Earth and Space Science
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Microorganisms
organisms so small a microscope is needed to see them
Example.
bacteria, fungus
Greenhouse Gases
gases which, when present in elevated quantities in Earth's atmosphere, trap solar radiation and cause the planet to warm
Example.
carbon dioxide
Tenacity
the mineral's ability to resist separation or breaking when subjected to stress
Example.
quartz is brittle and will be crushed to a powder when hammered
Greenhouse Effect
the trapping of the sun's heat in the atmosphere due to the increased presence of gases in the atmosphere; light is allowed to pass through, but heat is trapped, similar to the glass walls of a greenhouse
Northern Hemisphere
The half of the earth north of the equator
Ultraviolet Radiation
radiant energy which can heat up the planet and damage the cells of living organisms
Taste
Term definition.
the mineral's taste; only soluble minerals have a taste
Example.
halite has a salty taste
Aquifer
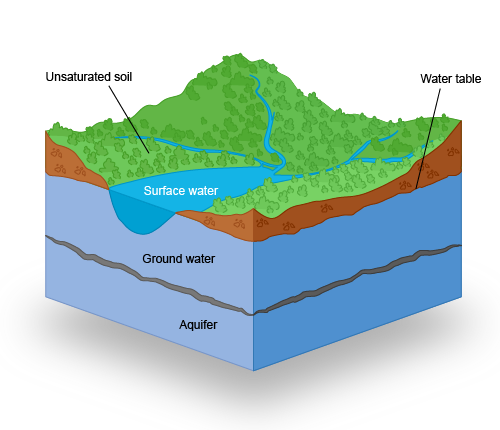
an underground body of water-saturated rock
Example.
Ogallala aquifer
Surface Current
a river-like flow of water of different temperature within Earth's oceans
Example.
Humboldt Current
Surface Water
water held on the surface of the earth
Example.
lake
Coriolis Effect
A curving of the flow of wind or water caused by Earth's rotation; to the right in the northern hemisphere, to the left in the southern hemisphere.
Nuclear Fission

a process in which the nuclei of an atom is split, releasing a massive amount of energy.
Ionosphere
a layer of ions and free electrons in the atmosphere; can reflect and direct radio waves
Water Table

the level below which the soil and rock remain saturated with water
Troposphere
the layer of gases closest to the earth where weather occurs
Plate Tectonics
the large-scale movements of portions of the earth's crust over long periods of time
Mechanical Weathering
the process of breaking down rocks by physical means
Example.
water freezes in a crack in the rock and breaks it apart
Meteoroids
small bodies of debris from space which move into Earth's atmosphere and can then turn into meteors
Acid Rain
rain with a lower pH than neutral
corrosive to many substances, including rocks
often caused by pollution
Example.
sulfur dioxide dissolves in the water droplets of clouds to make sulfuric acid
Hot Spot
a place far away from tectonic plate boundaries where upwelling magma creates a hole in Earth's crust and lava erupts onto the surface
Example.
Galapagos Islands
Continental Arctic Air Mass (cA)
A frigid, dry air mass that formed over arctic landmasses
Igneous Rock

rock formed when magma or lava cools; air pockets or crystals
Example.
basalt; granite
Convergent Boundary / Destructive Boundary
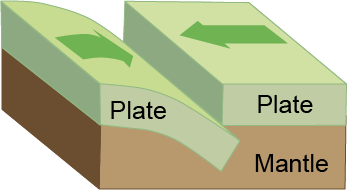
a boundary between tectonic plates where the two plates move toward one another; creates mountains and trenches
Example.
Cascade mountain range
Hardness
the mineral's resistance to scratching; measured on the Mohs scale, where talc, the softest mineral, has a score of 1 and diamond, the hardest, has a score of 10
Example.
diamond is hard, talc is soft
Hot Spring
a geological feature produced when water is heated by geothermal activity and pushed to Earth's surface
Example.
Banff Upper Hot Springs in Banff National Park
Continental Polar Air Mass (cP)
A cold, dry air mass that formed over polar landmasses
Southern Hemisphere
The half of the earth south of the equator
Plastic
a state in which a material is solid but can flow (generally slowly)
Divergent Boundary / Constructive Boundary
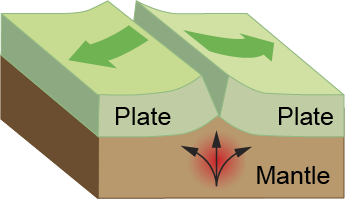
a boundary between tectonic plates where the two plates move away from one another; creates new crust
Example.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Iceland
Feedback Loop (In Systems)
the part of a system in which some (or all) of the system's output is used as input for future operations
Example.
body temperature regulation - the body temperature is achieved and then measured for future changes needed
Destructive Processes
processes that break down or destroy landforms
Example.
water running across a rock causes the rock to wear down
Sedimentary Rock

