6 - Sampling Samples + Central Limit Theorem
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Population
Large group
Area to be studied
Entire group
Whole
Sample
Small group selected from population
Size depends on research needs
Representative (make generalisations)
Can’t study everyone
Sample vs Population
Sample:
Subset of population
Representative
Minimise sampling error
Population:
Everybody fitting population criteria
Must be clearly defined
Selecting a Sample
Population characteristics must be clearly defined - strong sample data
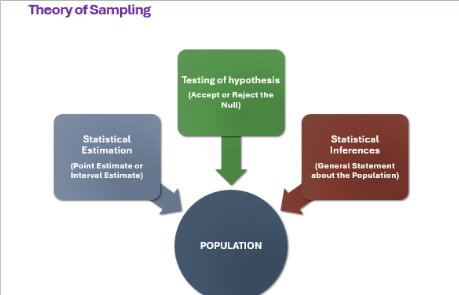
Theory of Sampling
Statistical estimation
Testing of hypothesis
Statistical inference
Features of Sampling
Economy
Reliability
Detailed study
Scientific base
Greater sustainability
Limitations of Sampling
Less accurate
Changeability of units
Misleading conclusions
Need for specialised knowledge
Characteristics of an Ideal Sample
Representativeness
Independence
Adequacy
Homogeneity
Methods of Sampling
Probability Sampling
Non-probability sampling
Probability Sampling
Random sampling
Simple random sampling
Stratified
Systematic
Multistage
Advantages of Probability Sampling
Detailed info about population
Measured precisely
Inherently unbiased
Evaluate relative effectiveness of sample designs
Disadvantages of Probability Sampling Methods
High degree of skill / expertise
Time consuming to plan
Higher costs
Probability Sample - Simple Random Sampling
Individual units constituting the sample are selected at random
Guarantee equal chance of being chosen
Allocate number
Random generator e.g. hat
Advantages of SRP
Simple - math procedures
Unbiased
Representative - equal chance
Errors easy to detect
Disadvantages of SRP
Selection strictly from random basis not possible
Lack control of research
Probability Sample - Stratified Sampling
Proportionate
Disproportionate
Stratified weight sampling

Advantages of Stratified Samples
Greater control of the investigator
Representative
Replacement of units possible
Disadvantages of Stratified Samples
Bias
Difficult to achieve proportion
Difficult making sample representative
Difficult placing cases under level
Probability Sampling - Systematic Sampling
Advantages of Systematic Sampling
Simple drawing sample
Smaller variances
Ordered population - reduces variability
Disadvantages of Systematic Sampling
Interval - increase variability
Stratification effect - estimates of error
Probability Sample - Multistage Sampling
Uses a form of random sampling in each of the sampling stages where there are more than 2 stages
Advantages of Multistage Sampling
Complete list of population not required
Lists only required for sampling units selected in sample
Geographically defined - cut down field costs
Disadvantages of Multistage Sampling
Errors larger than other sampling
Error increase as numbers of selected sampling units decrease
Non Probability Sampling Methods
Non-random sampling
Judgement/purposive
Convenience
Snowball
Quota
Non Probability Sample - Judgement Sampling
Sampling the choice of sample items depends primarily on judgement of the researcher
Advantages of Judgement Sampling
Inclusion of important units
Representative - look into unknown traits
Practical
Disadvantages of Judgement Sampling
Risk of conforming to researcher preconceived ideas
No objectivity evaluating reliability of sample results
Non Probability Sampling - Convenience Sampling
Unsystematic, accidental, opportunistic
May be used:
Population not well defined
Sample unit unclear
Complete source unavailable
Non Probability Sampling - Snowball Sampling
Researcher contacts small number of people in target group then uses these people to establish new contact
Disadvantges of Snowball Sampling
Inaccessible sampling frame
Unrepresentative - difficult to generalise
Non Probabilty Sampling - Quota Sampling
Non-random form of stratified sampling
Classify population into various types - assume to be relevant to characteristics being researched
Determine proportion of population - fall into each type based composition of population
Setting quotas for each interviewer - responsible of selecting respondents so total sample interviewed contains proportion of each level
Advantages of Quota Sampling
Reduce cost of preparing sample/field work
Stratifaction effect
Disadvantages of Quota Sampling
Investigator bias
No random sampling - errors of method cannot be estimated by statistical procedures
Reliability of Sampling
Size of sample - adequate for study
Representative of sample - possess characteristics of all units
Parallel sampling - another sample for testing
Homogeneity of samples - possess same features of population
Unbiased selection - free from bias + prejudice
Types of Sample Errors
Sampling Variability - different sample from same population not always produce same mean + SD
Sampling Error - mean of sample not same as mean of population
Non-sampling Error - errors not connected with sampling method e.g. leading Q’s
How Large Should a Sample Be?
