The peripheral nervous system
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Nerves which travel to the CNS from the body are ______
Afferent nerves
Nerves which travel to the body from the CNS are ______
Efferent nerves
What are the two main divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
Autonomic nervous system and Somatic nervous system
What are Ganglia?
Groups or knots of neurone cell bodies
What two antagonistic components make up the autonomic nervous system?
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic components.
What actions does the Sympathetic nervous system do?
Increased heart rate and force of contraction
Dilation of pupils
Relaxation of airway smooth muscle
Decreased stomach motility and gastric secretions
“Fight for Flight”
What actions does the Parasympathetic nervous system do?
Decreased heart rate and force of contraction
Constriction of pupils
Contraction of airway smooth muscle
Increased stomach motility and gastric secretions
“Rest and Digest”
Where are sympathetic nerve cell bodies found?
Thoracic and Lumbar spinal cord segments
What do sympathetic nerve cell bodies connect to?
Paravertebral ganglion chain (The sympathetic chain)
OR
To individual ganglia that are still quite distant from the target organ
Where do parasympathetic nerves arise?
From cranial nerves or the lumbo-sacral spinal cord (Between lumbar and sacral spinal cord segments)
Are sympathetic ganglions close or far from target organs?
Far from target organs.
Short pre-ganglionic neurones
Long post-ganglionic neurones
Are parasympathetic ganglion close or far from target organs?
Close to target organs.
Long pre-ganglionic neurones
Short post-ganglionic neurones
What is the somatic nervous system responsible for?
Conscious control of our bodies and the corresponding feedback.
Somatic nerves synapse multiple times once they have left the CNS in order to span long distances.
True or False.
False.
Once they have left the CNS, somatic nerves project directly to their target cells via a single neurone.
What information do afferent somatic nerves carry?
Pain, temperature, touch and proprioception information.
(Where the body is in space)
What information do efferent somatic nerves carry?
Motor information to effector skeletal muscles.
What are the two types of somatic nerves?
Spinal nerves - Arise from the spinal cord
Cranial nerves - Arise directly from the brain
What are spinal nerves?
Peripheral nerves which carry axons of neurons of the somatic and autonomic nervous systems to and from the spinal cord.
Where do spinal nerves leave the spinal cord?
Below each vertebrae
Except in the cervical region where they exit superior to the vertebrae
Which vertebrae has a spinal nerve both above and below it?
C7 vertebrae
One nerve above it (C7 nerve) and one below it (C8) nerve.
How many spinal roots in the human body?
31 spinal roots.
C1-C8 (8 as C7 has a root above and below it)
T1-T12 (12)
L1-L5 (5)
S1-S5 (5)
Coccygeal root (1)
8+12+5+5+1 = 31
What information do dorsal (posterior) roots usually carry?
Usually afferent/sensory information
Carry information from the periphery to the CNS.
What information do ventral (anterior) roots usually carry?
Usually efferent/motor information
Carry information from the CNS to the periphery in somatic motor and autonomic neurons.
The dorsal and ventral roots unite a short distance from the spinal cord to form what?
The mixed (motor and sensory) spinal nerve.
This nerve may go on to a nerve plexus or may become a single peripheral nerve.
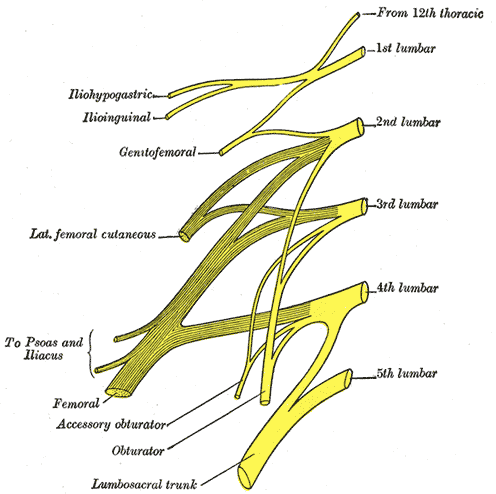
What is a nerve plexus?
