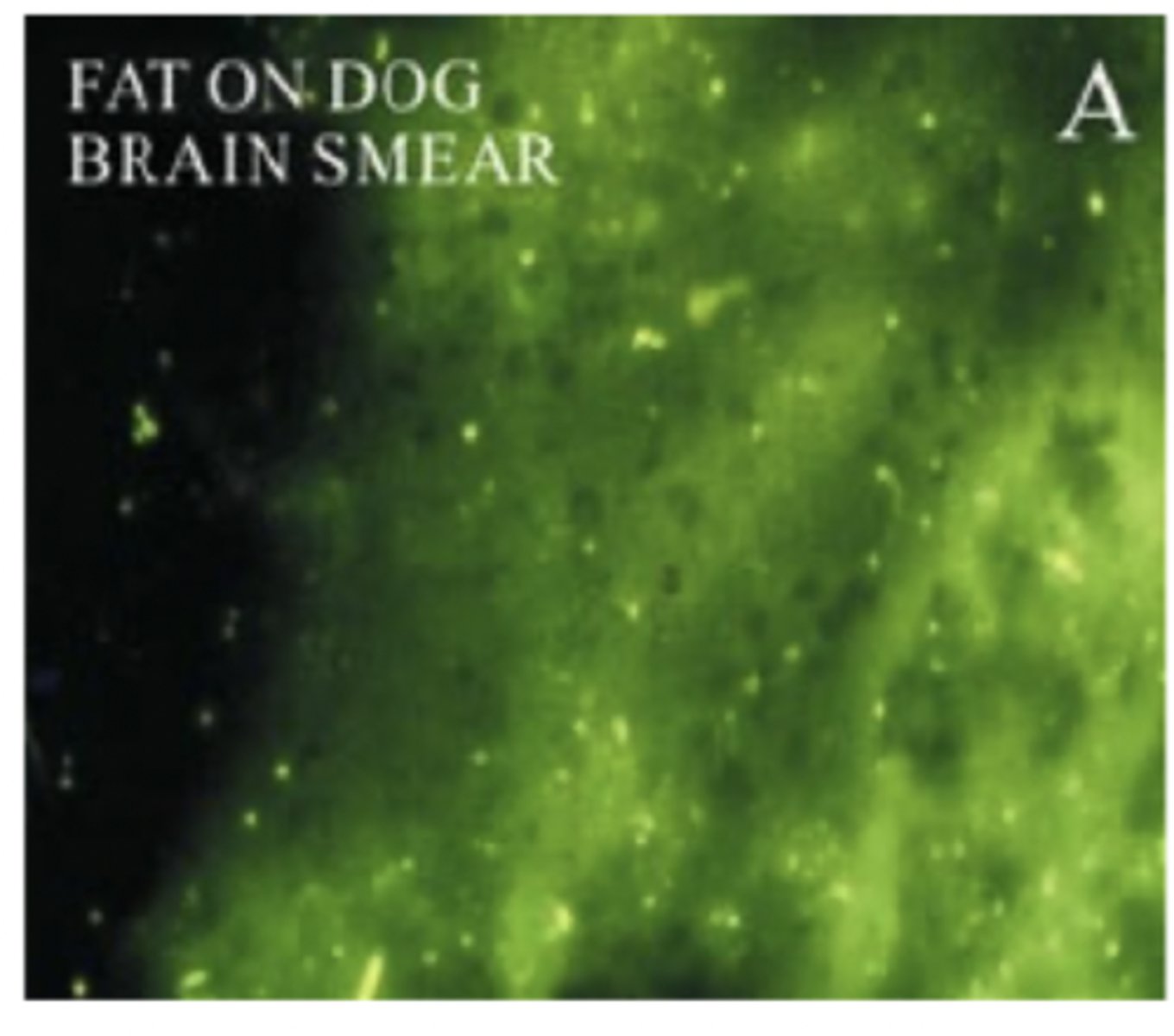
Describe the Diagnostic Techniques of rabies
Direct Flourescent Antibody technique
Also:
RT-PCR
Virus Isolation
Define Australian Bat Lyssavirus in terms of:
1. Infectious Species
2. Disease Presentation indistinguishable from what other disease
3. Clinical Signs
1. All Australian Bat Species
2. rabies
3. Aggression, paralysis, Neurological Signs
Define Bovine Ephemeral Fever Virus in terms of:
1. Common Name
2. Hosts
3. Transmission
4. Epidemiology
1. 3 Day Sickness
2. Cattle
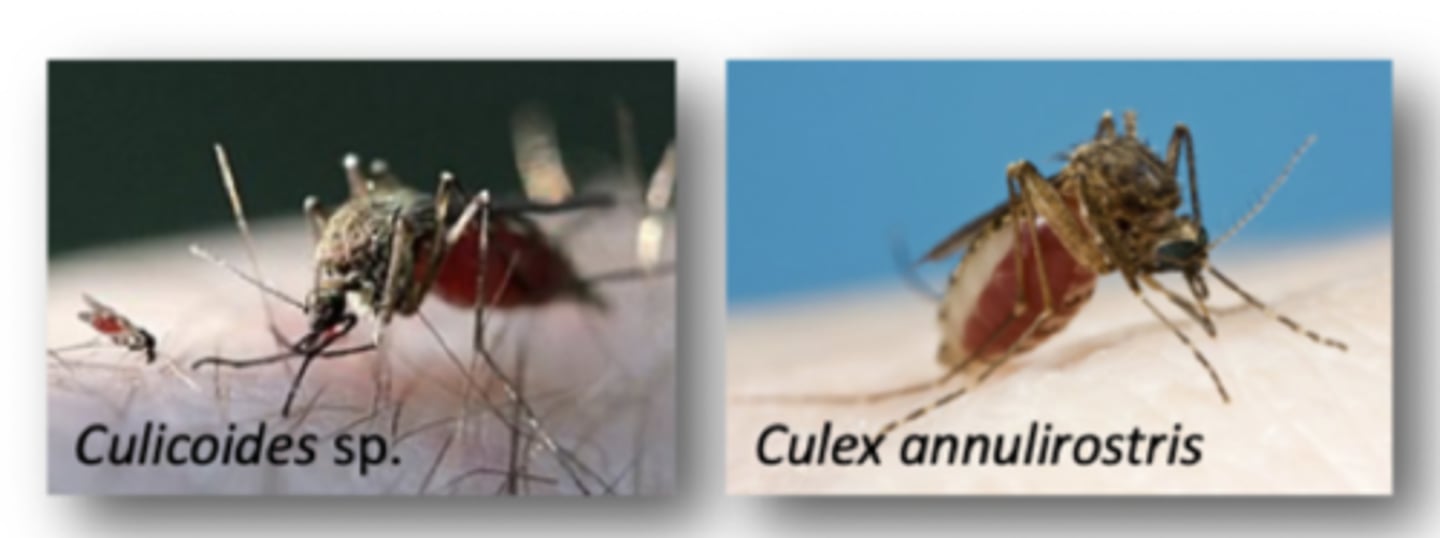
3. Via mosquitos and Midges
4. Endemic in Northern Australia, Epidemic in Subtropical/temperate areas (Seasonal Mosquitoes/midges)

Describe the 3 Progressive stages of the Clinical Signs of Bovine Ephemeral Fever Virus:
1. Acute Febrile Stage
2. Muscular Stiffness
3. Recovery
1. Fever, Shiver, arched back with low heads and salivating, discharge from eyes and nose, stop feeding, ↓ milk production
2. Lameness, stiff/swollen joints
3. Most animals resume eating and drinking, however some animals go down (Heavy animals in good condition more prone) some remain down due to muscle degradation/Nerve damage

Define the Impacts of Bovine Ephemeral Fever in terms of:
1. Long term effects
2.Dairy Herd Production
1. Prolonged recumbancy, paralysis, death, temporary ↓ Bull fertility
2. ↓ Milk Production, Cows dry up, Abortion
Explain Post Mortem signs of Bovine Ephemeral Fever
Fluid in cavities, Oedema/lesions in lungs, Joint damage (in downing cows)
Describe the Diagnosis of Bovine Ephemeral Fever
Lameness, muscular stiffness, pain, short fever, PCR Test
Describe the Prevention of Bovine Ephemeral Fever
1. Live Vaccine
Define Vesicular Stomatitis in terms of:
1. Hosts
2. Incubation Period
3. Infection Length
1. Cattle, Horses, Pigs
2. 2→7 Days
3. Short lived and self limiting, mortality is rare
Describe the Clinical Signs of Vesicular Stomatitis
1. Excessive Salivation
2. Vesicles in mouth
3. Lesions of hooves and feet
4. Teat Lesions in dairy herd