Population with greater variability (Big SD) - larger sample
Fit with study budget
Greater precision requires larger sample
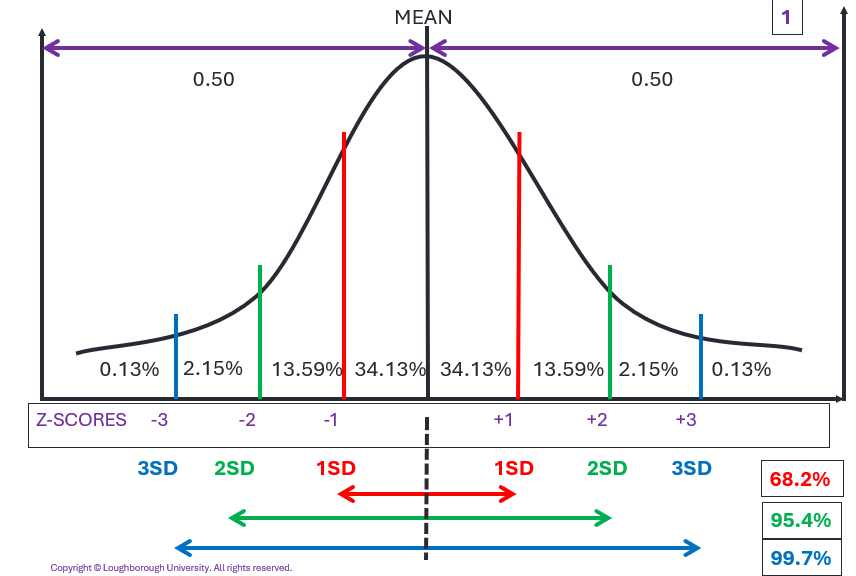
Areas Under Normal Distribution Curve
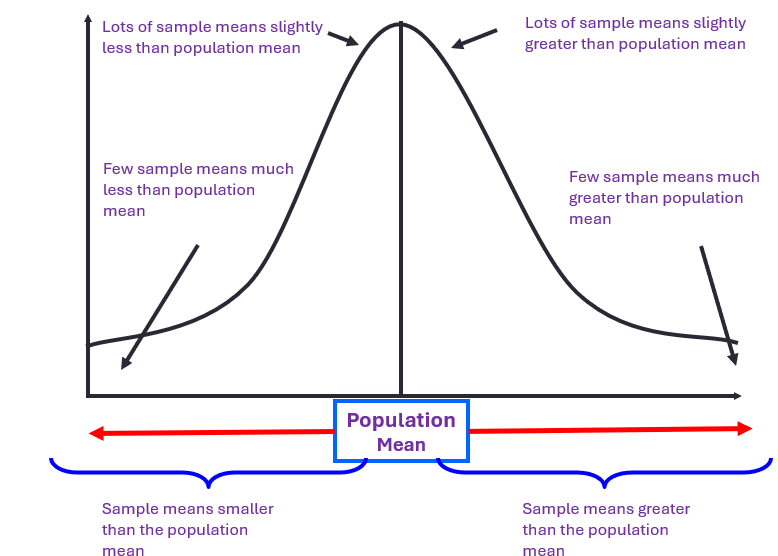
Sample Means
Means of different samples
Distribution of SM from pop - approximately normally distributed
Mean of SM approximately equal pop mean
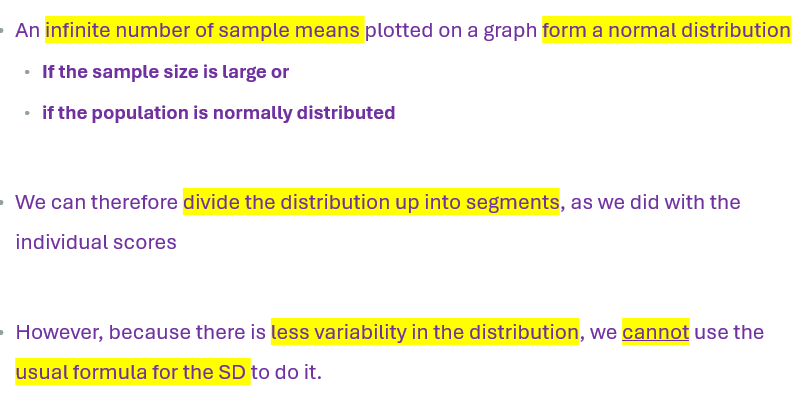
Distribution of Sample Means
SM forms normal distribution
Each sample has mix of high scores which tend to be cancelled out by low ones
SD of SM is smaller than SD of individual scores in the population.
Sample Distribution Properties
SD of SM smaller than SD of individual pop values