rock formed when sediments build up and cement together; visible layers
Example.
sandstone; siltstone; coal; shale
Mineral
a naturally occurring, inorganic solid with an orderly, network structure and definite chemical composition
Example.
diamond
Ocean Basin
depressions on the earth's surface due to the sinking of oceanic crust, forming oceans
Groundwater

water below the earth's surface held in the spaces between rock and soil particles
Example.
aquifer
Outer Core
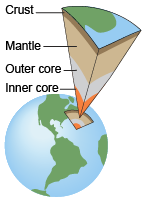
the layer of the earth just beneath the mantle; composed of very hot, liquified rock
Odor
the smell of a mineral; some minerals give off an odor when moistened or heated
Example.
pyrite gives off a rotten egg odor when heated
Mesosphere
the coldest layer in the atmosphere; protects the earth from meteoroids
Tectonic Plates
plates or portions of Earth's crust and upper mantle, which glide across the asthenosphere
Example.
Pacific Plate
Atmosphere
the gases surrounding the surface of the earth
Luster
the ability of the mineral's surface to reflect light; can be metallic, submetallic, or nonmetallic
Example.
galena has a metallic luster
Specific Gravity
the ratio of the density of the mineral to the density of water
Example.
sapphire has a specific gravity of about 4, meaning it is 4 times heavier than an equal amount of water
Transform Boundary
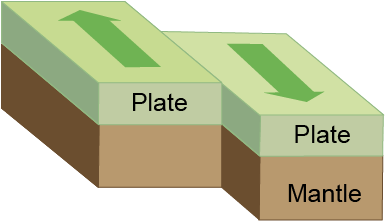
a boundary between tectonic plates where the two plates slide past one another; the earth around the boundary is crumpled
Example.
San Andreas fault
Maritime Tropical Air Mass (mT)
A warm, moist air mass that formed over tropical oceans
Air Pressure / Atmospheric Pressure
the force exerted on an area due to the weight of the air in the atmosphere above
Cleavage
the pattern along which the mineral breaks
Example.
halite has cleavage in three directions
Chemical Weathering
the process of breaking down rocks by chemical means
Example.
acid rain
Air Masses
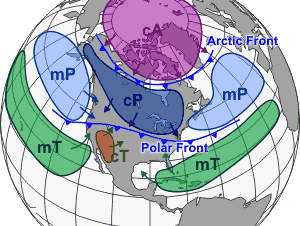
Regions of warm or cold, wet or dry air that tend to move as a unit across Earth's surface, carrying their temperature and humidity compositions with them
Erosion
the slow wearing away of the surface of the land by wind or water
Example.
wind erosion, water runoff
Constructive Processes
processes that add new landforms to the surface of the earth
Example.
hot spots causing volcanoes
Geyser
a hot spring of water that intermittently jets water and steam into the air; caused by magma heating the groundwater
Example.
Old Faithful
Asthenosphere
part of the upper mantle, just below the lithosphere, solid rock in a plastic state
Crystalline Structure
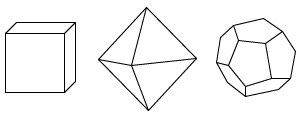
the degree to which the mineral is arranged in a crystal lattice structure; the more crystalline the mineral is, the harder that lattice is to see with the naked eye
Example.
Sodium chloride crystals typically have a cubic shape, while graphite has a layered sheet-like structure.
Exosphere
a layer in the atmosphere which provides a boundary between the thermosphere and outer space
Metamorphic Rock