Describe the following Epidemiology of Vesicular Stomatitis:
1. Saliva
2. Fomites
3. Vectors
1. Infected animals salivate excessively, saliva has high levels of Virus
2. Saliva Easily contaminates fomites
3. Mechanical by biting/non-biting flies and midges
Describe the Diagnosis of Vesicular Stomatitis
ELISA Most Common
- PCR
- Viral Isolation
Rapid Lab Diagnostics to rule out FMD/Swine Vesicular Disease/Vesicula Exanthema of swine
Define Caliciviridae in terms of:
1. Viral Genome
2. Location/Spread
1. Positive sense, ssRNA
2. GIT pathogens, Faecal-Oral Spread
Define Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus in terms of:
1. Clinical Signs:
2. Post Mortem
3. Transmission
4. Uses
1. Hepatitis. fever, anorexia, neuro signs, resp. signs. 80-90% Mortality
2. Liver Necrosis
3. Direct contact with all types of animal excretions. Flies are mechanical vectors
4. Feral Rabbit Population control
Define Vesicular Exanthema of Swine Virus in terms of:
1. Host
2. Indistinguishable from
1. Swine
2. FMD, Swine Vesicular disease, Vesicular Stomatitis Disease
Describe the Clinical signs of Vesicular Exanthema of Swine Virus
1. Vesicles in mouth, tongue, lips, snout, feet
2. Encephalitis, Myocarditis, Abortion
Describe the Control of Vesicular Exanthema of Swine Virus
1. Test and slaughter
2. Prevention of Swill Feeding

What is the Natural Reservoir of Vesicular Exanthema of Swine Virus
Aquatic Species (seafood). Infection given to pigs through swill feeding

Define Feline Calcivirus in terms of:
1. Virus Shedding
2. Infectioun Routes
1. Shed in Oral/Nasal secretions, sheds virus for 30 days after infection
2. Nasal/oral/conjunctival routes
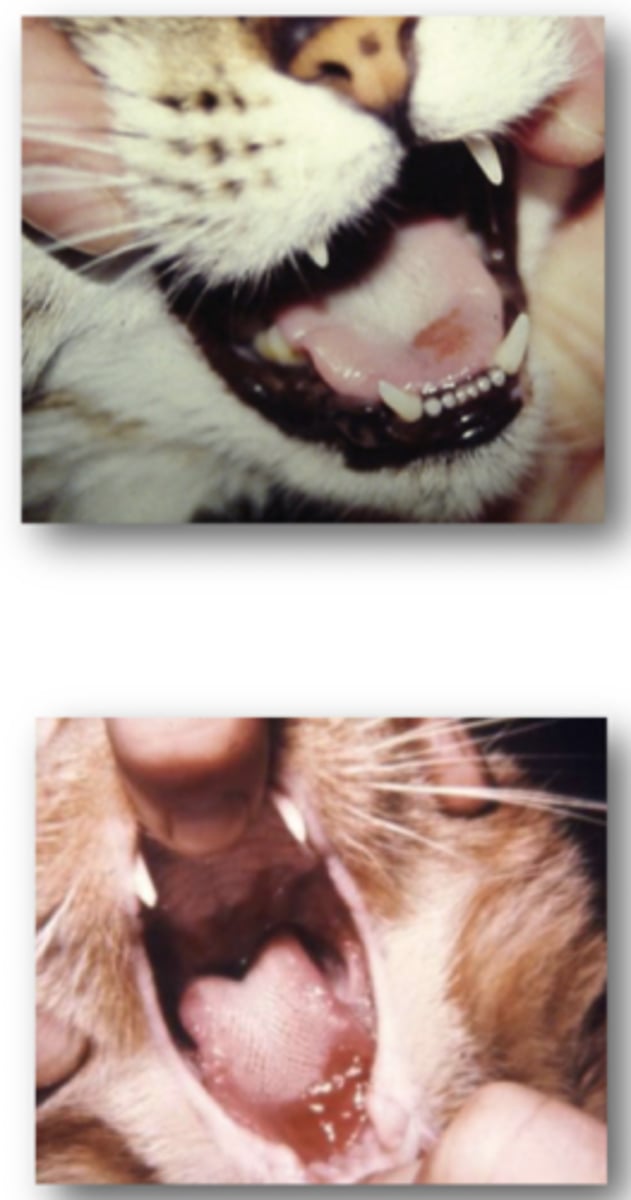
Define Feline Calcivirus in terms of
Oral and Upper Respiratory tract Disease
Oral Ulceration most common with this disease form
1. Vireamia occurs 3-4 Days after infection
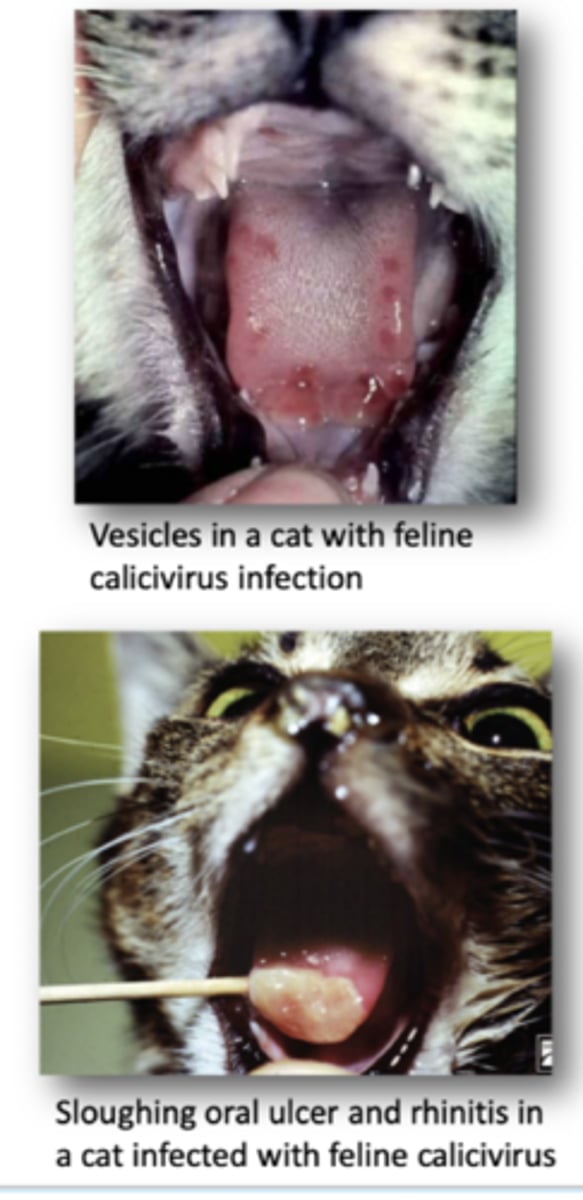
Define Feline Calicivirus in terms of
Associated Lameness
Limping Syndrome
1. Lesions in joints, thickening of synovial membrne and ↑ Synovial FLuid
2.