Larger number of samples have less variability
Standard Error (New SD) accommodates this
Standard Error (SE) Formula
1 Z score = 1 SE

Null Hypothesis
no effect, no difference, or no relationship between variables in a study. It represents the default assumption that any observed differences are due to chance
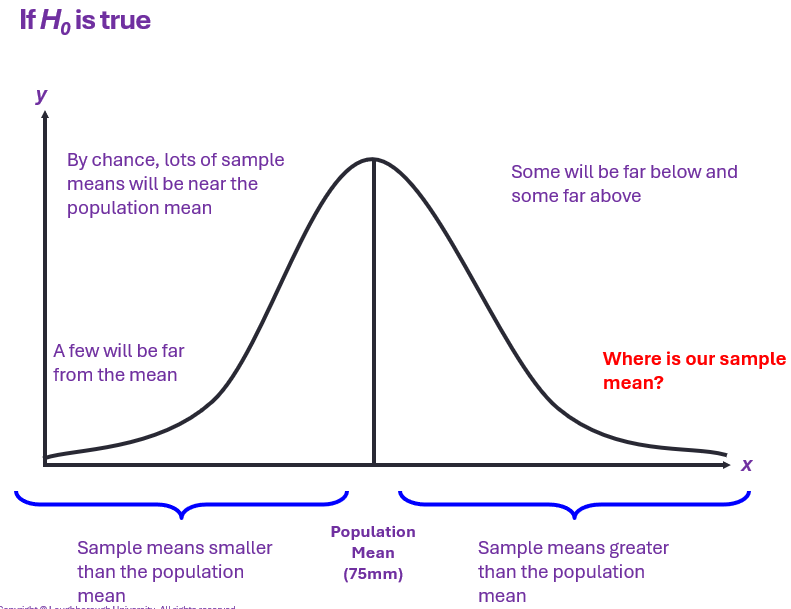
Rejecting Null Hypothesis
5% + 1% are common thresholds
SM is in rarest (5% or 1%) - NH not true
Reject NH, accept Alternate Hypothesis (H1) = there is an effect/difference (maybe wrong 5%/1% of the time)

Conclusions of Central Limit Theorem
Samples of size n from pop will have:
*Approx normally distributed means
*Mean of SM = Pop mean
*SD of SM = SE