Network of nerves in the body.
When spinal nerves leave the spinal cord, they often blend with other spinal nerves from different spinal levels.
Can form a plexus such as the lumbar plexus (made up of spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord below vertebrae T12-L5)
What are dermatomes and myotomes?
The distinct area of skin (dermatome) and muscles (myotomes) that is supplied by and supplies a spinal nerve.
Why is understanding of dermatomes and myotomes important?
The location of a spinal lesion or damage can be identified based on loss of sensation/motor function in distinct areas.
What do Sciatic nerves supply?
Supply most of the muscles and dermatomes of the thigh and leg.
Motor neurones: Supply muscles of posterior thigh
Sensory neurones: Supply skin on lateral side of leg and skin on foot
Femoral motor and sensory functions:
Motor: Signals to muscles of anterior thigh (the quadriceps that act to extend the knee).
Sensory: sensory afferent from anterior thigh and medial leg.
How many cranial nerves are there?
12 cranial nerves.
Numbered using roman numerals (I - XII)
What is the function of cranial nerve I?
Olfactory nerve
Special sense. Innervates nasal mucosa and carries information relating to smell.
What is the function of cranial nerve II?
Optic nerve.
Special sense. Afferent for vision from the retina
What is the function of cranial nerve III?
Oculomotor nerve.
Somatic division: Controls movements of the eye and some control of the eyelid.
Autonomic division: Motor to pupil constrictors
What is the function of cranial nerve IV?
Trochlear nerve
Somatic: Motor to a muscle which moves the eye
What is the function of cranial nerve V?
Trigeminal nerve.
Somatic division: Afferent from surface of face. Senses touch from skin of face.
Motor division: Efferent to muscles of mastication (chewing)
What is the function of cranial nerve VI?
Abducent nerve.
Somatic: Motor efferent to a muscle of the eye.
What is the function of cranial nerve VII?
Facial nerve.
Special sense: Taste from anterior tongue and palate
Somatic division: Motor efferent to muscles of facial expression
Autonomic division: Motor efferent to saliva glands.V
What is the function of cranial nerve VIII?
Vestibulocochlear nerve.
Special sense: Hearing from cochlea of ear. Balance from vestibular apparatus of ear.
What is the function of cranial nerve IX?
Glossopharyngeal nerve.
Special sense: Taste from posterior tongue
Somatic division: Motor efferent to help with swallowing
Afferent: Sensation from external ear
Autonomic division: Secretomotor to one saliva gland (parotid)
What is the function of cranial nerve X?
Vagus nerve.
Slightly different to other cranial nerves. Supplies many structures beyond the head.
Somatic division: Motor to muscles of pharynx, larynx and palate
Autonomic division: Parasympathetic innervation of smooth muscle in trachea, bronchi, GI tract and cardiac muscle.
Afferent: Sensation from GI tract, heart and airways
What is the function of cranial nerve XI?
Accessory nerve.
Somatic: Motor to two big muscles in the neck
What is the function of cranial nerve XII?
Hypoglossal nerve.
Somatic: Motor to muscles of the tongue
Which cranial nerve does Bell’s palsy affect?
Causes palsy of the Facial Nerve (CN VII) which causes one sided facial paralysis
What is Guillian Barre syndrome?
Condition which occurs after an infection.
Immune system fights off the infection but then attacks the myelin sheath of peripheral nerve cells
Disproportionately affects longer neurones first.
Symptoms
Tingling (Paraesthesia) and muscle weakness (paresis) in feet and hands
As it progresses it can cause paralysis and will ascend proximally up arms and legs from the hands and feet.
In some cases, it can affect abdomen, thorax and cranial nerves.
This can potentially cause weakness of respiratory muscles leading to respiratory failure.