Define Feline Calcivirus in terms of Feline Stomatitis
Progressively Worsening inflammation of Oral Mucosal Tissue
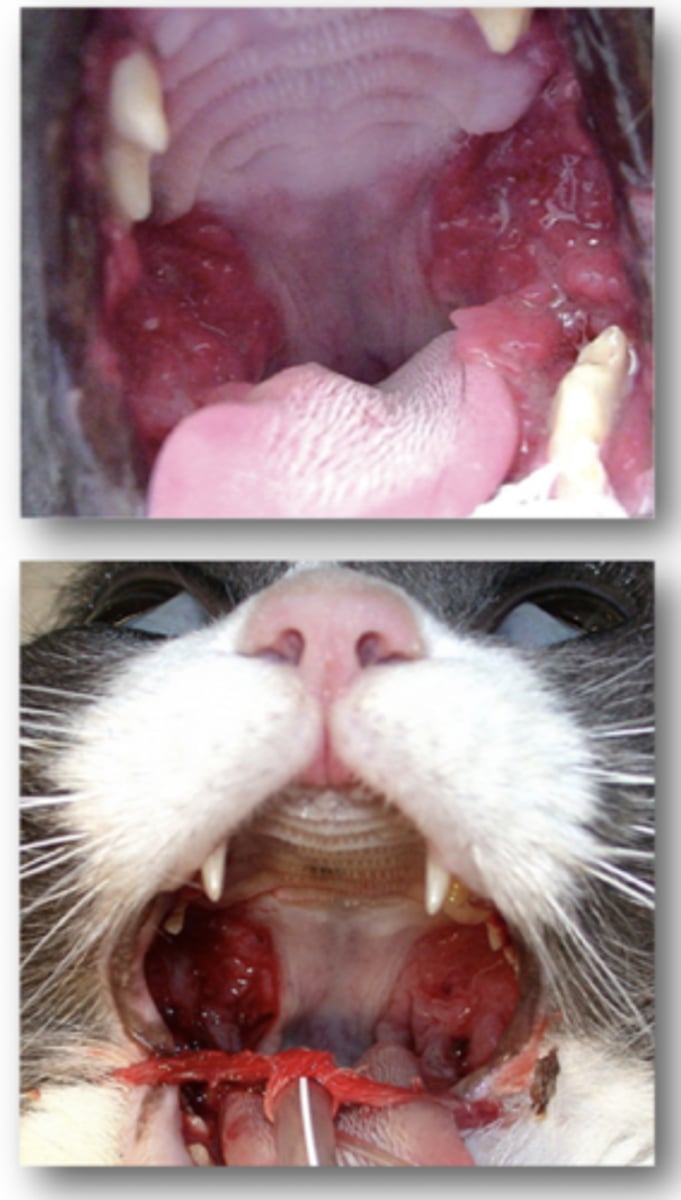
Define Feline Calcivirus in terms of Virulent Systemic Feline Stomatitis
Exists due to Mutations within Feline Calcivirus viral genome
1. Widespread lesions and subcutaneous oedema.
2. Systemic Lesions
Describe the Epidemiology of Feline Calcivirus in terms of:
1. Shedding
2. Transmission
3. Recovery
4. Environmental Resistance
1. Shed in resp., urine, faeces
2. transmission occurs via aerosole and fomites
3. Recovery Followed by prolonged oropharyngeal carrier state
4. Remains infectious in environment for over 1 month
Describe the Diagnosis and Vaccination of Feline Calcivirus
Diagnosis:
- Swabs of secretions
- RT-PCR
- Cell Cultures
Vaccination:
Reduces severity but doesn't prevent infection
Define Avian Nephritis Virus in terms of
1. Host
2. Clinical Signs