form when rock is subjected to great heat and pressure; banding or stripes
Example.
marble
Magma
underground molten rock, present before and during a volcanic eruption
Mantle

the layer of the earth just beneath the crust; composed of very hot rock
Weathering
a destructive process by which rock is gradually worn away and broken into smaller sediments and/or soil
Example.
water gradually breaking down and smoothing rock
Crust

the outermost and coolest layer of the earth
Maritime Polar Air Mass (mP)
A cold, moist air mass that formed over polar oceans
Organic Material
dead plant and animal material in the soil
Example.
decomposing blades of grass
Oceanic Crust
crust found under oceans; made of mostly silicon, oxygen, and magnesium
Stratosphere
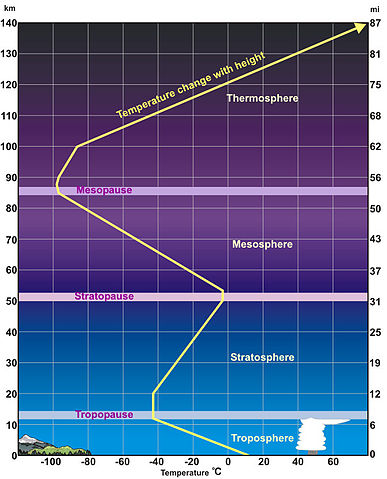
the layer above the troposphere; contains jet streams and the ozone layer
Soil
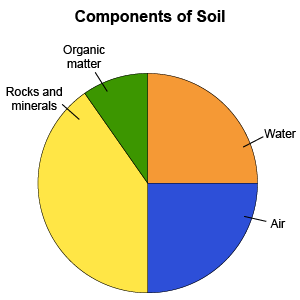
the upper layer of the earth's surface; formed from the weathering of rocks
Example.
clay
Streak
the color of the mineral in powder form; obtained by dragging a piece of the mineral across a piece of unglazed porcelain
Example.
amethyst has a streak color of white
Thermosphere

a very thin layer of atmosphere which has high temperatures; contains the ionosphere and exosphere
Rock
an accumulation of one or more minerals
Example.
sedimentary rock
Nutrients
substances in food and beverages that nourish the living things. They support growth, produce energy, and maintain the organism.
Example.
carbohydrates, fats, fiber, minerals, vitamins, or water
Convection Currents
the movement of fluid which transfers heat from one place to another
Example.
air in a hot air balloon - hot air travels upward and cools, then the denser, cooler air sinks, resulting in the circular motion of the air
Inner Core

the extremely hot innermost layer of the earth; composed of mostly solid iron and nickel
Continental Crust
crust found under continents; made of mostly silicon, oxygen, and aluminum
Jet Streams
strong eastward winds in the stratosphere which blow horizontally around the earth
Lithosphere
the rigid, outermost layer of the earth composed of the crust and the uppermost mantle
Global Warming / Climate Change
an overall increase in average global temperatures due to the greenhouse effect (the increasing amount of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere trapping more heat)
Color
the color of the mineral
Example.
purple amethyst
Ozone Layer
a layer of ozone in the stratosphere that blocks harmful ultraviolet radiation from reaching the earth's surface
Magnetism
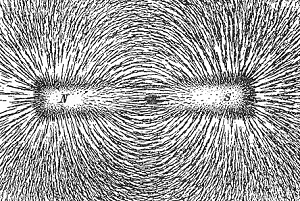
the response of a mineral when exposed to magnetic materials; a physical property
Example.
magnetite displays strong attraction to magnetic fields
Continental Tropical (cT)
Term definition.
A warm, dry air mass that formed over tropical landmasses
Fossil Fuels
a natural non-renewable fuel source. derived from underground, fossilized (petrified) remains of living organisms.
Example.
natural gas, petroleum, coal
Diaphaneity
the transparency of the mineral or ability of light to pass through it
Example.
witherite is translucent, allowing some light through