3. Transmission
1. Chickens
2. Diarrhoea, Growth Retardation, kidney damage
3. Direct or indirect contact
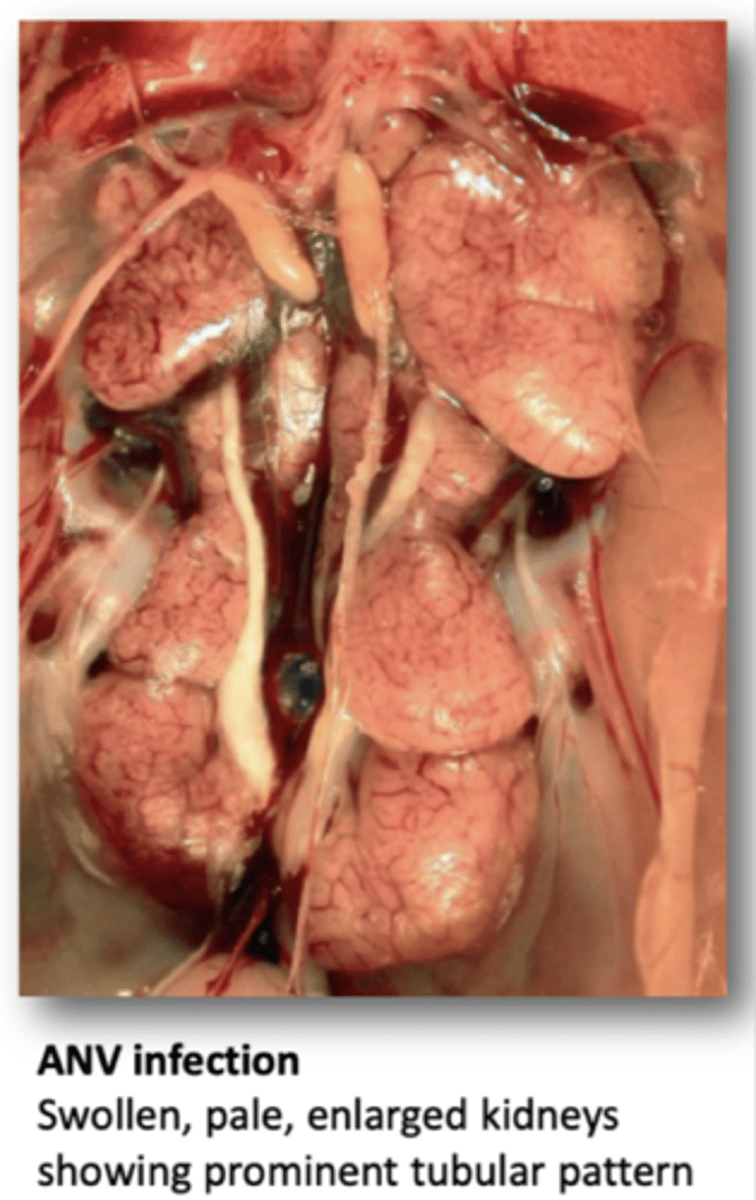
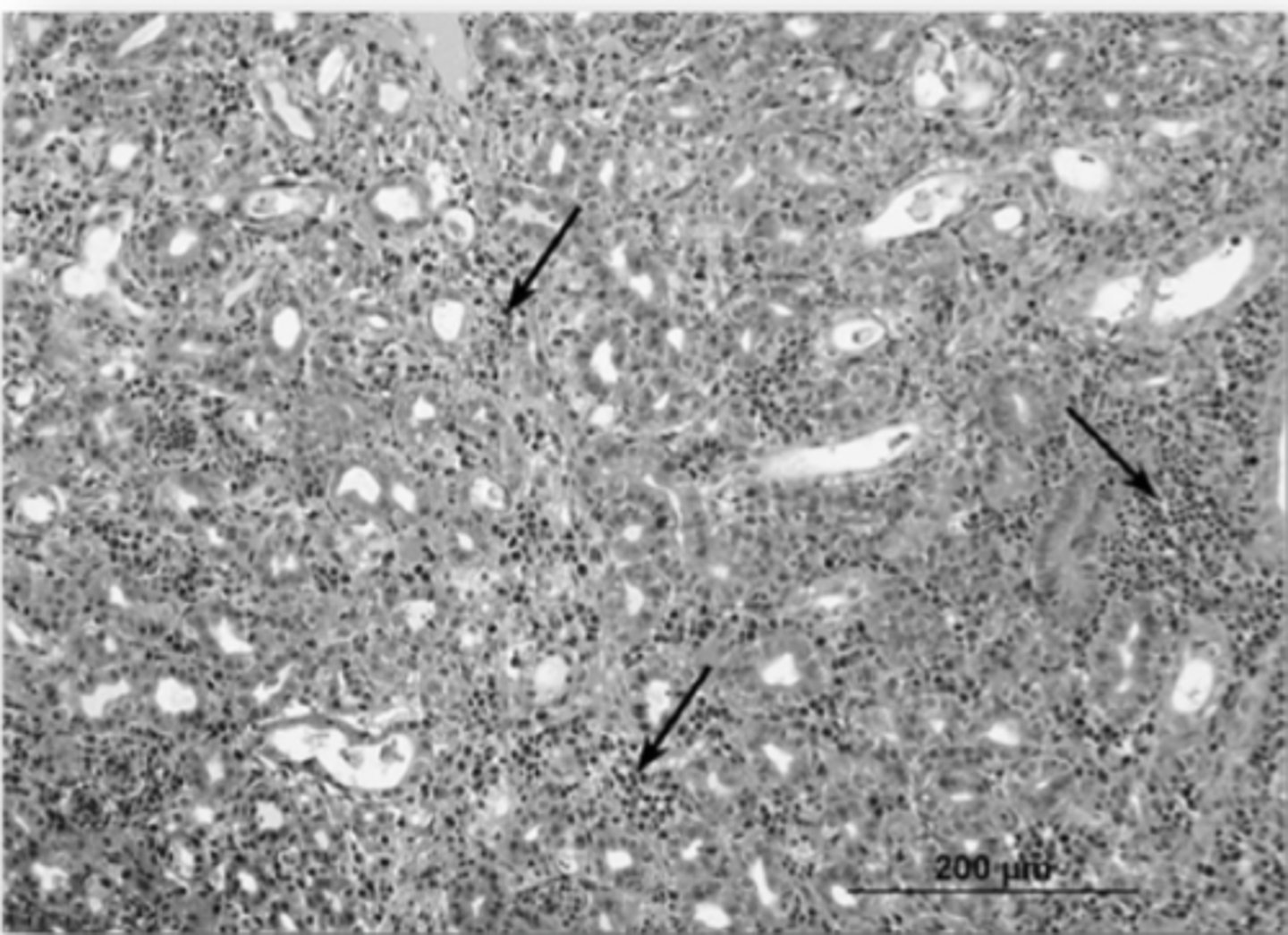
Define the Pathology of Avian Nephritis Virus
1. Histological Change of Kidneys
2. RT-PCR
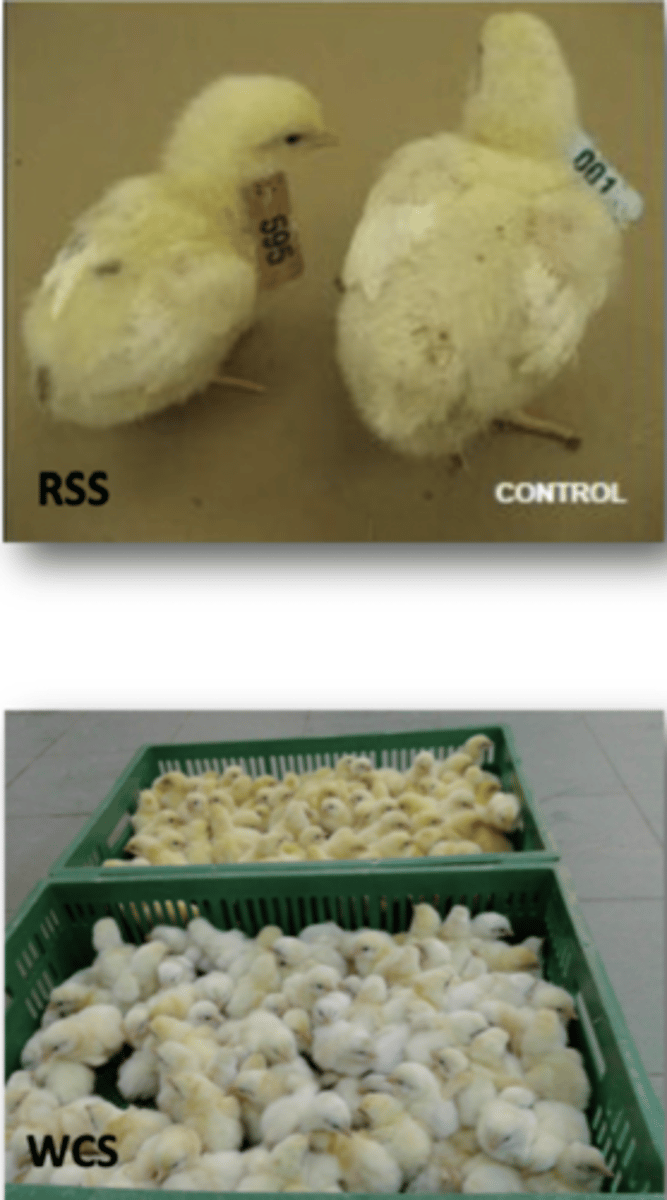
Define Chicken Astrovirus in terms of:
1. Runting-Stunting Syndrome
2. White Chick Syndrome
1. Diarhoea, poor weight gain, mortality
2. Embryo mortality, weakness, White chicks
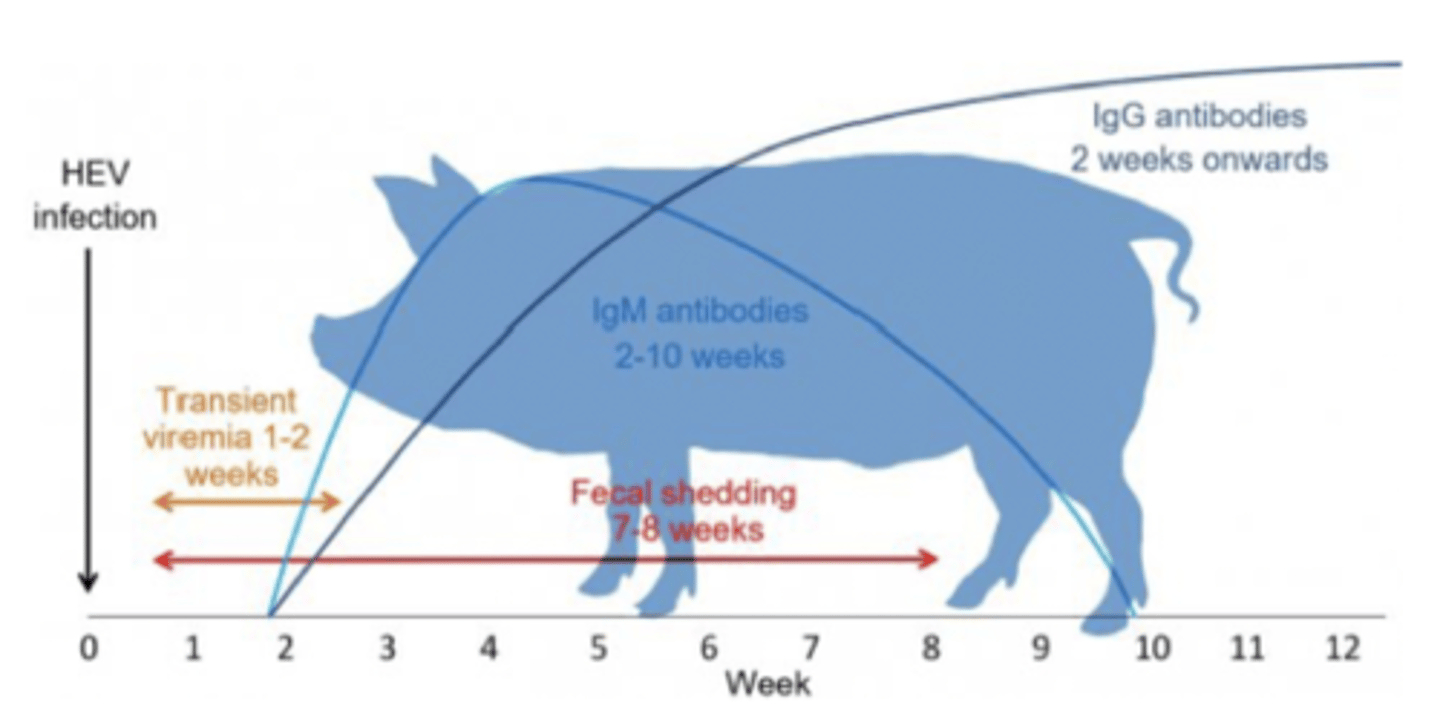
Define Hepatitis E Virus in term of:
1. Humans
2. Clinical Signs
3. Transmission
4. Genotypes
5. Antibodies in pigs
1. Most common cause of enteric viral hepatitis infection in humans
2. Low mortality, usually asymptomatic, subclinical
3. Spread via direct contact with faeces, faecal-oral
4. HEV1/2 (Human → Human), HEV3/4 (Pig → Human)
5. Most pigs in the world have HEV antibodies (feral and domestic)
Define Avian Hepatitis E Virus in terms of:
1. Hosts
2. Associated Diseases
3. Transmission
1. Avian Species
2. Big liver and spleen disease
3. Faecal-Oral
What are the Clinical Signs of Avian Hepatitis B Virus
1. Slight ↑ Mortality
2. ↓ Egg Production
Describe the Diagnosis of Avian Hepatitis B Virus
Signs Variable, Lab test for virus conformation
1. RT-PCR (For RNA)
2. ELISA (for Antibodies)
Define Canine Coronavirus in terms of:
1. Clinical signs
2. Where the Virus is common
1. Mild gastro-intestinal signs
2. Where dogs are housed in large groups
Describe the Pathogenesis of canine Coronavirus in terms of:
1. Transmission
2. Age susceptible
3. Where it replicates
1. Faecal-Oral
2. Puppies under 12 weeks of age
3. Intestine Epithelia
What is Pantropic Canine Coronairus?
Causes Fatal Multi-systemic illness
New strains of canine Coronavirus capable of replication outside the intestines.
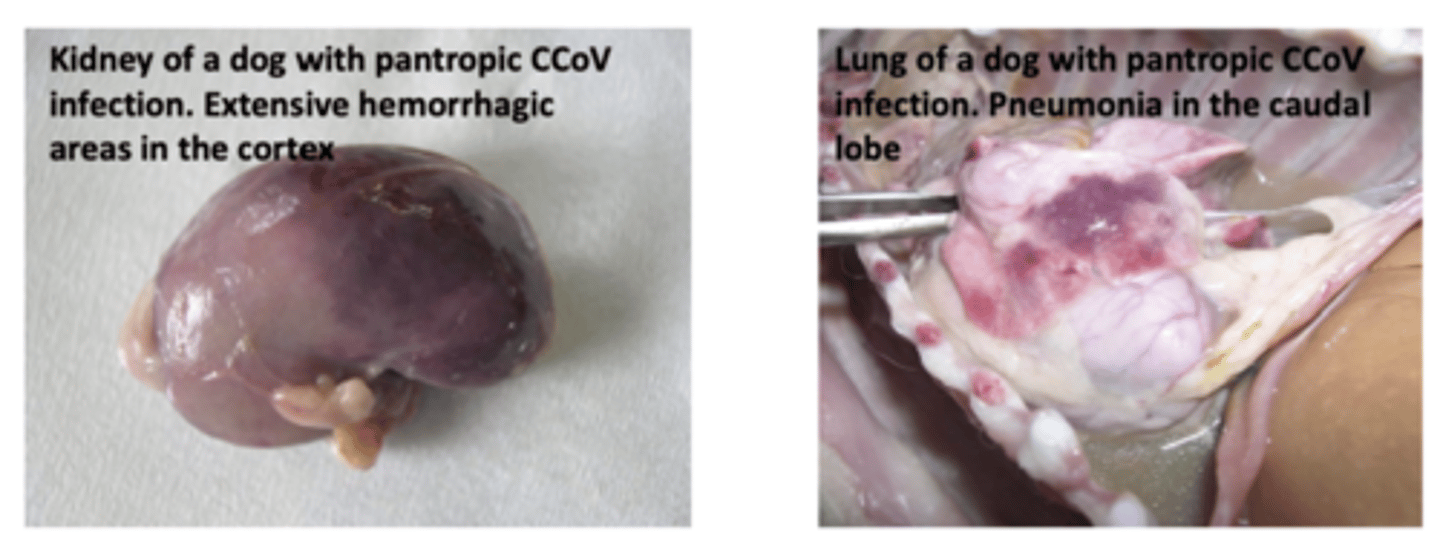
Describe the Treatment and Prevention of Canine Coronavirus
Supportive Care: Fluid and Electrolytes
Vaccination not recommended
Define Canine Respiratory Coronavirus in terms of:
1. Susceptible age
2. Transmission
3. What it Causes
1. All Ages
2. Spreads via Inhalation of droplets or contact with secretions and contaminated surfaces
3. Mild resp. illness
Define Feline Enteric Coronavirus in terms of:
1. Susceptible age
2. What it causes
3. Faecal Shedding
4. Transmission
5. Clinical Signs
1. Kittens
2. Mild GIT Illness
3. Up to 2 Years (15% lifelong)
4. Faecal oral/droplet ingestion, Fomites
5. Diarrhoea is most common sign
Define Feline Infectious Peritonitis in terms of:
1. Ages susceptible
2. Mortality
3. Where it Occurs
1. Any age, most common under 3 Years
2. Extremely high once clinical signs appear
3. Catteries/Shelters

Describe the Internal Mutation of Feline Infectious Peritonitis
FIPV arises from internal mutation of Feline Enteric Coronavirus unique to each cat
Occurs in 1-5% of animals with FECoV
Describe the Clinical Signs of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus
1. Abdominal Distention
2. Pleural Effusion
3. Jaundice
4. Neural Signs
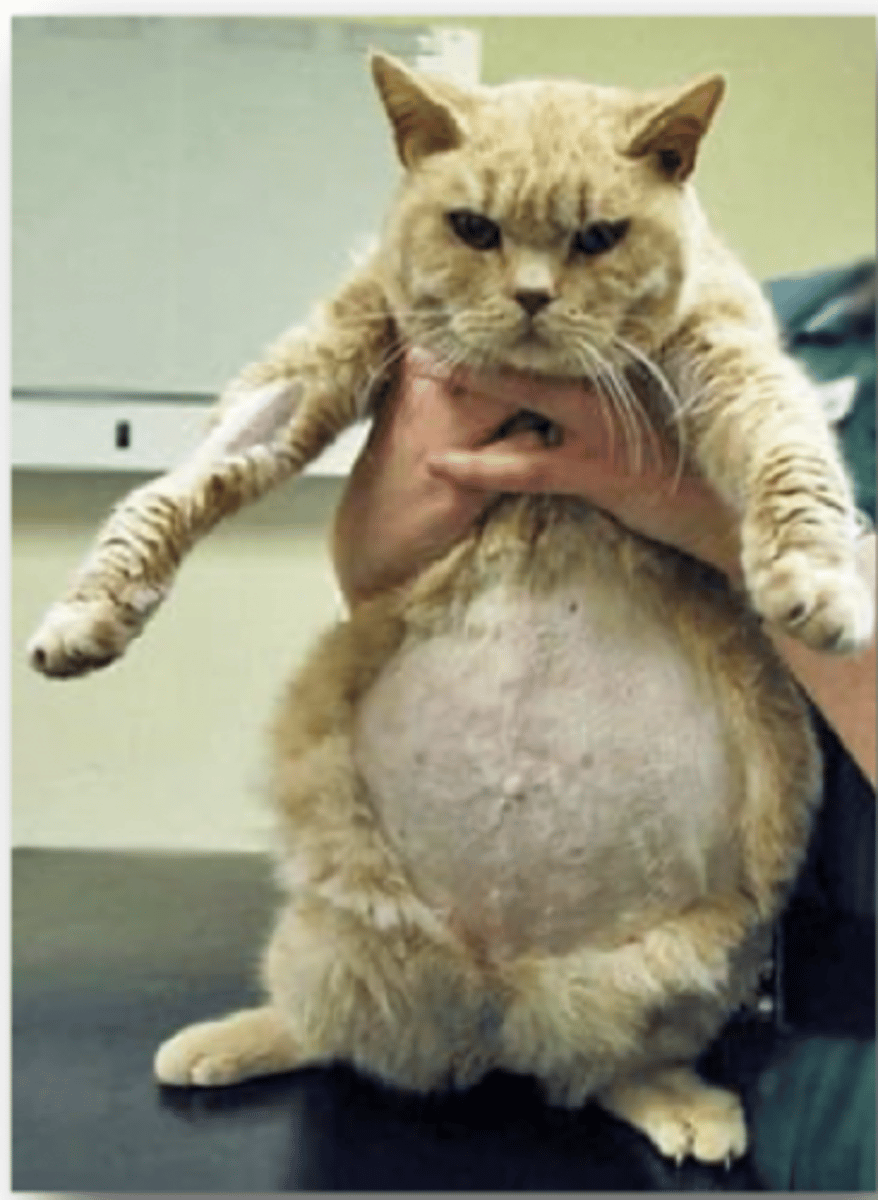
Define the following Clinical Signs of Feline Infectious peritonitis virus:
1. Effuse (Wet) Form
2. Non-Effuse (Dry) Form
1. Accumulation of fluid on abdomen/Chest
2. Similar signs but no fluid. Neuro signs more common
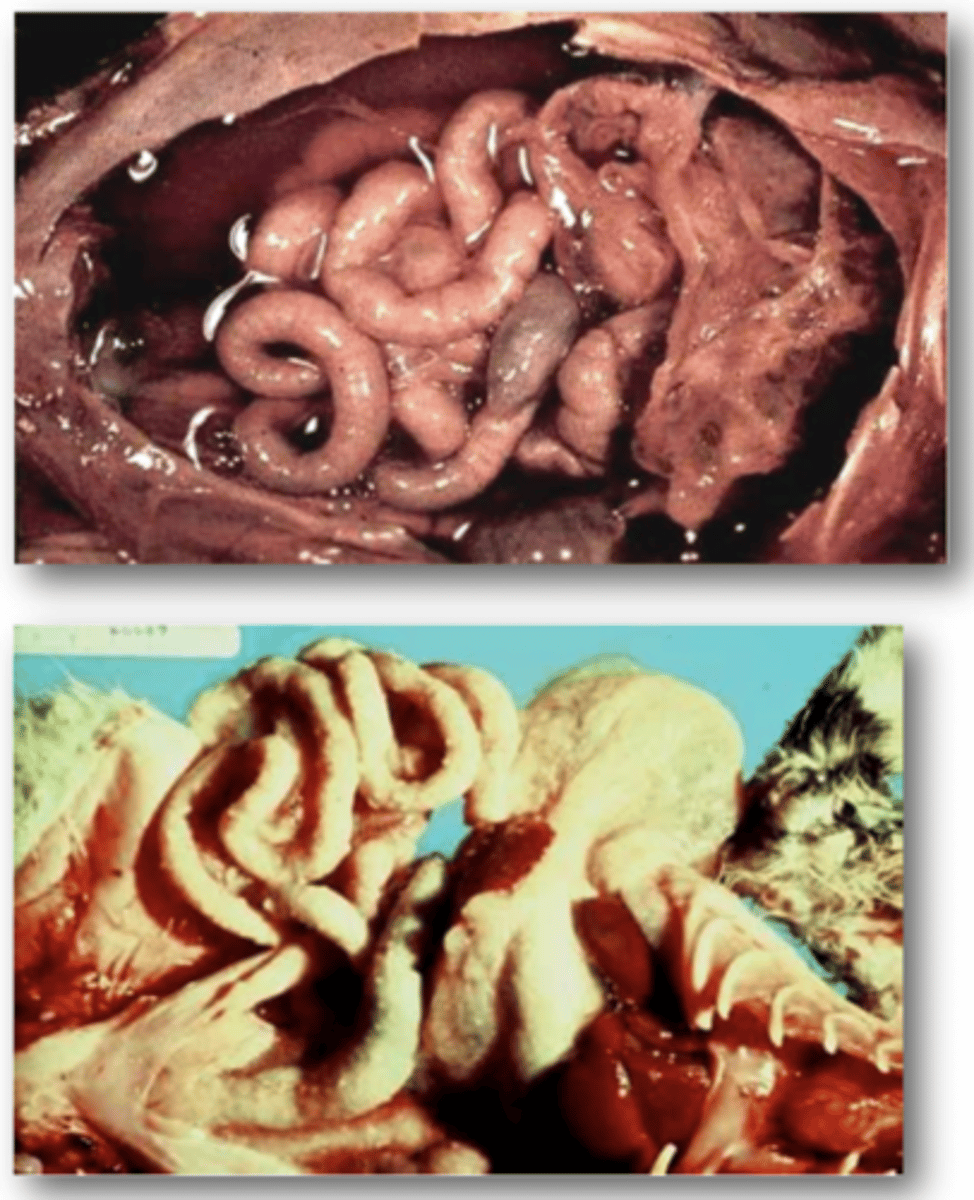
Define Porcine Transmissible Gastrointestinal Virus (TGEV) in terms of:
1. What it Effects
2. What it causes
3. Transmission
1. Villi of Small Intestine of Pigs
2. Vomiting/Profuse Diarrhoea
3. Animal Contact/Fomites
Describe the Clinical Signs of Porcine Transmissible Gastrointestinal Virus
1. Vomiting followed by profuse watery diarrhoea
2. Faeces of nursing pigs have undigested milk
3. 100% mortality in pigs under a week old
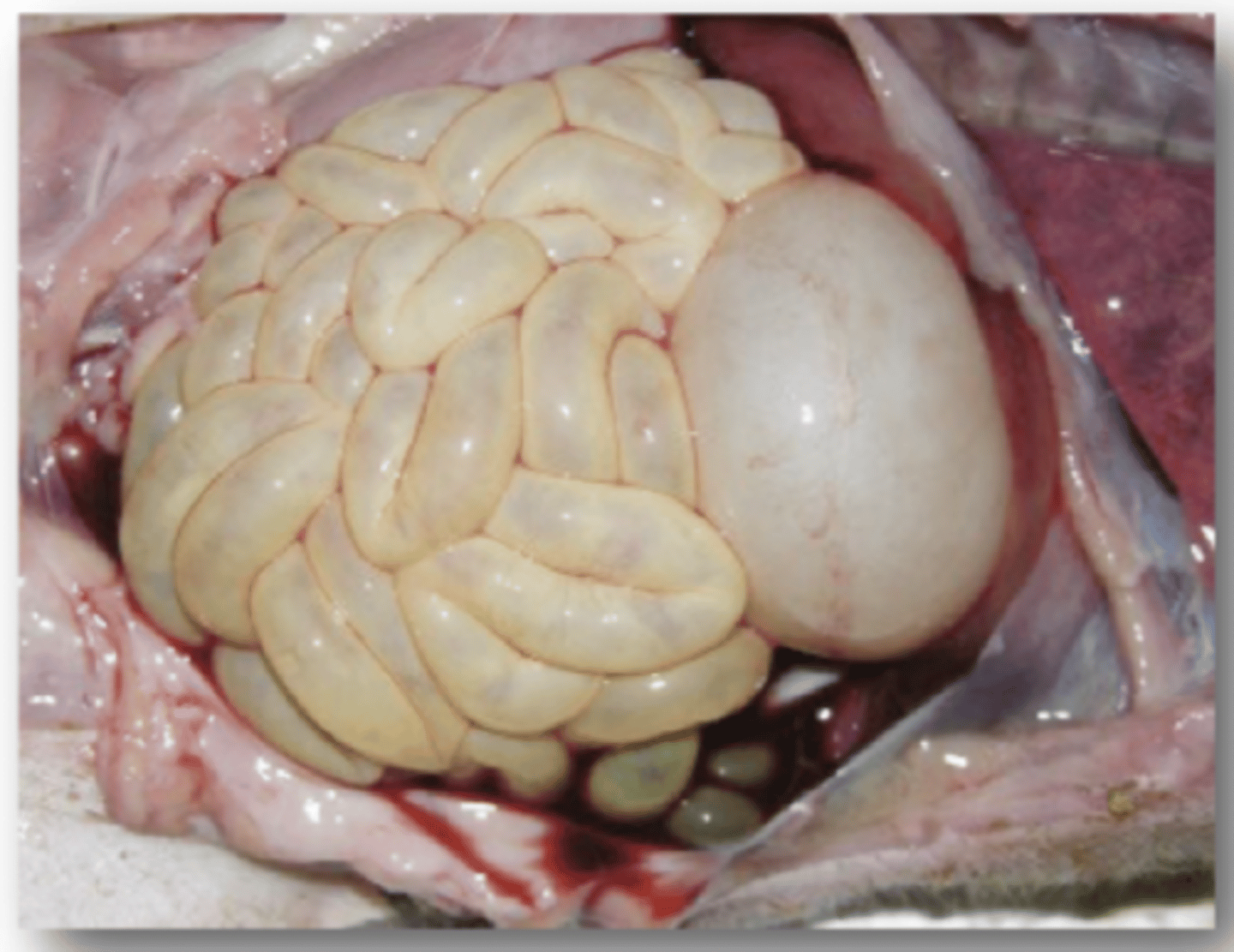
Define Porcine Respiratory Coronavirus in terms of:
1. Evolution
2. What it causes
3. Ages most common
4. Transmission
1. Evolved from Porcine Transmissible GIT Virus
2. Mild resp. signs
3. young piglets
4. Aerosole+Direct Contact
Define Porcine Haemagglutinating Encephalitis Virus in terms of:
1. Prevalence
2. Clinical Relevance
3. Replication
4. Clinical Signs
1. Worldwide
2. Subclinical
3. Resp., can move to CNS
4. Vomiting, constipation, anorexia,
Define Bovine Coronavirus in terms of:
1. What it causes
2. What complex it is part of
3. Treatment
1. GIT and resp. illness
2. Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex
3. Supportive
Define the Clinical Signs of Bovine Coronavirus
1. Enteritis
2. Profuse Watery Diarrhoea with blood clots
3. Calves cant suckle
Define Infectious Bronchitis Virus in terms of:
1. Hosts
2. Transmission
3. Mortality
1. Chickens
2. Aerosole, faeces, contaminated water/food ingestion
3. 5%
Describe the Clinical Signs of Infectious Bronchitis Virus
1. Chicks cough and sneeze
2. Conjunctivitis
3. Chicks looks depressed and huddle
4. Weight gain reduced
5

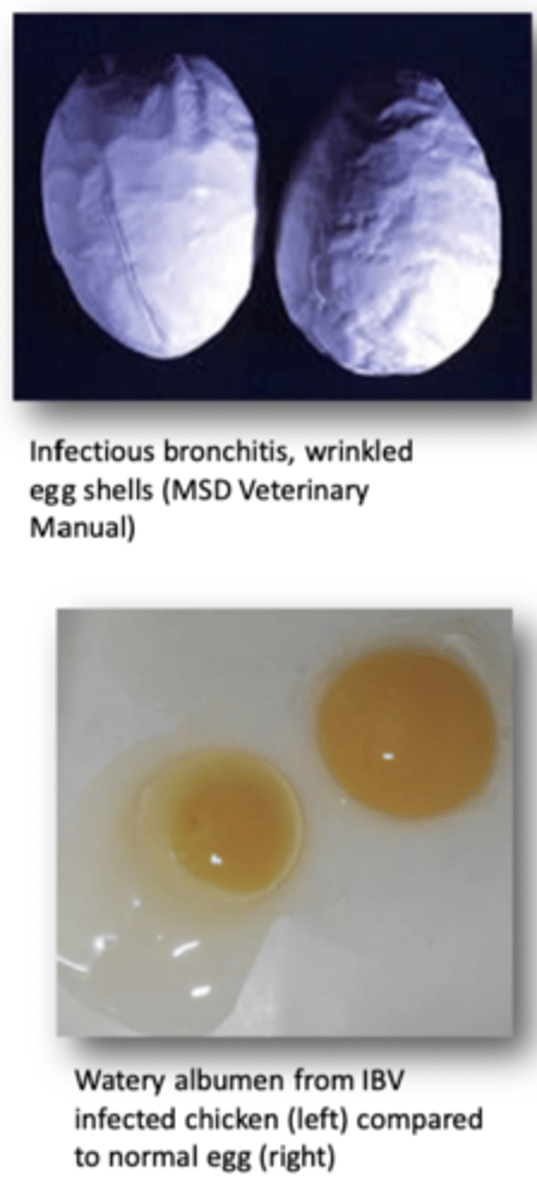
Describe the effects of Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Layers in terms of:
1. Egg Production
2. Egg Quality
3. Recovery
4. Chick infection
1. Drops up to 70%
2. Eggs misshapen, thin/soft/pale/rough shells
3. Returns to normal after 8 weeks
4. Causes Permanent Oviduct Damage
Describe the Detection and Vaccination of Infectious Bronchitis Virus
RT-PCR
Vaccine Widely Used. Vaccinated at one day old with 1-2 additional doses
Describe the Basic Characteristics of the 3 Herpesviridae Subfamilies Below:
1. Alphaherpesvirinae
2. Betaherpesvirinae
3. Gammaherpesvirinae
1. May Cross Placenta
2. Low Grade Infections
3. Highly cell associated
Define Herpesviridae Latency/Persistance in terms of:
1. Establishment
2. Maintenance
3. Reactivation
1. Virus enters neurons and lymphocytes
2. DNA can't be detected
3. External factors (stress/immunosuppresiom)
Define Equid Alpha Herpes Virus 1+4 in terms of:
1. 2 Serotypes
2. EHV 1 Signs
3. EHV 4 Signs
4. General Signs
5. Susceptible Ages
1. EH1+4
2. resp. disease, abortion, neurologic disease
3. resp. disease and only occasionally abortion and neurological disease
4. Coughing, Nasal Discharge, enlargement of
mandibular/retropharyngeal Lymph Node
5. Young Horses, Adults asymptomatic